Method and structure for mitigating instrumentation differences
a technology of instrumentation and structure, applied in the field of method and structure for mitigating instrumentation differences, can solve the problems of reducing the range of expected range of instruments, yielding differences between laboratory group results and peer groups, and unable to provide an adequate peer group to construct a proper range of expected, etc., to achieve meaningful data analysis and reduce statistical differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
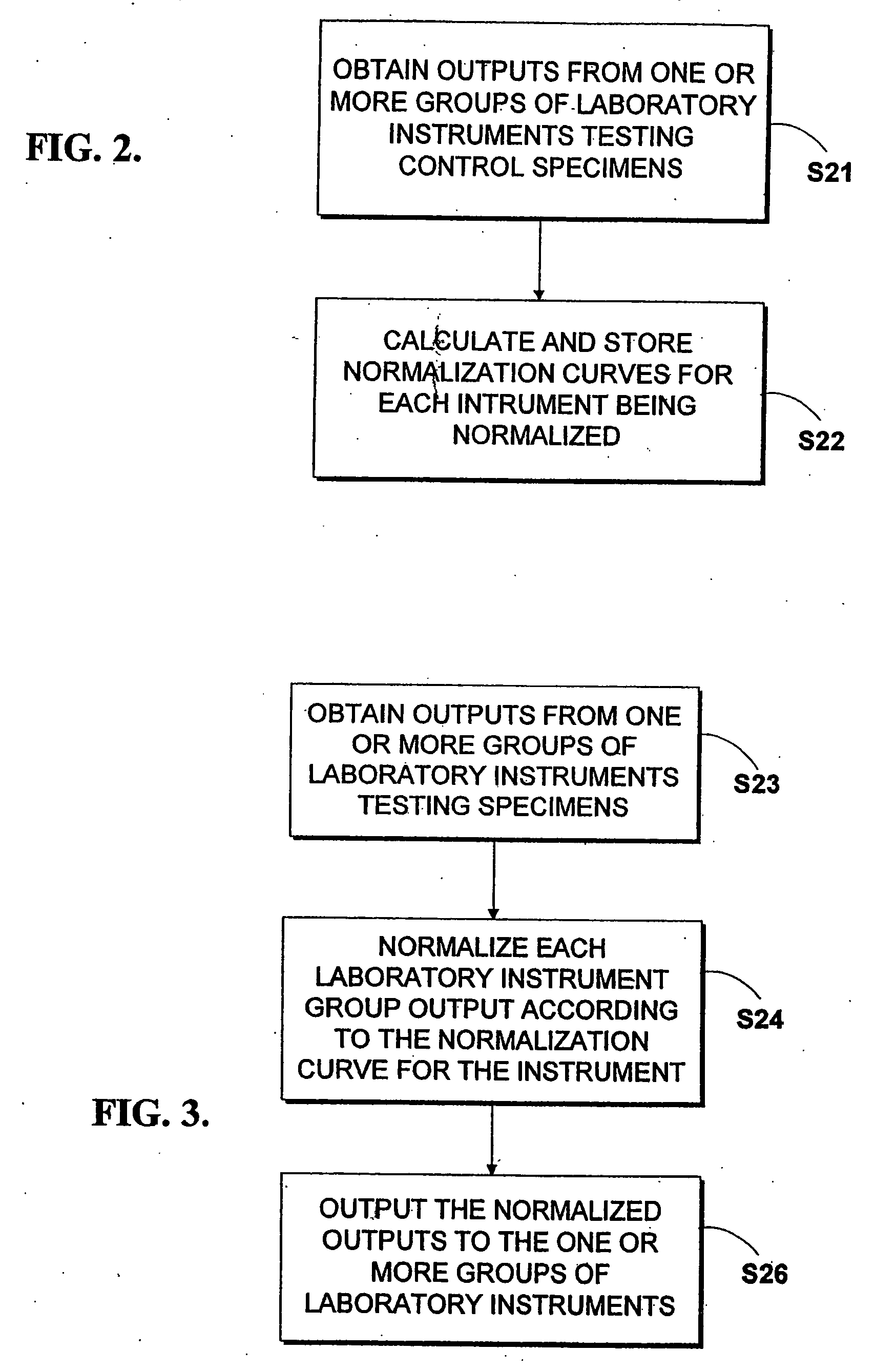
[0021] The present invention provides a method and device for mitigating instrumentation differences in laboratory equipment outputs by normalizing the output from the group of laboratory instruments to a control group. Preferably, the present invention is implemented in a computing environment commensurate with the number of laboratory instruments in the system and the quantity of data being normalized. The invention is operable with numerous general purpose or special purpose computing system environments. Examples of well known computing systems that may be suitable for use with the invention include personal computers, server computers, hand-held or lap top devices, multiprocessor systems, network personal computers, minicomputers, and mainframe computers. As would be readily understood by someone skilled in the art, additional computing environments are within the scope of the present invention.
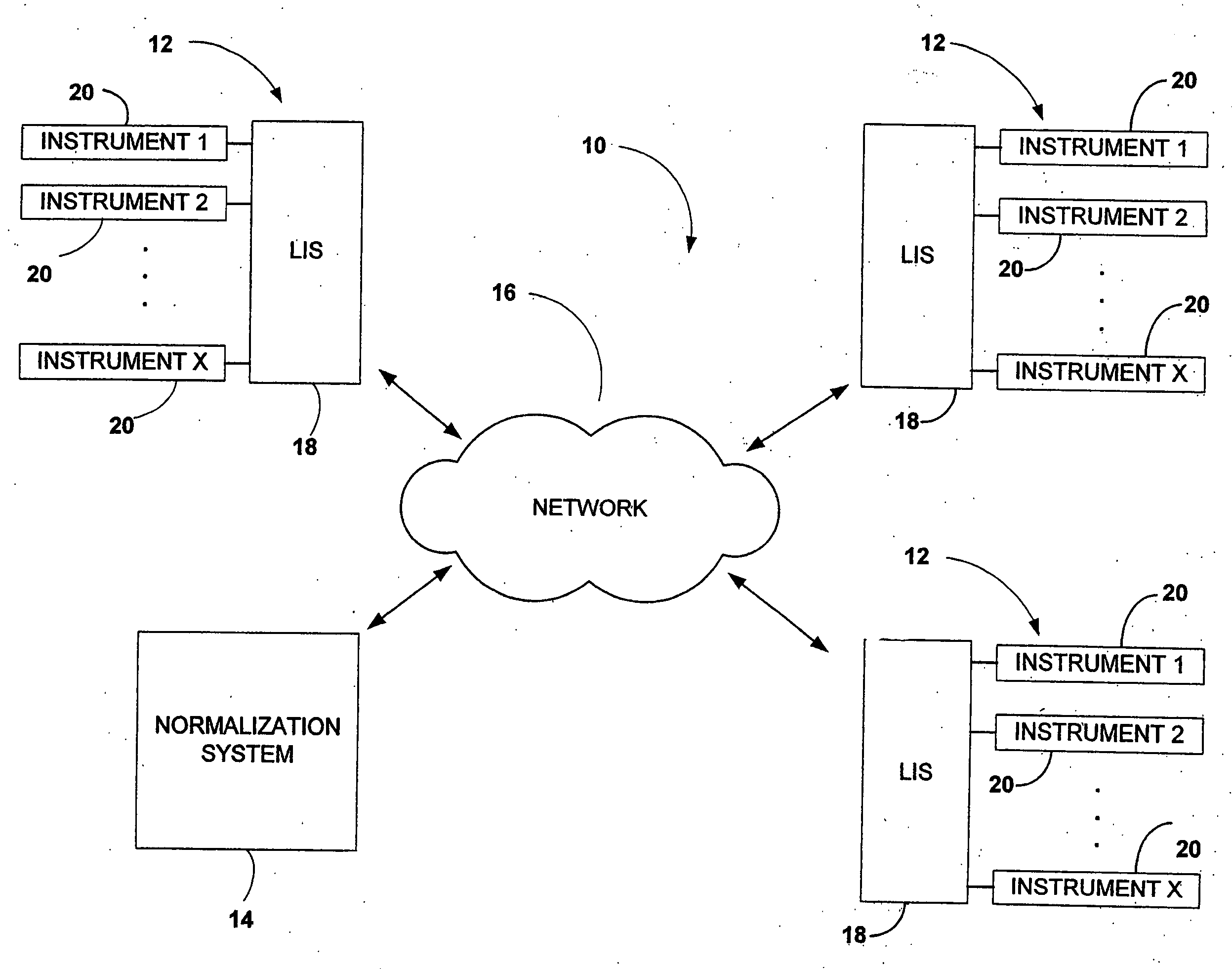
[0022]FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrative of the normalization system of the pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com