Methods for detection of a target nucleic acid by capture using multi-subunit probes
a multi-subunit, target nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of methods of detecting or measuring a target nucleic acid, can solve the problems of inaccessible probes, amplified materials require additional manipulation, and none of these patents teach the generation of signals, so as to improve the performance of allele-discriminating probes. the effect of strong stabilizing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Probe Design and Preparation
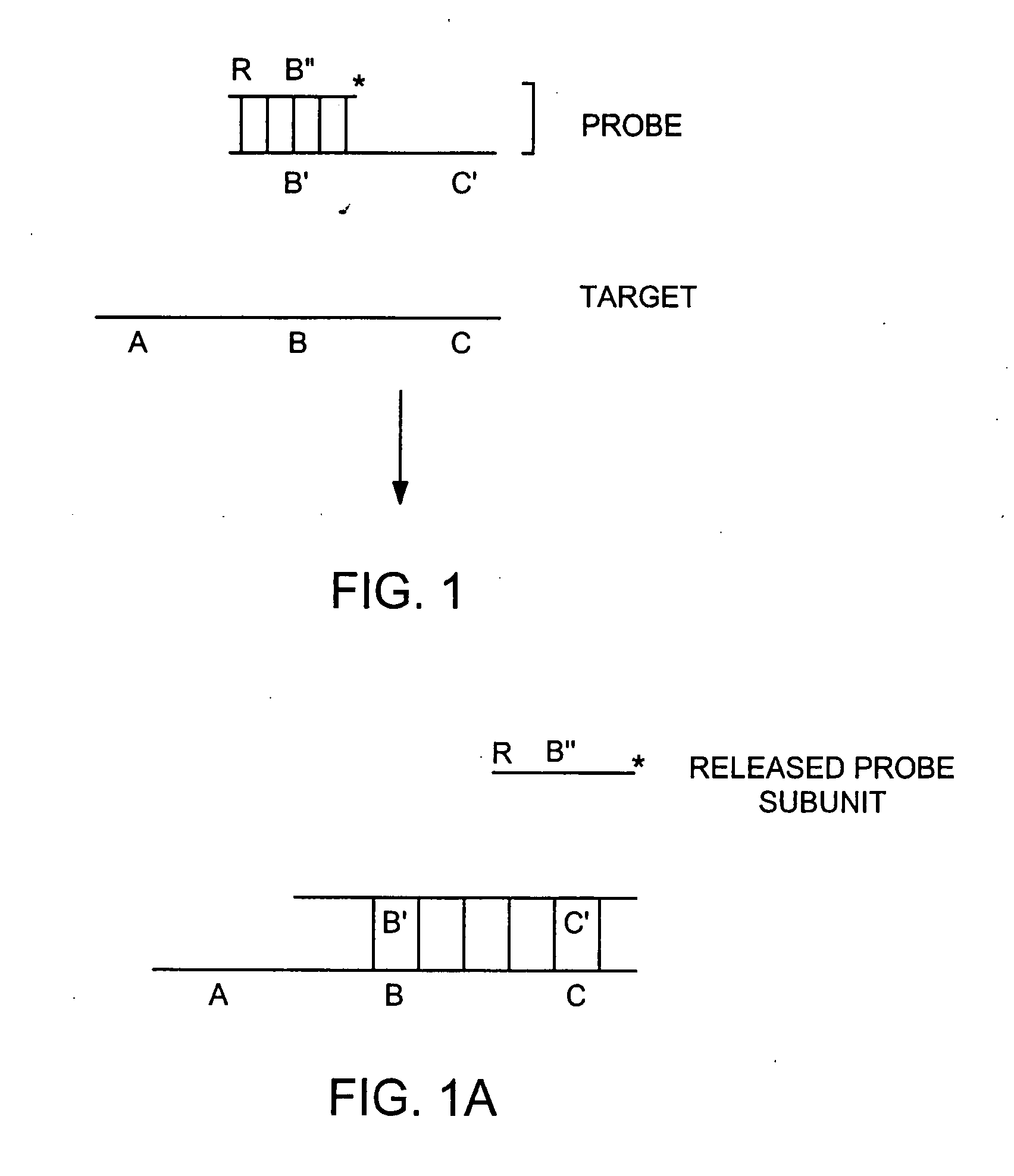
[0428] The invention provides for a probe comprising at least two subunits, one of which comprises a binding moiety, wherein a subunit of the probe dissociates from the remaining subunits of the probe upon binding of the probe to a target nucleic acid. The invention also provides for a probe comprising at least two subunits, a secondary structure that changes upon binding of the probe to a target nucleic acid and a binding moiety. A probe according to this embodiment of the invention also binds to a target nucleic acid such that a subunit of the probe dissociates from the remaining probe subunits.
[0429] A subunit of a probe according to one embodiment of the invention is 5-250 nucleotides in length and ideally 17-40 nucleotides in length. At least one subunit of the probe has a target nucleic acid binding sequence that is from 7 to about 140 nucleotides, and preferably from 10 to about 140 nucleotides. Probes may also comprise non-covalently bound or co...
example 2
Probe Design and Preparation
[0440] The invention provides for a probe comprising at least two subunits, one of which comprises a tag, and wherein a subunit of the probe dissociates from the remaining subunits of the probe upon binding of the probe to a target nucleic acid. The invention also provides for a probe comprising at least two subunits, a secondary structure that changes upon binding of the probe to a target nucleic acid and a tag. A probe according to this embodiment of the invention also binds to a target nucleic acid such that a subunit of the probe dissociates from the remaining probe subunits.
[0441] A subunit of a probe according to one embodiment of the invention is 5-250 nucleotides in length and ideally 17-40 nucleotides in length. At least one subunit of a probe has a target nucleic acid binding sequence that is from 7 to about 140 nucleotides, and preferably from 10 to about 140 nucleotides. Probes may also comprise non-covalently bound or covalently bound subun...
example 3
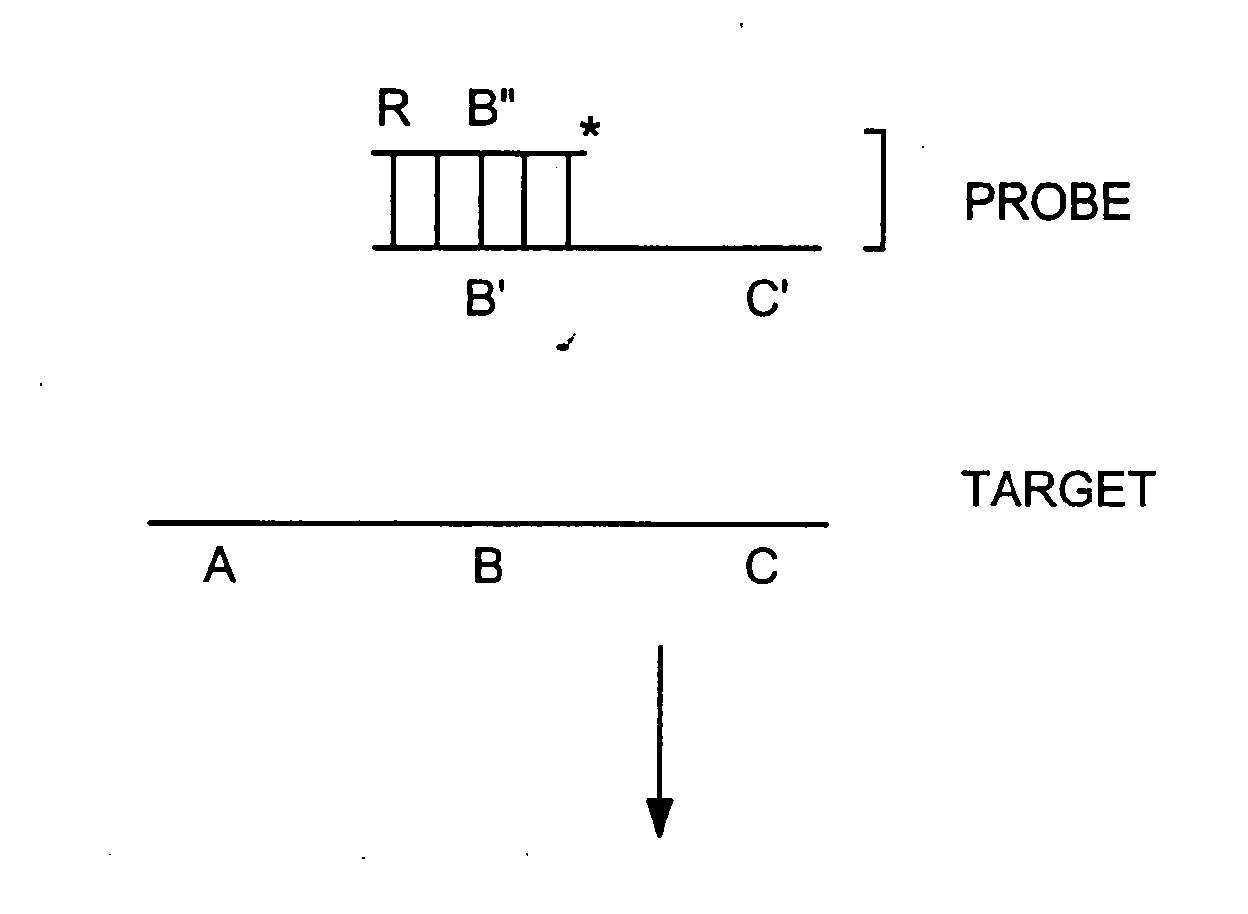
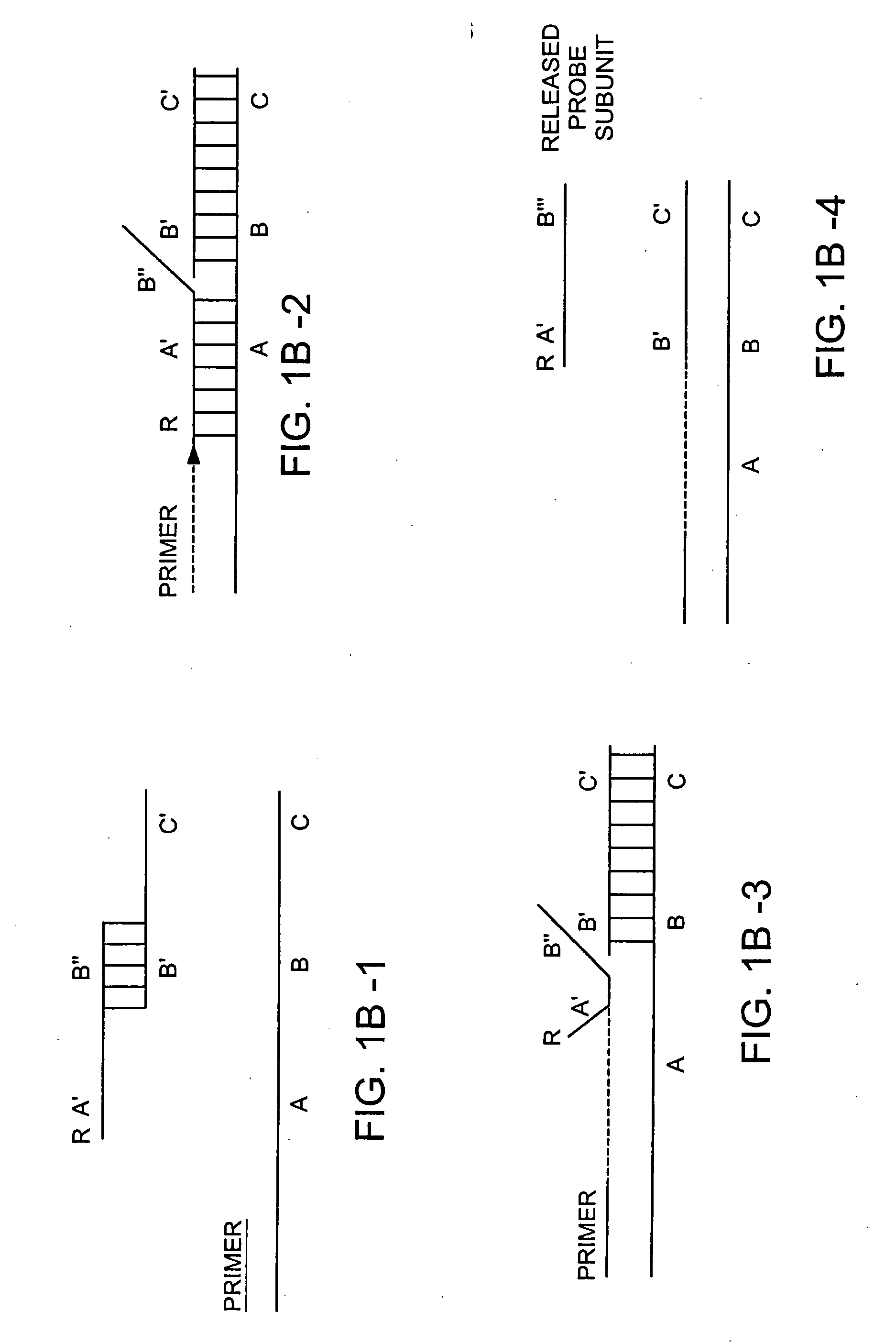
[0452] A target nucleic acid can be detected and / or measured by the following method. A labeled detection complex is formed by annealing at 95° C. for 5 minutes and then cooling to approximately 50-600 C (a) a sample containing a target nucleic acid (ABC in FIG. 1B) and (b) a downstream, labeled oligonucleotide probe comprising two subunits and a binding moiety (for example the combination of A′B″ and B′C′ in FIG. 1B, comprising a nucleic acid sequence 5′AGCTACTGATGCAGTCACGT3′), wherein the probe specifically hybridizes to a region of the target nucleic acid. Annealing is carried out in the presence of 1× Sentinal Molecular beacon core buffer or 10×Pfu buffer. Following annealing, the labeled first subunit of the probe dissociates from a second subunit of the probe and is released to generate a signal.
[0453] Alternatively, a labeled detection complex is formed by annealing a target nucleic acid to a labeled oligonucleotide probe comprising two subunits and having a secondary struct...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com