Tungsten wire, cathode heater and vibration service lamp filament
a technology of cathode heater and filament, which is applied in the direction of lamp incadescent body, discharge tube/lamp details, metal-working apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the durability and longevity of the products in use, reducing strength and elongation, and losing its elongation, etc., to achieve ideal strength and durability, high processing rate, and effective raising of the recrystallization temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1 and 2
[0069]50 ppm of potassium (K) was doped into tungsten (W) powder of 3 μm average grain diameter, and after adding rhenium (Re) powder of 2 μm average grain diameter at a ratio of 3±0.3% by mass, the blended materials were uniformly mixed for 2 to 20 hours so as to prepare a raw material mixture. After the obtained raw material mixture was molded at a molding pressure of 200 MPa, and after pre-baking at 1100° C. in a hydrogen ambient atmosphere, electricity application sintering was performed, whereby 1.5 kg of W sintered body was prepared.
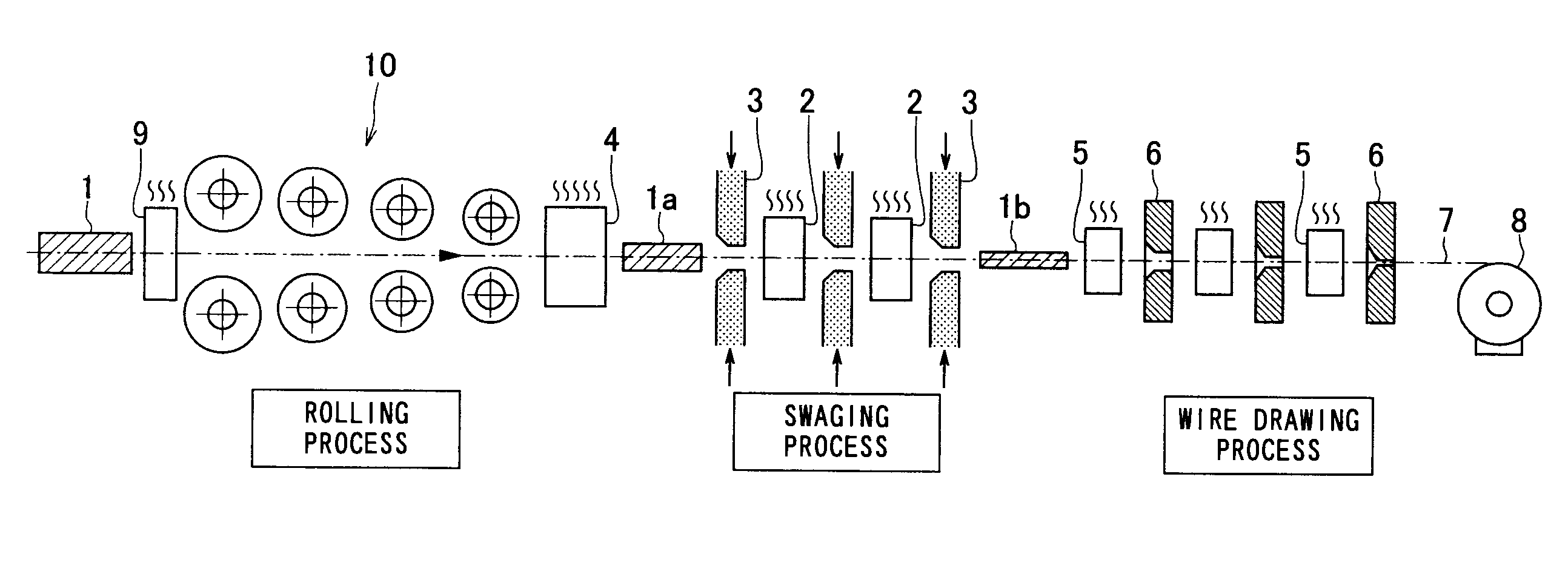
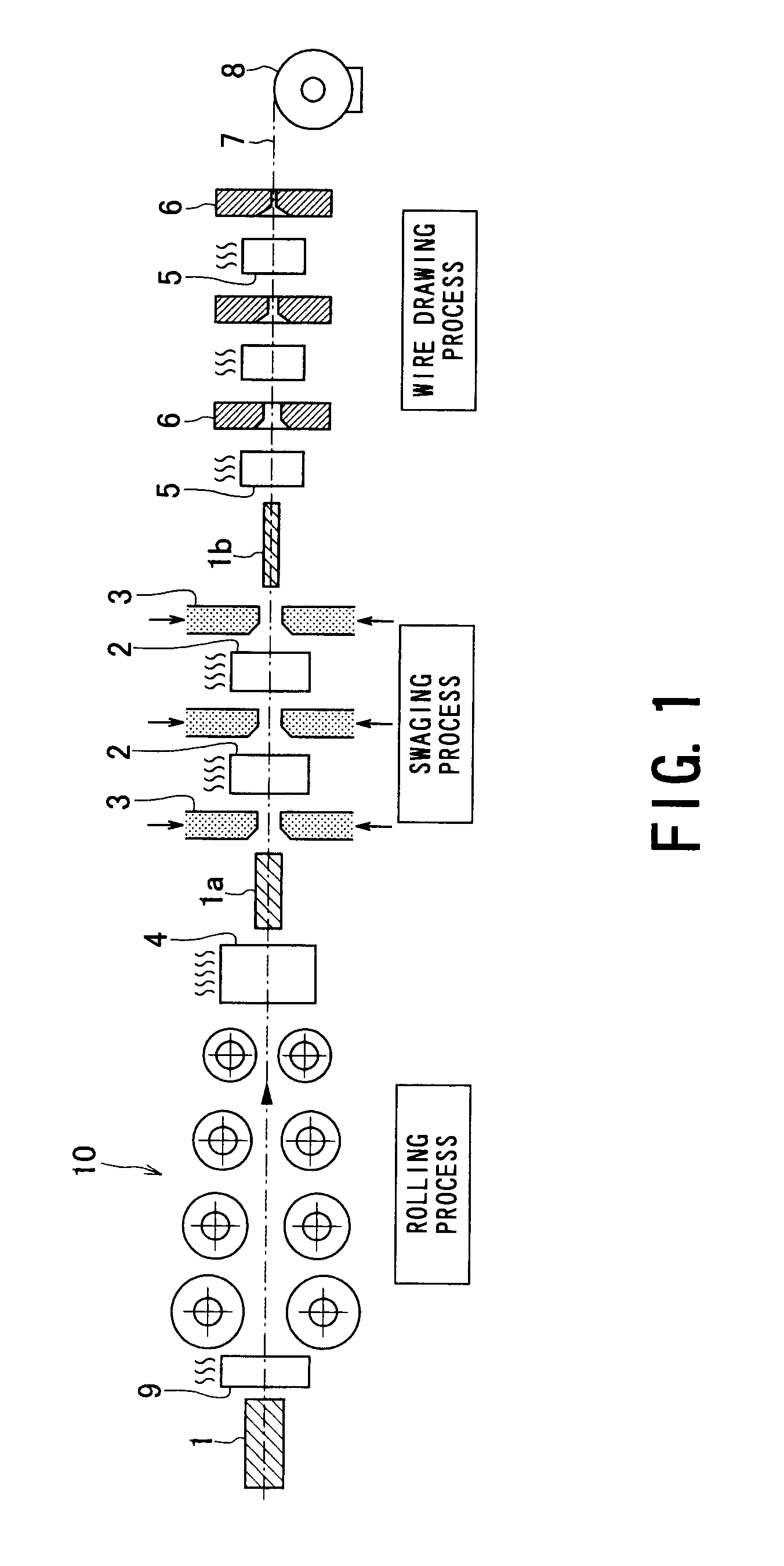
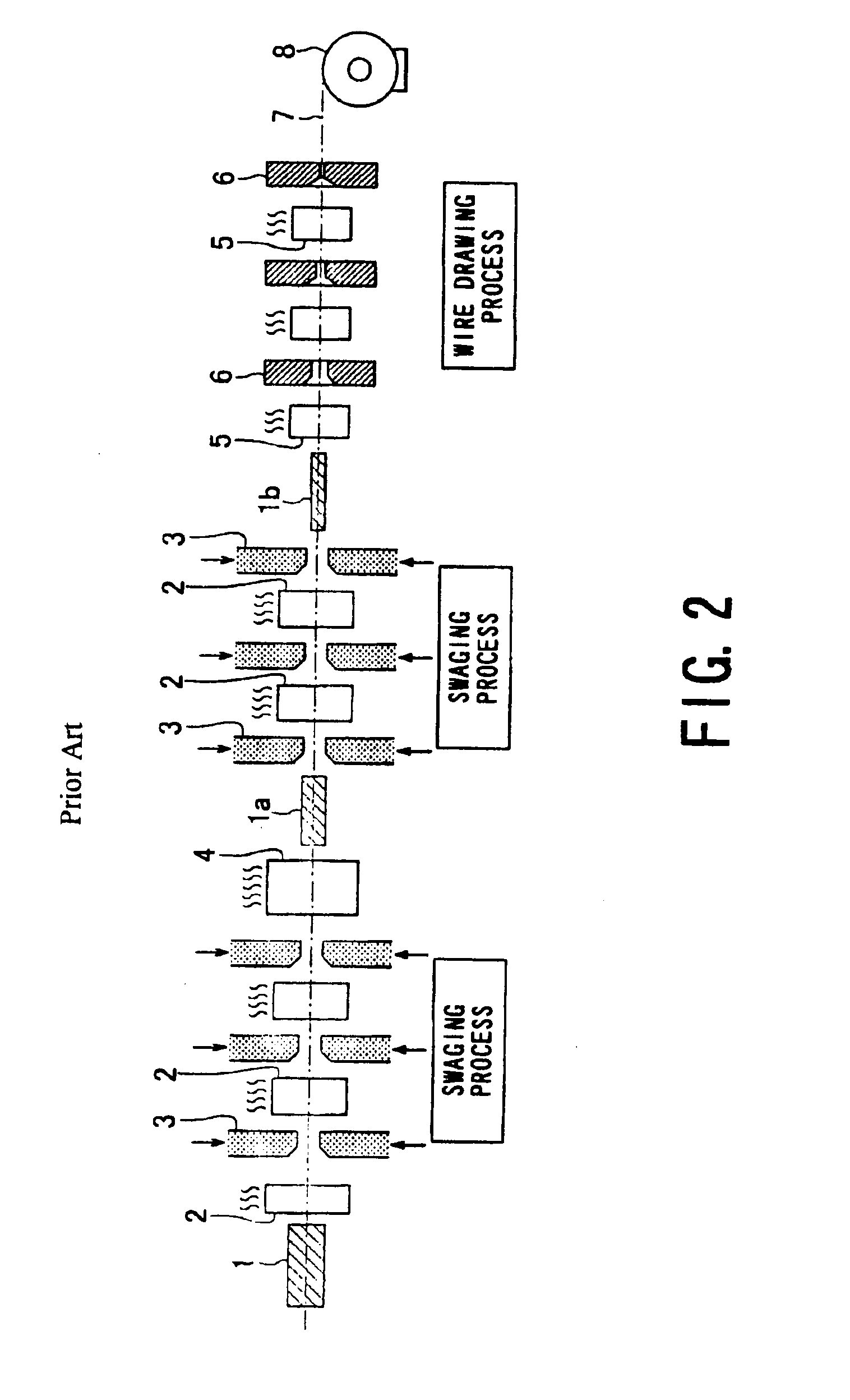
[0070]Next, the tungsten wire 7 according to the example wherein the final nominal wire diameter is set to 20-90 μm, was manufactured by following the manufacturing process illustrated in FIG. 1, and the W sintered body was processed in the order of rolling, recrystallization, swaging, and wire drawing. Now, the heating temperature in rolling heating apparatus 9 for the rolling process was set to 1300° C., while the processing rate was set at 50%. ...
examples 3 and 4
[0079]Rhenium (Re) powder having an average grain diameter of 2 μm was added to the tungsten (W) powder having an average grain diameter of 3 μm at a ratio of 26±0.5% by mass without doping potassium. Then the blended materials were uniformly mixed for 2 to 20 hours so as to prepare raw material mixtures. Then, each of the raw material mixtures was subjected to molding treatment and the electricity application sintering treatment as the same manner as that in Example 1, whereby W sintered bodies each having a weight of 1.5 kg was prepared.
[0080]Next, each of the W sintered bodies was processed in the order of rolling, recrystallization, swaging, and wire drawing in accordance with the manufacturing process illustrated in FIG. 1, so that tungsten wires 7 relating to the example having the final nominal wire diameter of 20 to 90 μm were manufactured. Now, in the above manufacturing process, the heating temperature in rolling heating apparatus 9 of the rolling process was set to 1300° ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com