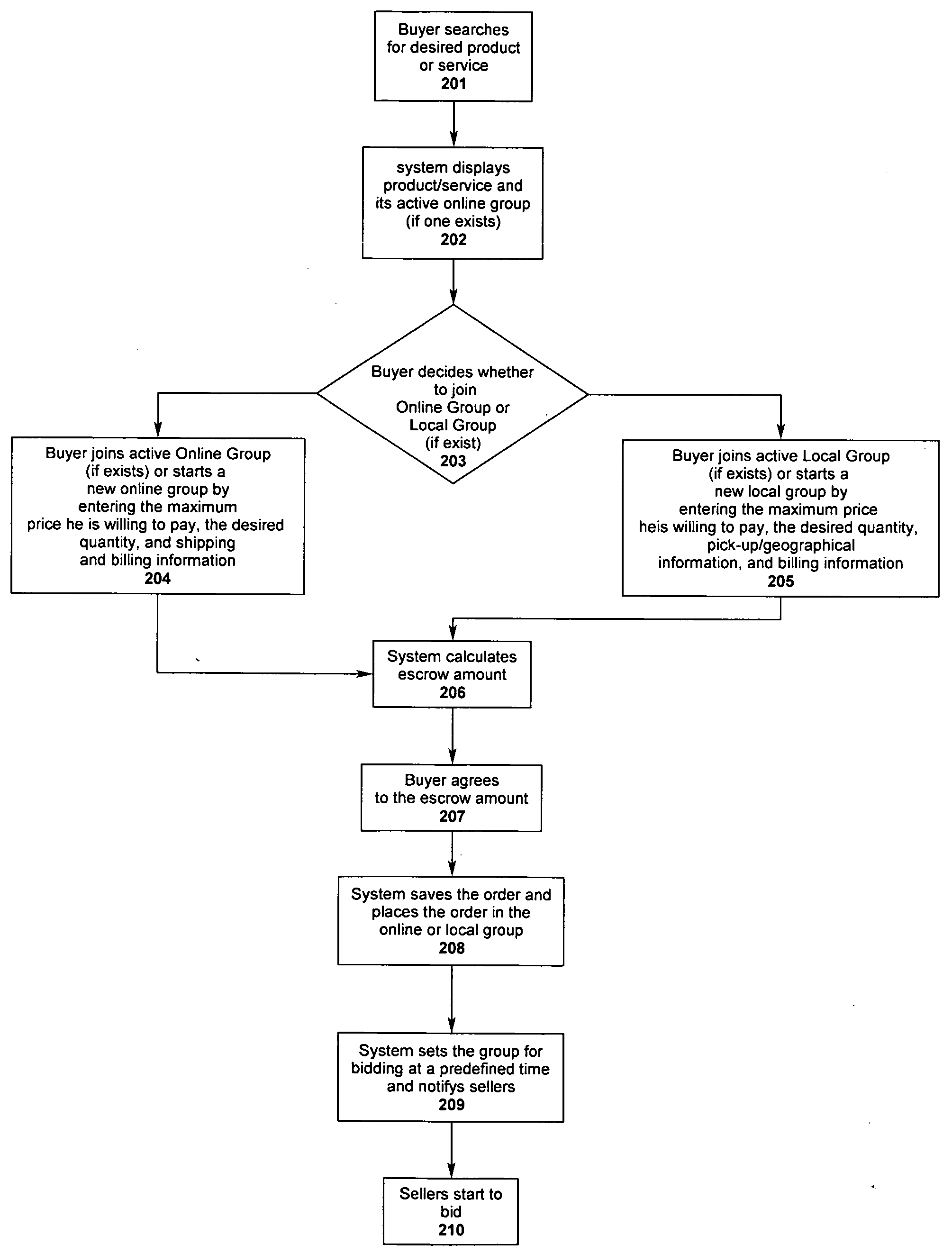
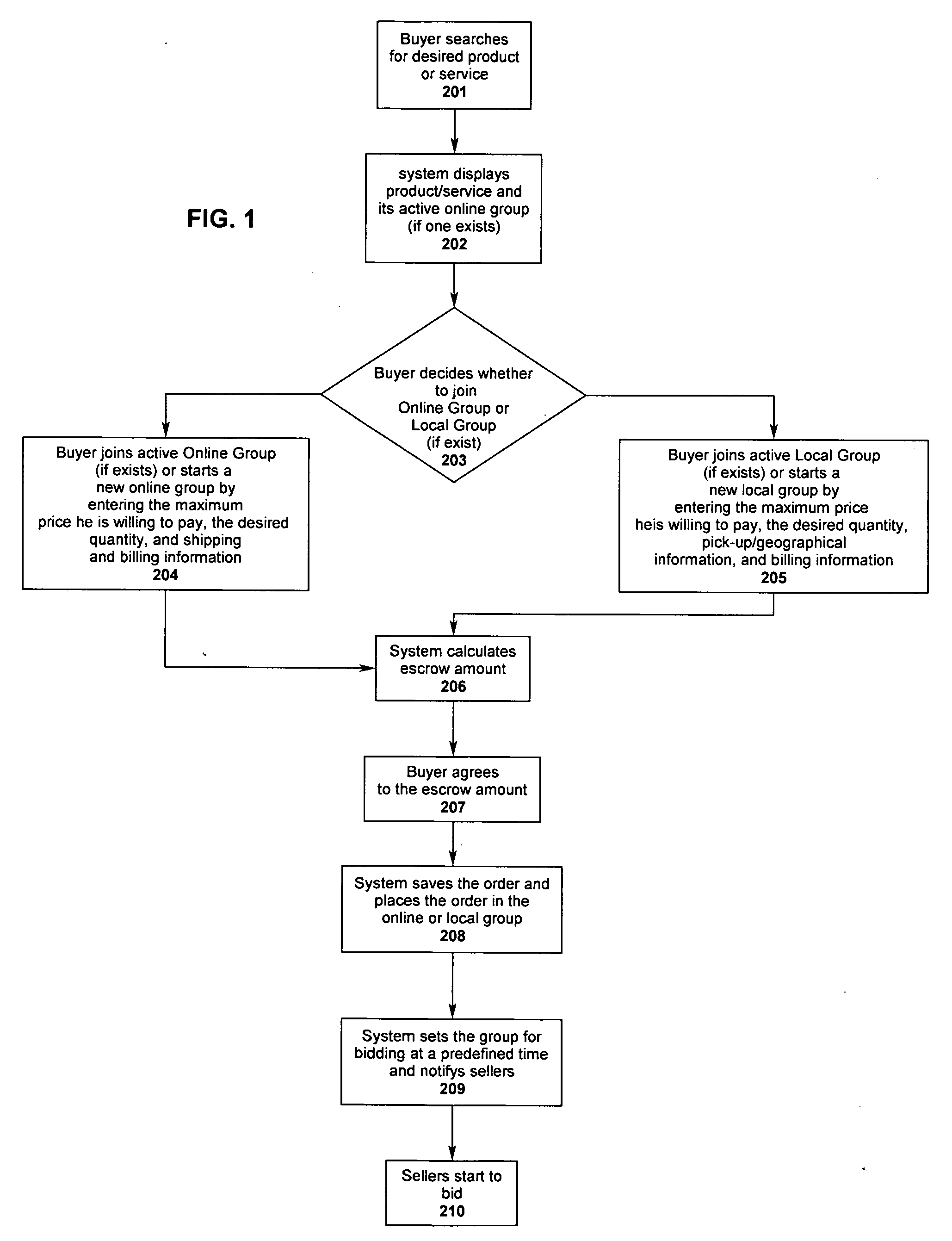
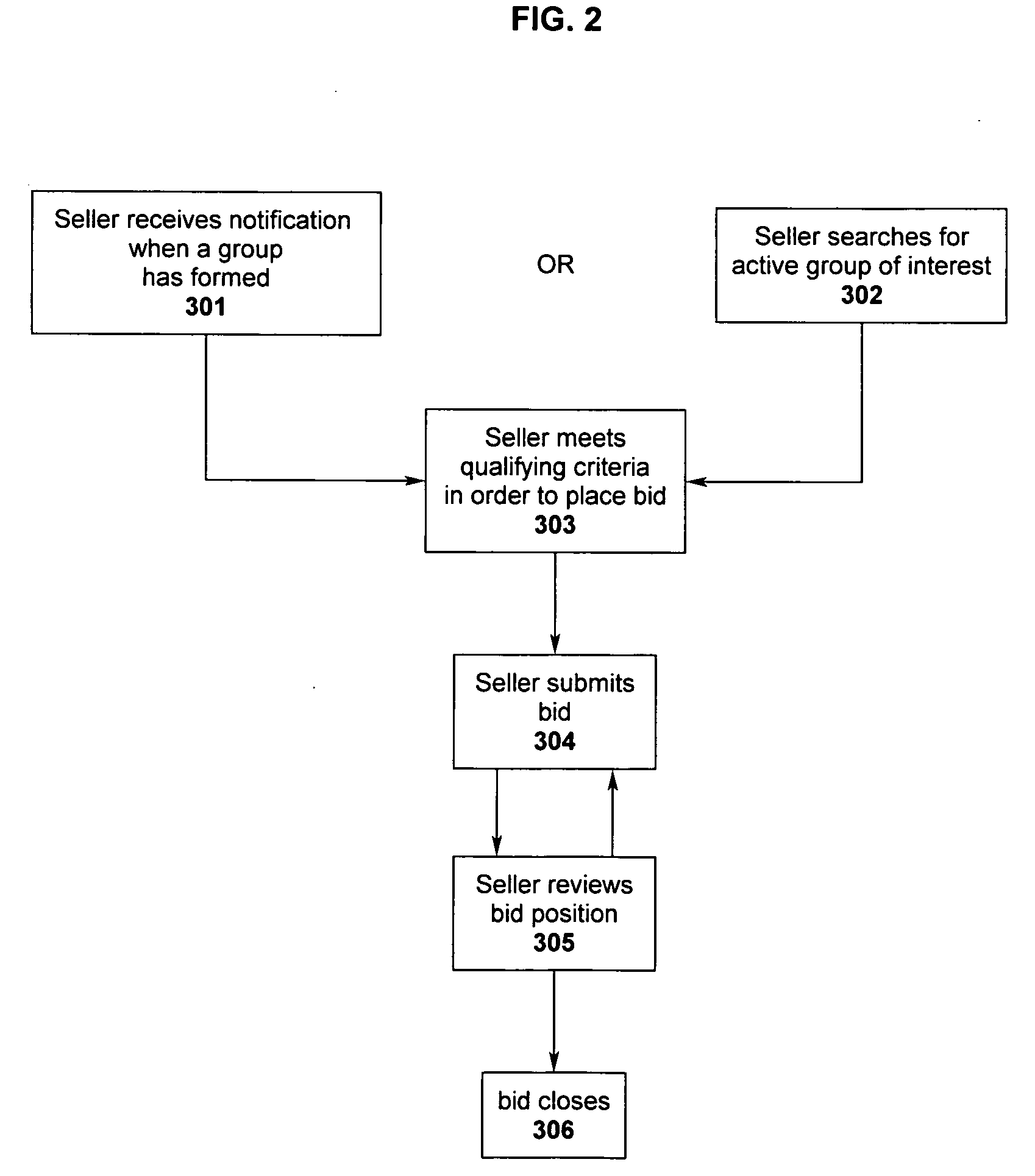
System of facilitating a sales transaction between a buying group and multiple sellers over and electronic network
a technology of electronic network and buying group, applied in the field of demand aggregation for goods and services, can solve the problems of overwhelming task, problem of anticipating demand, and the buyer cannot achieve a price less than, and achieve the effect of facilitating a sales transaction and reducing the price the buyer ultimately pays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
EXPLANATION OF EXAMPLE 1
[0030]Looking at Example 1 in terms of the logic of FIG. 3 results in the following:[0031]Step 401: All buyers with offering prices less than the lowest seller's bid price are excluded;[0032]Step 402: Buyers are sequenced based on the chronology of their order;[0033]Step 403: Sellers are then sequenced based on their bid price from lowest to highest;[0034]Step 404: There are enough buyers (quantity) with offering prices higher than the highest ranked seller's (i.e. Seller A) bid price to meet Seller A's minimum quantity;[0035]Step 406: Buyers are assigned to Seller A up to Seller A's maximum quantity;[0036]Step 407: There are no remaining buyers;[0037]Step 408: Notify all unmatched sellers;[0038]Step 409: Notify all matched buyers and sellers.
EXAMPLE 2
[0039]
Max.CreditUnitUnitCardPriceMin.BuyersQuantityPrice ($)GoodSellers($)QuantityMax. QuantityBuyer 11100YesA9012Buyer 22110YesB95210Buyer 3195YesC99320Buyer 4299YesD100220Buyer 51105Yes
EXAMPLE 2 RESULT AFTER M...
example 2
EXPLANATION OF EXAMPLE 2
[0041]Looking at Example 2 in terms of the logic of FIG. 3 results in the following:[0042]Step 401: All buyers with offering prices less than the lowest seller's bid price are excluded;[0043]Step 402: Buyers are sequenced based on the chronology of their order;[0044]Step 403: Sellers are then sequenced based on their bid price from lowest to highest;[0045]Step 404: There are enough buyers (quantity) with offering prices higher than the highest ranked seller's (i.e. Seller A) bid price to meet Seller A's minimum quantity;[0046]Step 406: Buyers are assigned to Seller A up to Seller A's maximum quantity;[0047]Step 407: Unmatched buyer / quantity remains;[0048]Step 410: There are remaining sellers;[0049]Return to Step 404: There are enough buyers (quantity) with offering prices higher than the second ranked seller's (i.e. Seller B) bid price to meet Seller B's minimum quantity;[0050]Step 405: Buyers are assigned to Seller B up to Seller B's maximum quantity;[0051]S...
example 3
EXPLANATION OF EXAMPLE 3
[0056]Looking at Example 3 in terms of the logic of FIG. 3 results in the following:[0057]Step 401: All buyers with offering prices less than the lowest seller's bid price are excluded;[0058]Step 402: Buyers are sequenced based on the chronology of their order. Buyer 2 has been omitted from the results since his credit card would not allow authorization of the escrow fee;[0059]Step 403: Sellers are then sequenced based on their bid price from lowest to highest;[0060]Step 404: There are enough buyers (quantity) with offering prices higher than the highest ranked seller's (i.e. Seller A) bid price to meet Seller A's minimum quantity;[0061]Step 406: Buyers are assigned to Seller A up to Seller A's maximum quantity;[0062]Step 407: Unmatched buyer / quantity remains;[0063]Step 410: There are remaining sellers;[0064]Return to Step 404: There are enough buyers (quantity) with offering prices higher than the second ranked seller's (i.e. Seller B) bid price to meet Sell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com