Component cooling system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
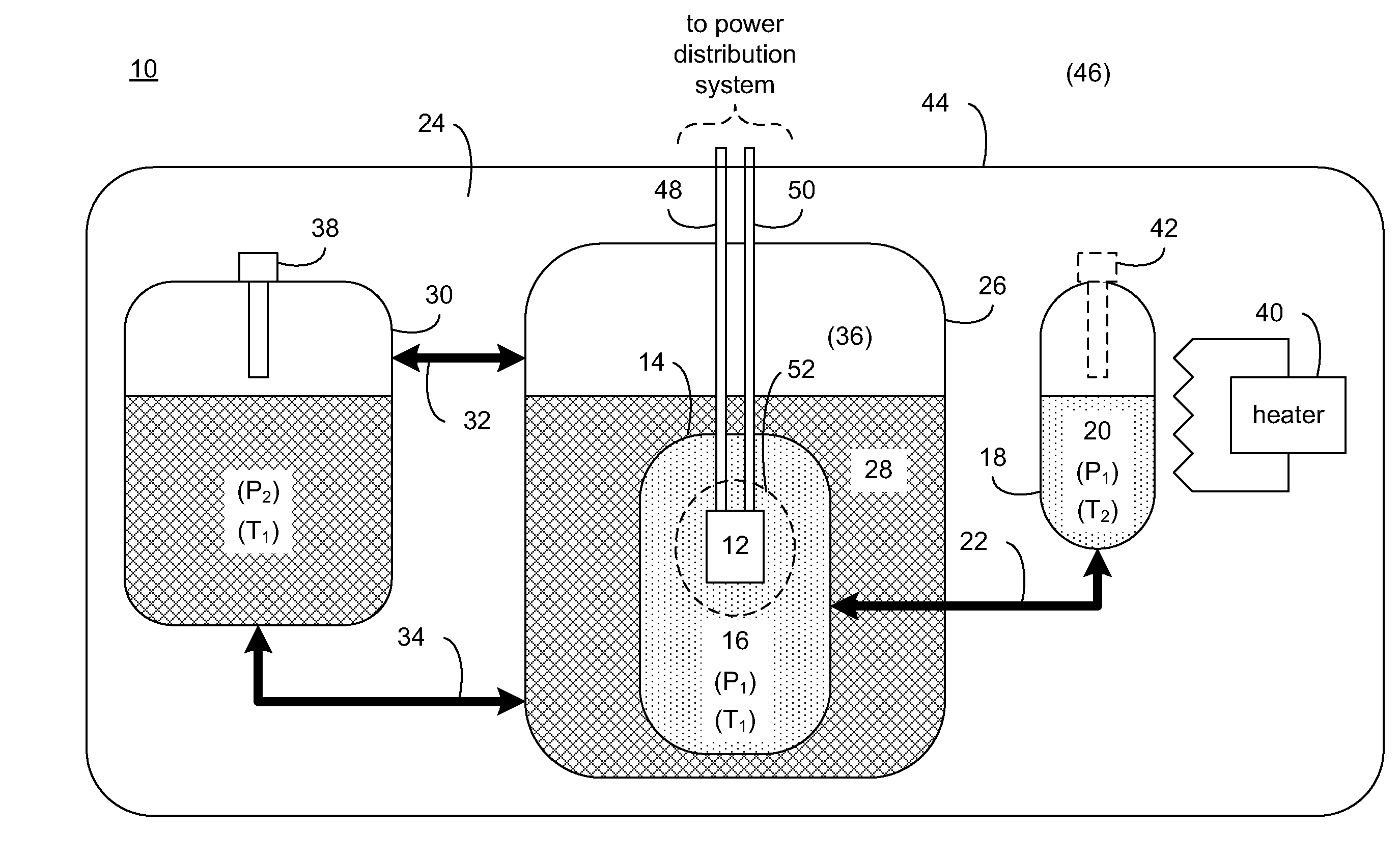
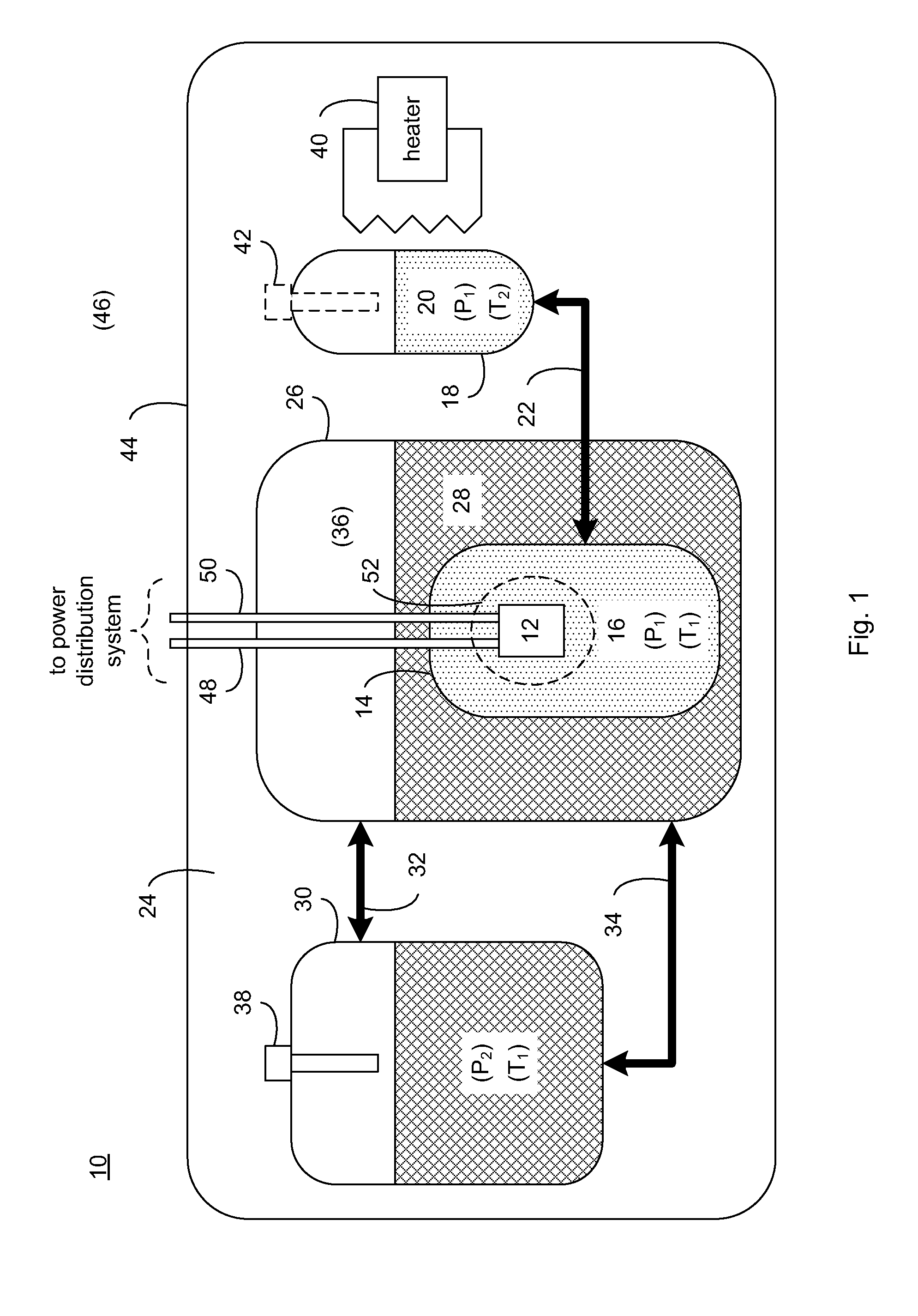
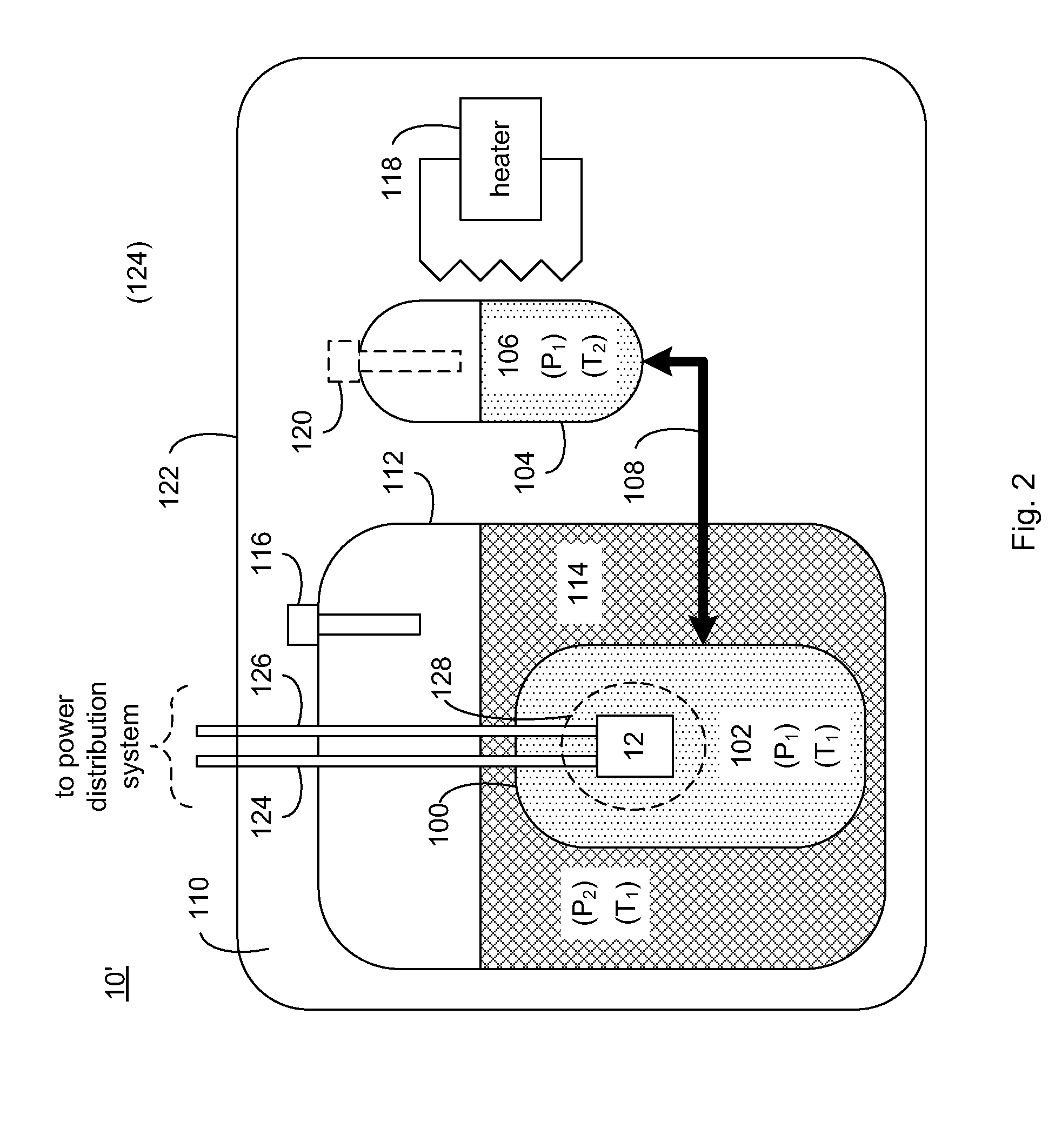
[0017]Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown a component cooling system 10 for absorbing thermal energy generated by heat-generating device 12. Examples of heat-generating device 12 may include, but are not limited to, HTS fault current limiters, a resistive electrical device, and a heat-generating mechanical device. A fault current limiter is a device that reduces the amplitude of a surge current within an electrical system that may occur due to e.g., the energizing / deenergizing of various portions of a power grid, electrical / mechanical failures within a power grid, lightening strikes, and storm damage.
[0018]A fault current limiter may be constructed using superconductor tapes or wires. When designing a fault current limiter, the superconductor windings (such as those made from high-temperature or low-temperature superconductor material) may be configured such that the impedance of the fault current limiter is negligible when subjected to normal current loads. However, when exposed to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com