Stent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
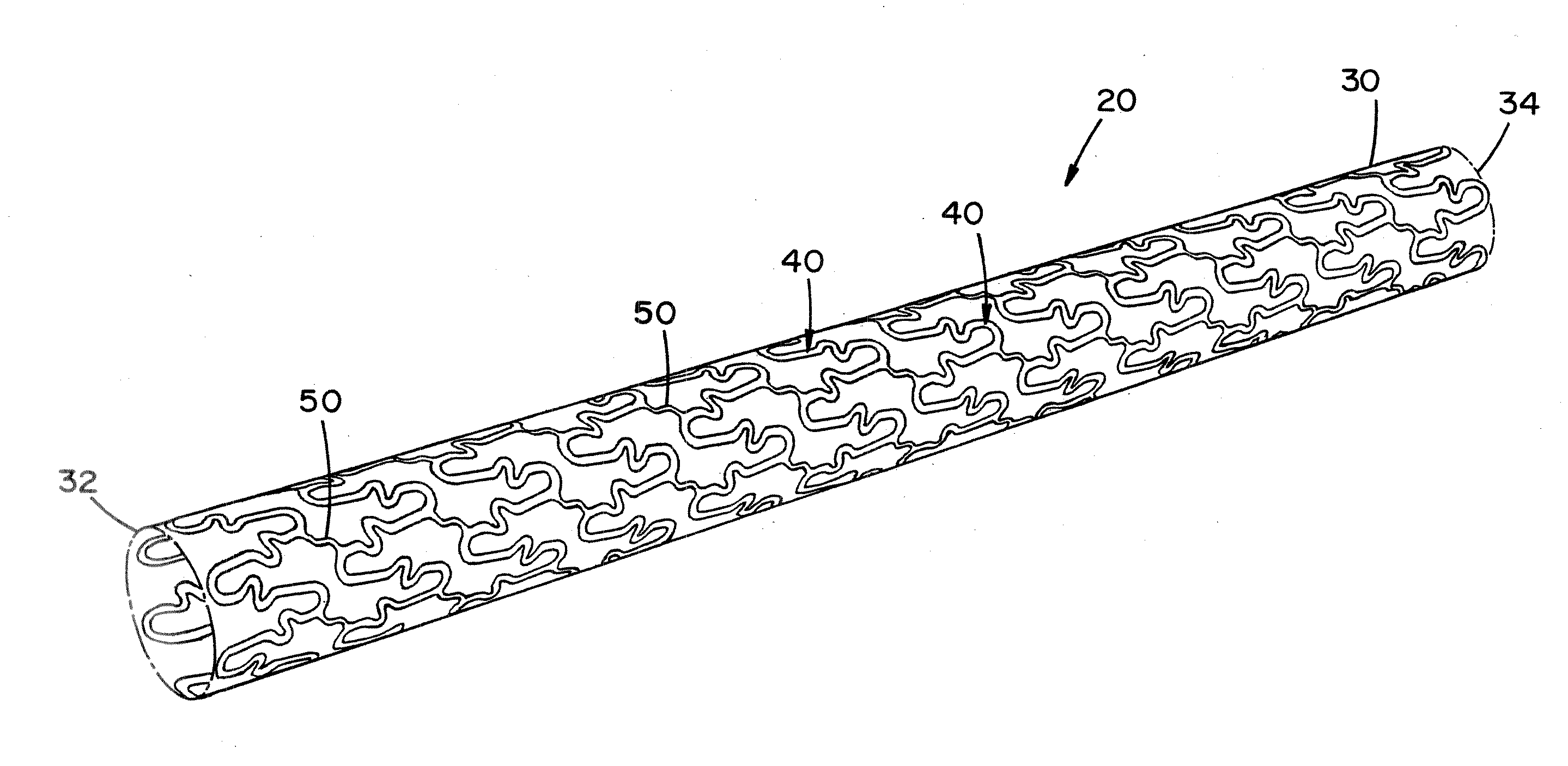
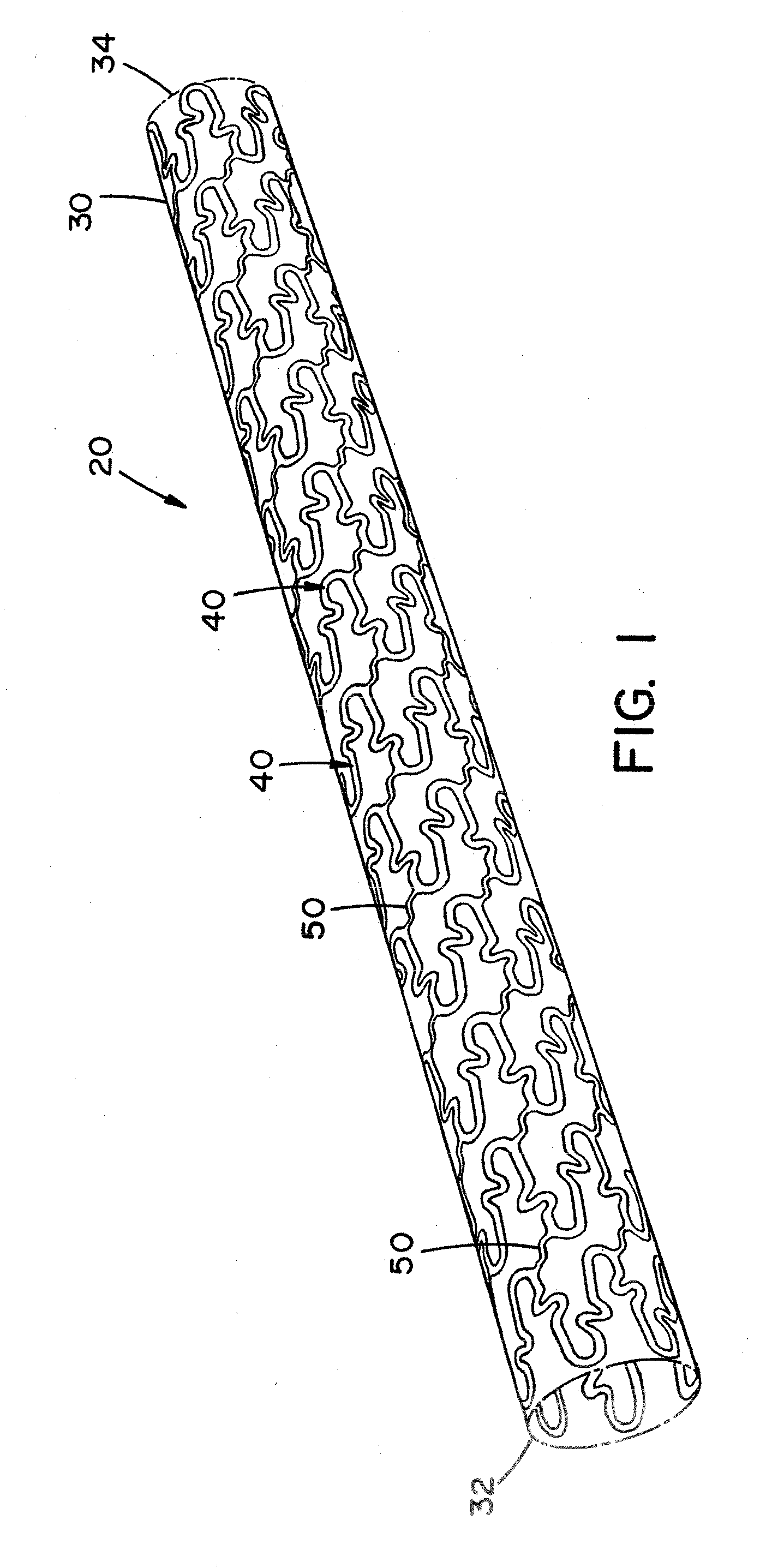
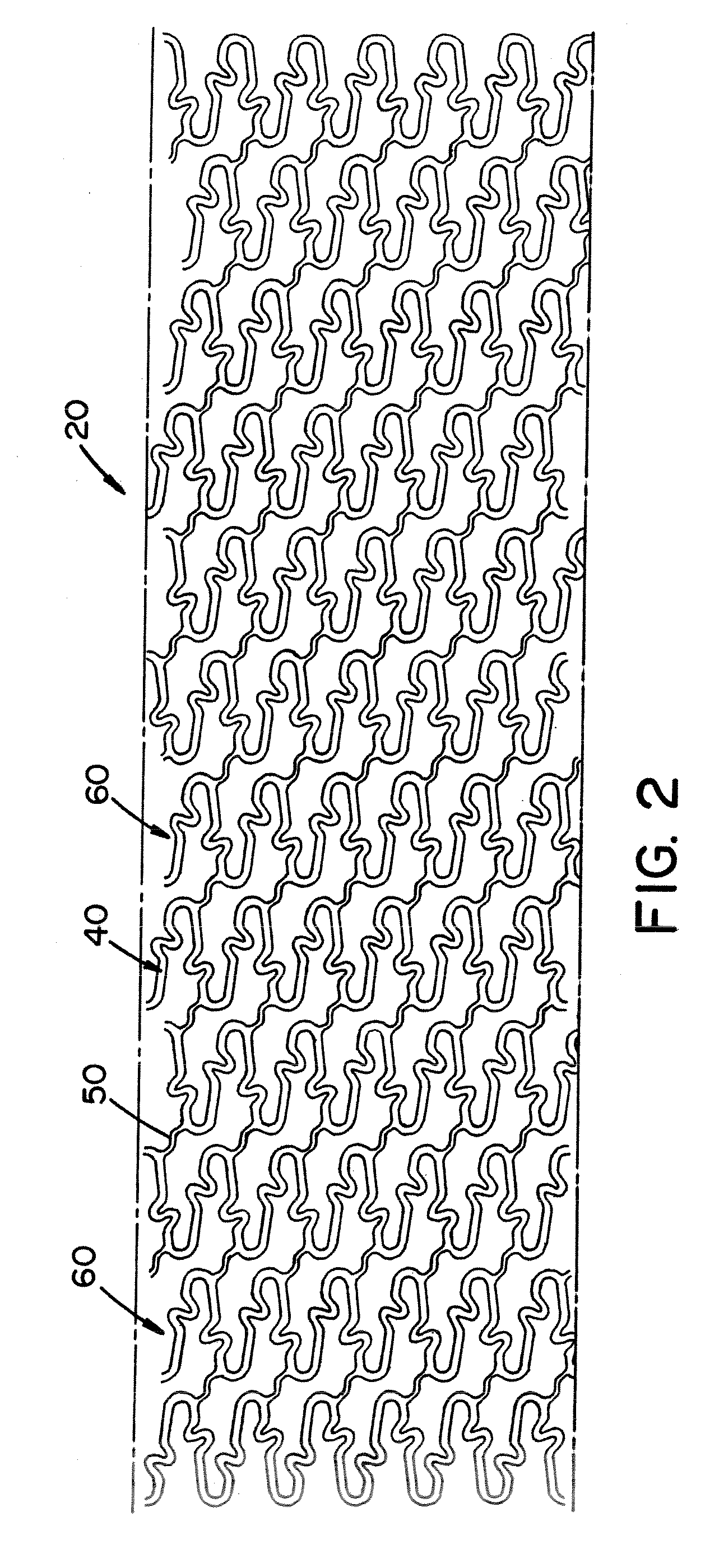
[0079]Referring now to the drawings wherein the showings are for the purpose of illustrating embodiments of the invention only and not for the purpose of limiting the same, FIGS. 1-10 disclose a stent in the form of a stent for use in a body passageway. The stent is particularly useful in the cardiovascular field; however, the stent can be used in other medical fields such as, but not limited to, orthopedic field, cardiology field, pulmonology field, urology field, nephrology field, gastroenterology field, gynecology field, otolaryngology field or other surgical fields. Additionally or alternatively, the stent is not limited to a stent, thus can be in the form of many other stents (e.g., a staple, an orthopedic implant, a valve, a vascular implant, a pacemaker, a spinal implant, a guide wire, nail, rod, screw, etc.).
[0080]The stent, when used for vascular applications, can be used to address various medical problems such as, but not limited to, restenosis, atherosclerosis, atherogen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com