Compression Garments And A Method Of Manufacture
a compression garment and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of compression garments, can solve the problems of reducing the effect of lymphatic drainage, affecting the quality of garments, creating undesirable effects, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing ill-fit, reducing ill-fit, and increasing stretch and recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
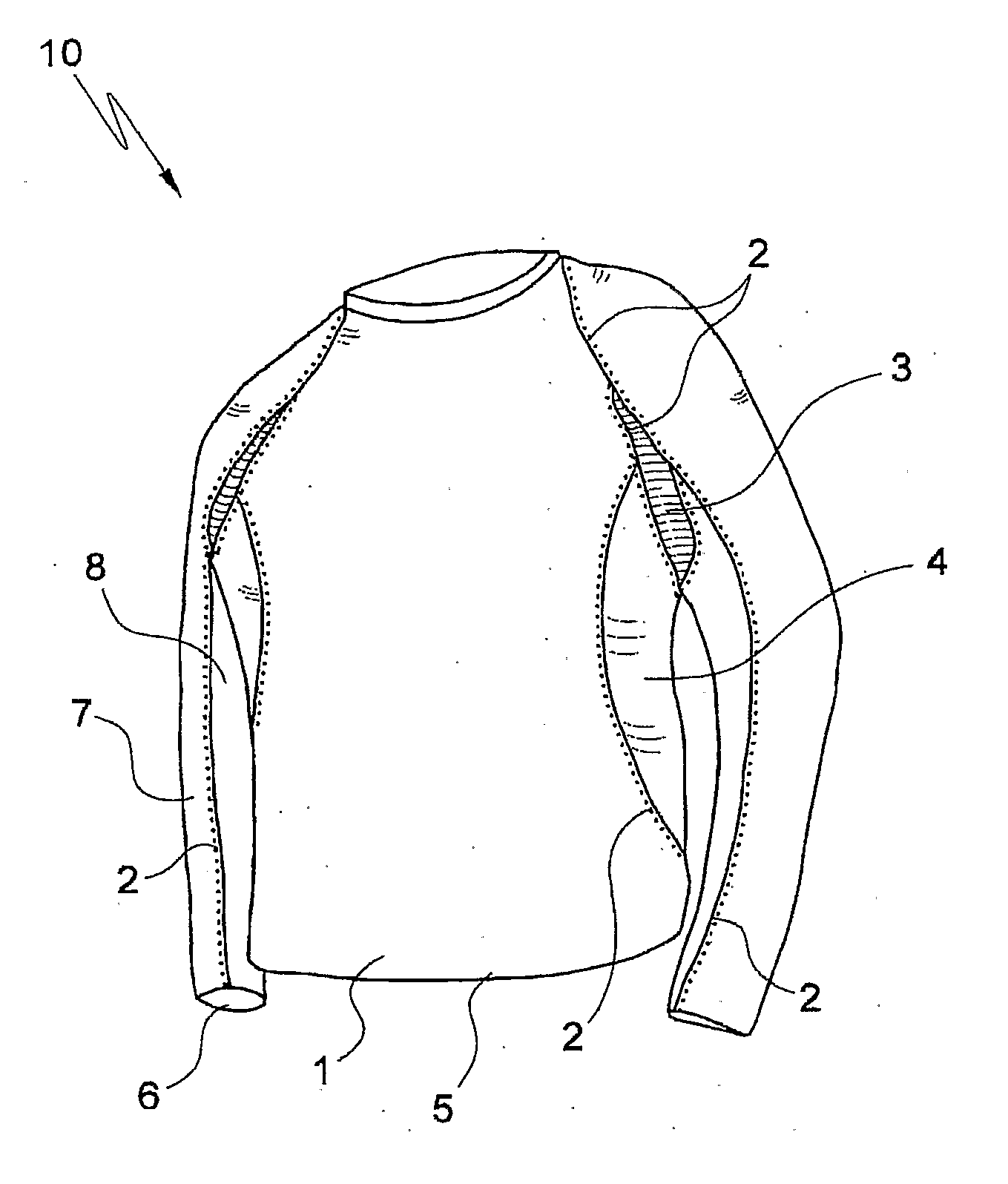
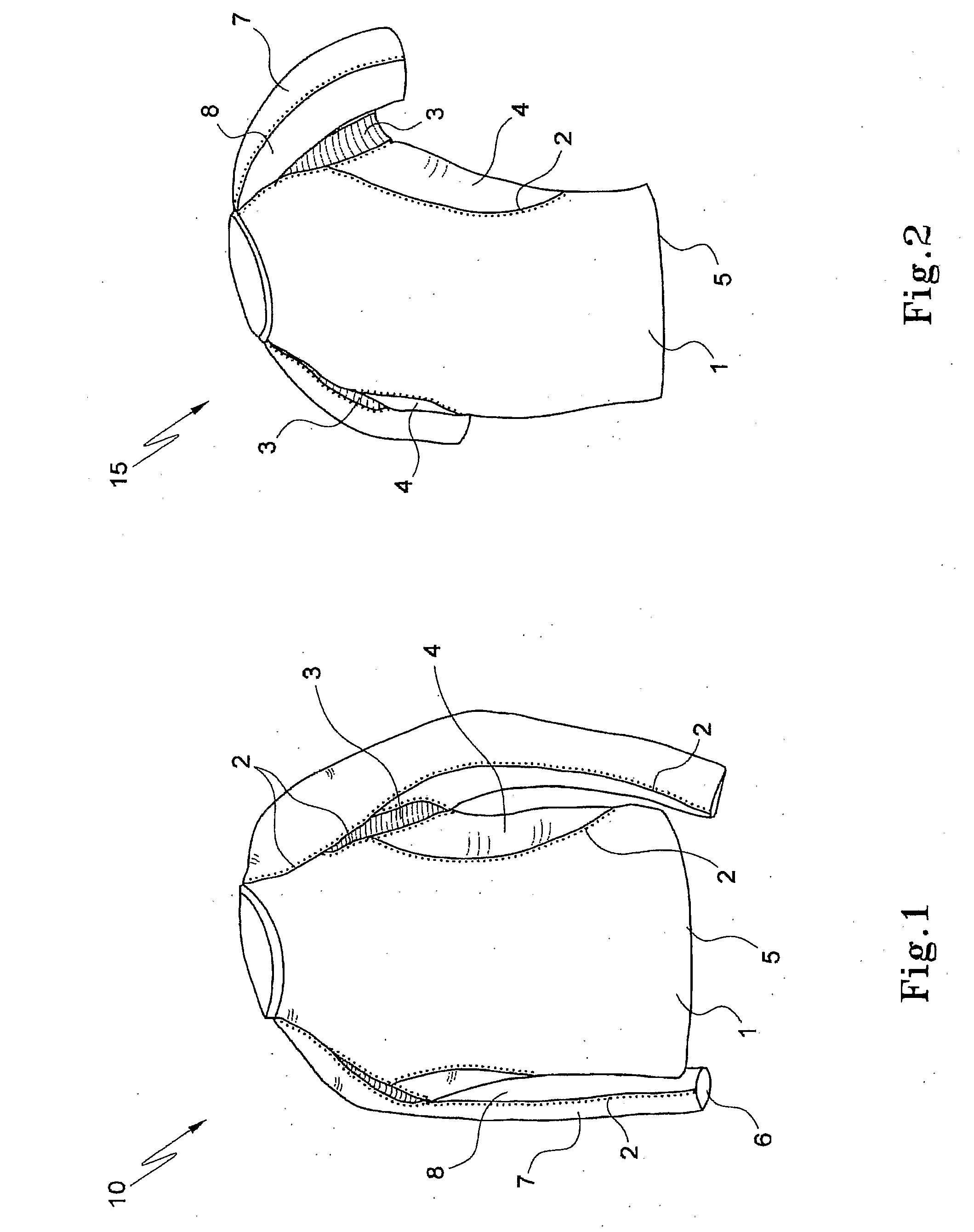
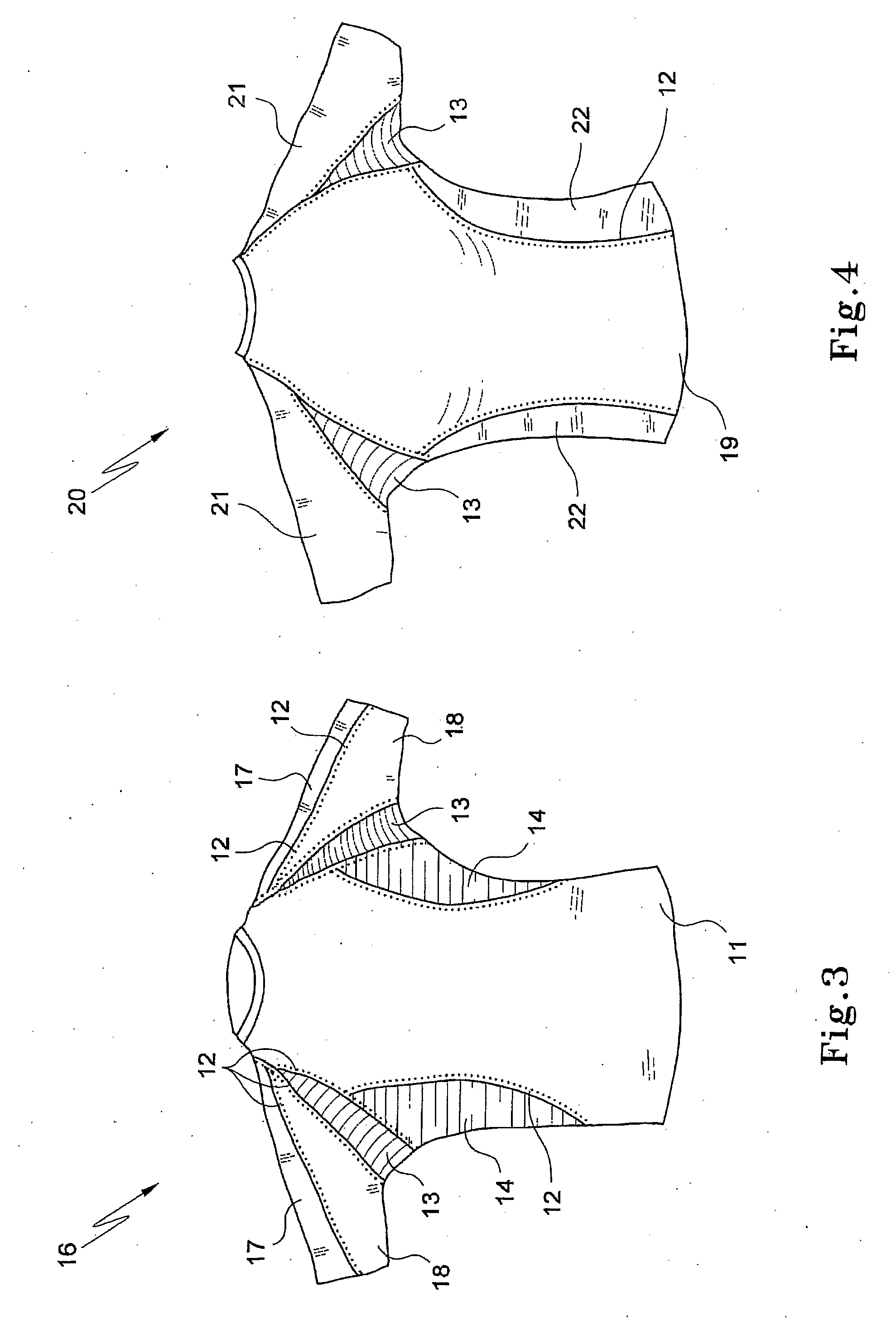
[0137]Referring to the drawings in detail, FIG. 1 shows a garment 10 having a body 1 with four- or six-needle flat bed stitching 2 situated in anatomical positions along the garment, namely along the serratus anterior muscle group. An area 3 under the armpits uses fabric of either a different or a higher compression level (including compositions of higher stretch Elastane) than that of body 1. Similar fabric to that used in area 3 is used on side panels 4 running along the sides of garment 10 to create better compression. Bottom edge 5 of garment 10 is hemmed in a manner that allows stretch and does not create a lateral pressure ridge. The wrist hem 6 is of similar design and constructions, so that pressure is not placed against the wearer's wrist (not shown).
[0138]The sleeves of garment 10 have an outer panel 7 and an inner panel 8. These can be of similar construction and specification to those of garment body 1, or they may be different to a muscle proprioception. The stitching 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com