Location management for radio frequency identification readers
a technology of radio frequency identification and location management, applied in the direction of burglar alarm mechanical actuation, using reradiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the coverage area of the reader, compromising the application of rfid,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
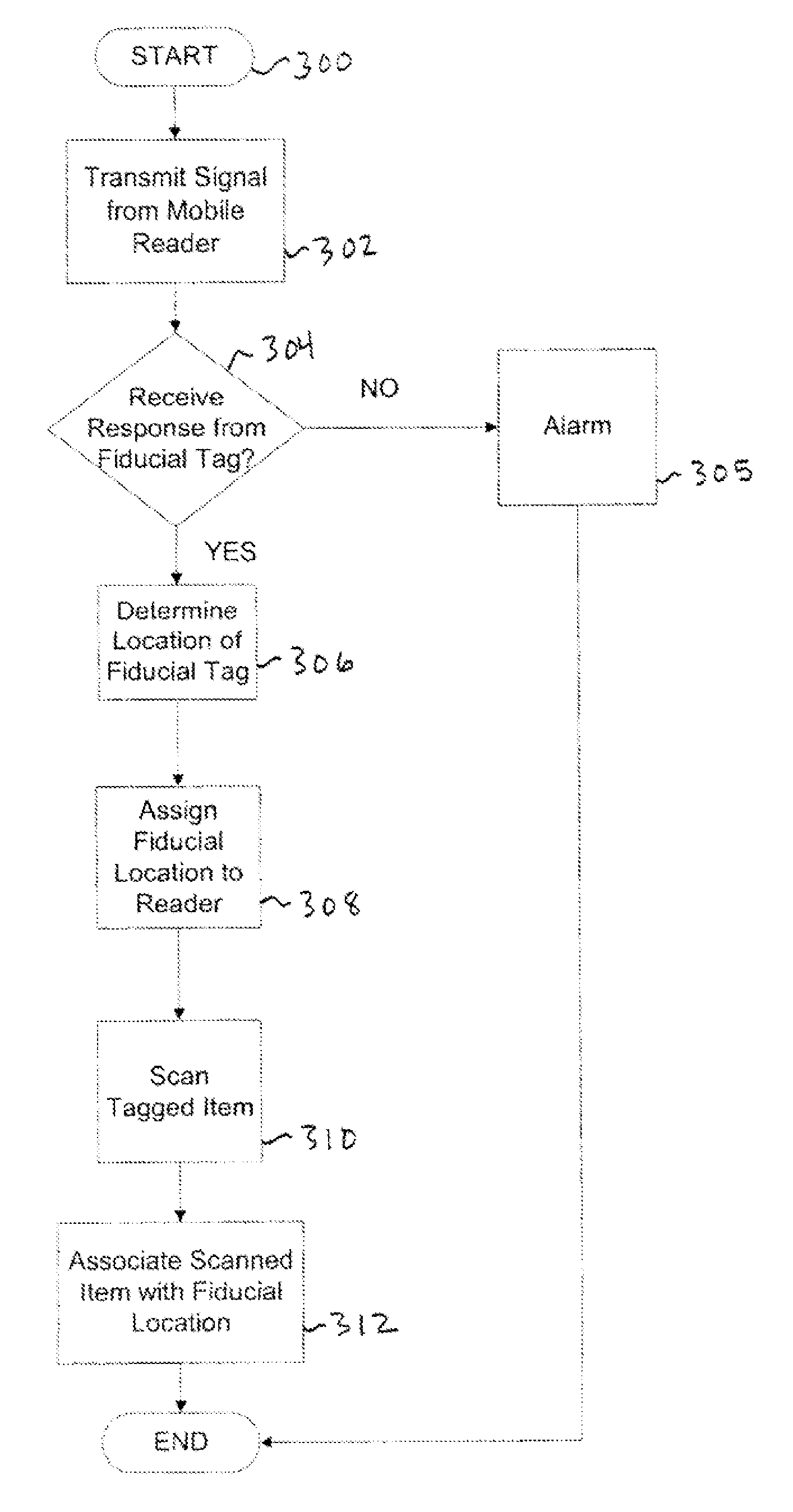
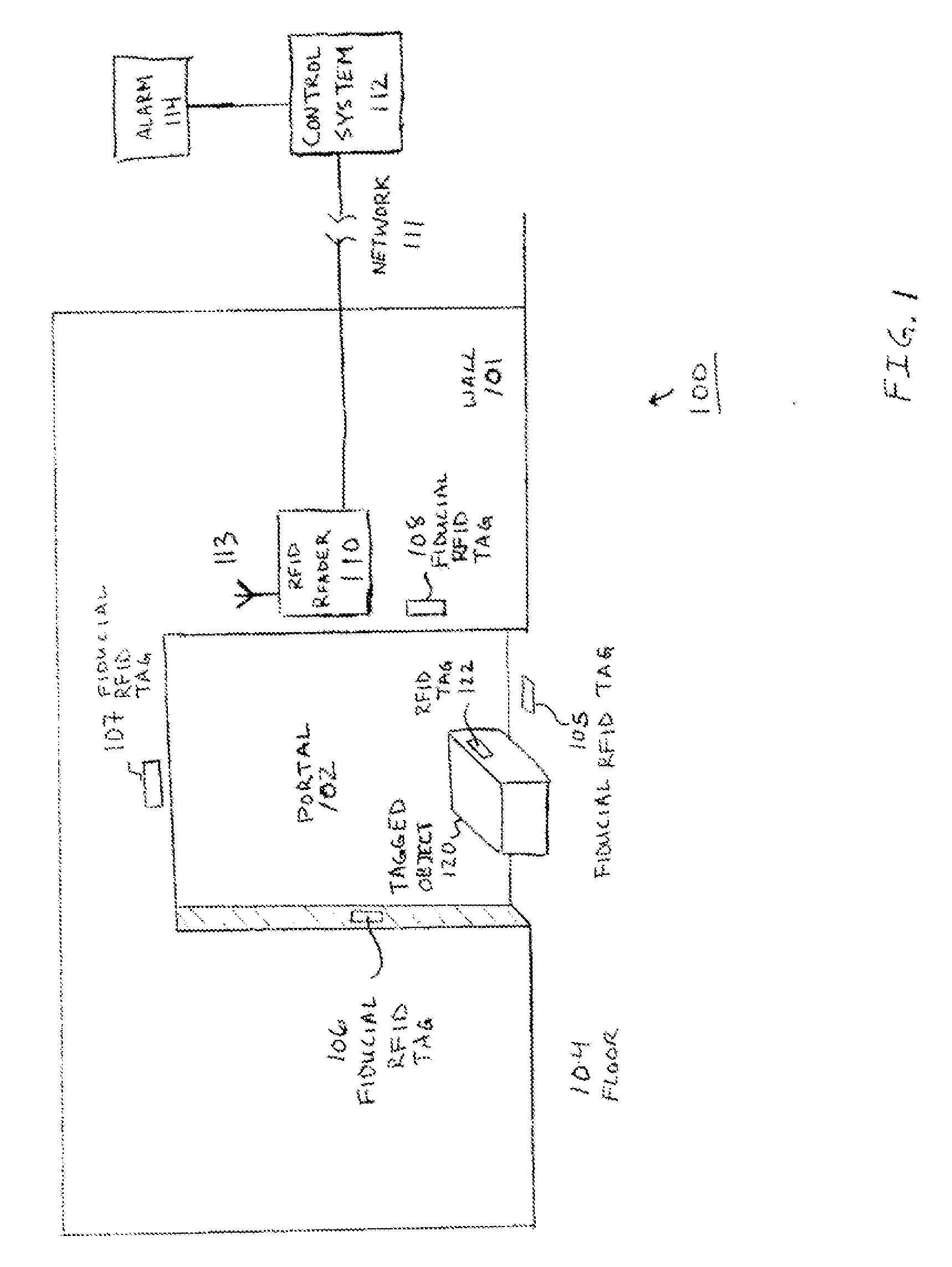
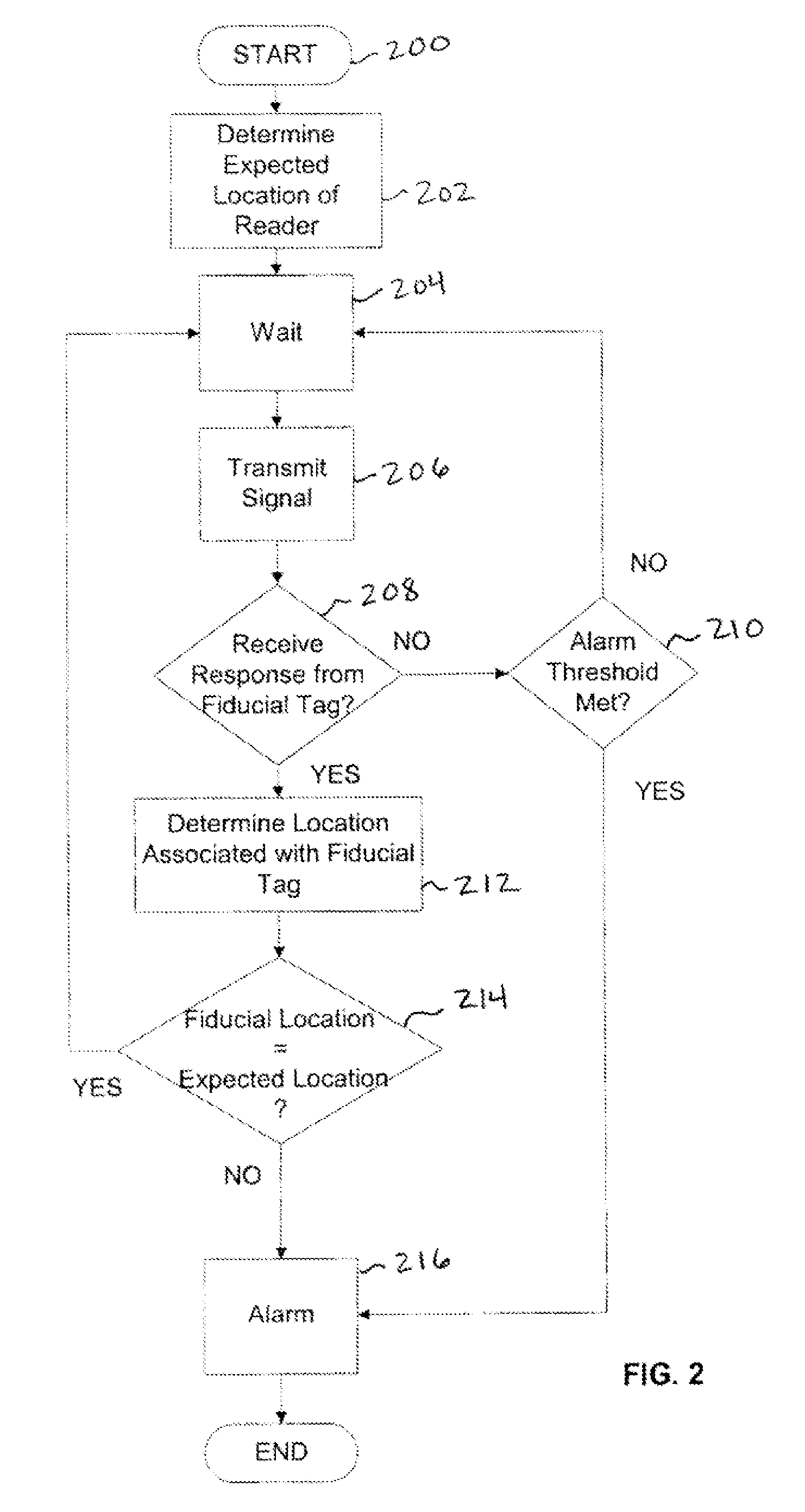
[0025]Embodiments of a system and method for radio frequency identification (RFID) location management are described herein. In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth to provide a thorough understanding of embodiments of the invention. One skilled in the relevant art will recognize, however, that the invention can be practiced without one or more of the specific details, or with other methods, components, materials, etc. In other instances, well-known structures, materials, or operations are not shown or described in detail to avoid obscuring aspects of the invention.
[0026]RFID systems can be active (transmitting) or passive (operating through a backscatter mechanism). Passive (backscatter) systems can be battery assisted (e.g. to increase range) or operate without a battery (e.g. for low cost and independence of any battery fife). This last category of WID systems are often called “beam-powered” tags. Embodiments of the present system should be particula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com