Real Time Data Replication
a data replication and real-time technology, applied in the field of data replication, can solve the problems of data transmission latency, application performance may be slowed to unacceptable levels, and the synchronization comes at a significant performance penalty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
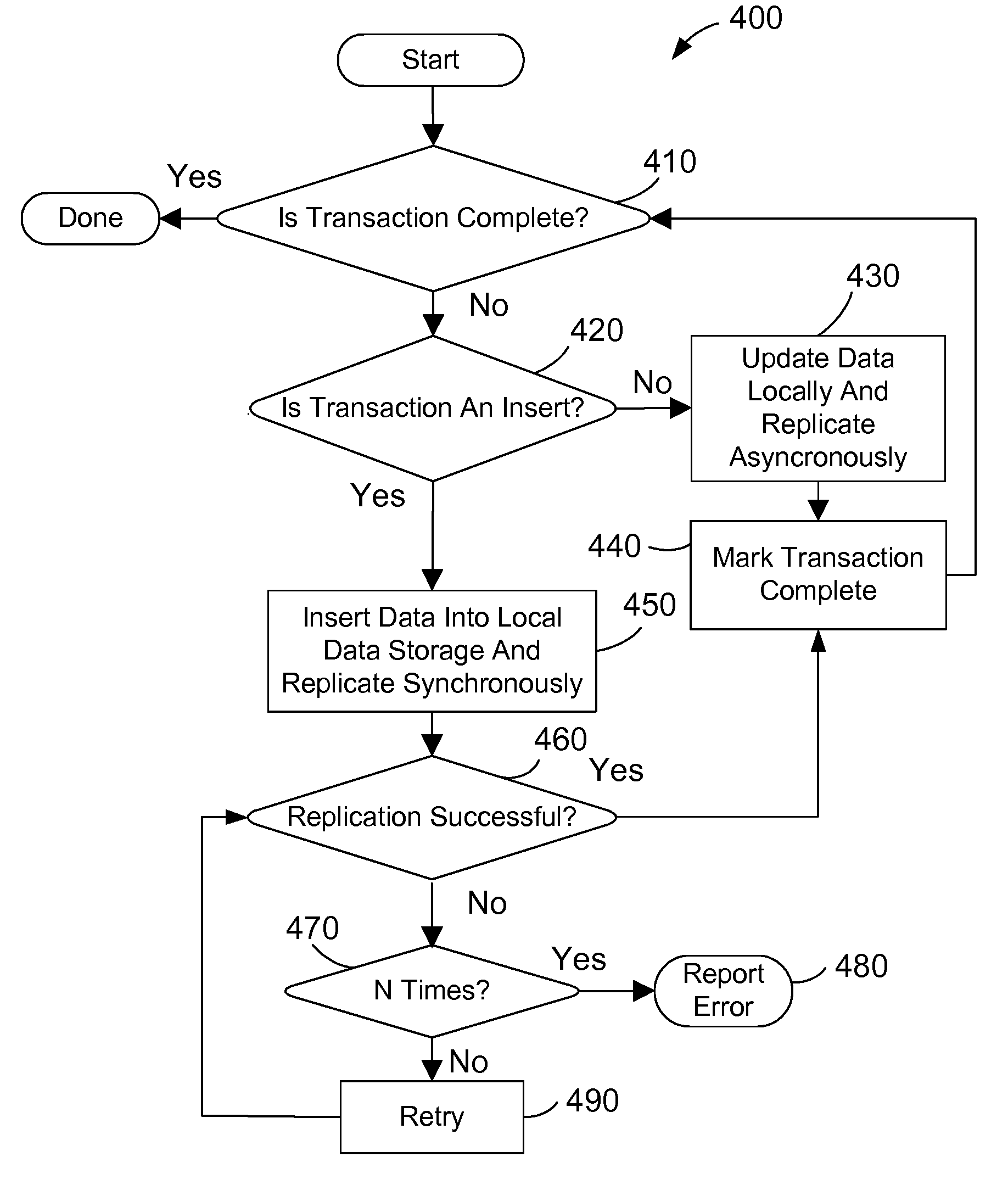
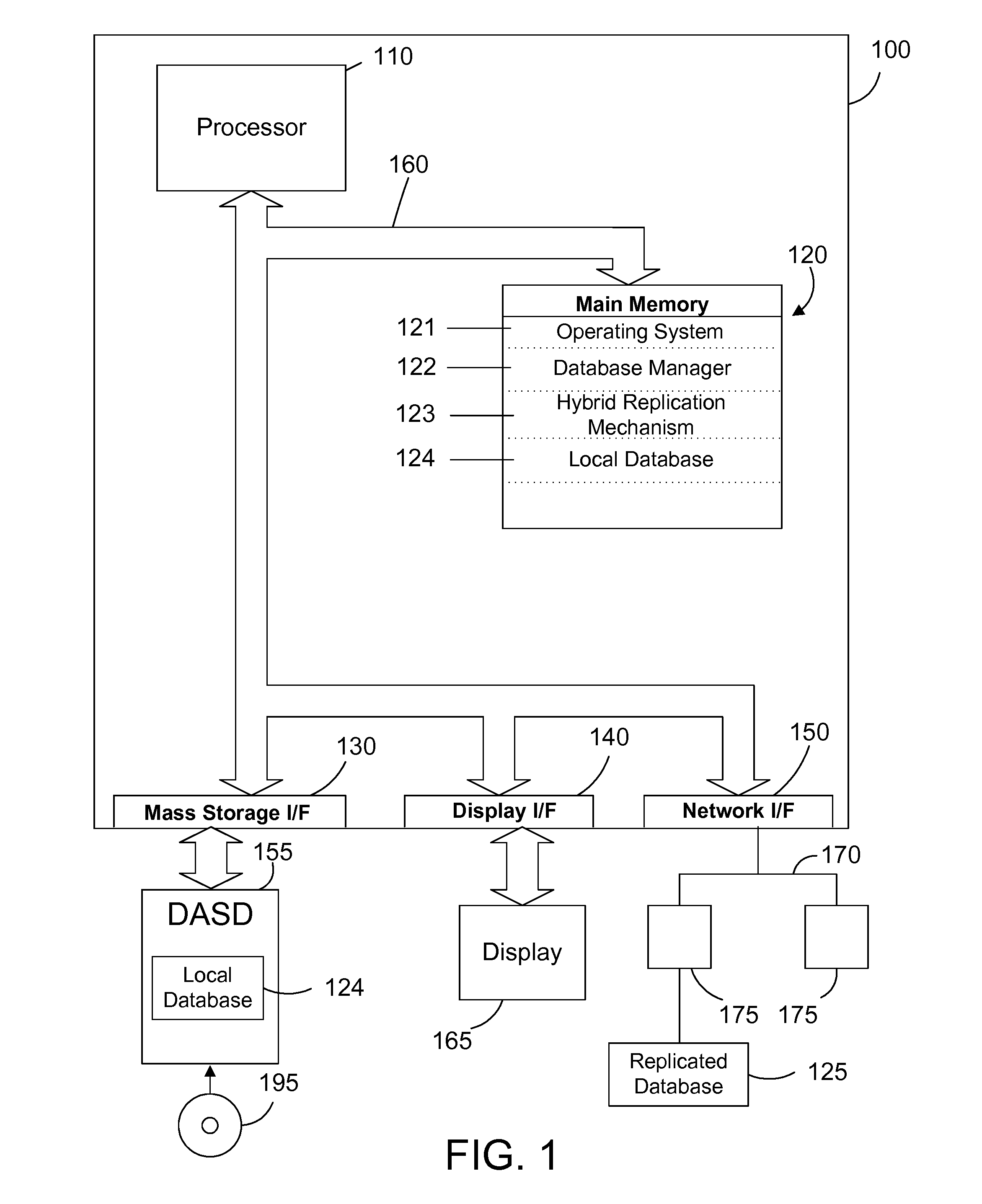
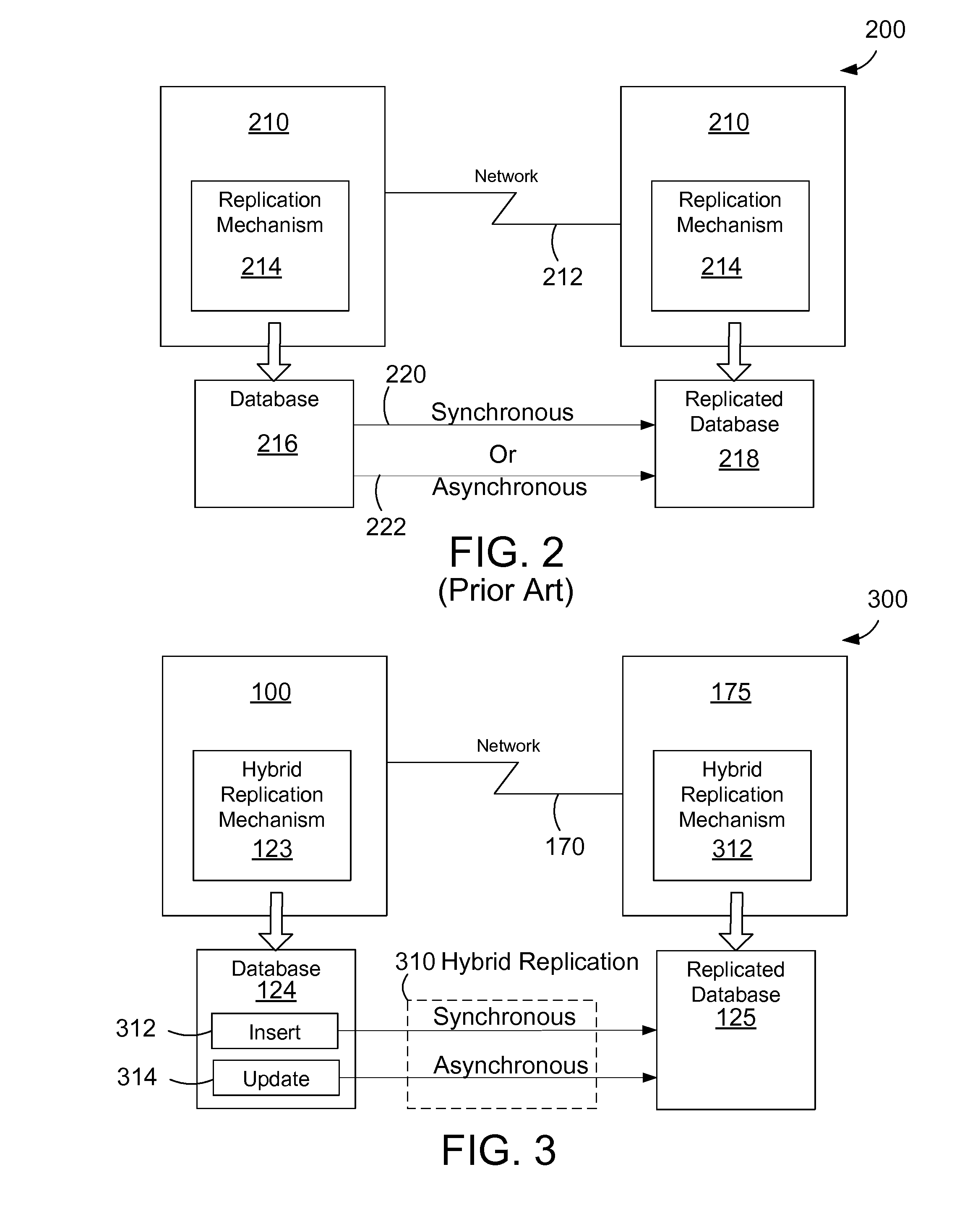
[0015]The disclosure and claims herein are directed to data replication using a combination of synchronous and asynchronous replication of data from a local database to a replicated database. The typical tradeoff between synchronous and asynchronous replication is optimized by using hybrid replication, which is to use synchronous replication for inserting new data and asynchronous replication for updating existing data. The combined use of synchronous and asynchronous in this manner provides an efficient replicated database where the replicated database can tolerate some delay in data updates but requires no data loss of new data.
[0016]As will be appreciated by one skilled in the art, aspects of the present invention may be embodied as a system, method or computer program product. Accordingly, aspects of the present invention may take the form of an entirely hardware embodiment, an entirely software embodiment (including firmware, resident software, micro-code, etc.) or an embodimen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com