Methods for self-aligned self-assembled patterning enhancement
a patterning enhancement and self-aligning technology, applied in the field of micro- or nano-scale device fabrication, can solve the problems of sup>nd /sup>pass pattern alignment inadequate, features consume time in many ways, and the resolution of the standard mask fabrication process is challenged
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
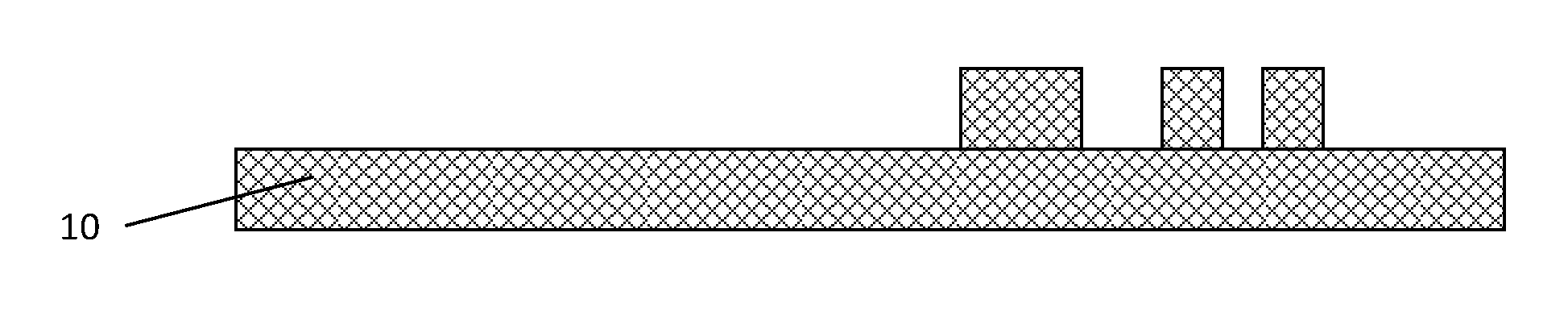
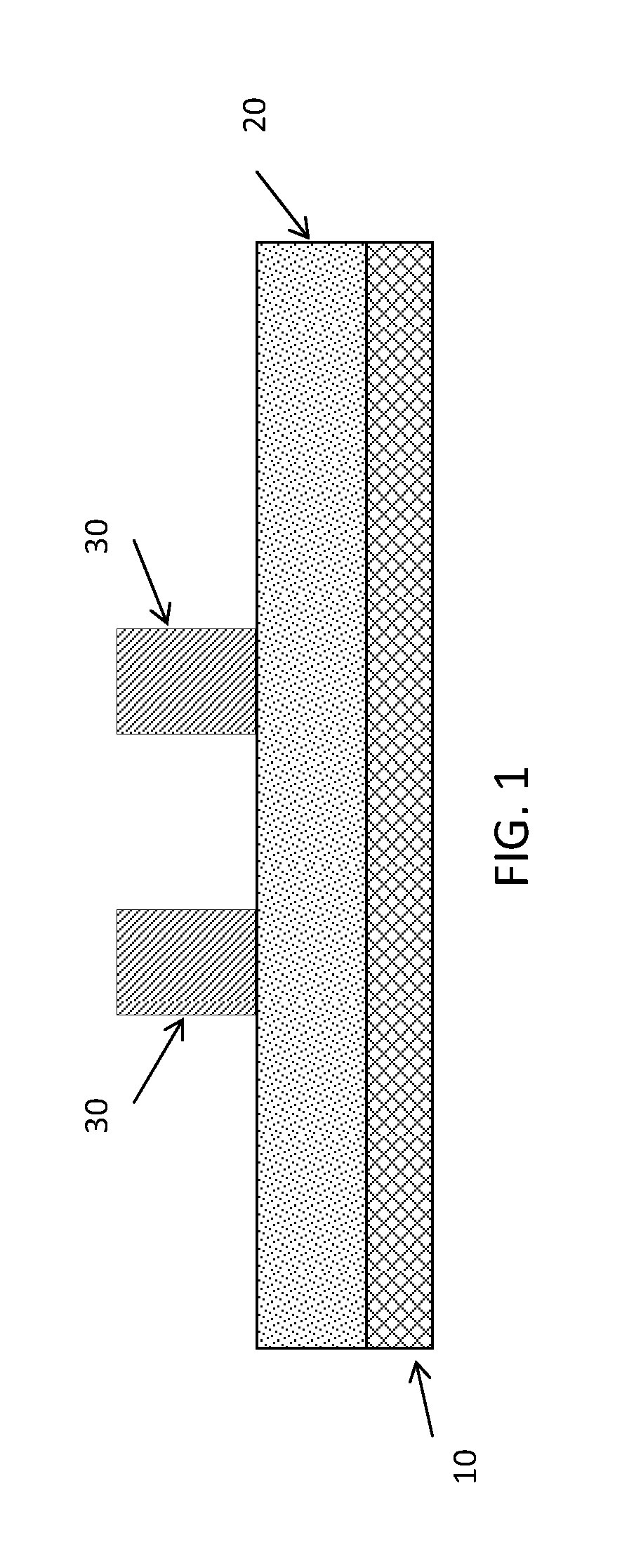
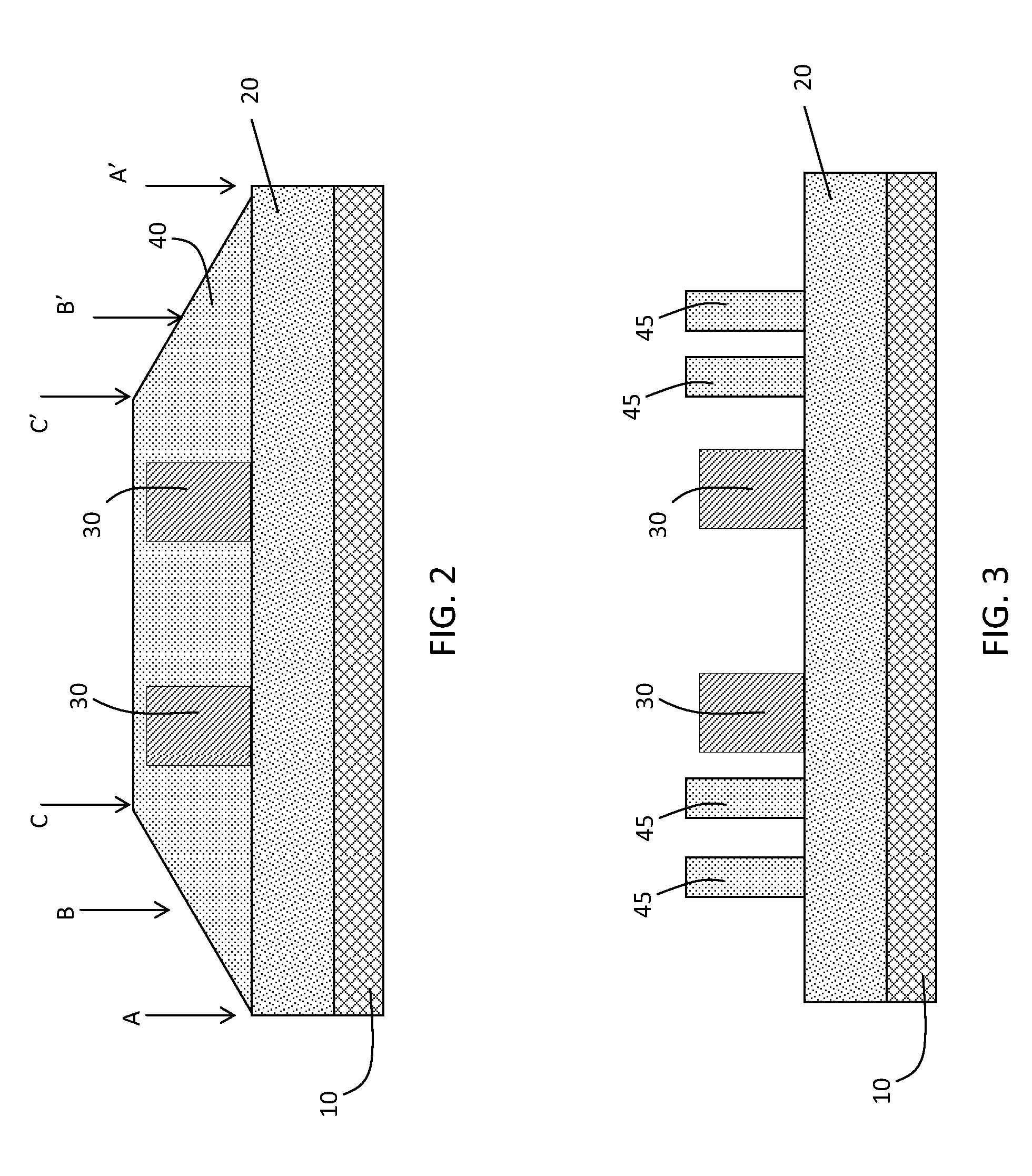
[0012]One approach in creating assist features is to begin with at least one mask patterned structure or structure 30 on top of a mask substrate 10 as shown in FIG. 1. Optionally, an image transfer material 20 may also be provided between the substrate and the patterned structures. Image transfer material 20 can be a temporary material used to transfer the pattern into mask substrate 10. Hard mask structure 30 is patterned using conventional techniques such as e-beam lithography. As demonstrated in FIG. 2, a self-assembly material 40, such as diblock copolymer, is spin coated in such a manner that the thickness of the copolymer layer varies from being thickest right next to structure 30, and being thinner as the distance away from the feature is increased. The spin speed and viscosity of the diblock is chosen so that the diblock thickness is in the right range for self-assembly to occur only between regions B and C, and B′ and C′, as show in FIG. 2. For sections between regions A an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com