Posterior stabilization systems and methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
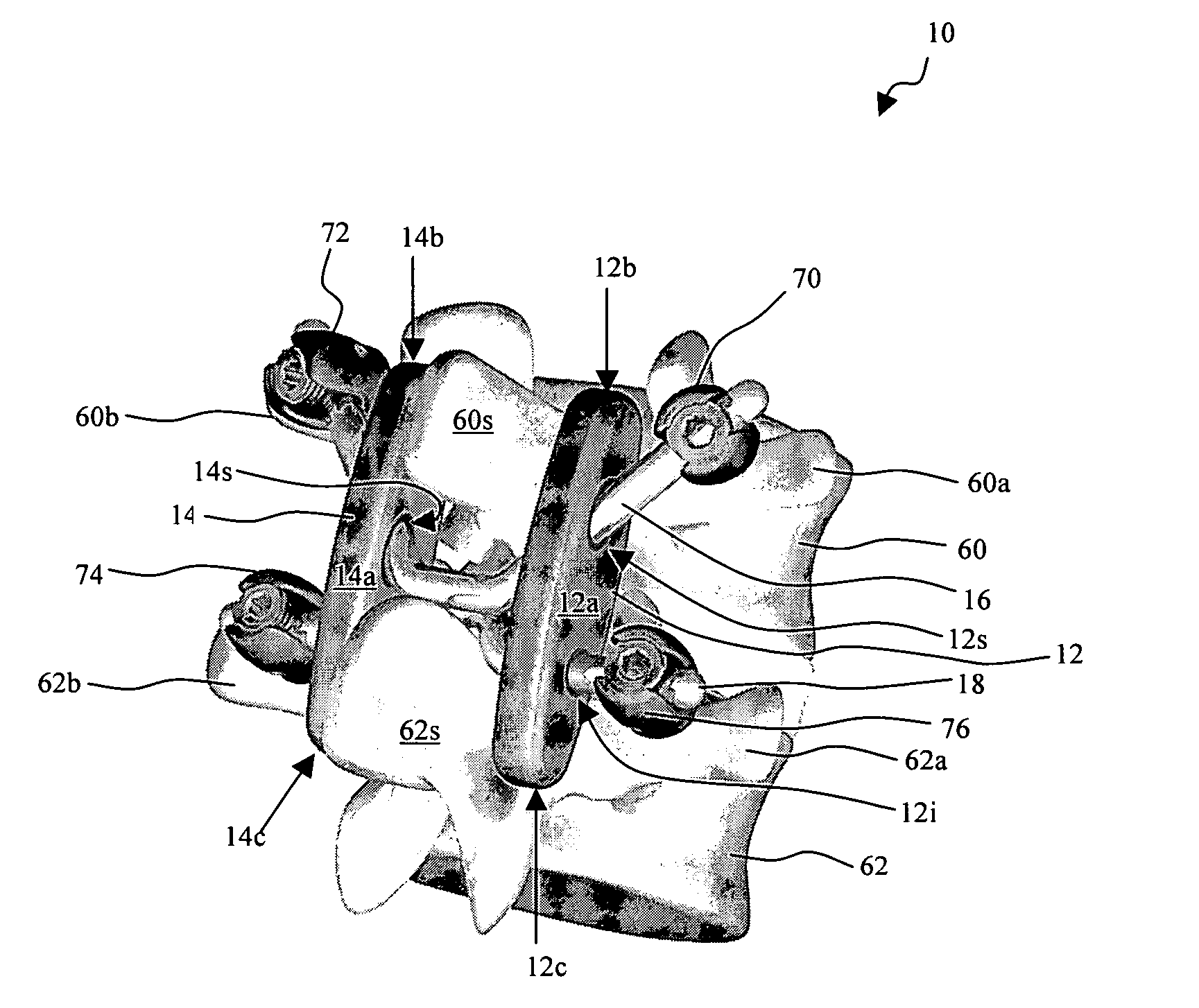
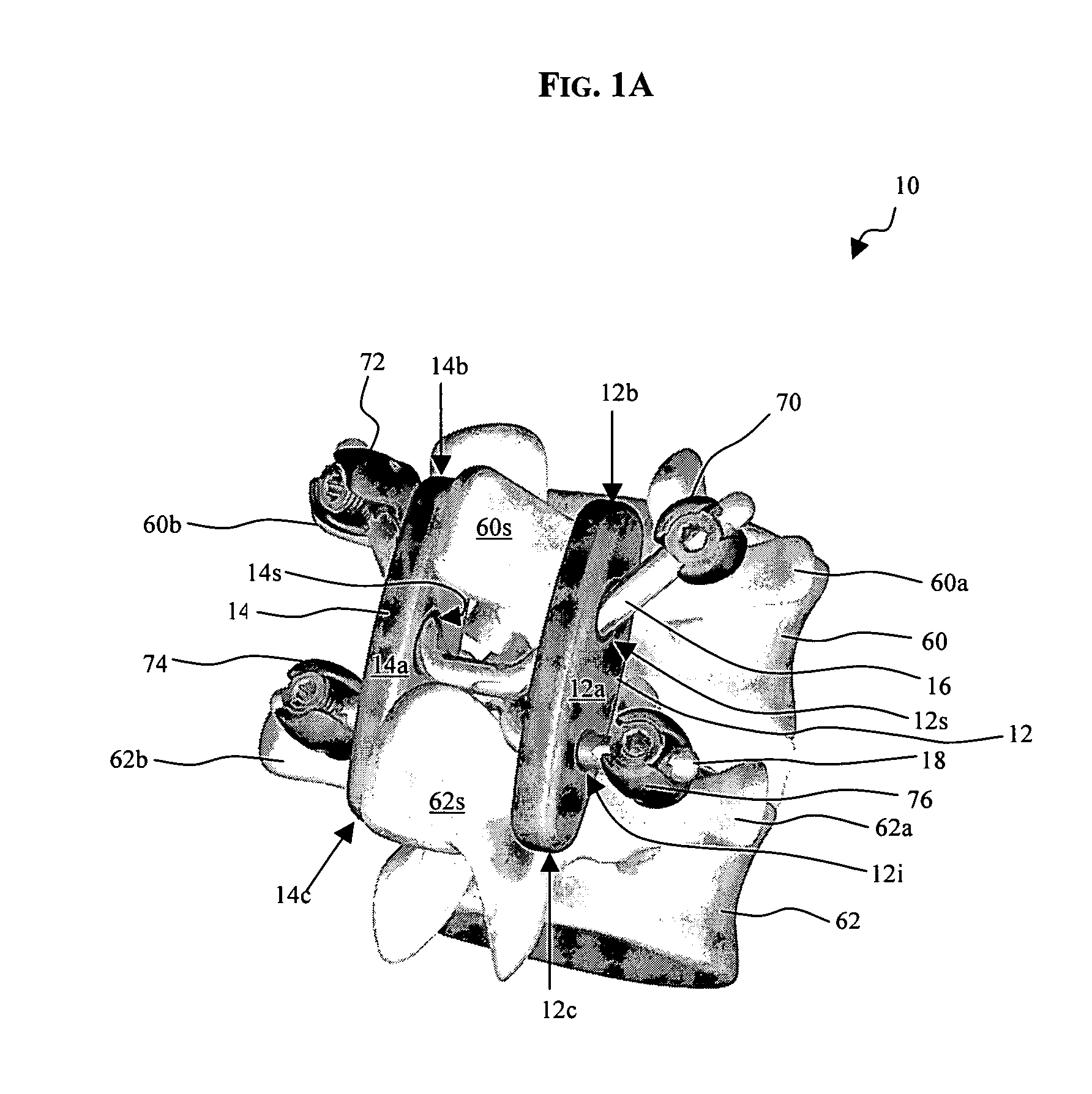
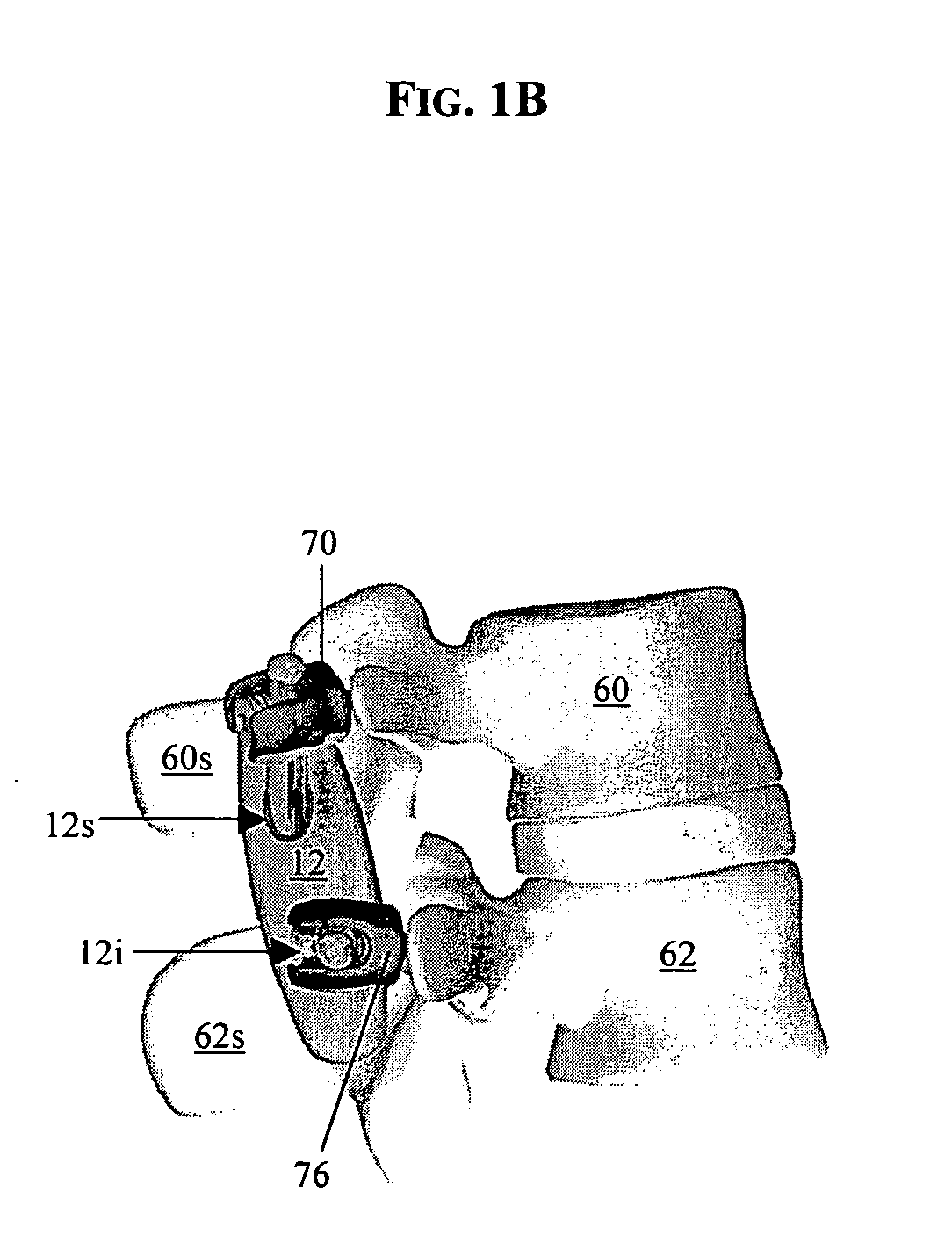
[0023] The present invention provides various methods and devices for replacing damaged, injured, diseased, or otherwise unhealthy posterior elements, such as the facet joints, the lamina, the posterior ligaments, and / or other features of a patient's spinal column. In an exemplary embodiment, the methods and devices are effective to mimic the natural function of the spine by allowing a high degree of flexibility between two adjacent vertebrae when the vertebrae are moved within a first range of motion, and by controlling or limiting movement of the adjacent vertebrae within a second range of motion beyond the first range of motion. A person skilled in the art will appreciate that, while the methods and devices are especially configured for use in restoring and / or replacing the facet joints and optionally other posterior elements of a patient's spine, the methods and devices can be used for a variety of other purposes in a variety of other surgical procedures.
[0024]FIGS. 1A-1C illus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com