Multi-layer nonwoven having a printed layer and products made therefrom
a multi-layer nonwoven and printed layer technology, applied in weaving, other domestic articles, hollow wall articles, etc., can solve the problems of inability to incorporate additional features into the finished nonwoven and/or the resulting end product, difficult to add attractive features, and the potential for the transfer of inks and/or pigments used, etc., to achieve convenient use, increase the utility of the effect of use and convenient us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
quantitative example
[0049]The fibers for the carded webs for use in a test batch are pre-mixed by hand in a box. The ratio of high opacity polypropylene (HOPP) to rayon is 60% HOPP to 40% rayon, or a ratio of 3:2. The HOPP fibers may be obtained from FIBERVISIONS, Product No. 6801060330211. The fibers are 1.5 denier, white, having a thickness of 0.060 inches and a cut length of 1.5 inches (38 mm). The rayon fibers may be obtained from Liberty Fibers Corp., type 8191, with dull regular luster. The denier for the rayon fibers is 1.50 dpf (1.7 dtex) cut to a length of 1.57 inches (40 mm). The fibers are used to make the carded webs.
[0050]The fiber mixture is fed using a feed system manufactured by Befama. The pre-blended fibers are fed into the system and formed into carded webs, each web having a basis weight of approximately 15 grams per square meter.
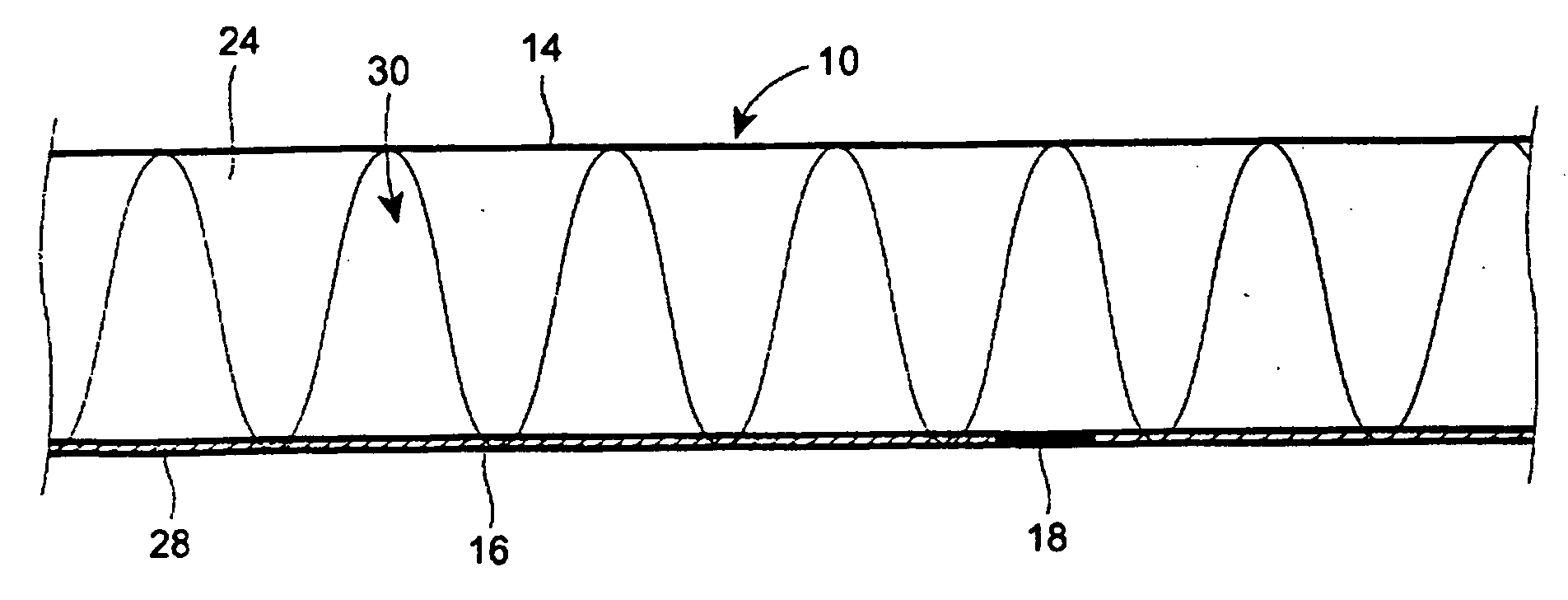
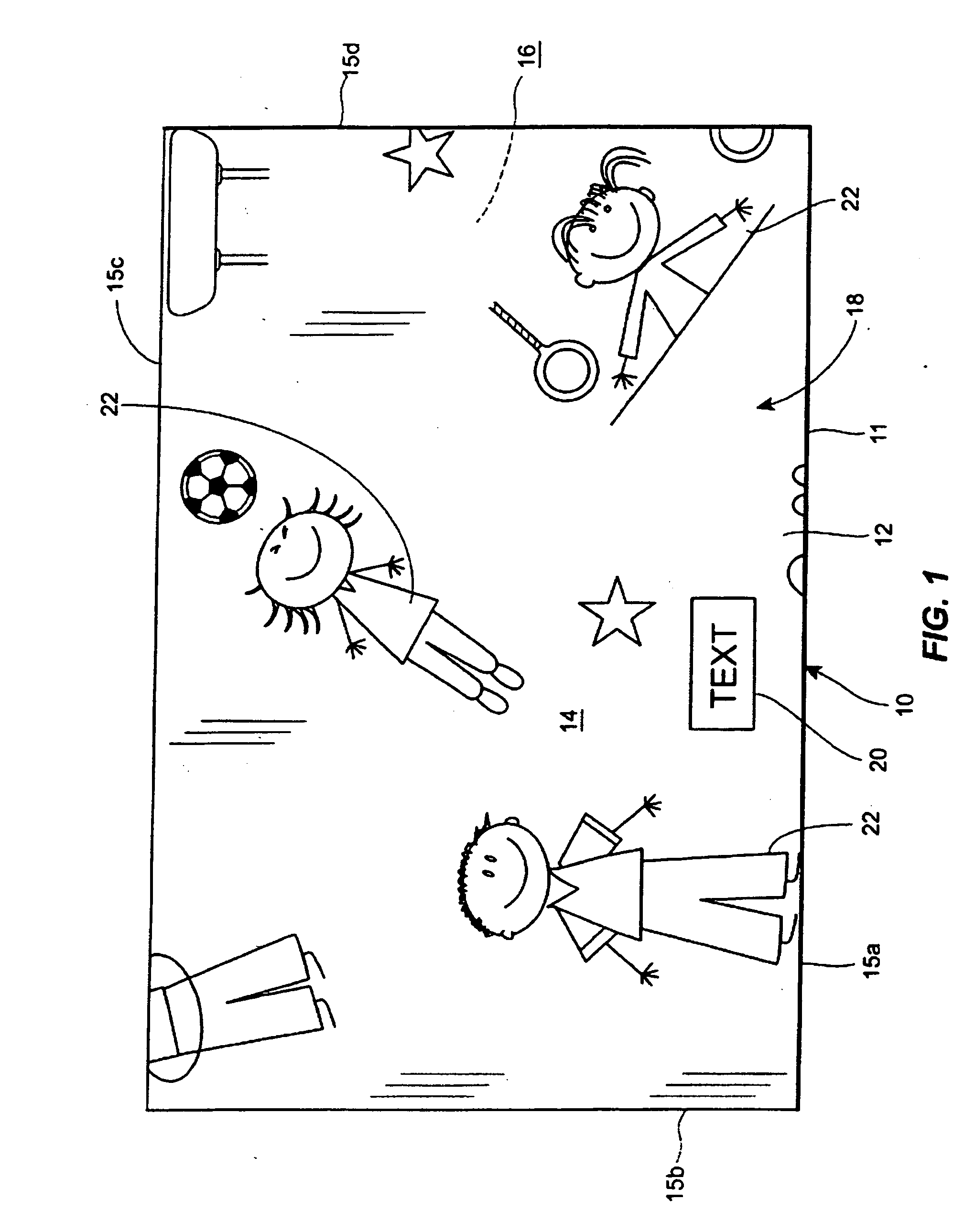
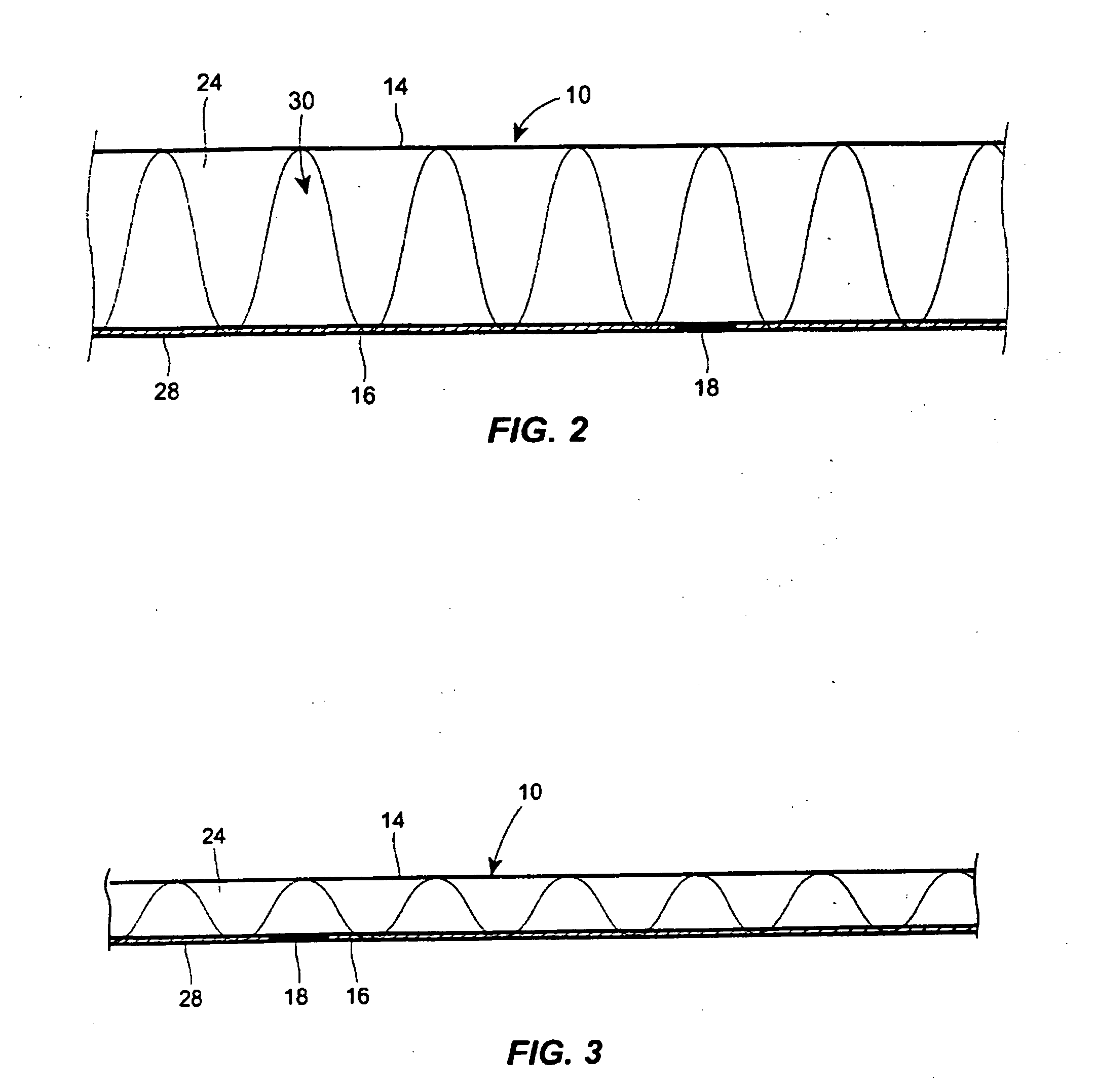
[0051]The carded webs are fed onto foam boards and cut to length with scissors. A sheet of 4-color printed UK Charmin Ultra single ply tissue is used, havi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cut length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com