Alpha-Synuclein Kinase
a technology of alpha-synuclein and kinase, which is applied in the field of alpha-synuclein kinase, to achieve the effect of reducing the activity of plk2, not plk1, and reducing the activity of alpha-synuclein phosphorylation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Screen for Kinases that Modulate Alpha-Synuclein Phosphorylation
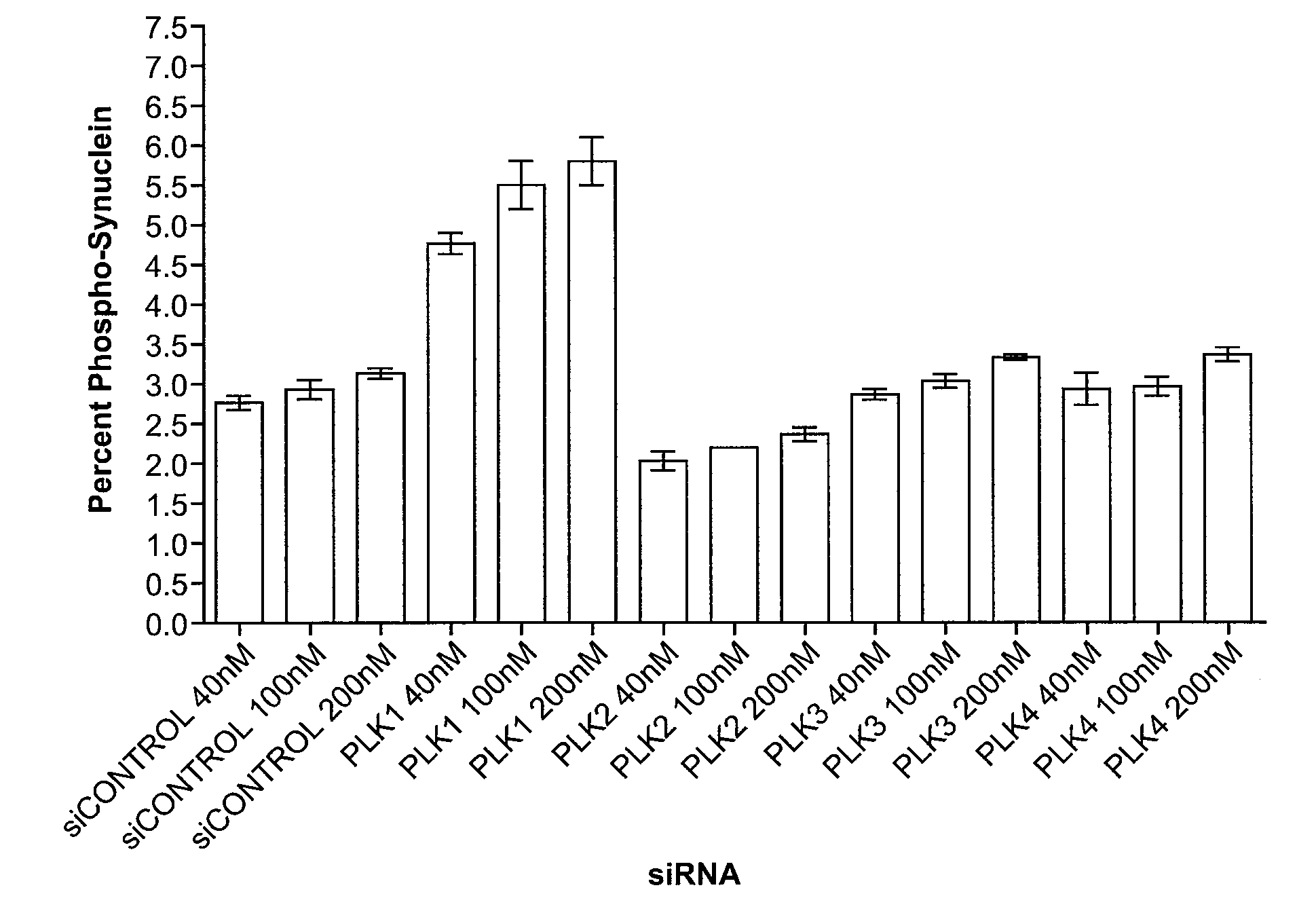
[0171]To identify the kinase or kinases that phosphorylates α-synuclein at serine-129 an siRNA kinase library (Ambion) was screened on cells containing a quantifiable amount of phosphorylated α-synuclein. Human embryonic kidney cell line HEK293 cells (PEAK cells) stably transfected with human wild-type α-synuclein under control of a CMV promoter (PEAK-Syn cells) were transfected with 100 nM siRNAs targeting 597 human kinases and were assayed by ELISA assays to quantitate total and phospho-synuclein levels. Ninety-five kinases with siRNAs that altered the percentage of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein were identified (see Tables 1-2). Of those, 28 belonged to the class of kinases that phosphorylate serine residues and hence were capable of directly phosphorylating α-synuclein at serine-129. Others were tyrosine kinases. Although tyrosine kinases do not phosphorylate α-synuclein at ser-129 directly, they can act as upstream...
example 2
Verification of Alpha-Synuclein Phosphorylation Modulation by Re-Screening and by qRT-PCR
[0176]The kinases that showed either an increase or decrease in alpha-synuclein phosphorylation from Example 1 were retested to verify the effect on alpha-synuclein. The confirmation screen was performed using 10 nM siRNA on the targets identified in Example 1 along with several additional kinases of interest. The higher concentration of siRNA in Example 1 was used to ensure that marginal knockdown caused by poorly designed siRNAs could be observed. By using a much lower siRNA concentration in the confirmation screens, the chance of effects due to a general response to the siRNA itself could be much reduced. Some siRNAs that were later reported by Ambion to be ineffective were also re-screened (see replacement library screen below). Finally, some newly identified kinases were screened and those results were added to the pool of results. The kinases that were identified as candidates were tested ...
example 3
Identification of Direct Phosphorylation of Alpha-Synuclein In Vitro
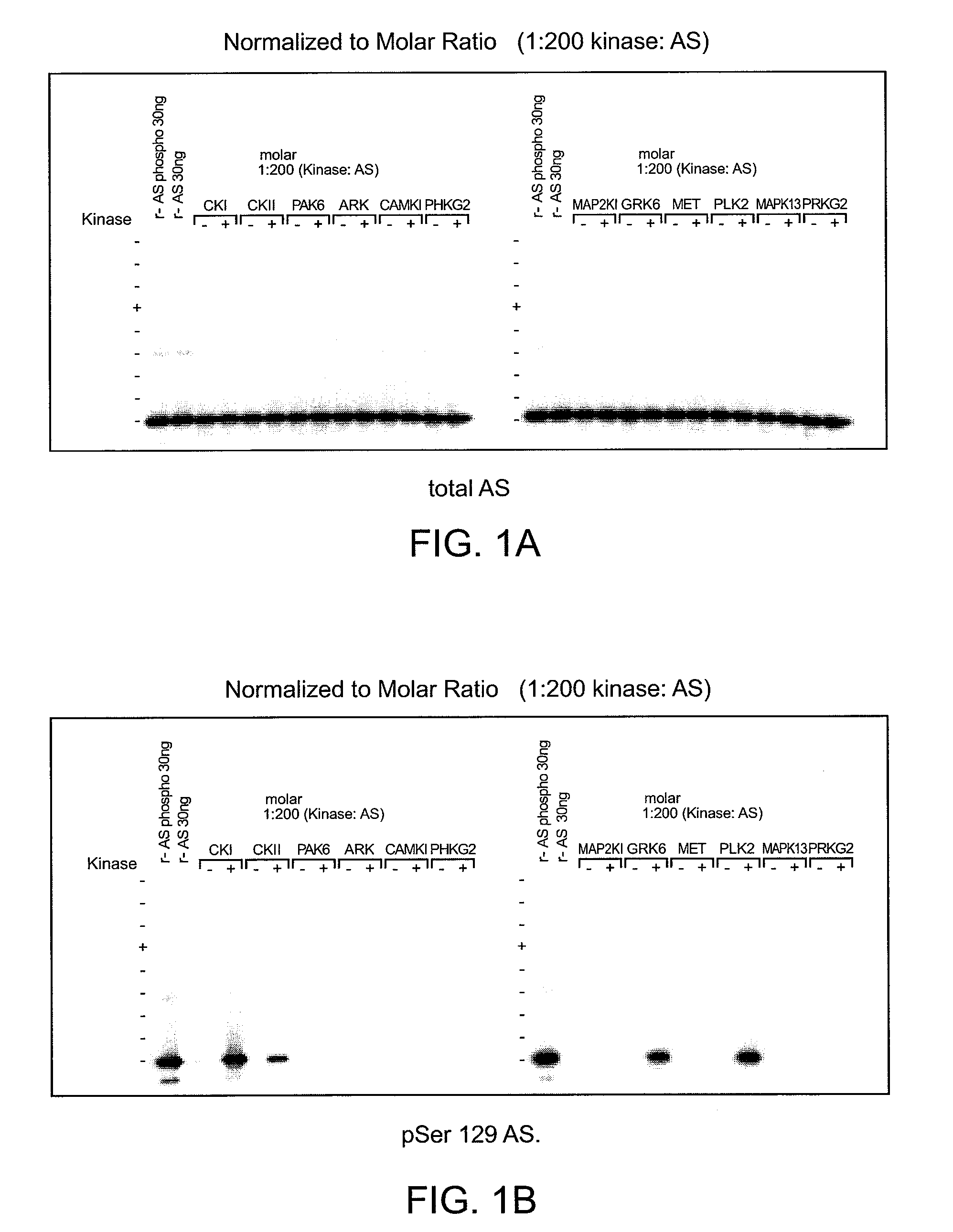
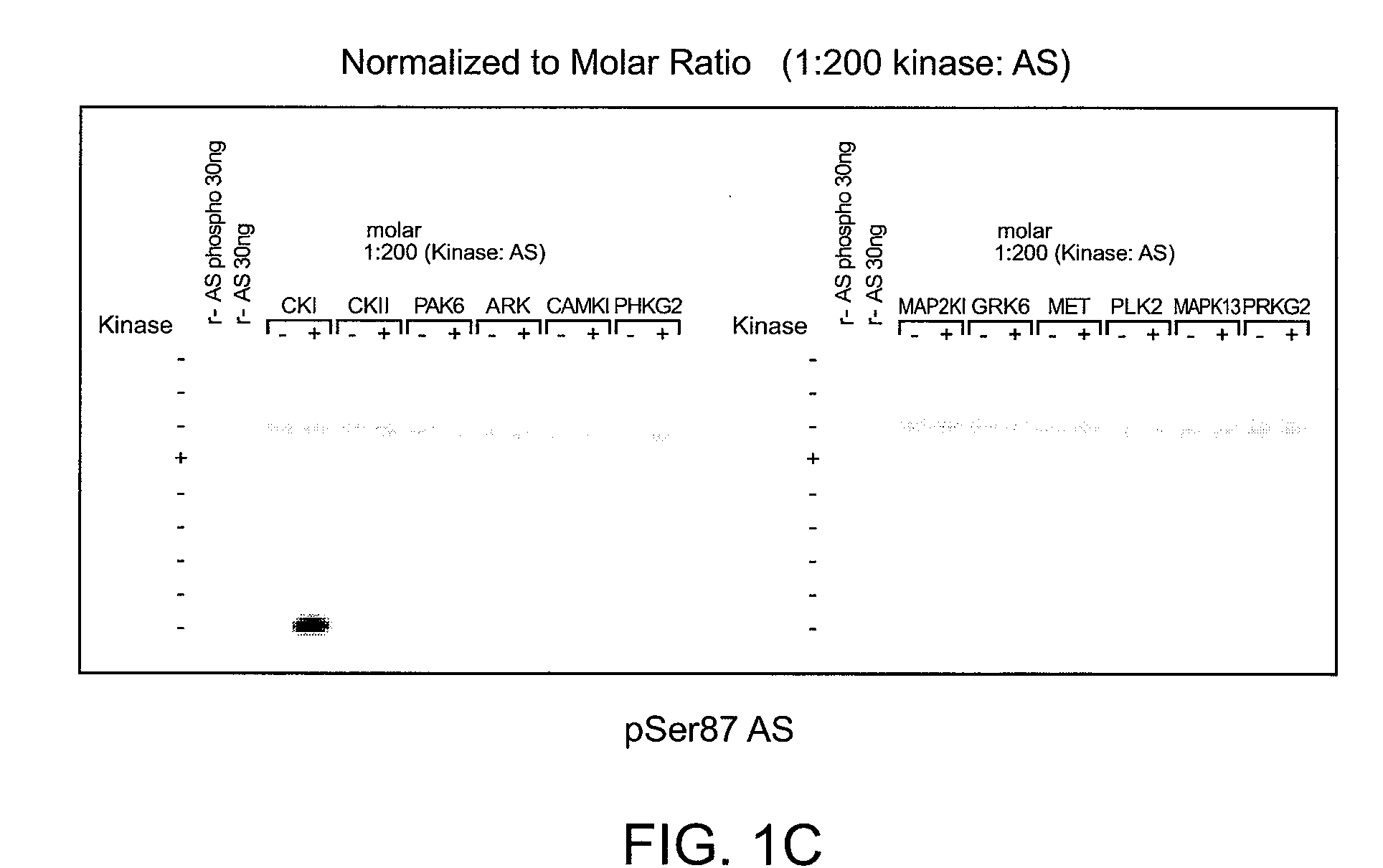
[0200]To determine which of the kinase(s) from the siRNA screen directly phosphorylated alpha-synuclein, purified kinases were incubated with alpha-synuclein in in vitro kinase reactions. These results showed that PLK2, GRK2, 5, 6. and 7 (GPRK2, 5, 6 and 7) were all capable of phosphorylating alpha-synuclein specifically at serine 129 and did not phosphorylate serine 87 in vitro, showing that they could directly phosphorylate alpha-synuclein. MET, CDC7L1, and IKBKB were shown to be incapable of directly phosphorylating alpha-synuclein (FIGS. 1A-C).
[0201]Assay conditions for testing recombinant kinase activities toward recombinant alpha-synuclein at serine 129 were established and found to be reproducible by immunoblot and ELISA analyses. Commercially available recombinant kinases were used when possible. Those that were not available were produced as indicated by recombinant means.
[0202]In FIGS. 1A-C, recombinant ki...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com