Voltage converter control apparatus and method
a voltage converter and control apparatus technology, applied in the direction of dynamo-electric converter control, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increased inner resistance, increased power consumption due to inner resistance of the battery, and inability to supply a certain amount of power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
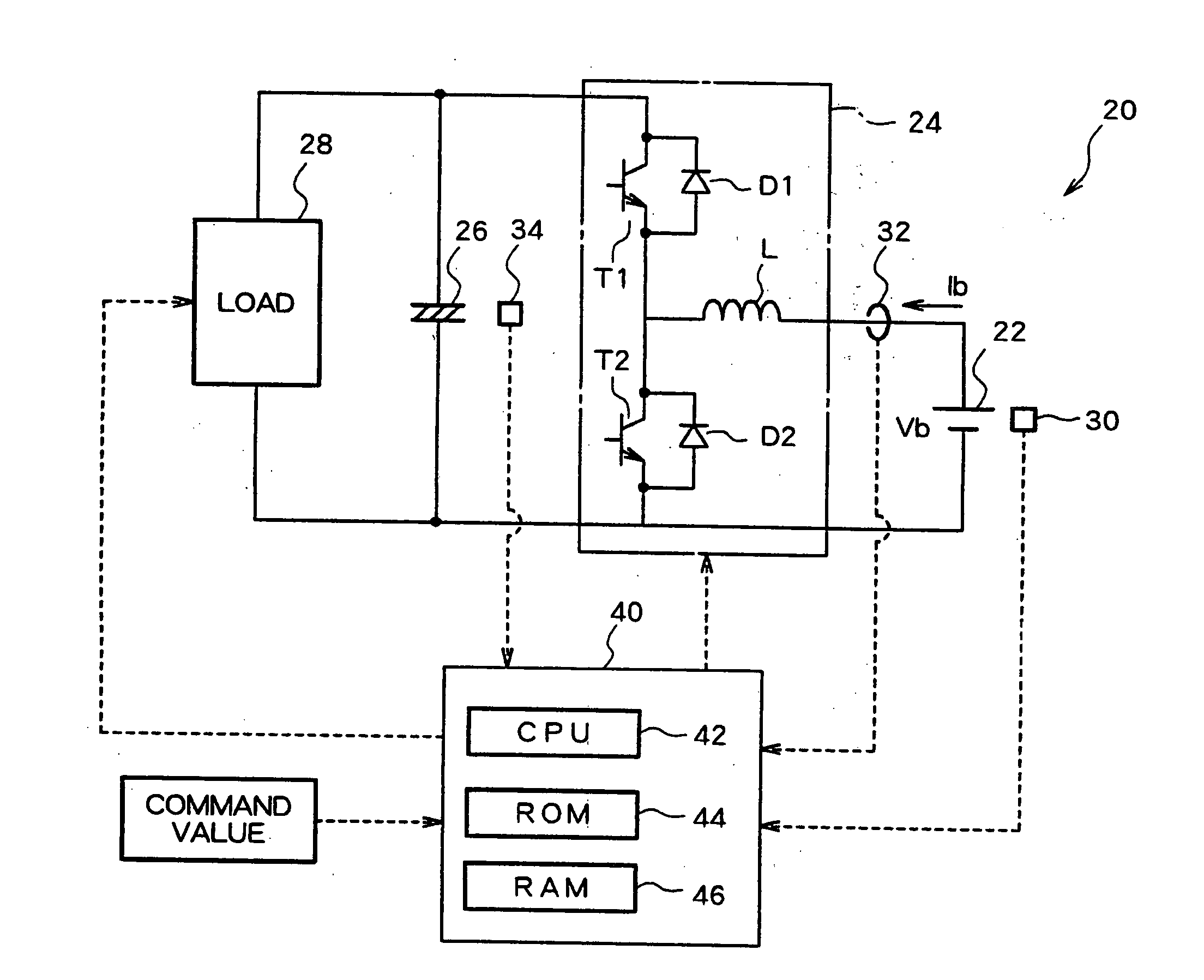
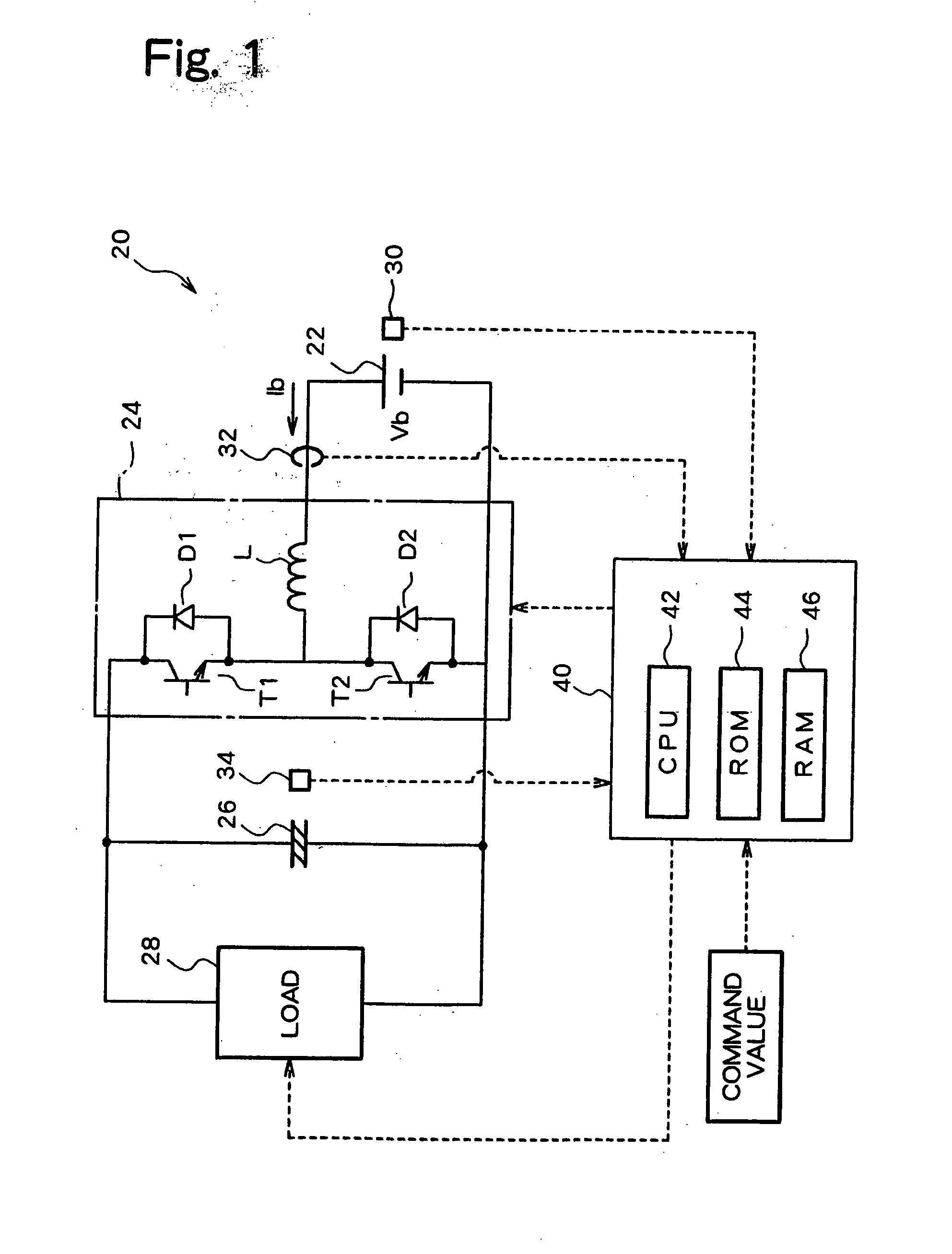
[0055] In the following, a driving system 120 according to the present invention will be described.
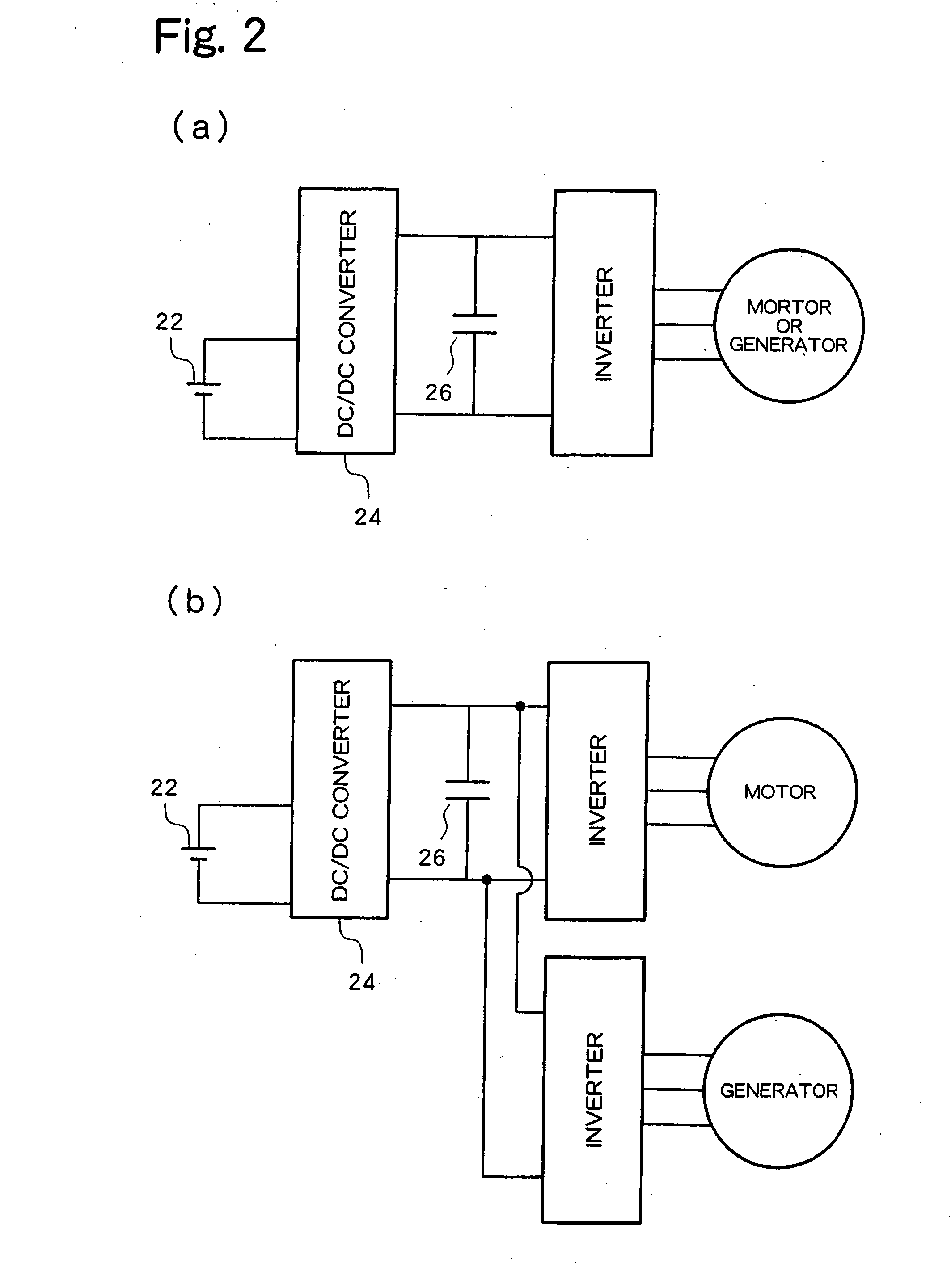
[0056]FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram showing a structure of a driving system 120 according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The hardware structure of the driving system 120 according to the second embodiment is identical to that of the driving system 20 in the first embodiment, with the notable exception that the driving system 120 does not have a current sensor 32, which is included in the driving system 20. Therefore, structural elements of the driving system 120 in the second embodiment, identical to those of the driving system 20 in the first embodiment are identified using similar reference numbers added by 100, and not explained again.
[0057]FIG. 9 is a flowchart of an example of a DC / DC converter driving control routine to be executed by the electronic control unit 140 of the driving system 120 in the second embodiment. That is, the driving system 120 in the secon...
first embodiment
[0074] Meanwhile, as a battery current Ib when the maximum output Bpmax is extracted from a battery is equal to a value Vbo / 2Rb, as described above with reference to the driving system 20 in the first embodiment, a battery voltage Vb at this time can be expressed using the expression (11) below.
Vb=Vbo / 2 (11)
[0075] From the fact that driving control of the DC / DC converter 24 is conducted such that a battery current Ib becomes less than or equal to a value Vbo / 2Rb in the driving system 10 of the first embodiment, it can be understood that driving control of the DC / DC converter must be conducted such that the battery voltage Vb becomes equal to Vbo / 2 or larger, in other words, a voltage drop due to the inner resistance of the battery becomes equal to a value Vbo / 2 or smaller in the driving system of the third embodiment. This is the significance of the determination as to whether or not the battery voltage Vb is greater than or equal to a value Vbo / 2. Therefore, the driving system in ...
fourth embodiment
[0078] In the fourth embodiment, a battery voltage Vb, a battery current Ib, and a battery electromotive voltage Vbo of the battery 22 are determined, similar to the above embodiments, and an inner resistance Rb of the battery 22 is always detected using the above-described expression (2). Further, the maximum permissible current Ibmax is determined based on at least one of the capacity of a current which can be supplied to the transistors T1, T2, which serve as switching elements of the DC / DC converter 24, or that which can be supplied to the battery 22, and stored in the ROM 44 or the like in the electronic control unit 40, for example. That is, the maximum permissible current Ibmax is determined by selecting either one, or a larger one, of the capacities of a current which can be supplied to the transistors T1, T2 or which can be supplied to the battery 22. It should be noted that any non-volatile memory may be employed for the ROM 44, with are writable EEPROM or a flash memory b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com