Method for treating obesity
a technology for treating obesity and obesity, applied in the field of obesity, can solve the problems that the available pharmacological therapies for facilitating weight loss fail to provide adequate benefit to many obese patients, and achieve the effect of enhancing the activity of norepinephrine and/or dopamine and minimizing metabolic risk factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Experimental Details
Subjects
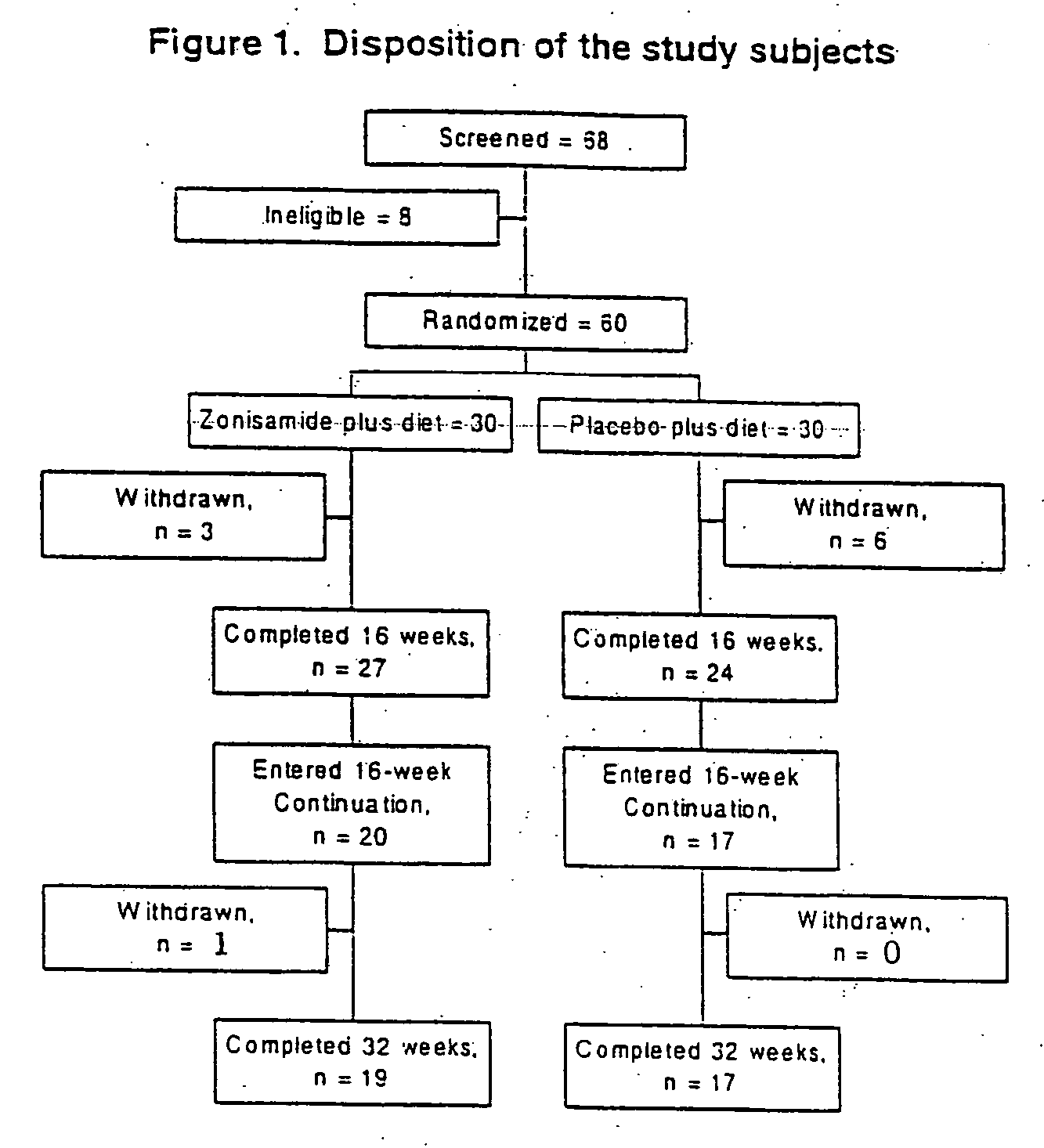
[0024] Sixty-eight subjects were screened for participation and 60 subjects were randomized.
[0025] Inclusion criteria were: male or female, aged 21-50 years, with body mass index (BMI) of ≧30 kg / m2.
[0026] Exclusion criteria were: obesity of a known endocrine origin, such as hypothyroidism and Cushing's syndrome; serious / unstable medical or psychiatric illness; current major psychiatric disorder; current drug or alcohol abuse; history of or current kidney disease or renal calculi; significant liver disease; uncontrolled hypertension; current diabetes mellitus (DM), type 1 or 2 DM receiving pharmacotherapy; untreated or uncontrolled thyroid disease; weight loss or gain greater than four kilograms in past three months; history of obesity surgery; current or recent use of any weight loss medications, herbs, or supplements; current or recent use of drugs, herbs, or dietary supplements known to significantly affect body weight; concomitant medications that...
example 2
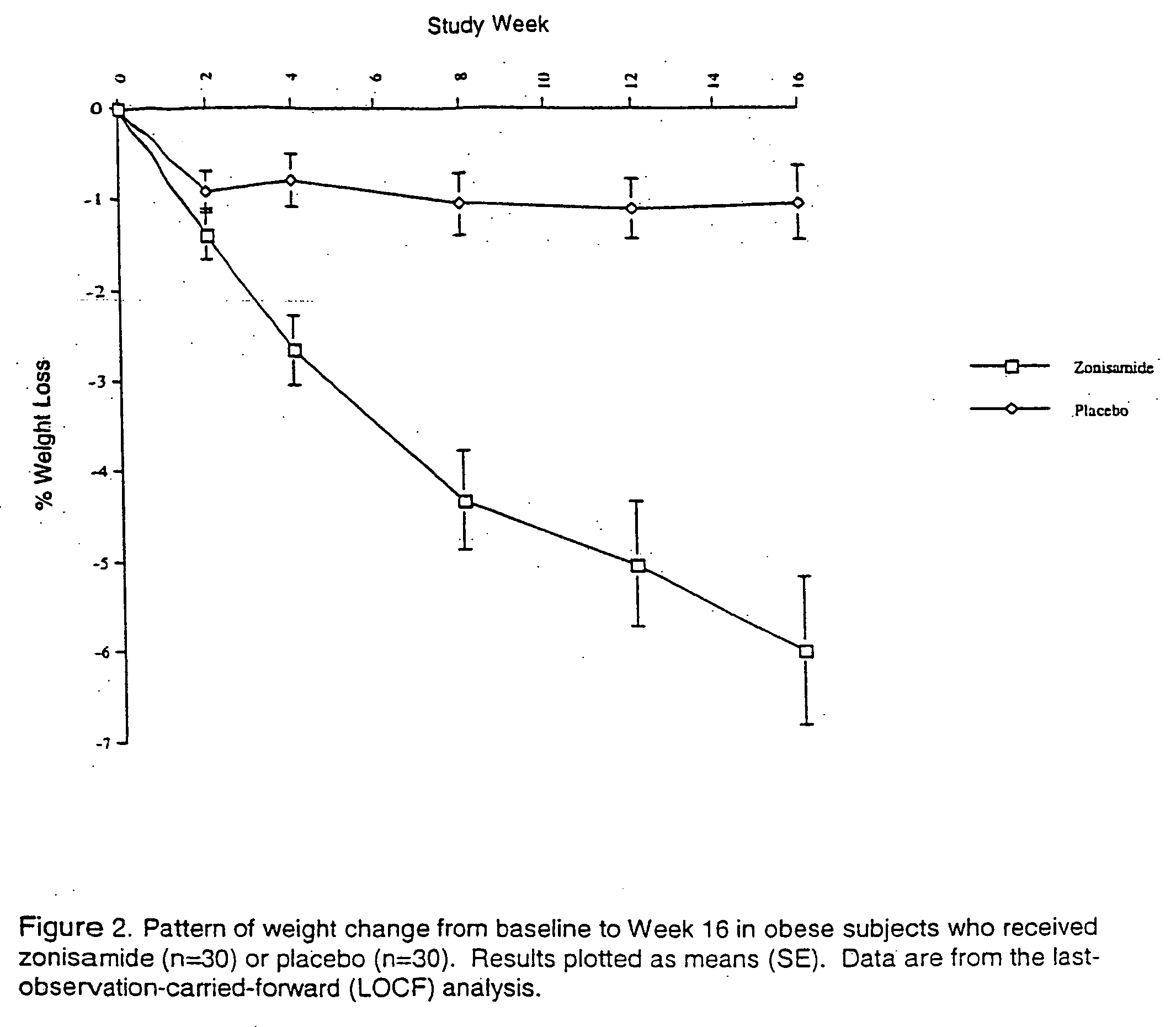
[0056] A 35 y.o. obese female (weight 271 lb, BMI 40 kg / m2), who failed to benefit from numerous weight loss interventions, was started on bupropion 150 mg / day and the dose was increased after 5 days to 150 mg twice a day. After one month of treatment, she lost 5 lbs, but regained 3.4 lbs during the second month—thus managing a net weight loss of 1.6 lbs after 2 months on bupropion. At this point, zonisamide was added to the regimen at 100 mg / day and the dose was increased after 2 weeks to 200 mg / day. After one month on the combination therapy, the patient had lost 11 lbs and reported no side effects. No further information is available as the patient has relocated.
example 3
[0057] A 47 y.o. obese female (weight 246 lb, BMI 41.4 kg / m2), who had not benefited from various treatments, was started on zonisamide 100 mg / day and the dose was increased gradually to 400 mg a day over the next 4 weeks. After one month of treatment, she lost 4.6 lbs, but there was no further weight loss during the second month. At this point, zonisamide dose was increased to 600 mg a day; the patient achieved an additional weight loss of 0.6 lb in the next month. Thus, after 3 months of zonisamide therapy, the total weight loss with zonisamide therapy was 5.2 lb. Zonisamide was continued at the same dose and bupropion SR was started at 100 mg a day. After 10 days, the dose of bupropion was increased to 200 mg a day. One month later, the patient had lost 8.2 lbs and reported no side effects. She reported that she felt “full” after eating small portions of food, and had more energy. She had lost over 35 lbs over ten months on the combination therapy with no side effects.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com