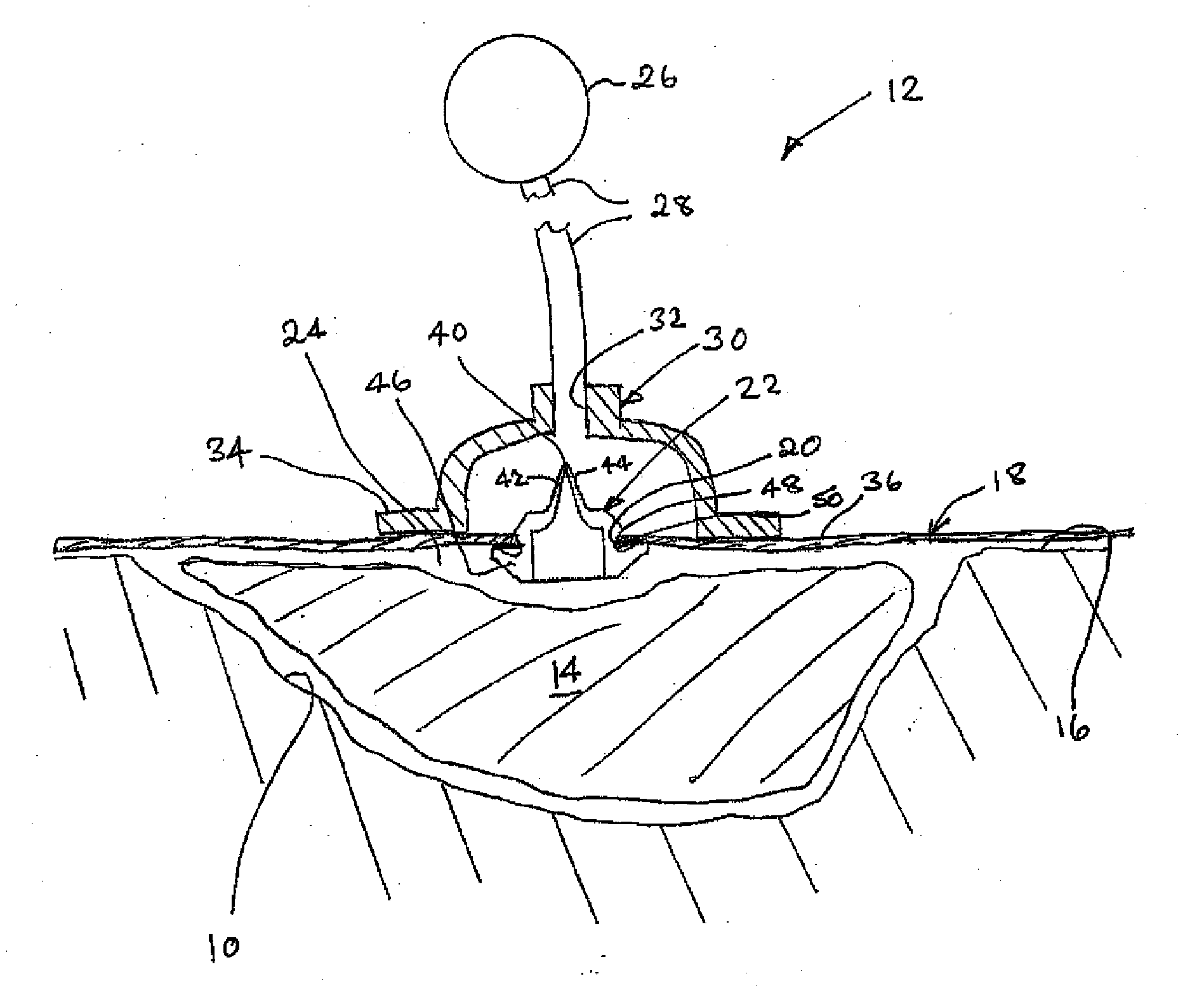
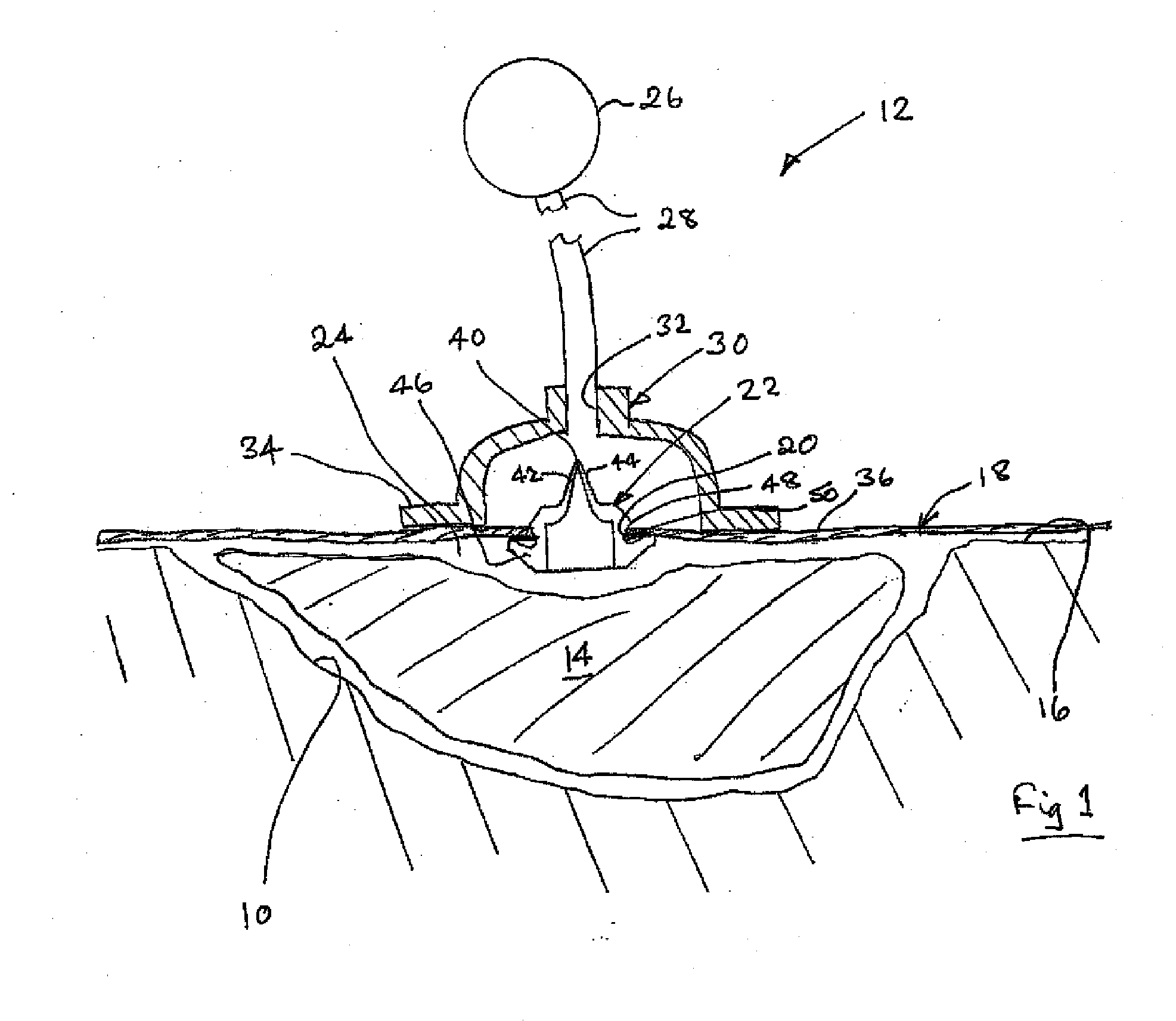
Vacuum assisted wound dressing
a technology of vacuum pressure and wound dressing, applied in the field of vacuum pressure assisted wound dressing, can solve the problems of not being the most appropriate solution, achieve the effects of enhancing self-cohesion properties, and reducing the loss of vacuum pressur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 5
Water Absorbency of Self-Coalescing Carboxymethylchitosan Fibres
[0101] The material resulting from Example 3 (100 mg) was immersed in water (4 ml) for 1 minute and withdrawn. Excess liquid was allowed to drain and then the hydrated transparent mass was weighed. The material was calculated to absorb approximately 25-times its own mass in water without significant dissolution.
example 6
Serum Absorbency of Self-Coalescing Carboxymethylchitosan Fibres
[0102] The material resulting from Example 3 (100 mg) was immersed in serum (4 ml) for 1 minute and withdrawn. Excess liquid was allowed to drain and then the hydrated transparent mass was weighed. The material was calculated to absorb approximately 13-times its own mass in serum without significant dissolution.
example 7
Self-Coalescence of Carboxymethylchitosan Fibres in Water
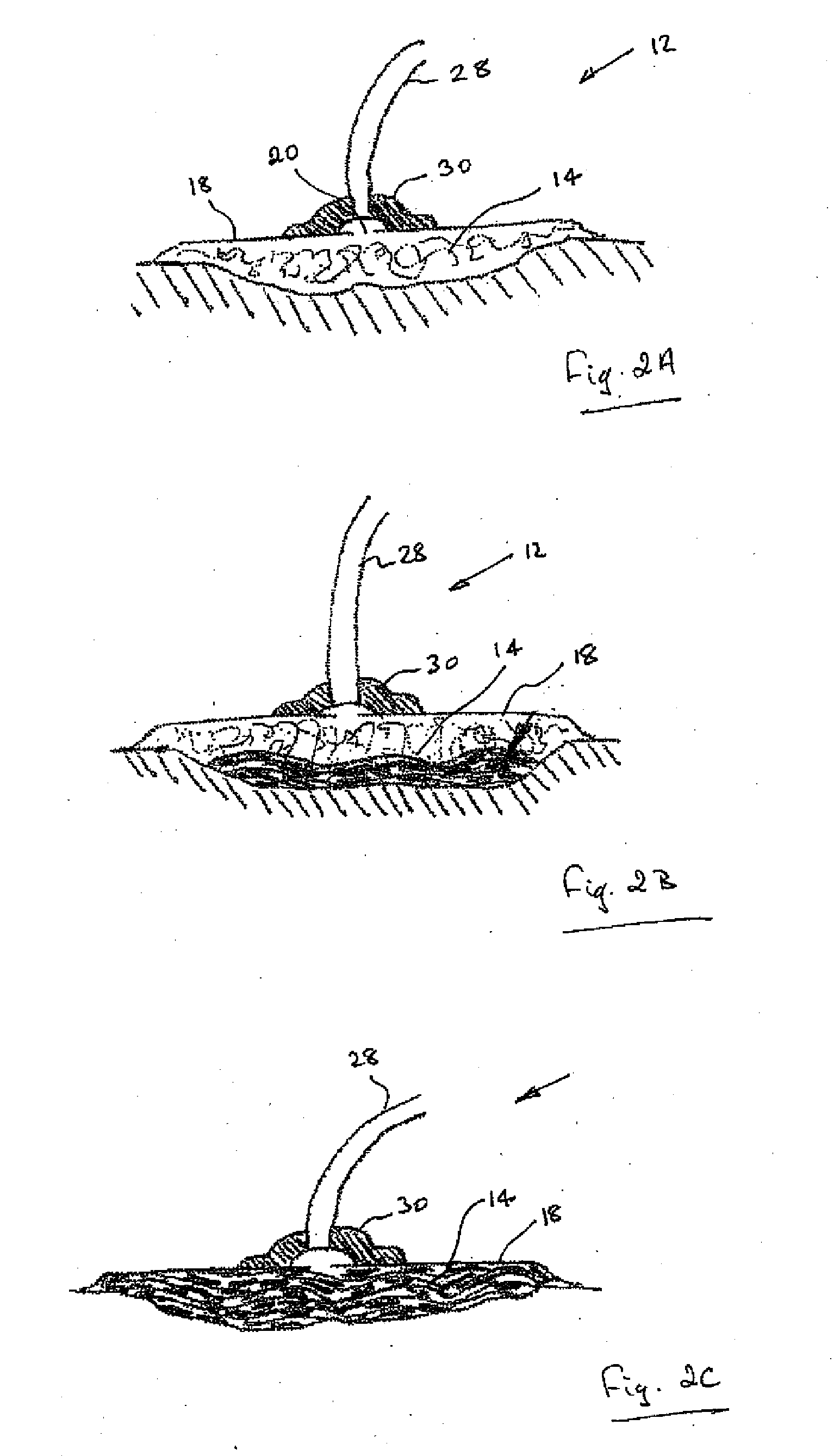
[0103] The material resulting from Example 3 (100 mg) was immersed in water (4 ml) for 1 minute and withdrawn. Excess liquid was allowed to drain and then the hydrated transparent mass was allowed to stand for 4 hours. After this time, the individual fibres of the material had self-coalesced and the material was then effectively a homogeneous, elastic hydrogel able to stably retain its physical geometry under loading (FIG. 2).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com