Woven fabric structure
a technology of woven fabric and fabric seams, applied in the field of woven fabric structure, can solve the problems of increasing the protracted seaming process, affecting the quality of woven fabric, and already complicated, and achieve the effects of improving tensile strength, reducing the propensity for seams, and reducing the open spa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
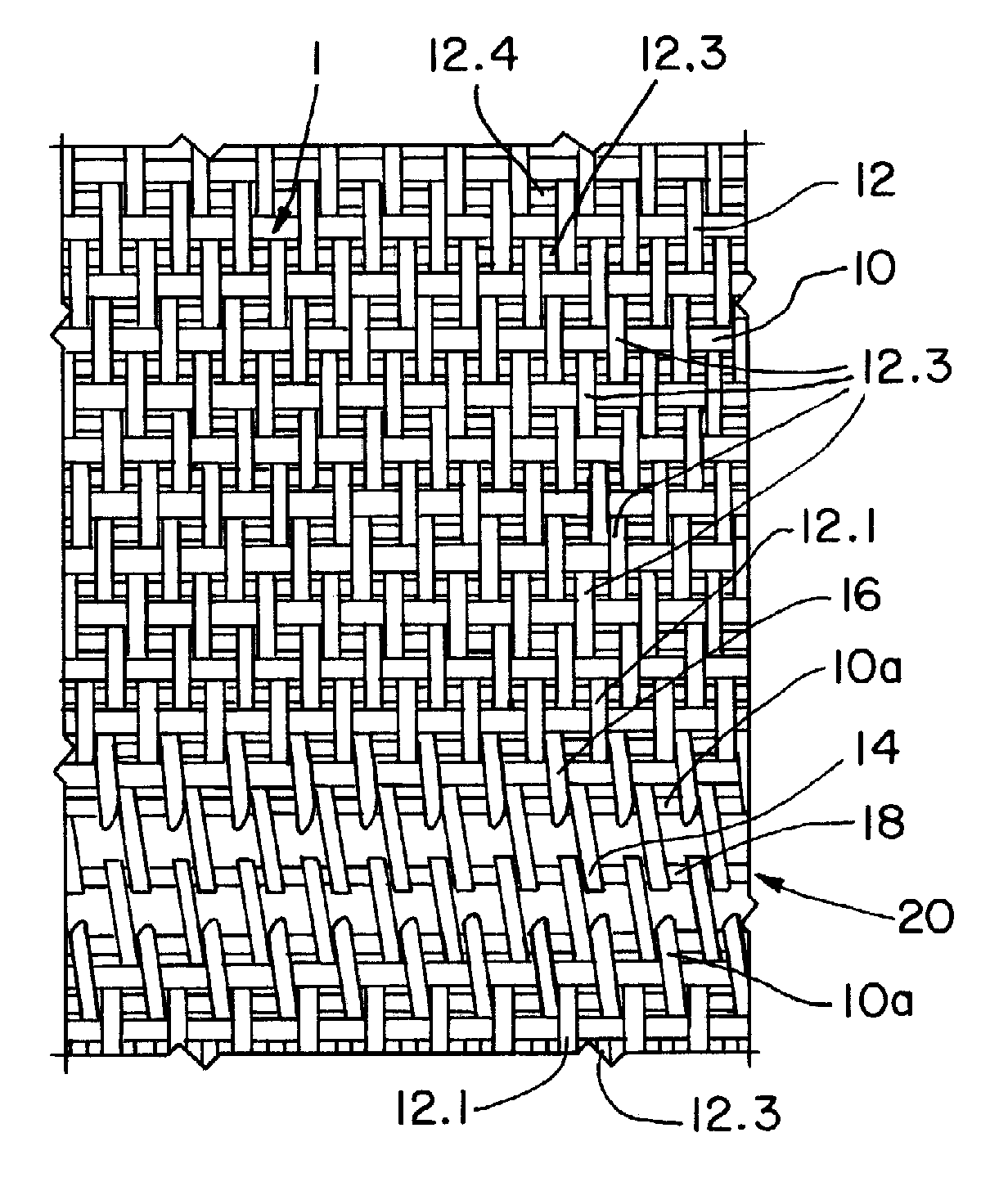
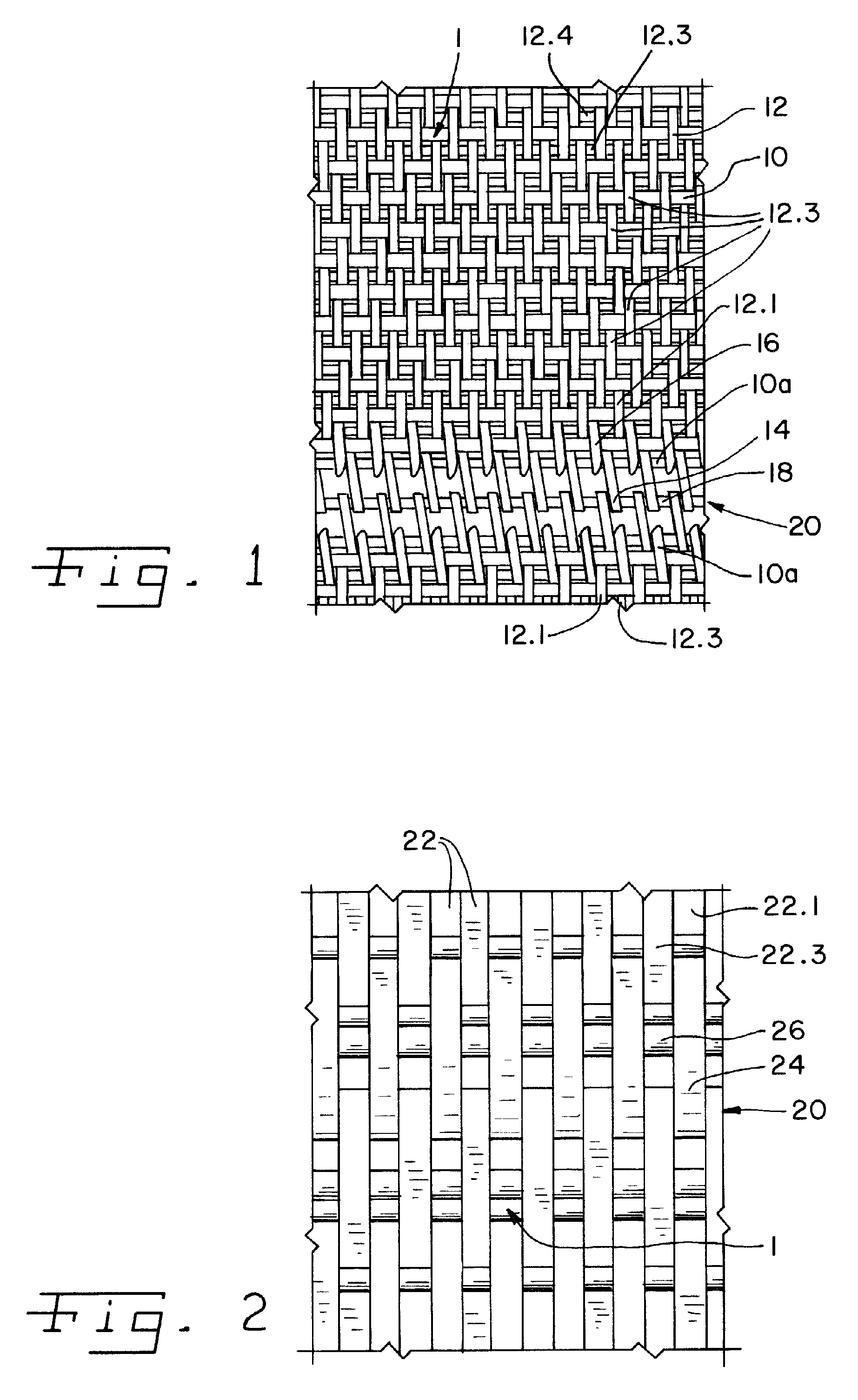
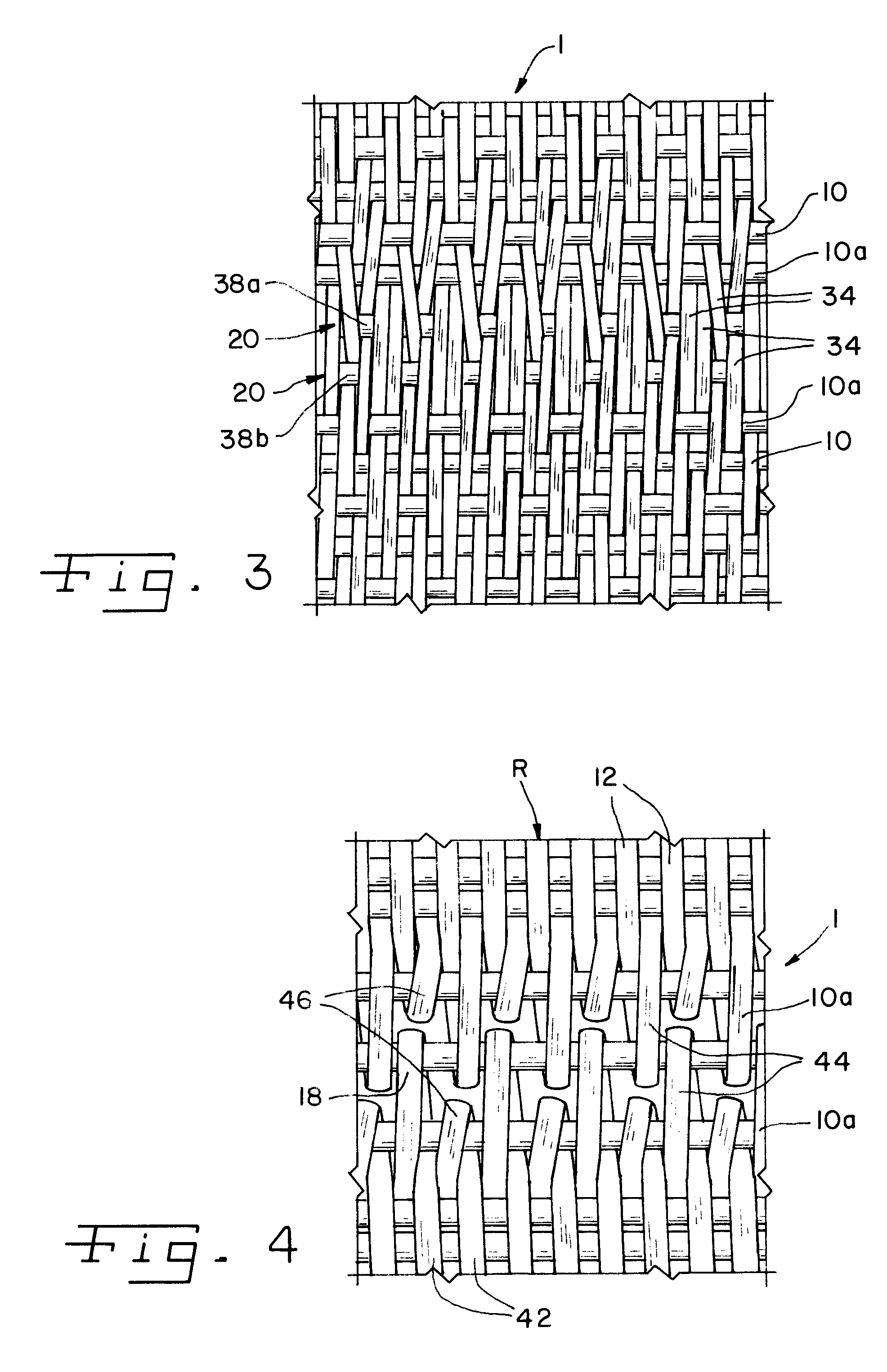
[0022] Referring now to the drawings, and more particularly to FIGS. 1-4, there is shown a woven fabric structure for a papermachine clothing or another belt, such as a filter or conveyor belt, including an array of cross-machine direction weft yarns 10, extending parallel to an edge of the fabric 1, and a last weft yarn 10a, defining the edge. An array of warp yarns 12 is woven through the weft yarns 10 substantially orthogonally to the weft yarns 10 of, and in machine direction of, the fabric 1.
[0023] It is shown in the embodiment of FIG. 1, which shows a fragmentary, enlarged, detail view of part of a seam region of a woven fabric 1, that a normal loop seam is made by reweaving the first machine direction warp yarn 12.1 back into the fabric 1 to form a loop 14. The second machine direction warp yarn (12.2 is not visible) is brought out of the fabric within the seam area. This leaves a space for the first machine direction warp yarn to replace the pathway of the second machine di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com