Optical Device
a technology of optical devices and optical components, applied in the field of optical devices, can solve the problems of spot size limitation, low efficiency, and reduced price of the medium itself, and achieve the effect of high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0061] Next, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
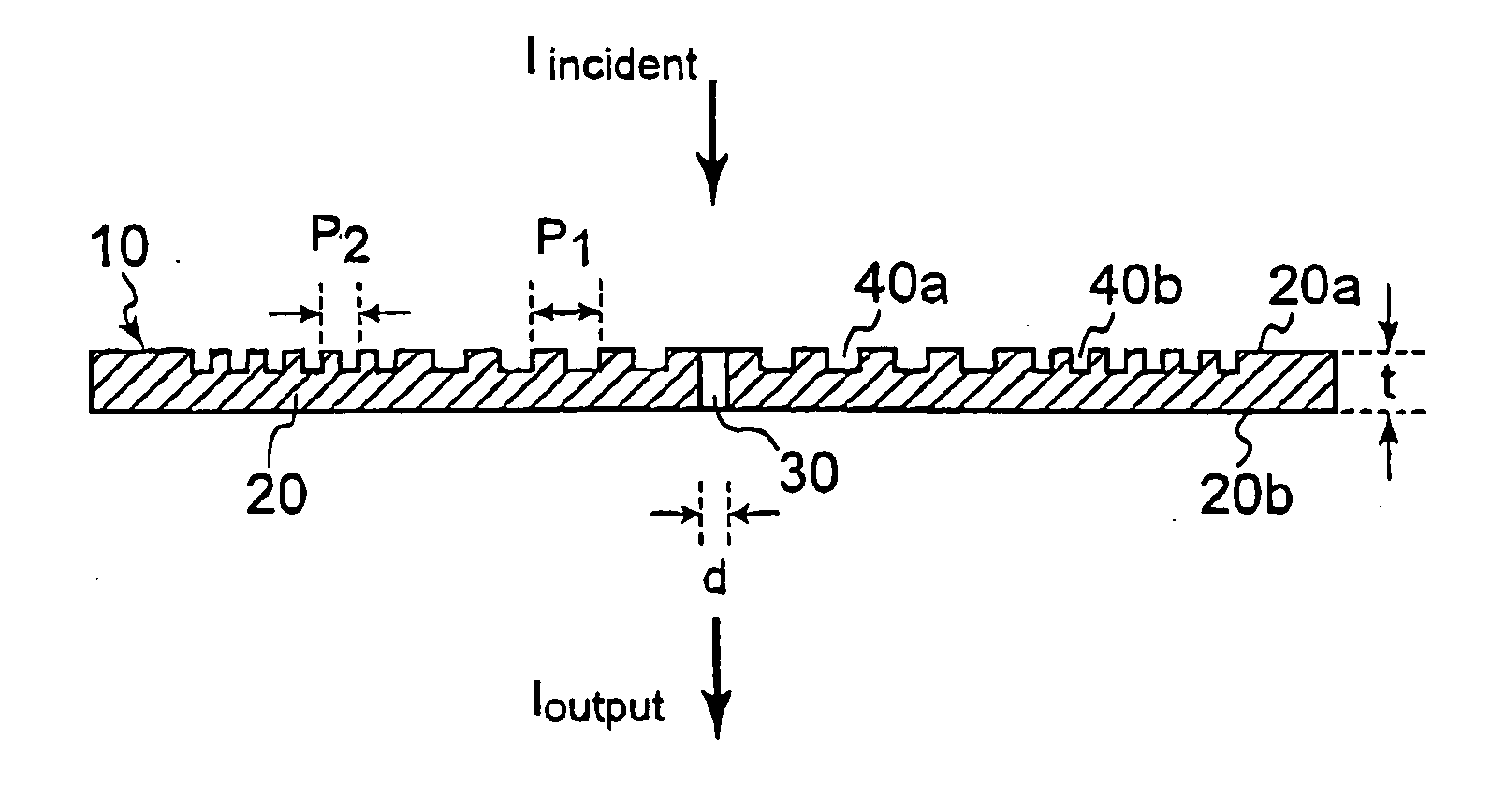
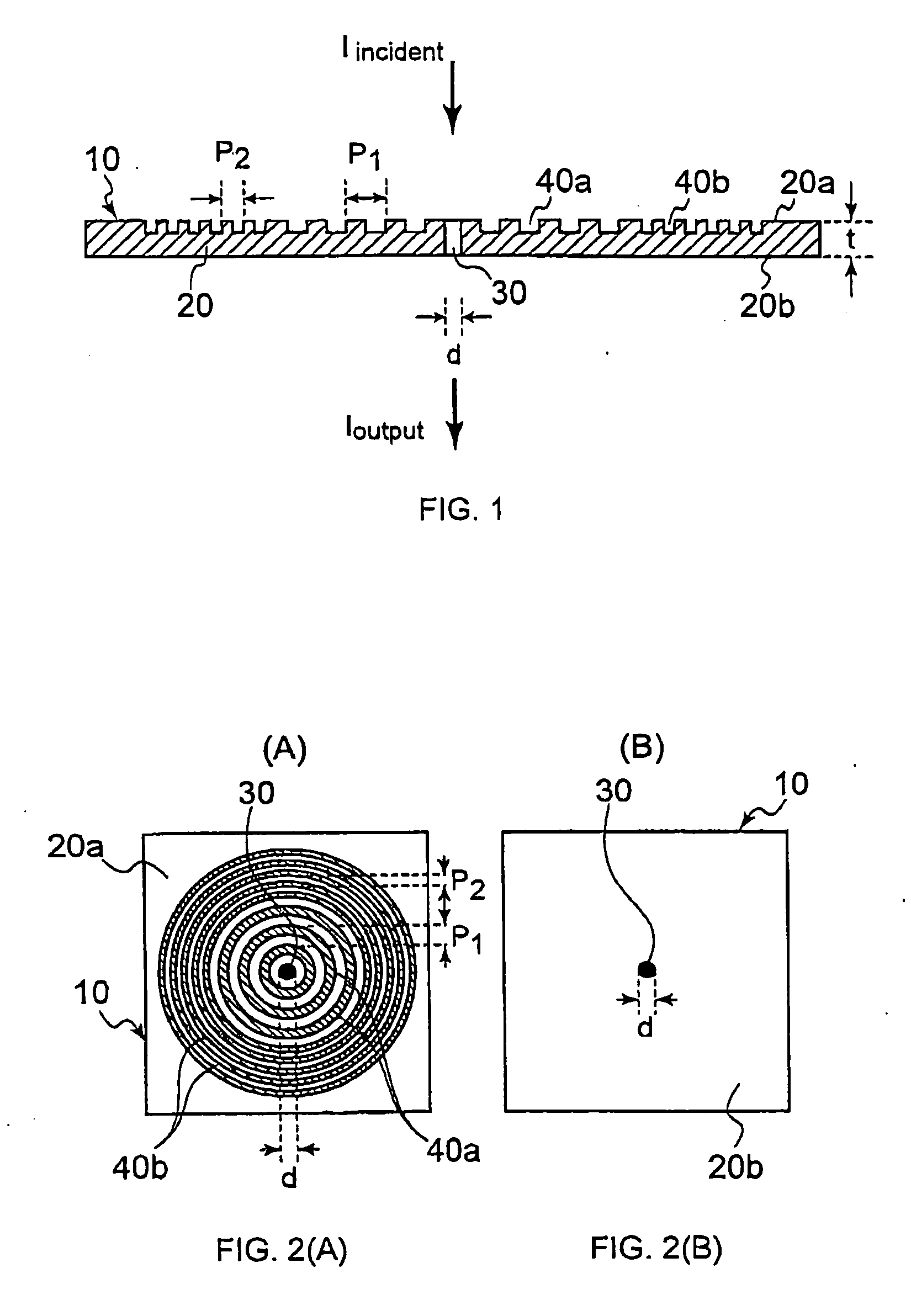
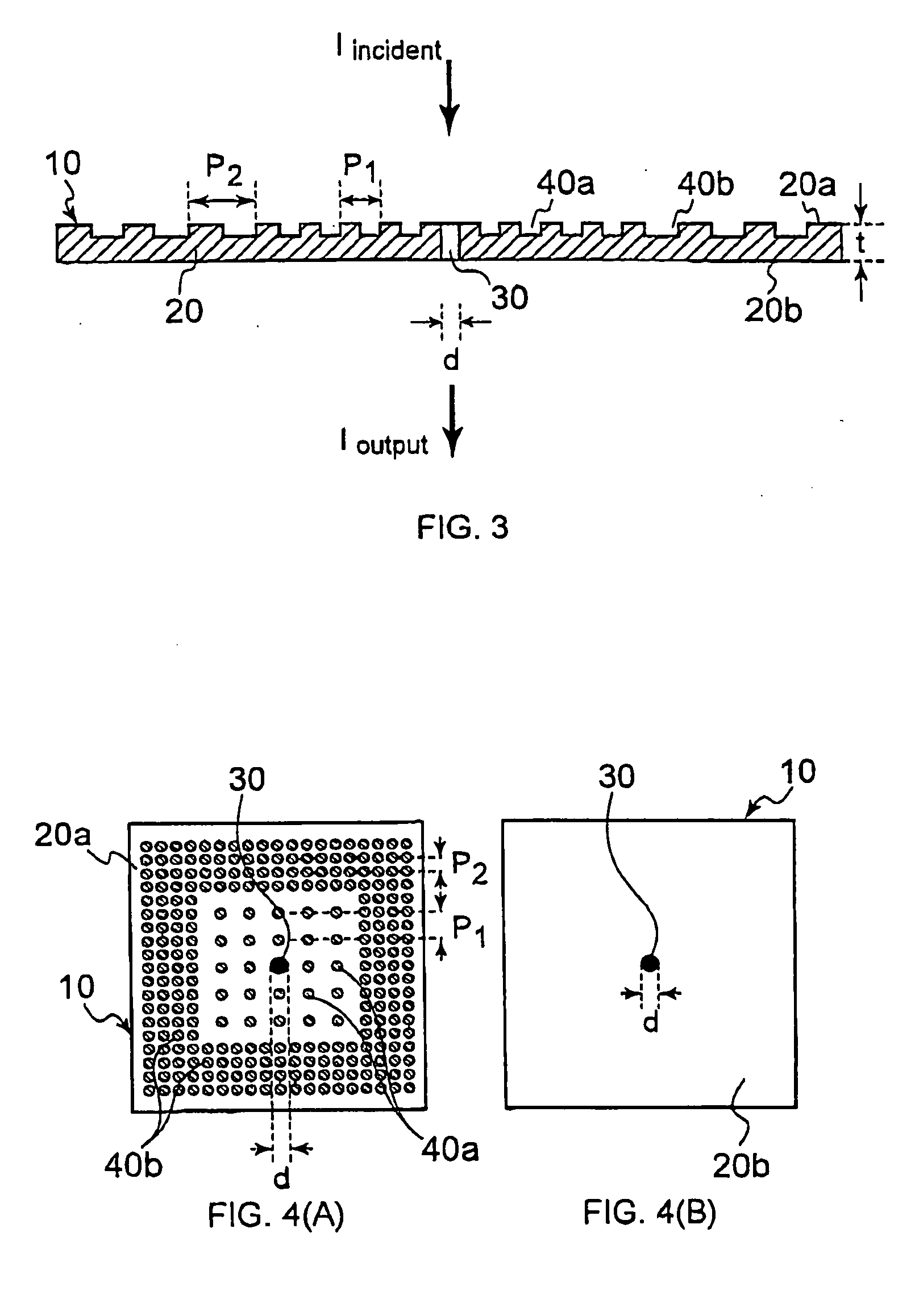
[0062]FIGS. 1, and 2(A) and (B) are diagrams showing an optical device 10 in a first embodiment of the present invention. The optical device 10 has a conductive thin film 20 including a first surface 20a and a second surface 20b. The first surface 20a of the conductive thin film 20 is irradiated with incident light. The conductive thin film 20 has at least one hole whose diameter is d, that is, an opening 30. The conductive thin film 20 is made of a metal or a doped semiconductor material, and aluminum, silver, gold, chromium or the like is preferable. In a case where light of a visible light region is used as incident light, silver is preferable from a viewpoint of optical loss, but the material is not necessarily limited to silver.
[0063] The conductive thin film 20 is provided with a first periodic surface pattern 40a in at least one of the first surface 20a and the second surfac...
embodiment 2
[0093] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 11 to 13.
[0094]FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an optical device 10 of the present embodiment. The optical device 10 has a conductive thin film 20 including a first surface 20a and a second surface 20b. The first surface 20a of the conductive thin film 20 is irradiated with incident light. The conductive thin film 20 has at least one hole having a diameter d, that is, an opening 30.
[0095] The conductive thin film 20 is provided with a third periodic surface pattern 40c on the second surface 20b of the conductive thin film 20. Here, a reason why the periodic surface pattern 40c formed on the second surface 20b is referred to as the third periodic surface pattern is that the pattern can be combined with the first and second periodic surface patterns 40a and 40b shown in FIG. 1 or 3 as shown in FIG. 12 or 13. A period length P3 of the third periodic surface pattern 40c is the odd time(s) ...
embodiment 3
[0116]FIG. 17 shows one embodiment of an optical head constituted using an optical device of the present invention.
[0117] An “optical recording medium” used in description of the present embodiment means an arbitrary medium with respect to which data is written or read using light, but the present invention is not limited to a phase change medium, a magnetic optical medium, and a dyestuff medium. When the medium is a magnetic optical medium, writing is optically performed, and reading is performed magnetically, not optically in some case.
[0118] An optical head 200 in FIG. 17 is formed into a slider shape for floating the optical head at a predetermined height by rotation of an optical recording medium 150. Laser light emitted from laser 80 is introduced via an optical fiber 100, and collimated by disposing a collimator lens 60 constituted of a micro lens. Furthermore, the collimated light changes its optical path at right angles by a total reflection mirror 70, and the light is fu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| period length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com