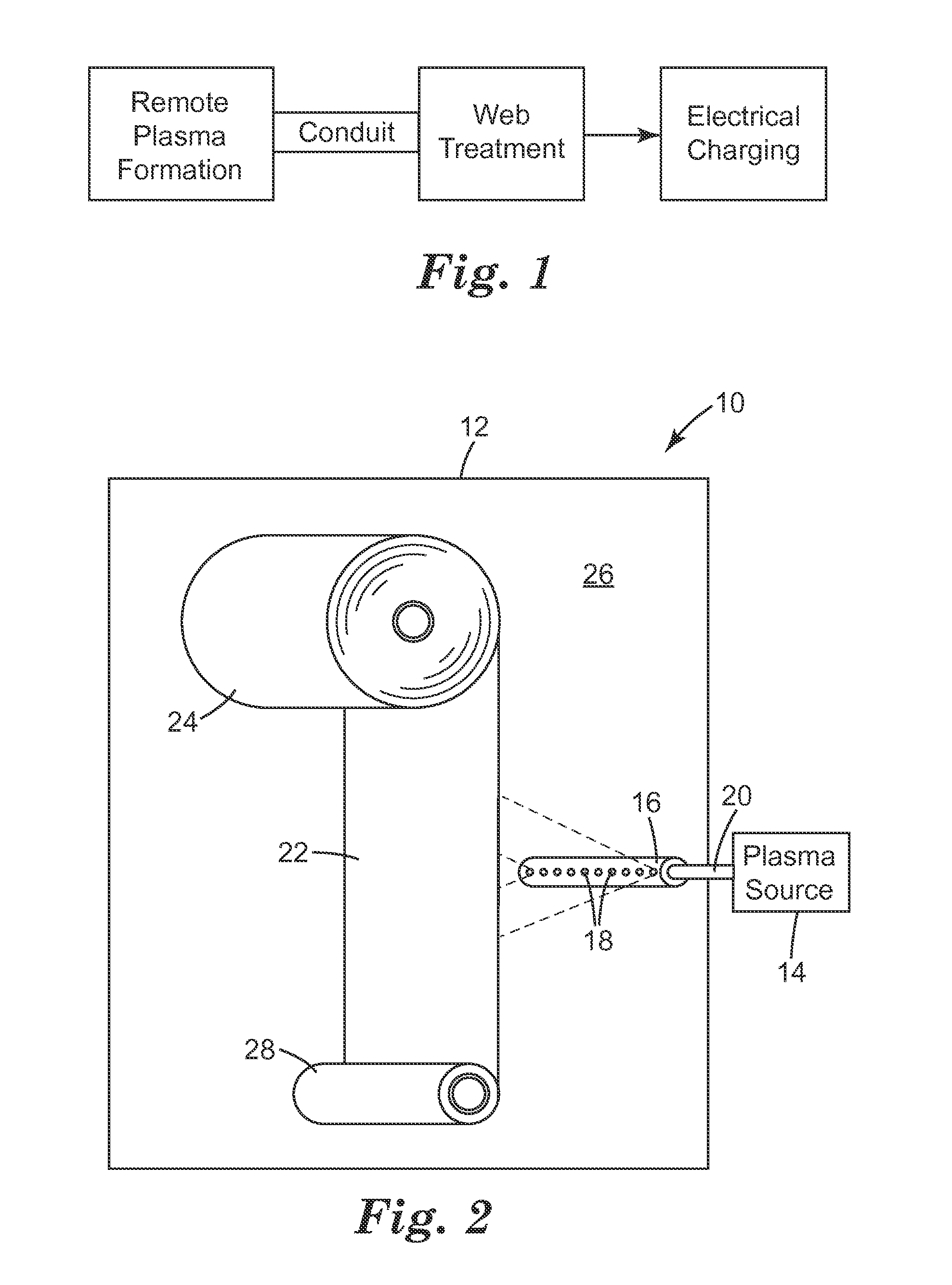
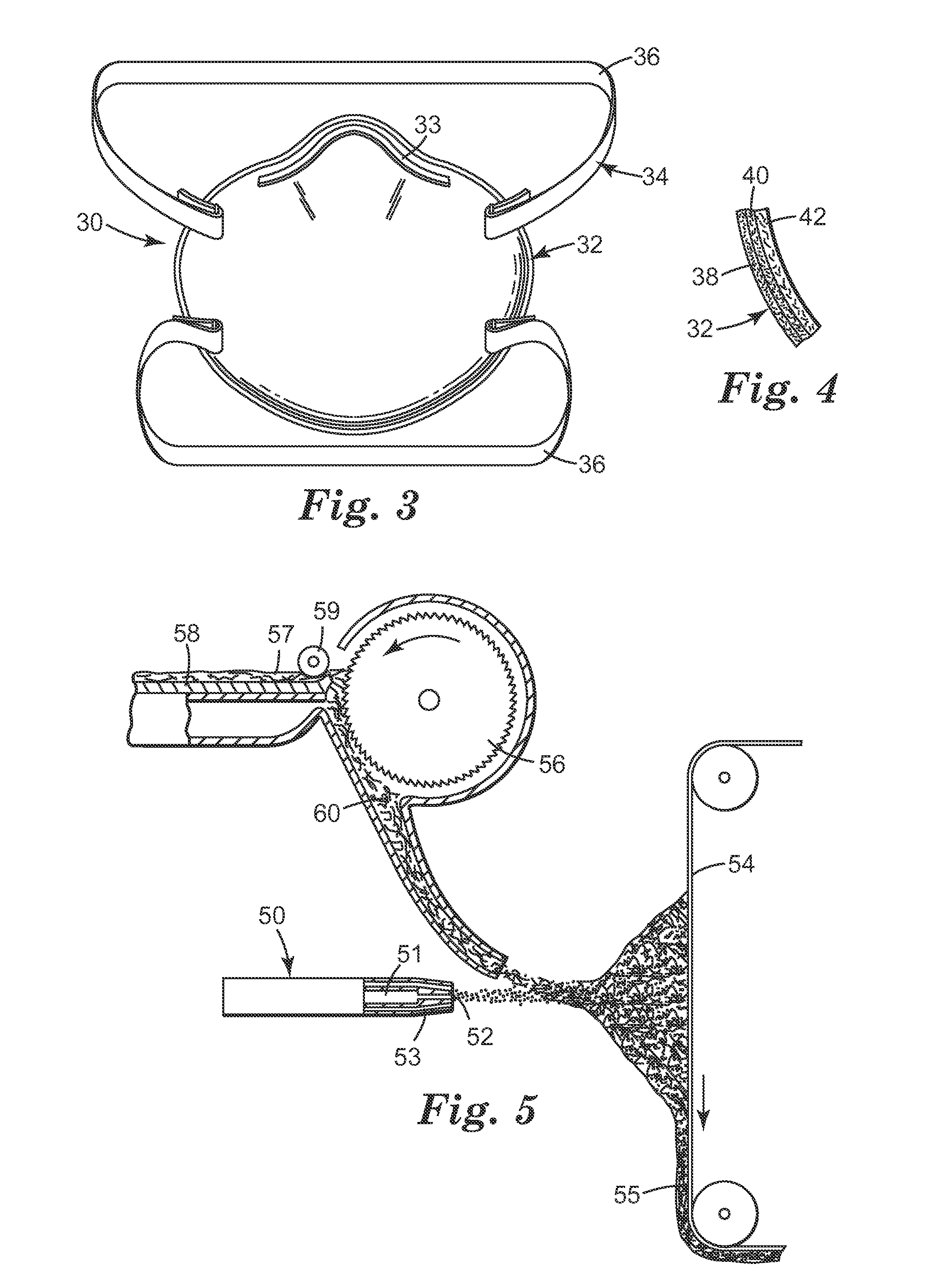
Remote fluorination of fibrous filter webs
a technology remote fluorination, which is applied in the field of remote fluorination of fibrous filter webs, can solve the problems of no known technique for delivering fluorine atoms to the surface of a nonwoven web that contains polymeric fibers, and achieves the effects of avoiding fluorinated carbons, high power levels, and good performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Test Methods
Quality Factor (QF) Testing Method
[0070]The samples were tested for % DOP aerosol penetration (% Pen) and pressure drop (ΔP), and the Quality Factor (QF) was calculated. The filtration performance (% Pen and ΔP) of the nonwoven microfiber webs were evaluated using an Automated Filter Tester AFT Model 8130 (available from TSI, Inc., St. Paul, Minn.) using dioctylphthalate (DOP) as the challenge aerosol. The DOP aerosol is nominally a monodisperse 0.3 micrometer mass median diameter having an upstream concentration of 70-125 mg / m3. The aerosol was forced through a sample of filter medium at a calibrated flow rate of 42.5 liters / minute (face velocity of 6.9 cm / s) with the aerosol TSI Model 8113 Aerosol Neutralizer turned off. The total testing time was 23 seconds (rise time of 15 seconds, sample time of 4 seconds, and purge time of 4 seconds). Simultaneously with % Pen, the pressure drop (ΔP in mm of water) across the filter was measured by the instrument. The concentration...
example 2
Remote Plasma Treatment Example 2
[0092]For Remote Plasma Treatment Example 2, the web was treated as in Remote Plasma Treatment Example 1, with the following exceptions. For Remote Plasma Treatment Example 2 a remote plasma sources (Xstream 3151806 model from Advanced Energy Fort Collins Colo.) was mounted on the outside of the vacuum chamber and the output of this source was connected to a port on the vacuum chamber. On the interior side of the vacuum chamber, the RFDM system consisted of two 2-inch diameter aluminum tubes each with a row of 0.062×0.625 inch slots spaced 0.125 inch apart and the tubes were placed approximately 4 inches away from opposite sides of the target web, with the slot surface normal opposing and parallel to the web surface normal.
[0093]The data in Table 3 compare surface analysis for samples treated by the described remote plasma fluorination process and comparative examples treated with a local plasma. The data in this table show that the two plasma treatm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com