Ultrasonographic method and ultrasonographic device
a technology of ultrasonography and ultrasonography, applied in the field of ultrasonography, can solve the problem of not considering reducing the time side lobe, and achieve the effect of time side lob
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
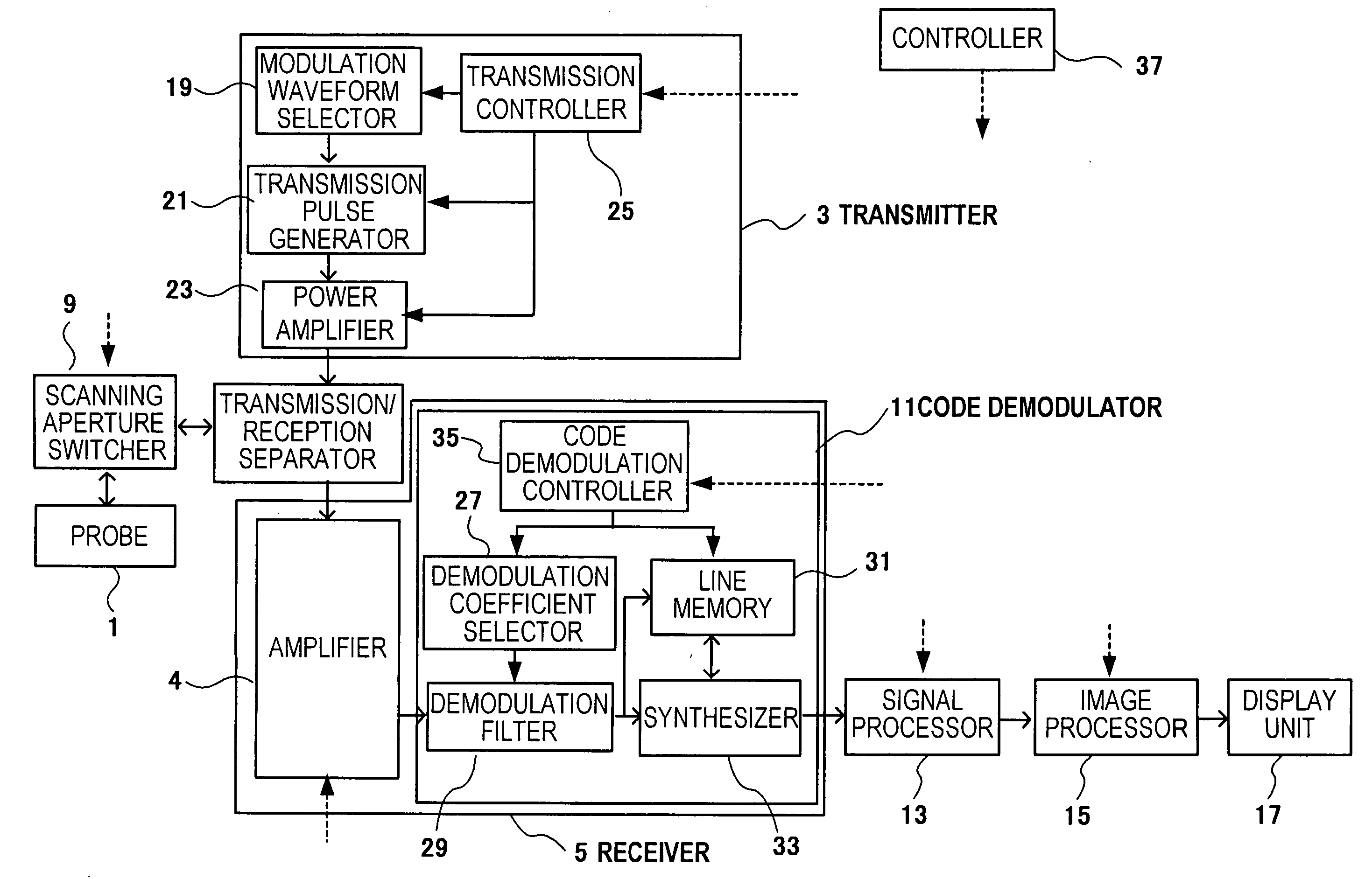
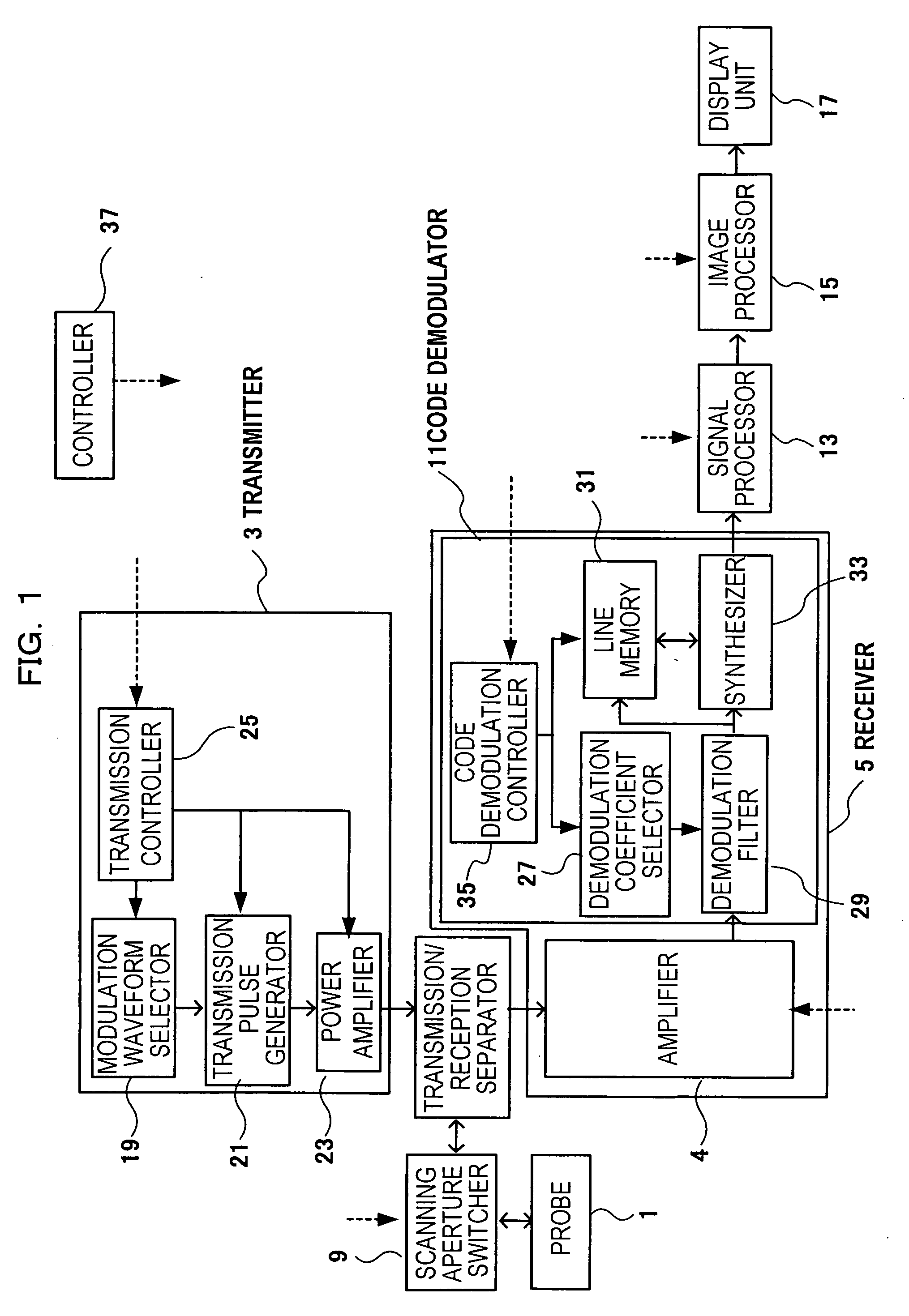
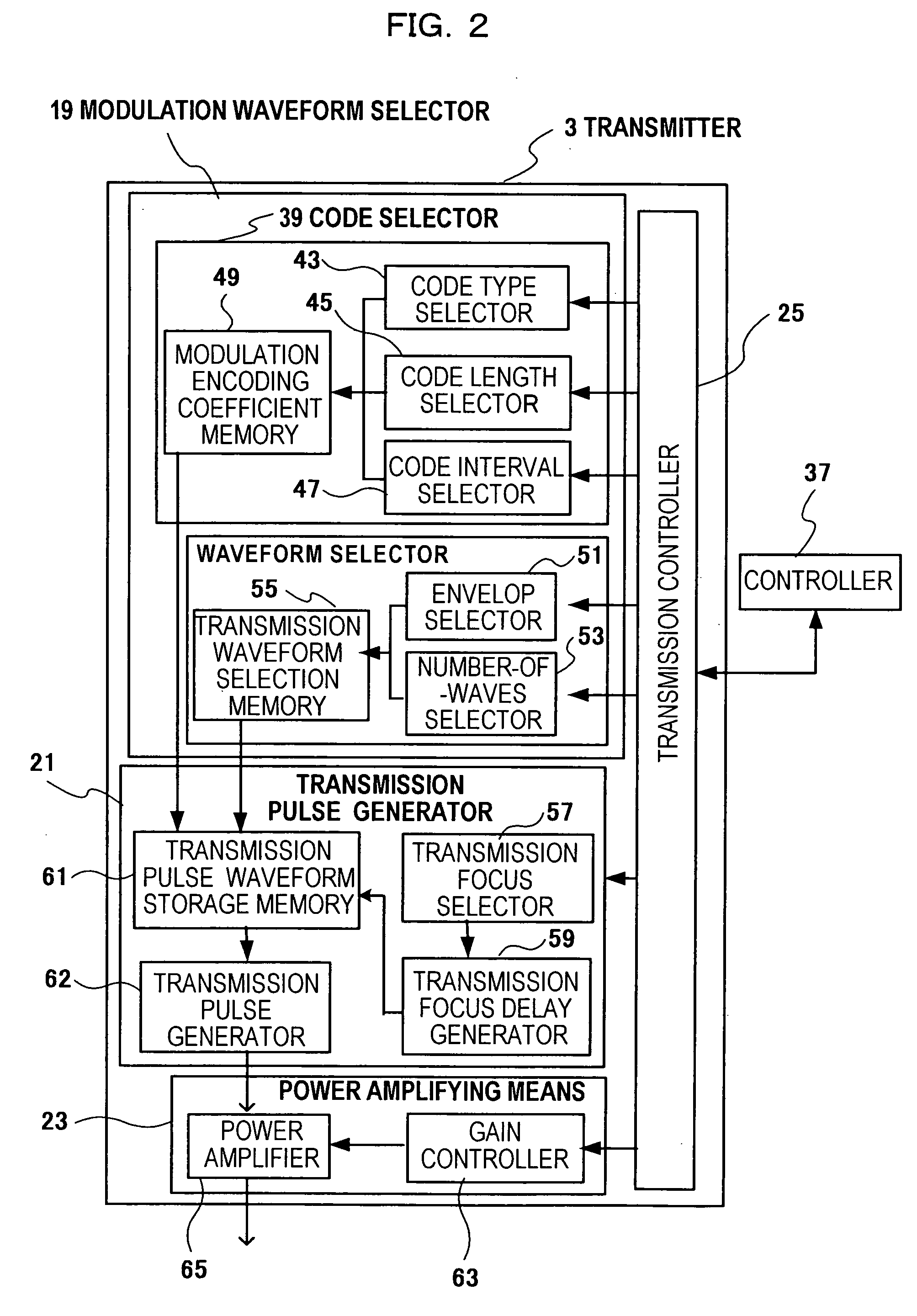
[0037] A first embodiment of an ultrasonographic device applying the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a construction of an ultrasonographic device of this embodiment. The ultrasonographic device includes a probe 1, a transmitter 3 and a receiver 5. The probe 1 transmits / receives an ultrasonic wave. The transmitter 3 outputs a drive signal for the probe 1. The receiver 5 is for a reflection echo signal (called reception signal, hereinafter) output from the probe 1. Furthermore, a transmit / receive separator 7 is provided therein for transmitting a drive signal output from the transmitter 3 and transmitting a reception signal output from the probe 1 to the receiver 5.
[0038] A scan aperture switcher 9 is provided between the probe 1 and the transmit / receive separator 7. The scan aperture switcher 9 selects a transducer having the aperture of the probe 1 from multiple transducers of the probe 1. Furthermore, a signal processor 13, an image processor...
example 1-1
[0070]FIG. 7 shows simulation results and the fact that the time side lobe is reduced even when an amplification distortion occurs in a reception signal due to a body motion of a subject, for example. FIG. 7 shows graphs having waveforms of an encoding reception signal, demodulation signal, first and second synthesis signals and third synthesis signal in order from the left column. The first and second synthesis signals are referred by the first and second demodulation synthesis signals, and the third synthesis signal is referred by the synthesis signal. The vertical axis of the graphs indicates strength of signals. The horizontal axis of the graphs indicates time. FIG. 7 shows a case of the first encoding transmission / reception based on the modulation code A, a case of the second encoding transmission / reception based on the modulation code B, a case of the third encoding transmission / reception based on the modulation code −B and a case of the fourth encoding transmission / reception ...
example 1-2
[0074]FIG. 8 shows similar graphs to those in FIG. 7 but shows a case that a phase distortion due to a body motion occurs in an encoding reception signal instead of an amplitude distortion. As shown in FIG. 8, the time side lobe due to a body motion occurs in each of the demodulation synthesis signals P1 and P2. Thus, in this example, as shown in the rightmost column in FIG. 8, further synthesizing the demodulation synthesis signal P1 and demodulation synthesis signal P2 results in a synthesis signal having a reduced time side lobe.
[0075] A case that a frequency distortion occurs in an encoding reception signal may be handled in the same manner as that of the case that an amplitude distortion occurs in an encoding reception signal (FIG. 8).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com