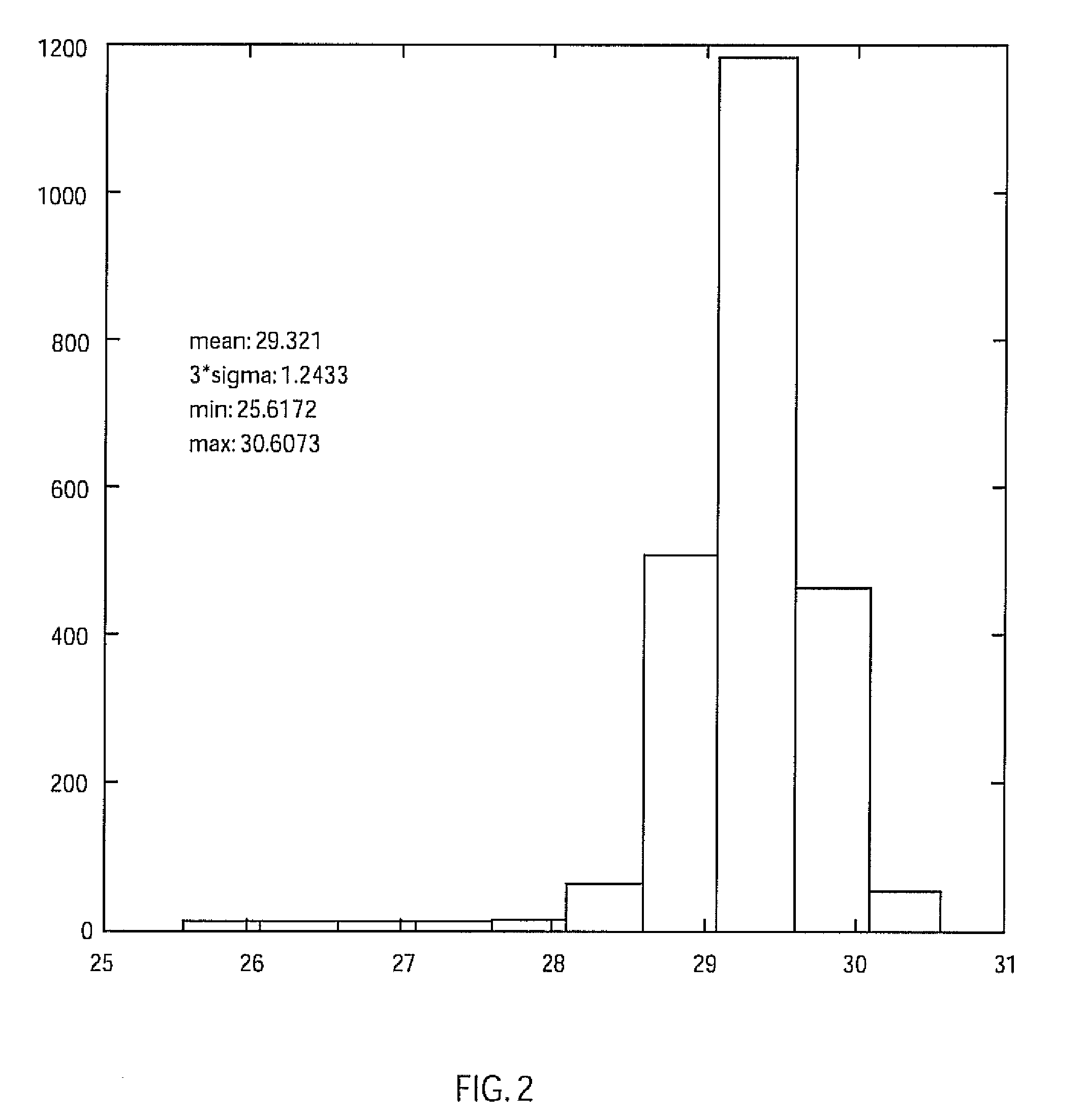Patents
Literature
50 results about "Ground rule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
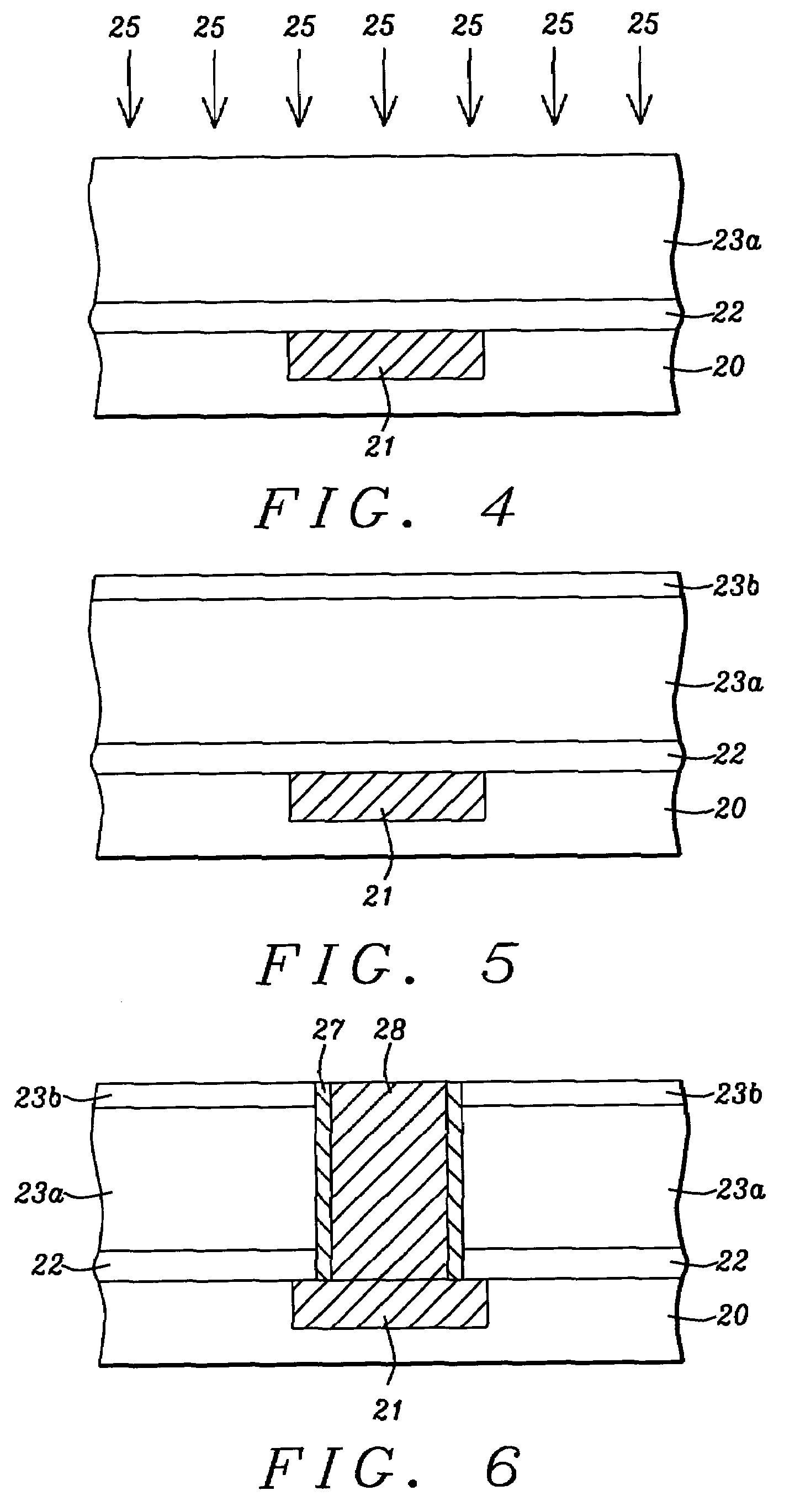
Two step post-deposition treatment of ILD layer for a lower dielectric constant and improved mechanical properties
InactiveUS20050064698A1Increase resistanceImprove the immunityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMoistureMechanical property
A method of lowering the dielectric constant of an organosilicon low k dielectric layer while improving the hardness and thermal stability is provided. A deposited layer of carbon doped oxide, HSQ, or MSQ is cured and treated with a He plasma which improves hardness for a subsequent CMP step and lowers the dielectric constant. There is no loss of H2O or CH4 during the He treatment. The low k dielectric layer is then treated with a H2 plasma which converts some of the Si—O and Si—CH3 bonds near the surface to Si—H bonds, thereby further lowering the dielectric constant and increasing thermal stability that improves breakdown resistance. Moisture uptake is also reduced. The method is especially useful for interconnect schemes with deep sub-micron ground rules. Surprisingly, the k value obtained from two different plasma treatments is lower than when two He treatments or two H2 treatment are performed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MASNUFACTURING
Electron beam projection lithography system (EBPS)
InactiveUS6069684AHigh resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsBeam energyBeam trajectory
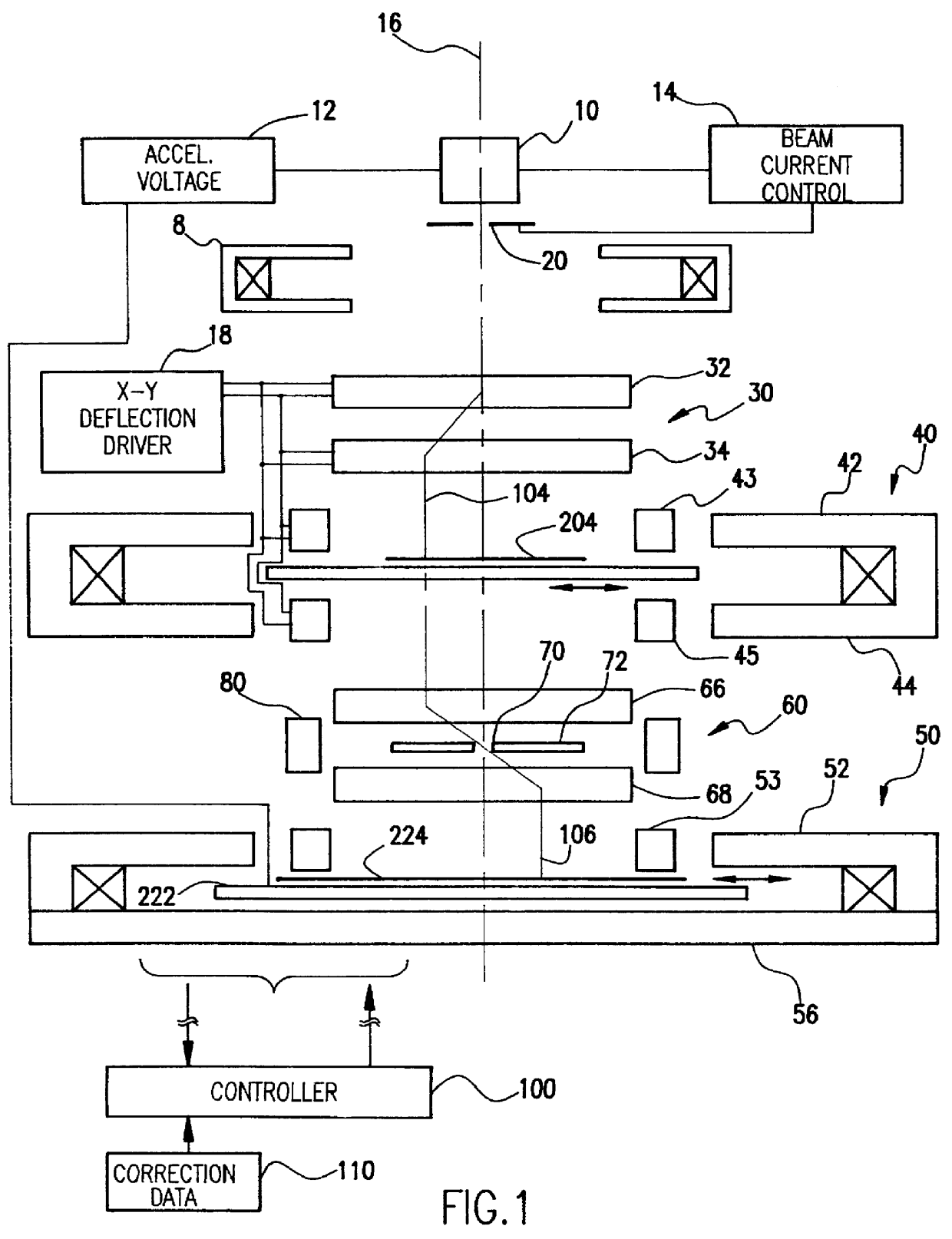
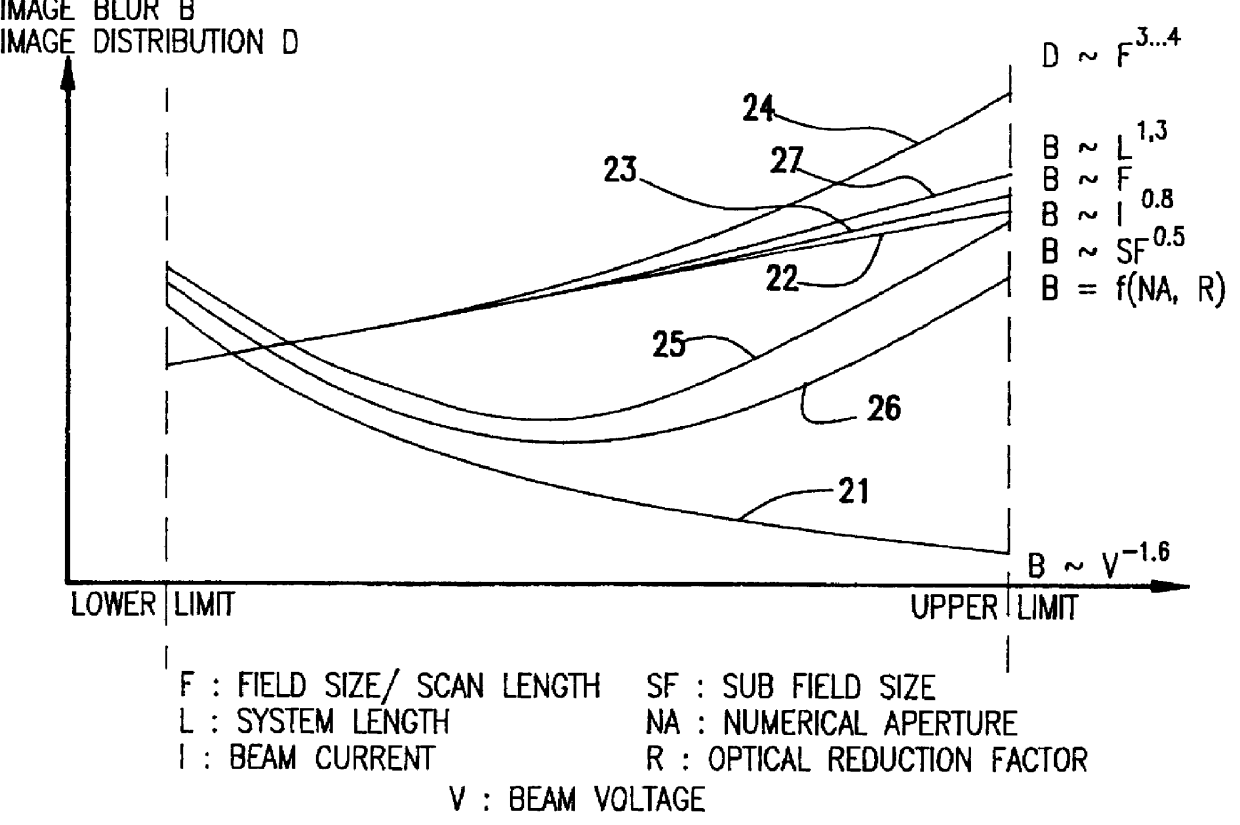
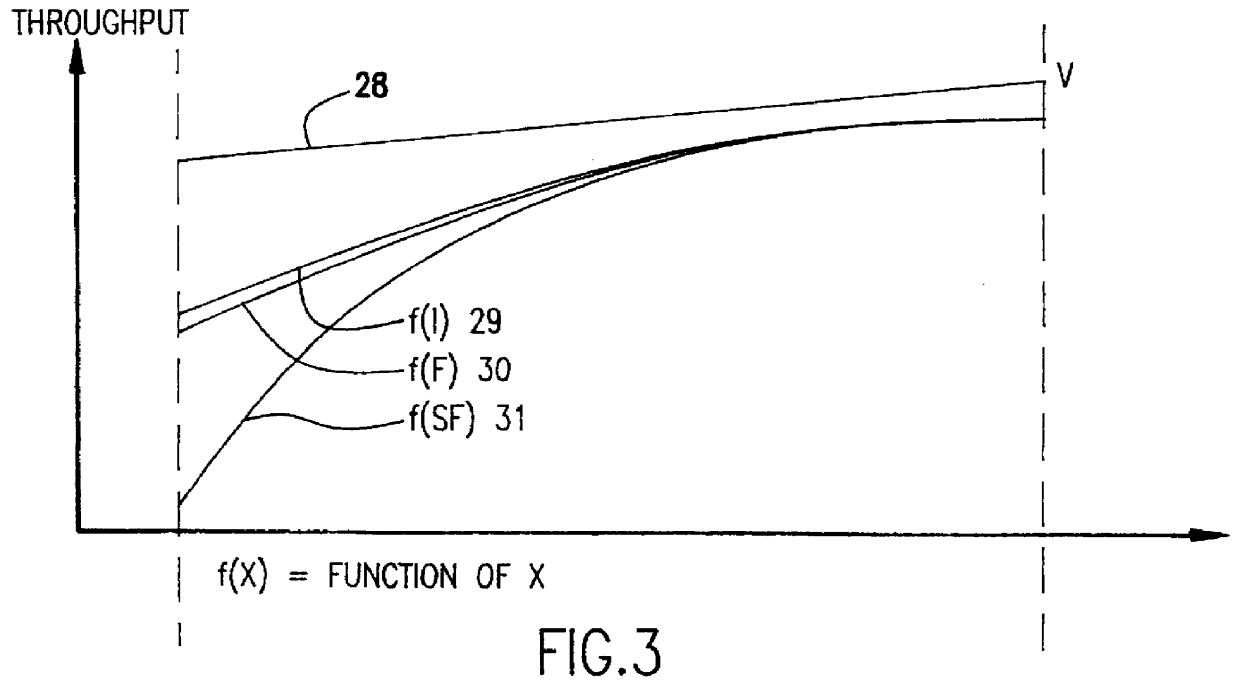
Numerous largely unpredictable criticalities of operating parameters arise in electron beam projection lithography systems to maintain throughput comparable to optical projection lithography systems as minimum feature size is reduced below one-half micron and resolution requirements are increased. Using an electron beam projection lithography system having a high emittance electron source, variable axis lenses, curvilinear beam trajectory and constant reticle and / or target motion in a dual scanning mode wherein the target and / or wafer is constantly moved orthogonally to the direction of beam scan, high throughput is obtained consistent with 0.1 mu m feature size ground rules utilizing a column length of greater than 400 mm, a beam current of between about 4 and 35 mu A, a beam energy of between about 75 and 175 kV, a sub-field size between about 0.1 and 0.5 mm at the target at an optical reduction factor between about 3:1 and 5:1, a numerical aperture greater than 2 mrad and preferably between about 3 and 8 mrad and a scan length between about 20 mm and 55 mm. Reticle and target speed preferably differ by about the optical reduction factor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Use of a layout-optimization tool to increase the yield and reliability of VLSI designs
InactiveUS6941528B2Easy to placeIncrease the number ofComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designGround ruleIntegrated circuit design
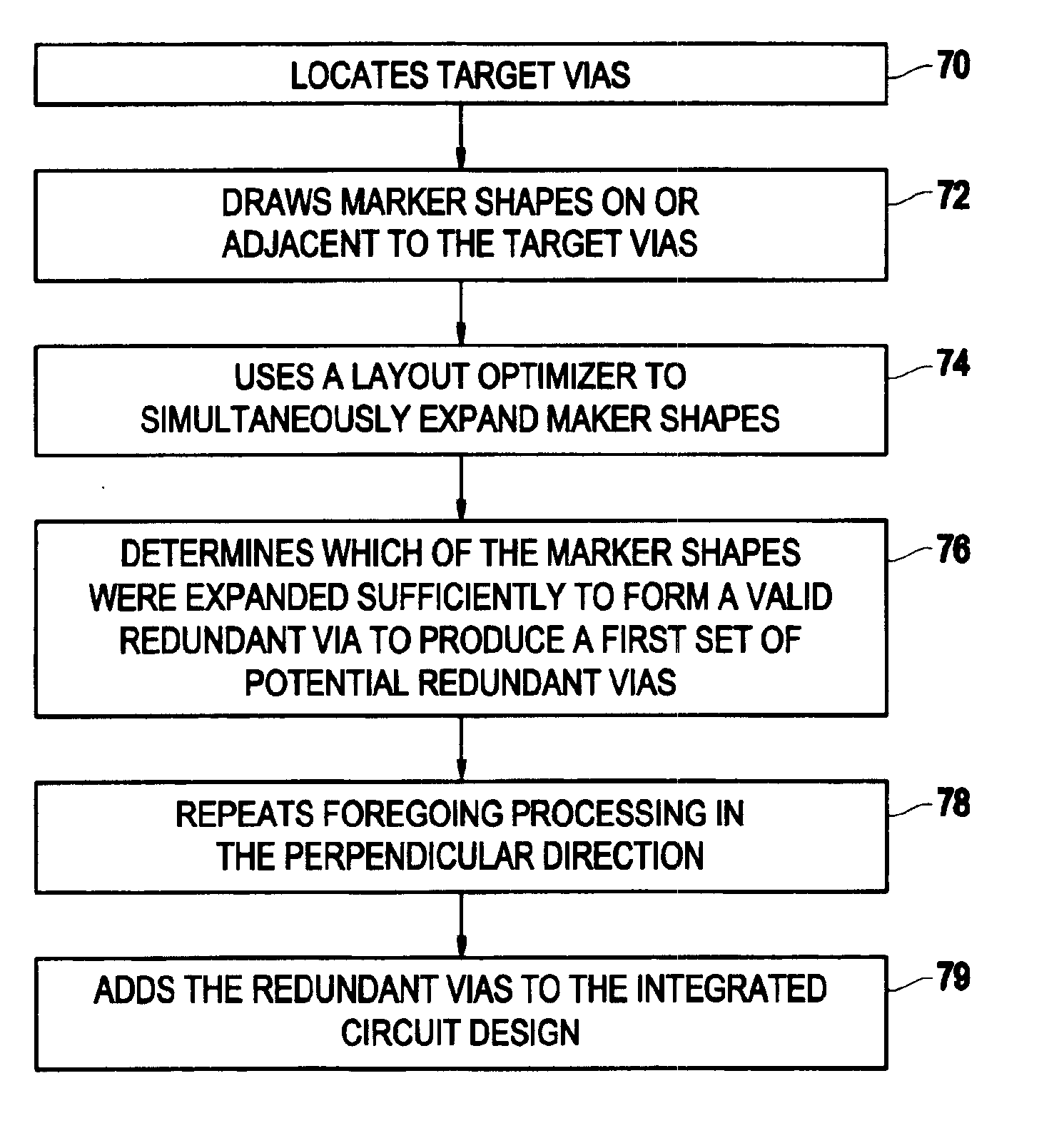
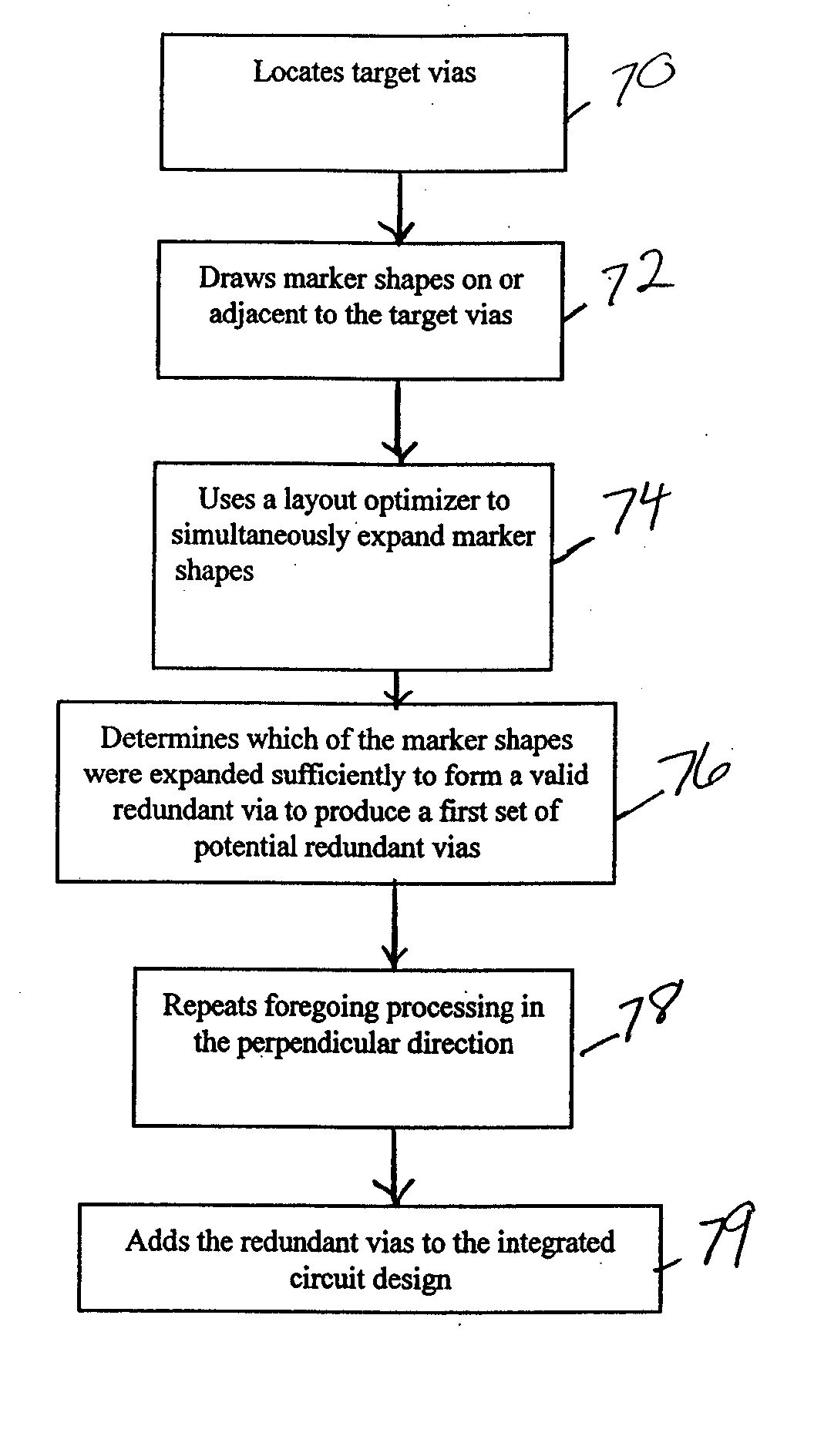
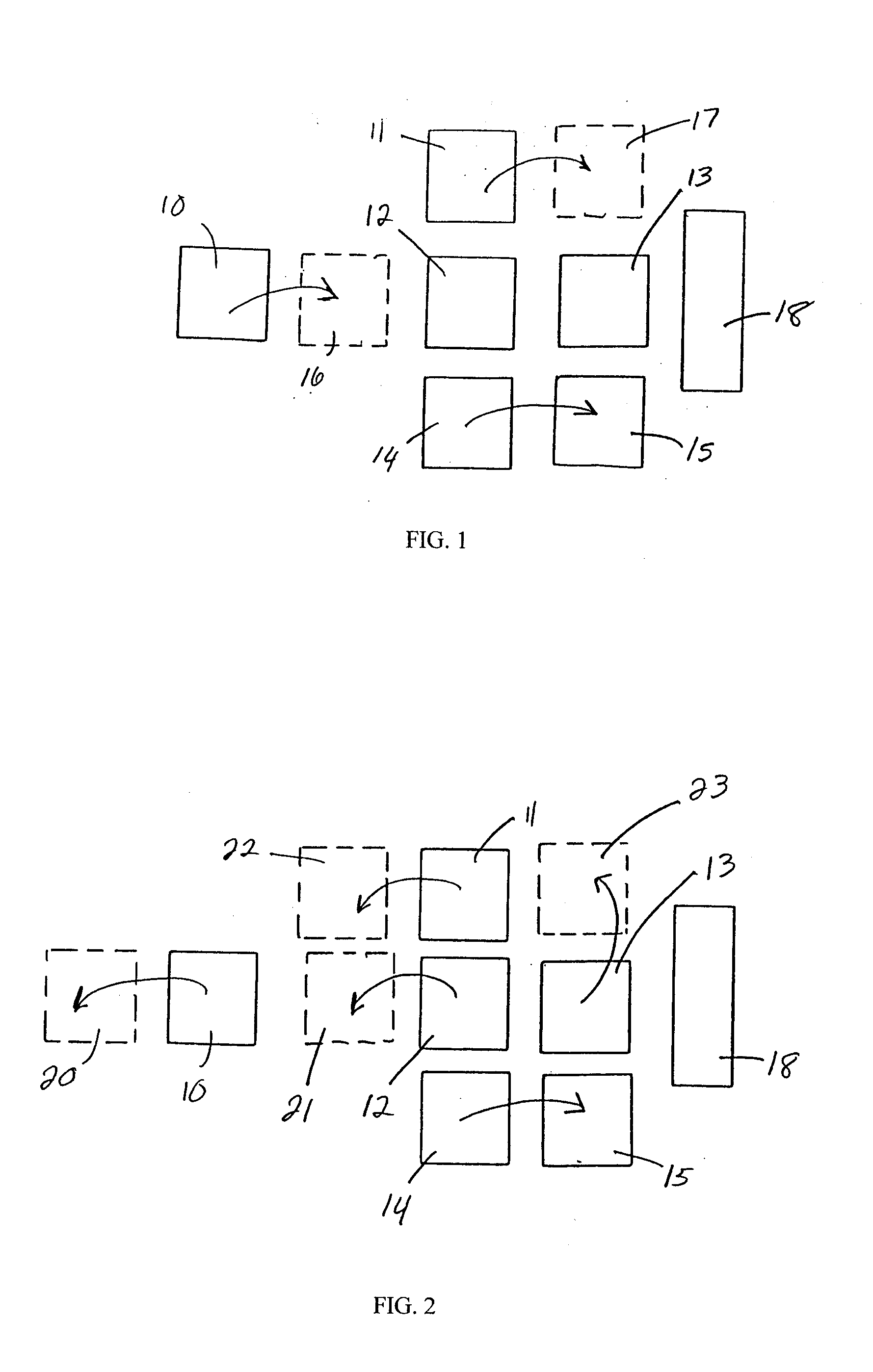
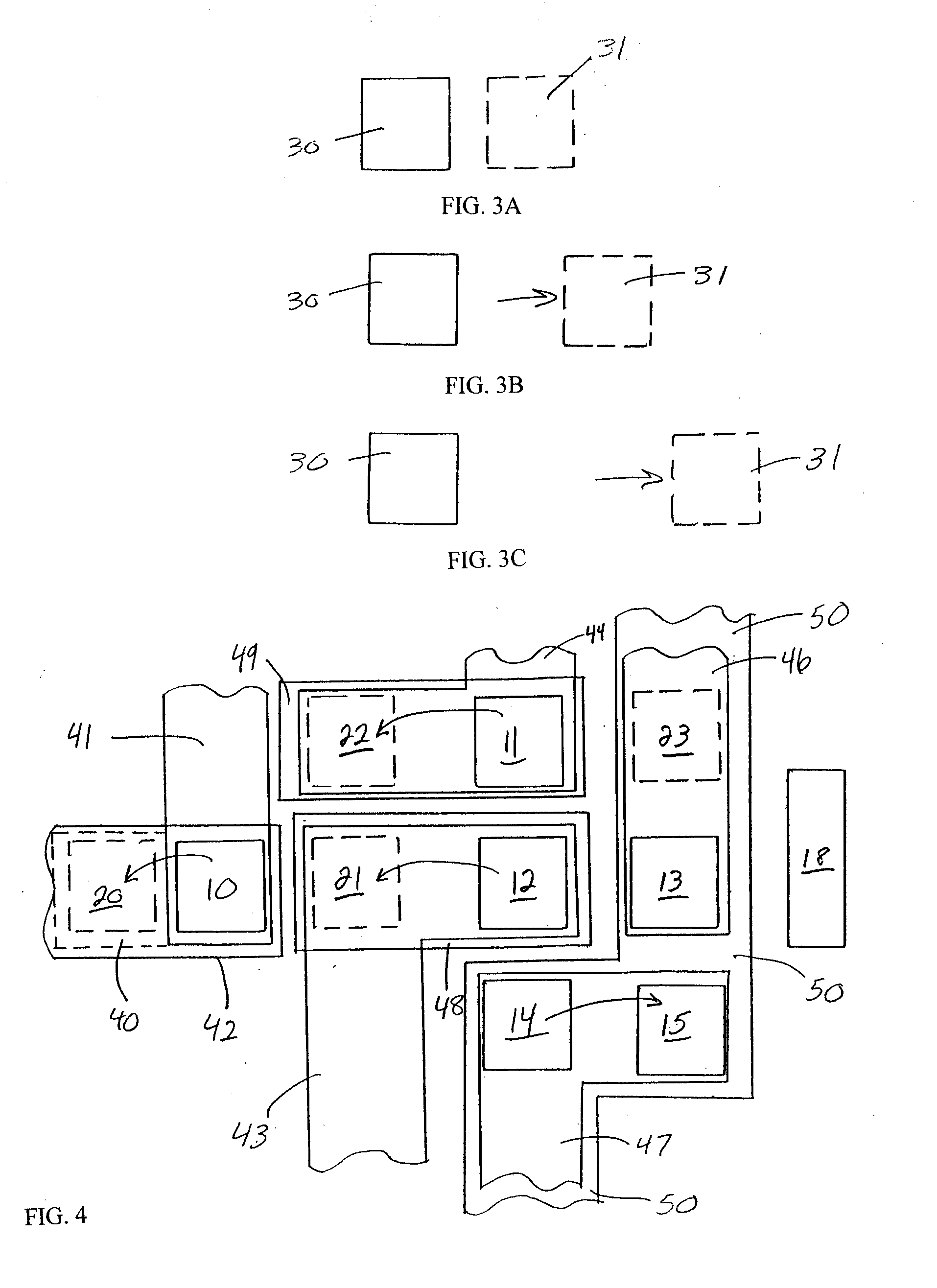
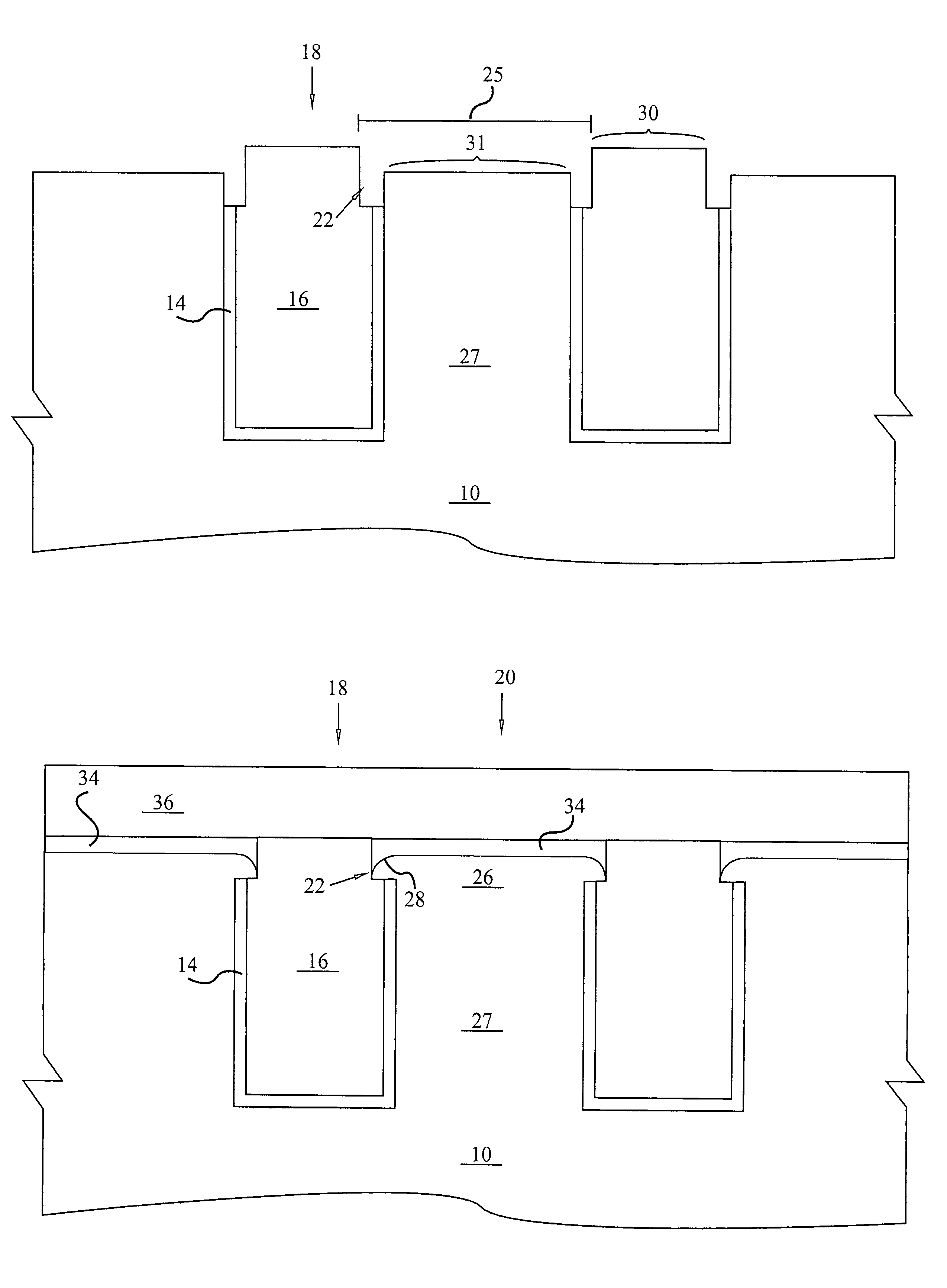
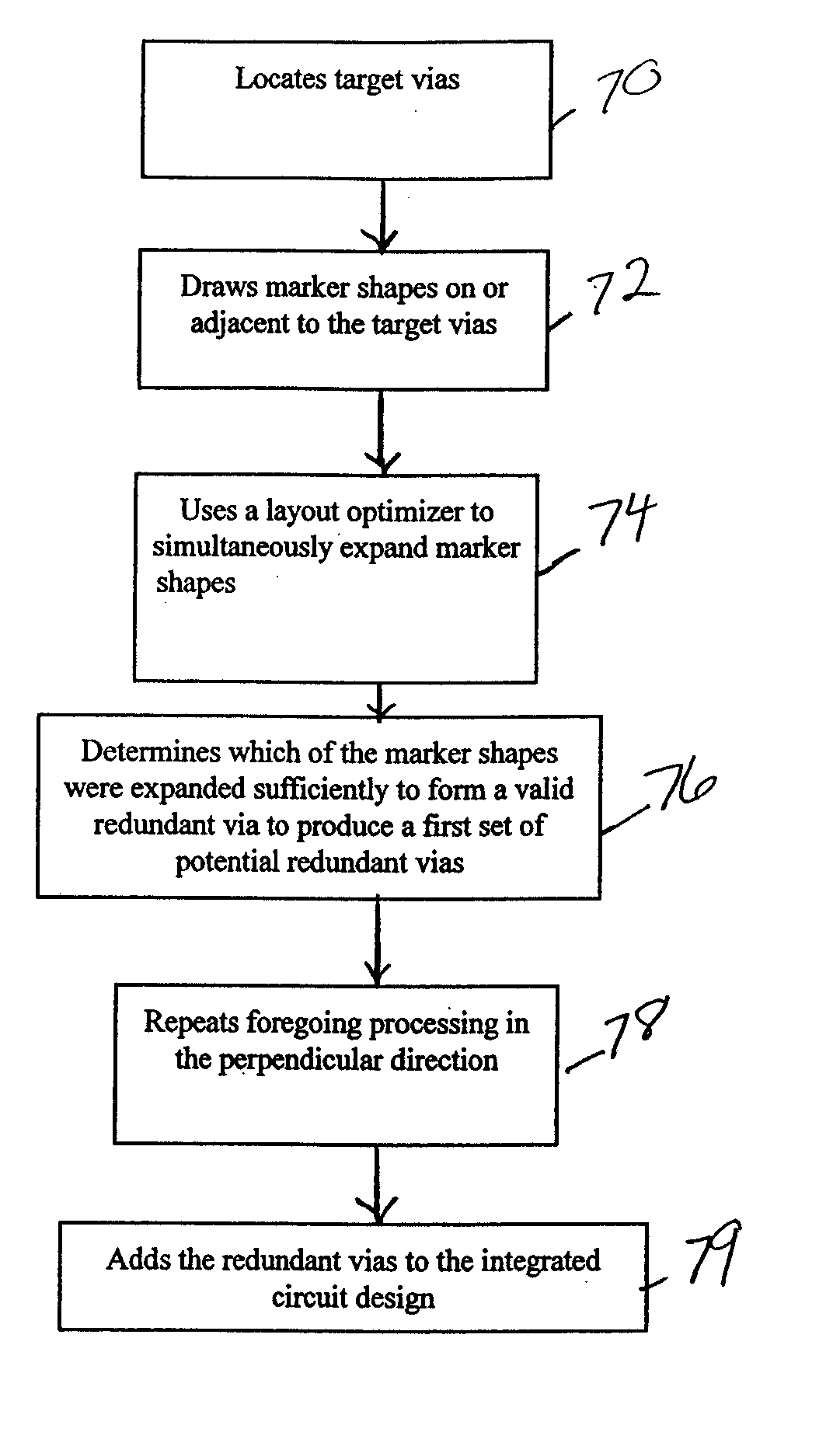
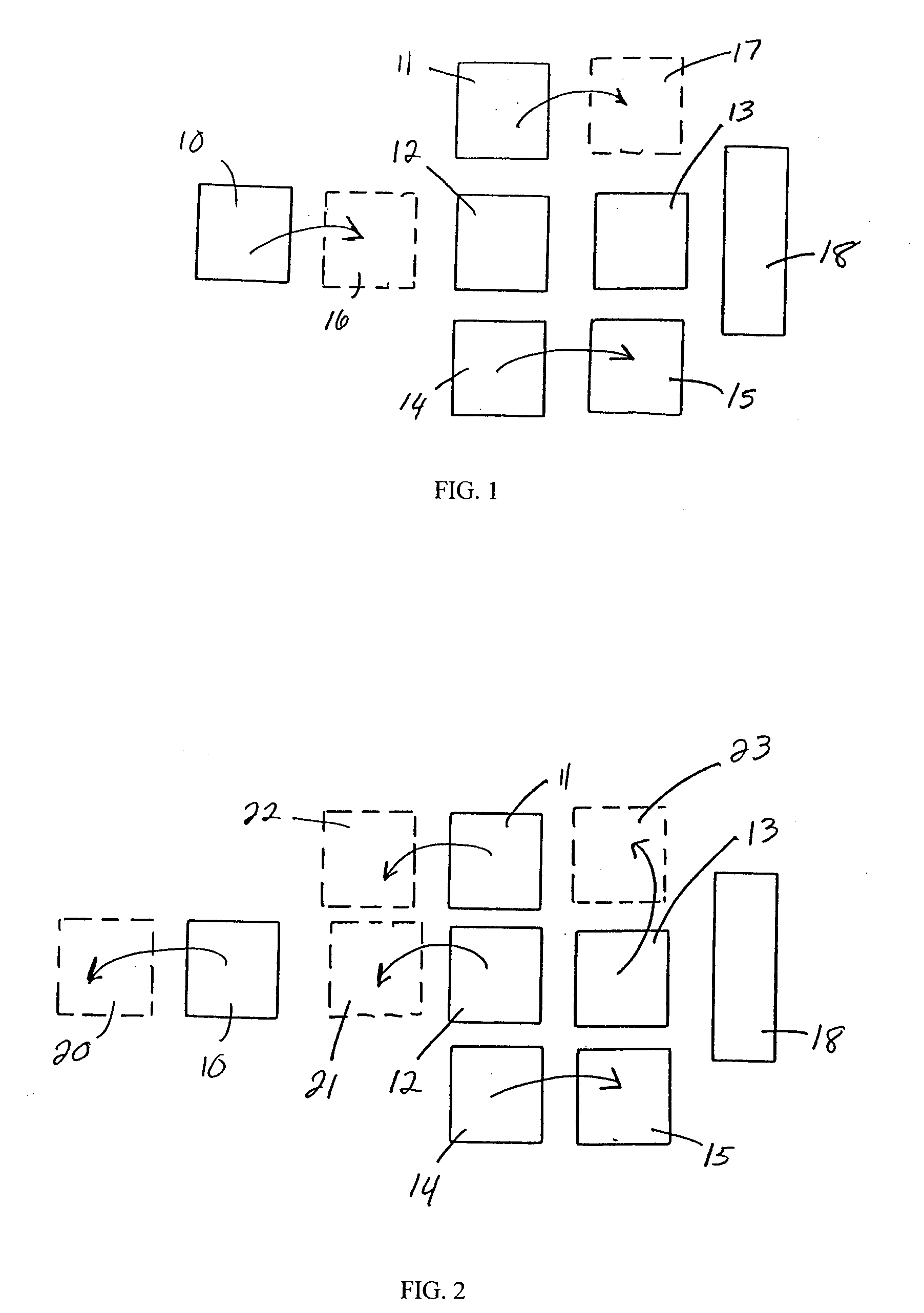
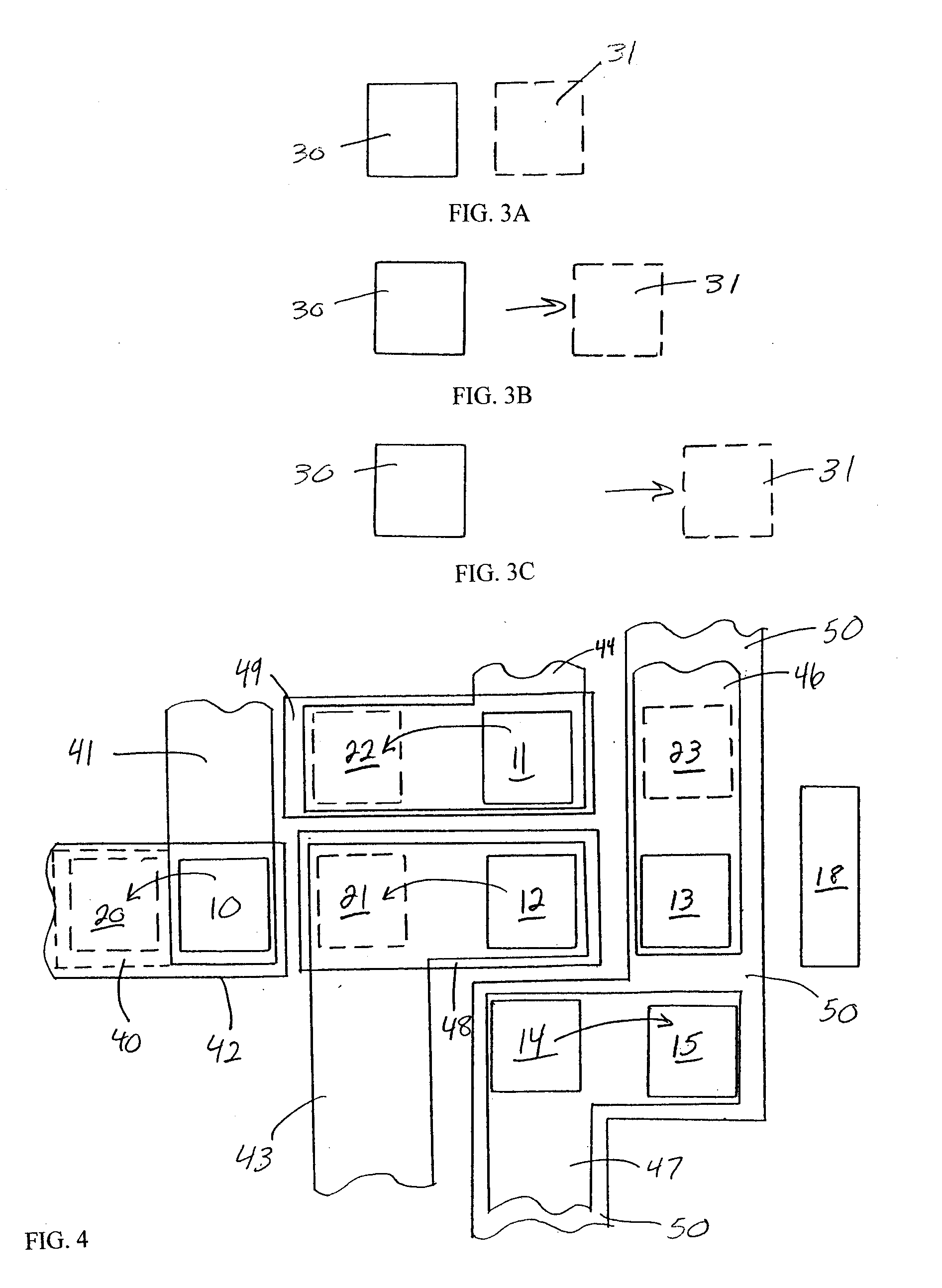
The invention provides a method and structure for optimizing placement of redundant vias within an integrated circuit design. The invention first locates target vias by determining which vias do not have a redundant via. Then, the invention draws marker shapes on or adjacent to the target vias. The marker shapes are only drawn in a horizontal or vertical direction from each of the target vias. The invention simultaneously expands all of the marker shapes in the first direction to a predetermined length or until the marker shapes reach the limits of a ground rule. During the expanding, different marker shapes will be expanded to different lengths. The invention determines which of the marker shapes were expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via to produce a first set of potential redundant vias and the invention eliminates marker shapes that could not be expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY INC
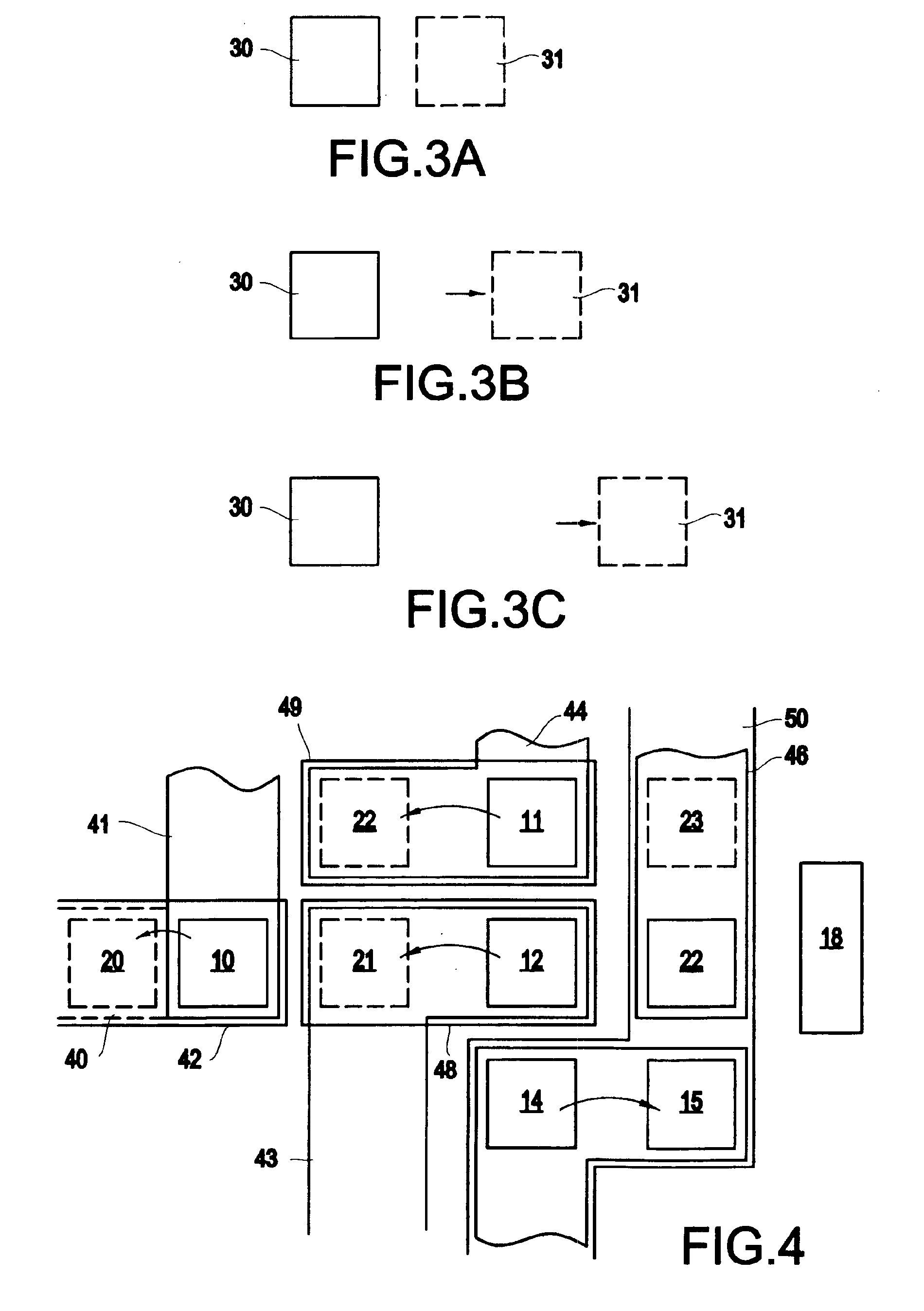
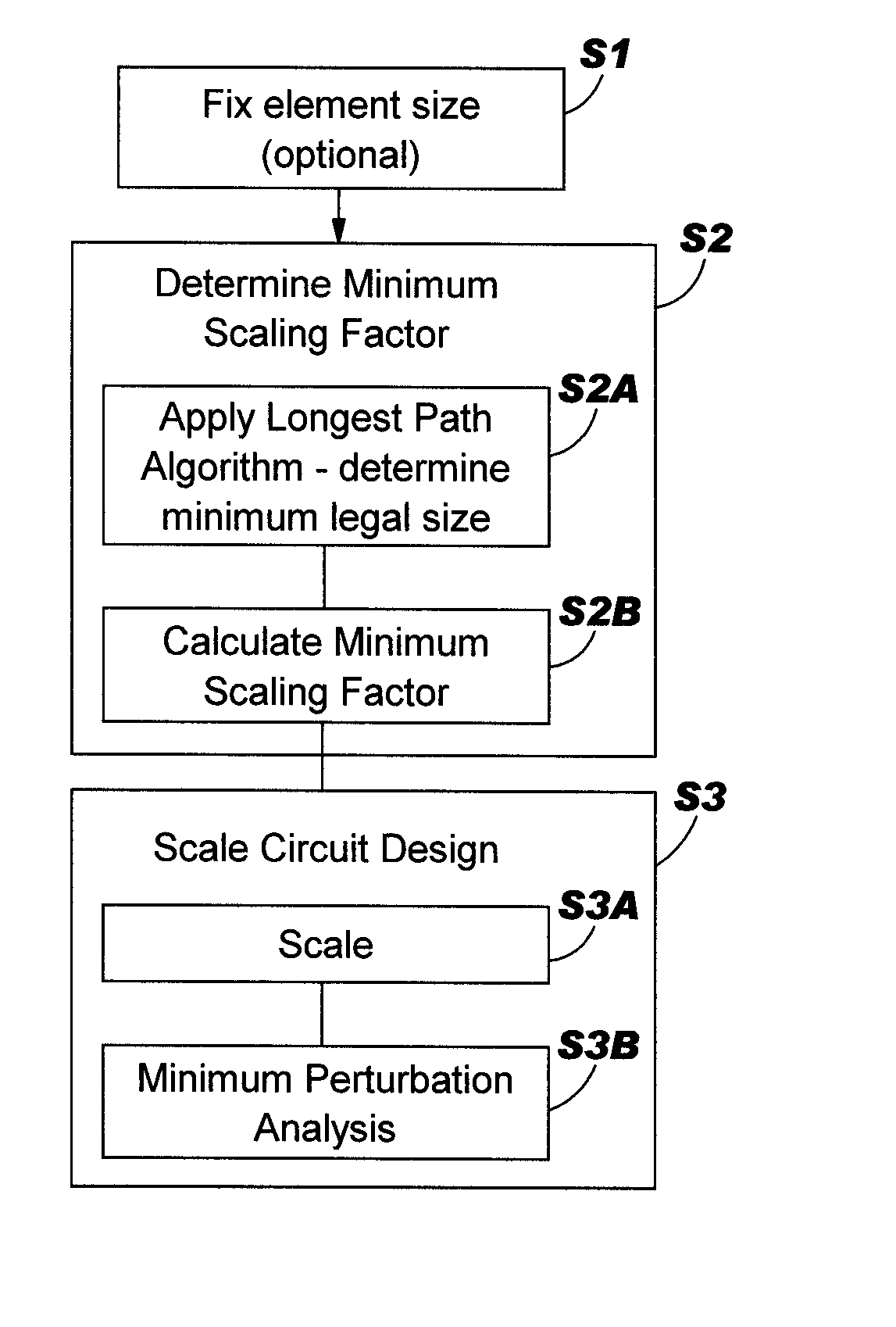
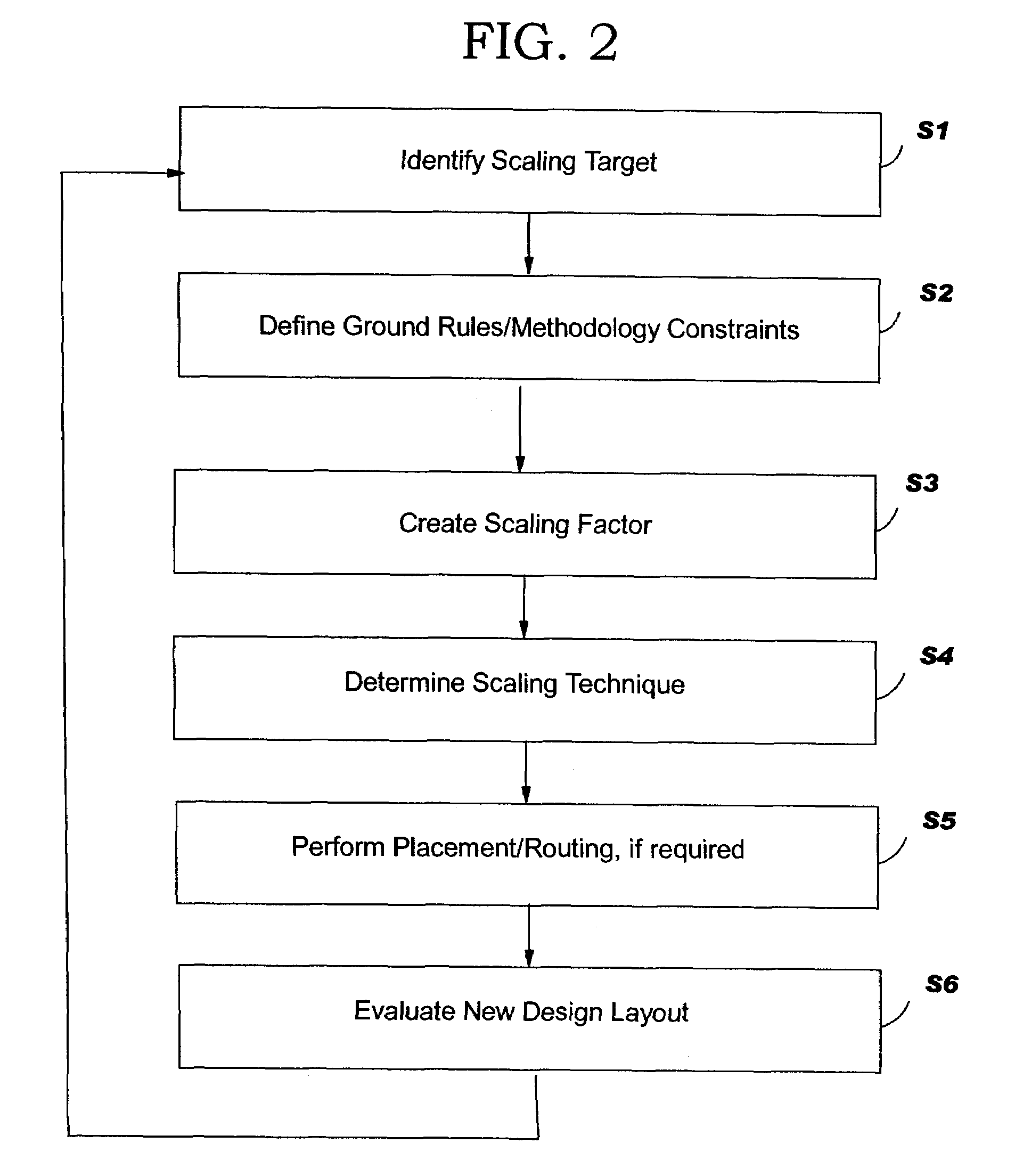
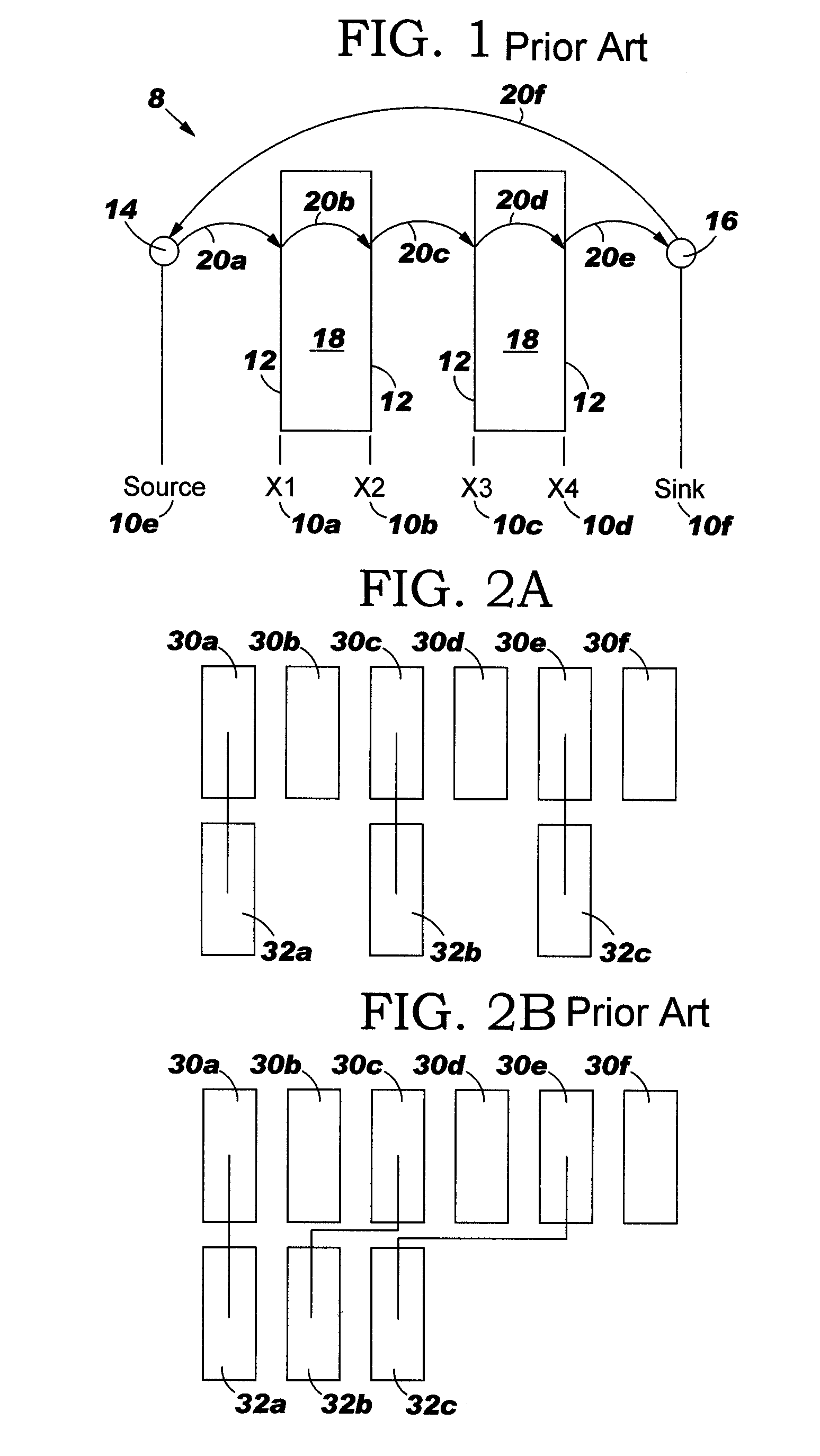
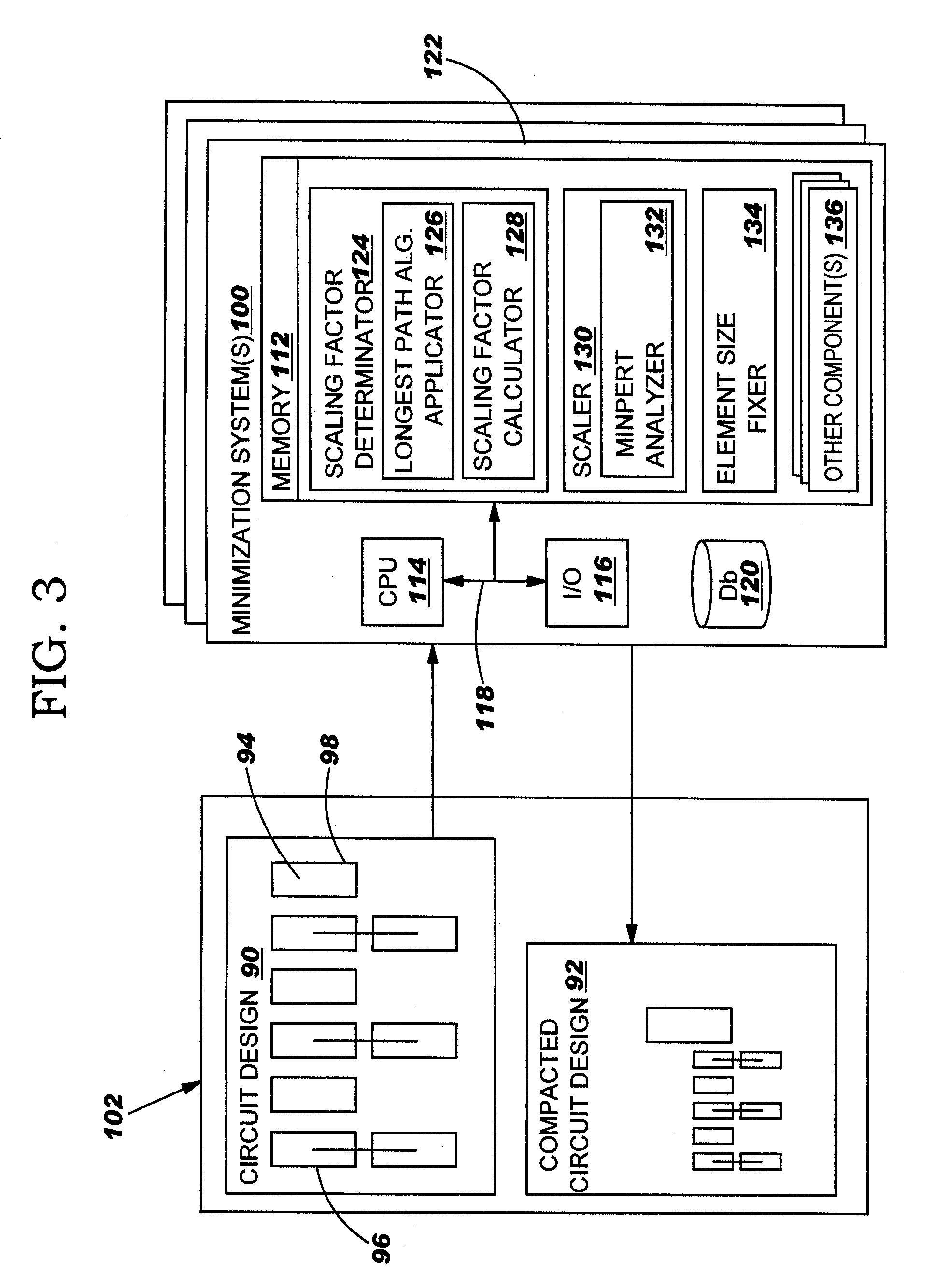
Circuit area minimization using scaling
InactiveUS20050125748A1Small sizeArea minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designComputer scienceGround rule
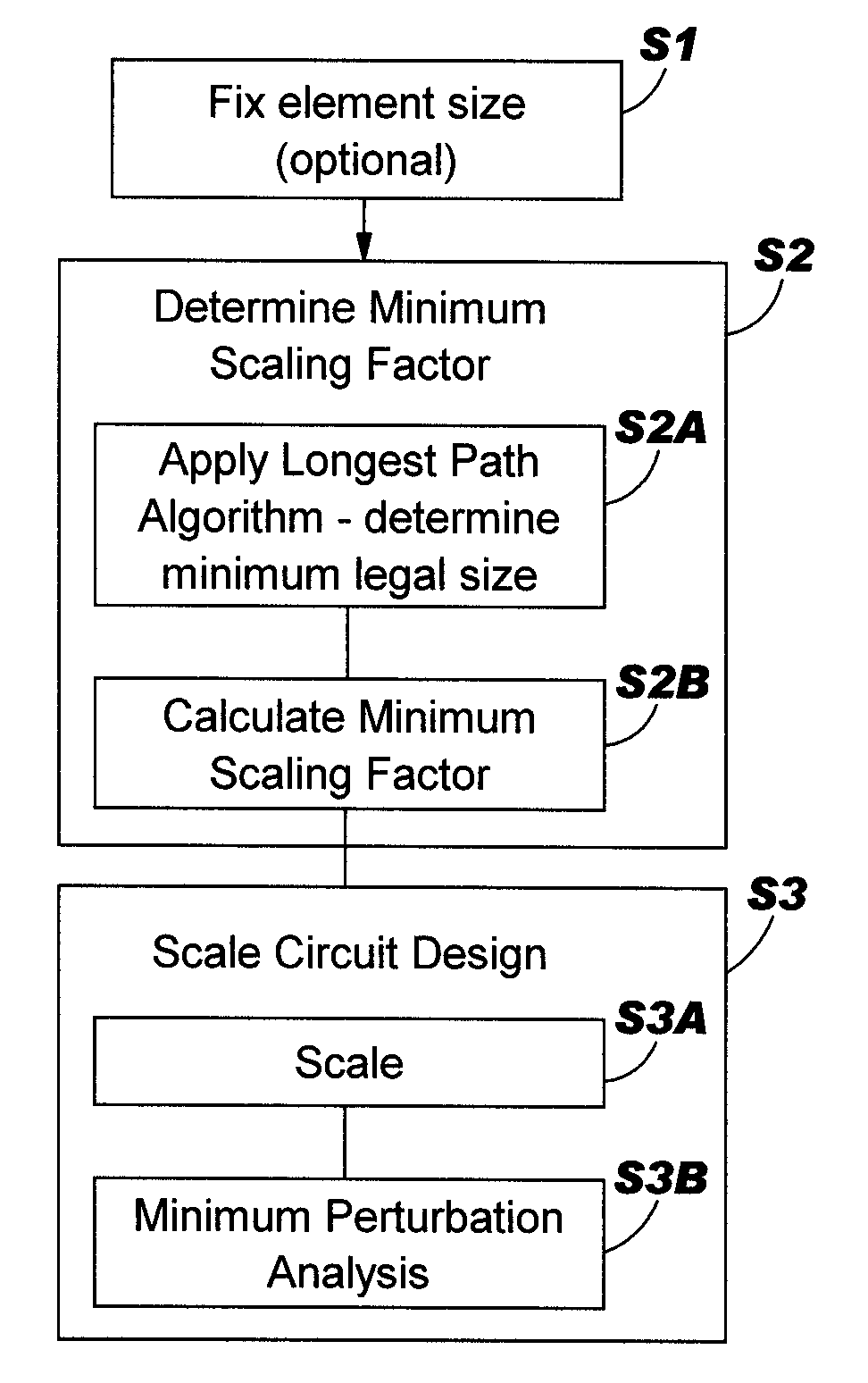
A method, system and program product that implements area minimization of a circuit design while respecting the explicit and implicit design constraints, in the form of ground rules and user intent. A longest path algorithm is used to generate a scaling factor. The scaling factor is used to reduce the size of the circuit design to the minimum legal size. The scaling may be followed by application of minpert analysis to correct any errors introduced by the scaling. The resulting design is shrunk (or expanded) with all elements shrinking (or growing) together by the same factor, and with the relative relationships of elements maintained. In addition, the invention is operational in the presence of a positive cycle, can be run with scaling that freezes the sizes of any structure or ground rule, and can be applied to technology migration.
Owner:IBM CORP
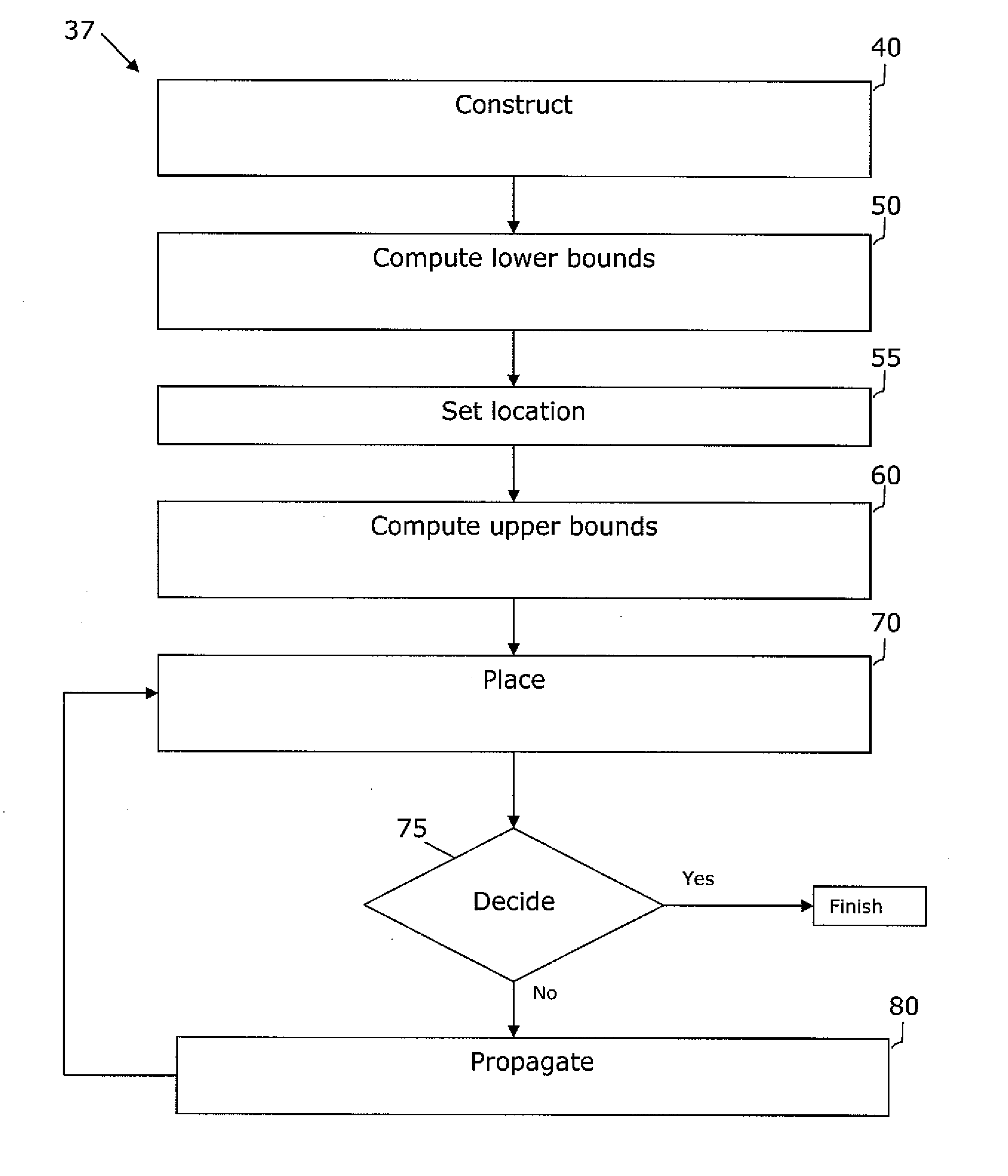
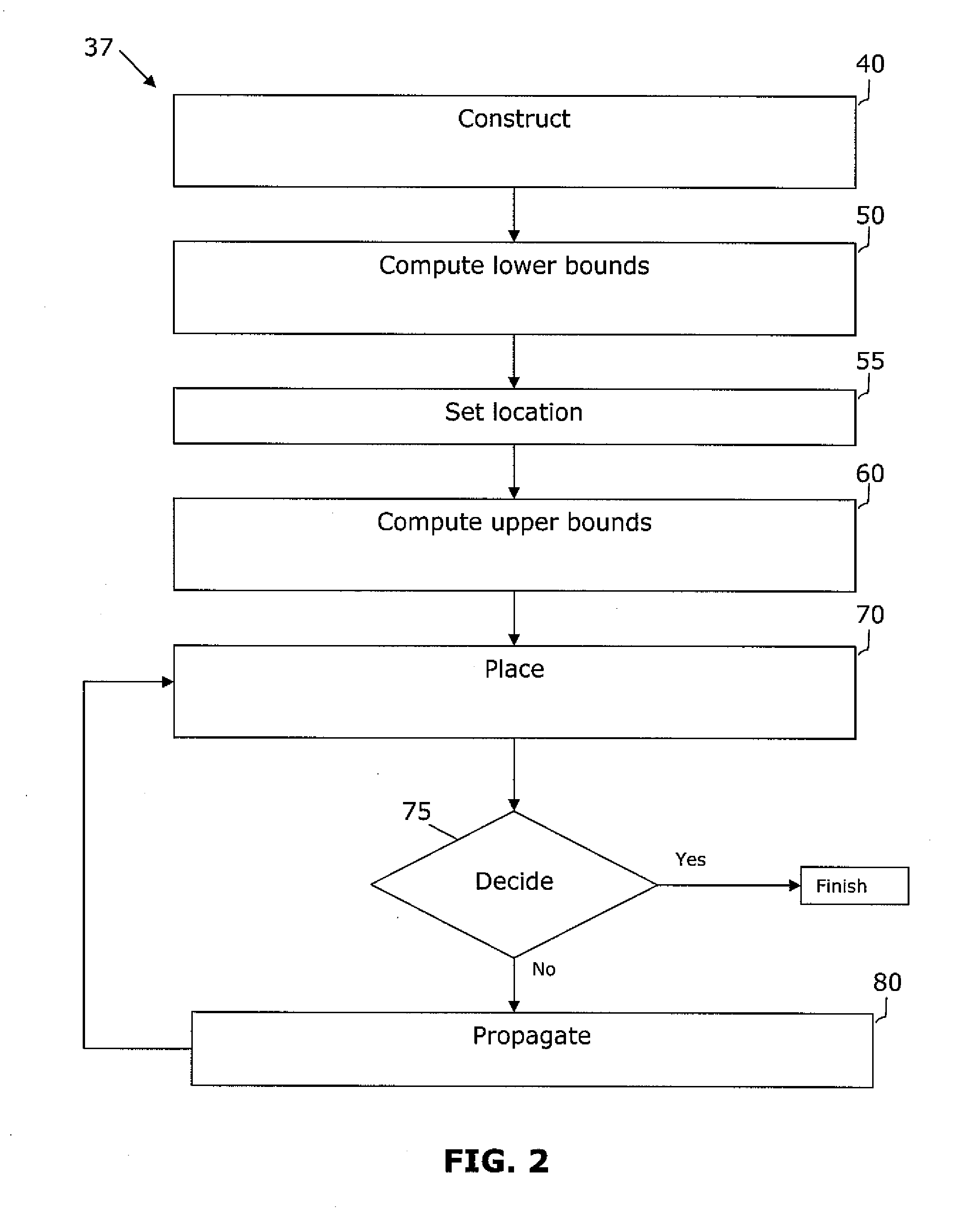
VLSI artwork legalization for hierarchical designs with multiple grid constraints
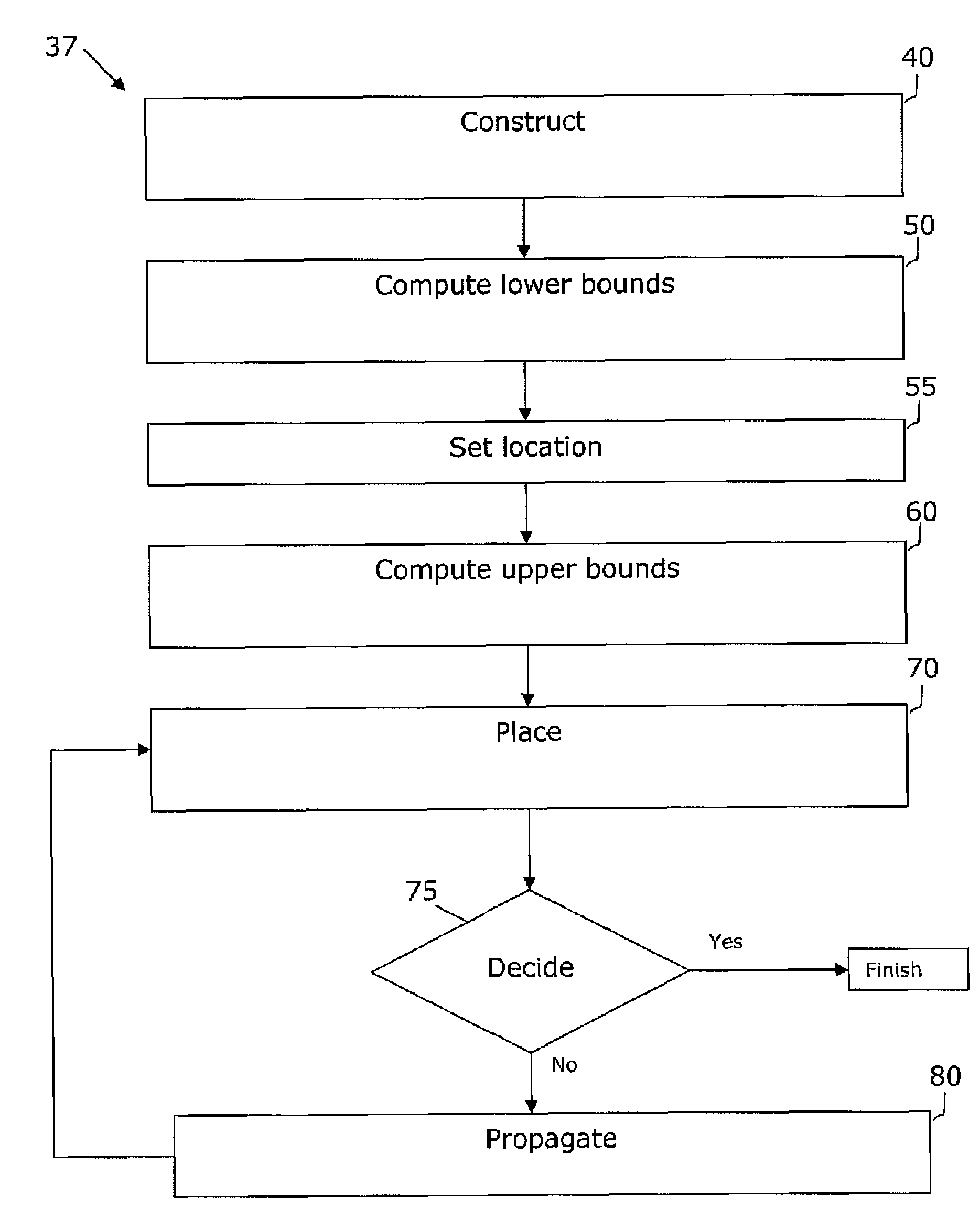
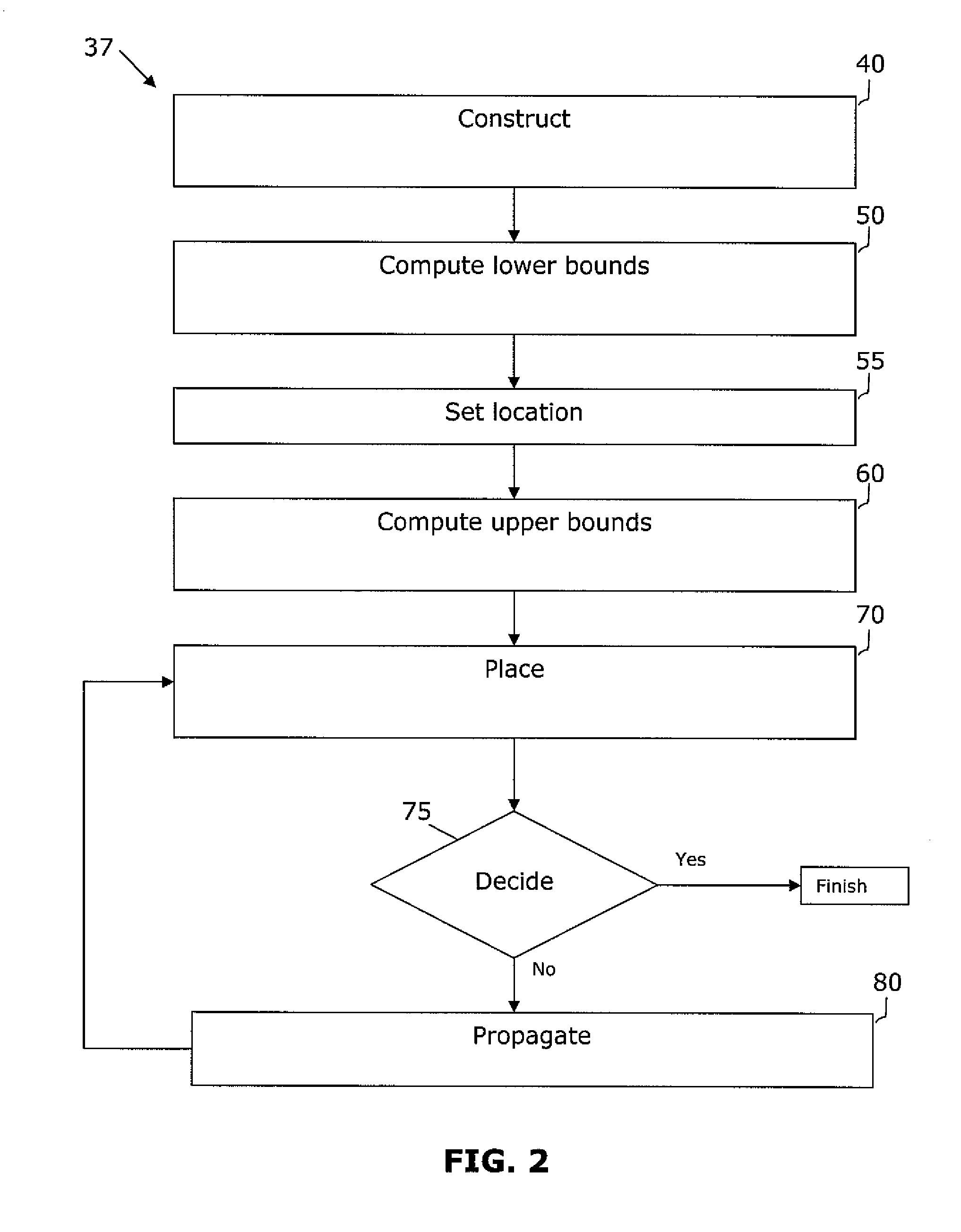
A system and method are disclosed for legalizing a flat or hierarchical VLSI layout to meet multiple grid constraints and conventional ground rules. Given a set of ground rules with multiple grid constraints and a VLSI layout (either hierarchical or flat) which is layout-versus-schematic (LVS) correct but may not be ground rule correct, the system and method provide a legalized layout which meets the multiple grid constraints while maintaining LVS correctness and fixing the ground rule errors as much as possible with minimum layout perturbation from the input design. The system and method support multiple grid pitch constraints for hierarchical design, and provide for LVS correctness to be maintained while an on-grid solution possibly with some spacing violations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
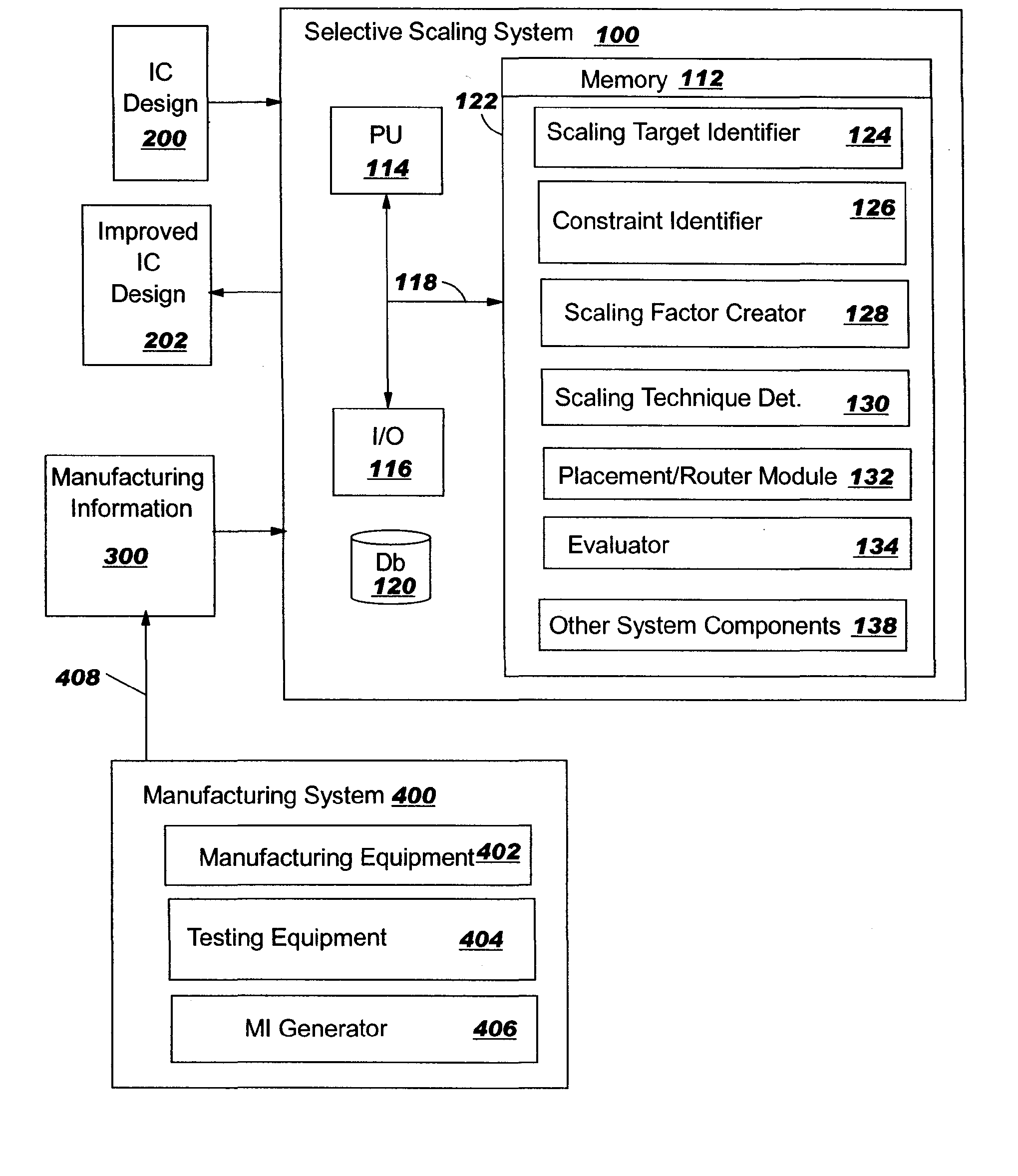
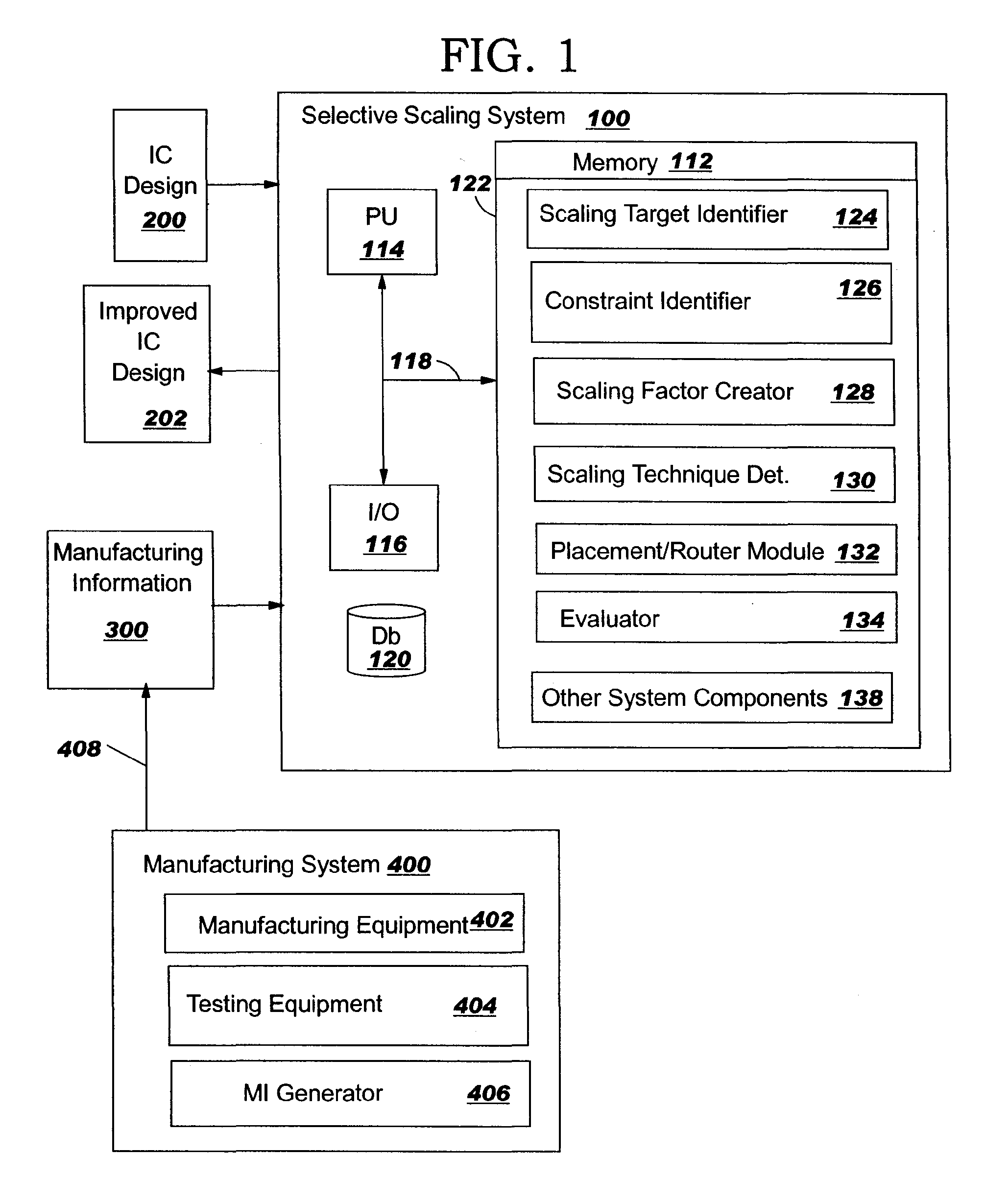
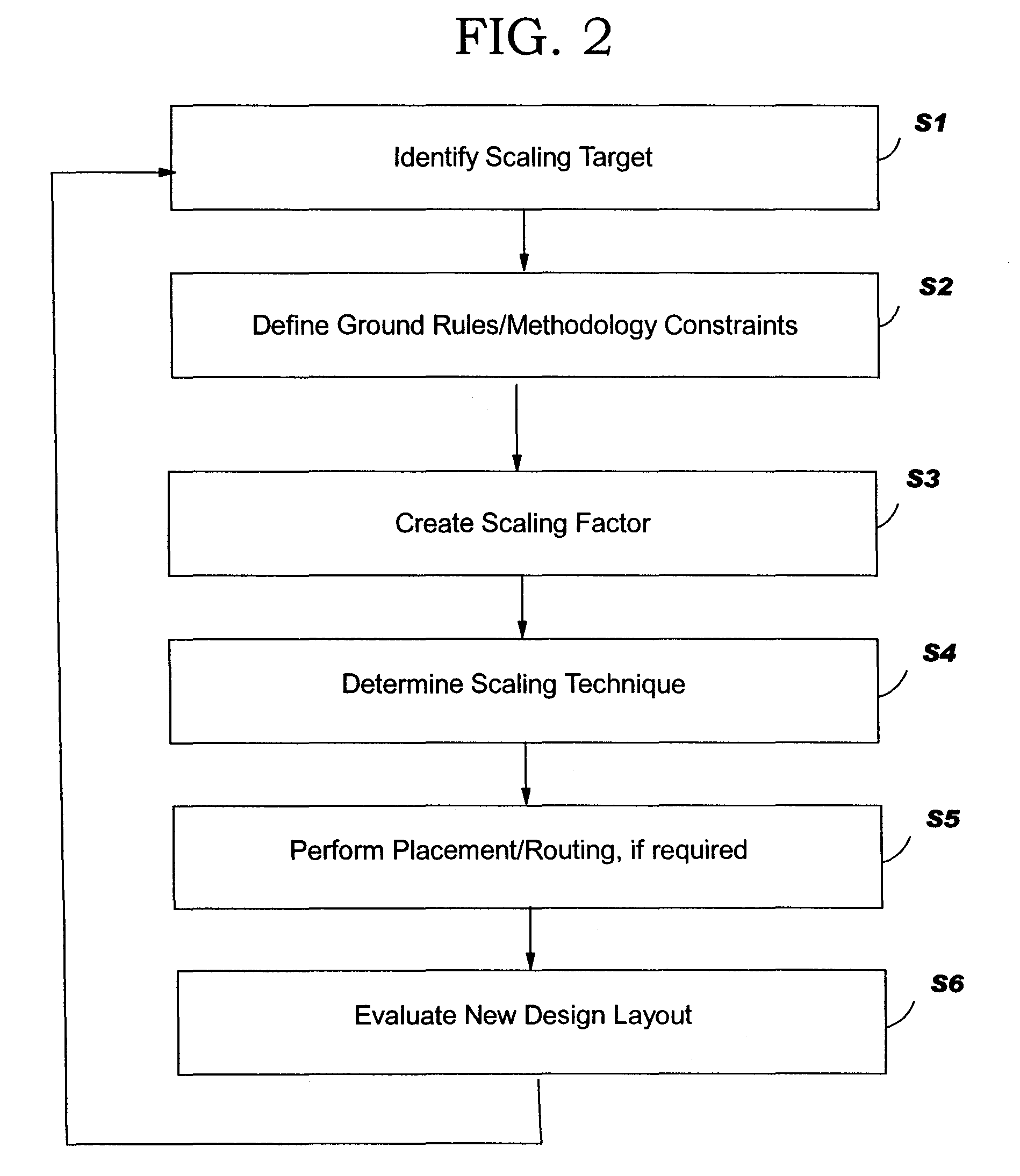
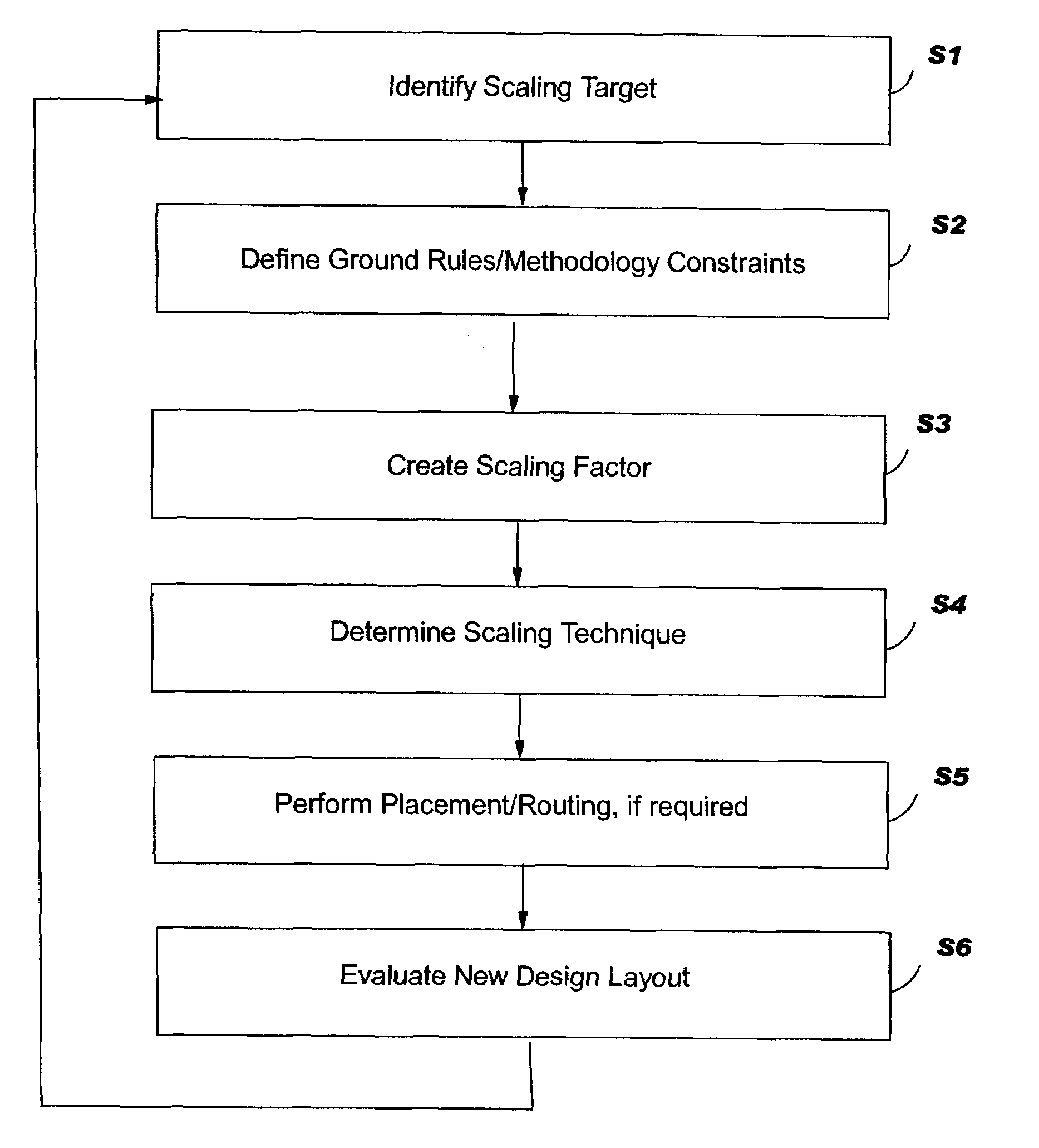
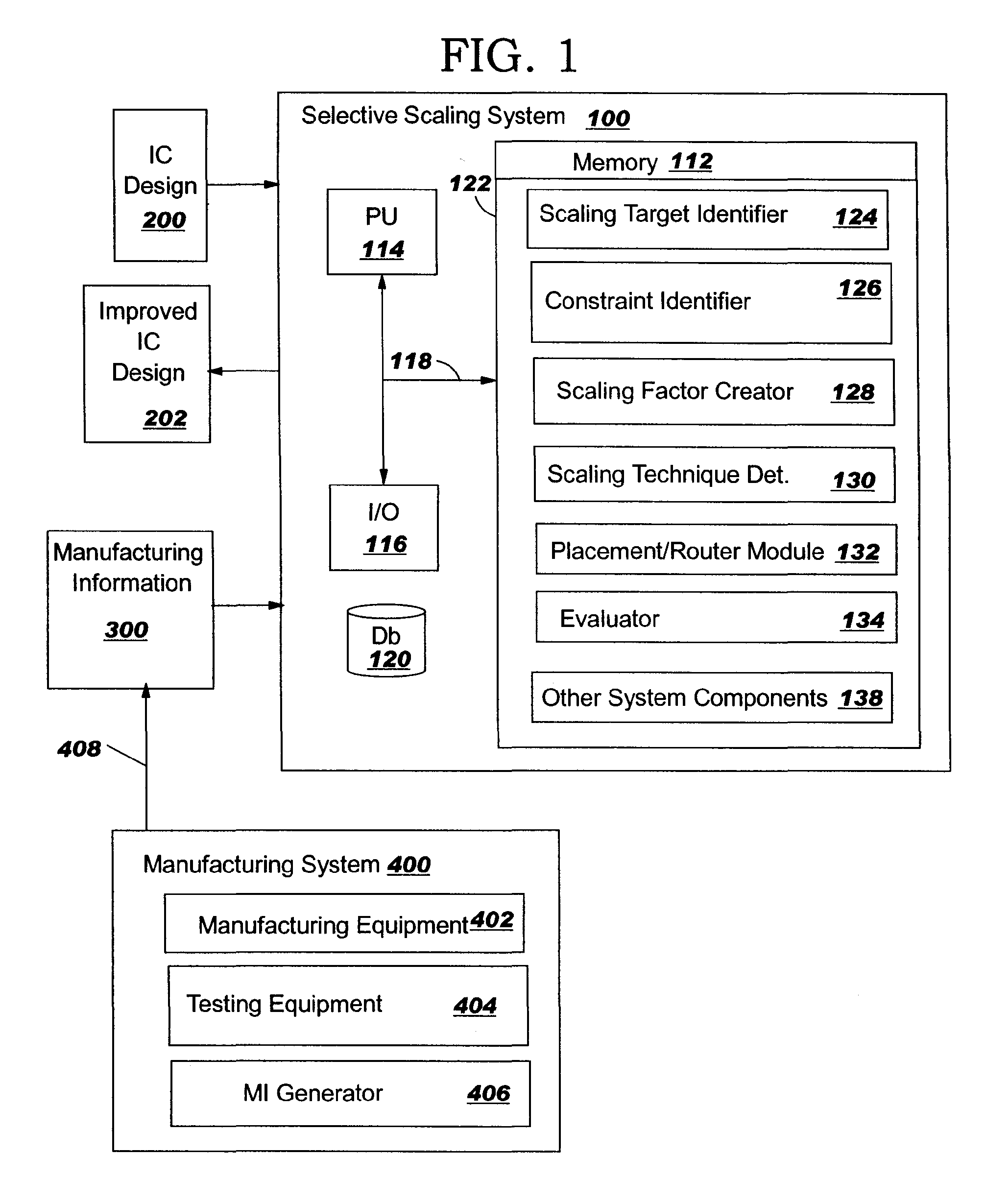
Integrated circuit selective scaling
InactiveUS20060085768A1Increase productionHierarchy is preservedCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringGround rule
Methods, systems and program products are disclosed for selectively scaling an integrated circuit (IC) design: by layer, by unit, or by ground rule, or a combination of these. The selective scaling technique can be applied in a feedback loop with the manufacturing system with process and yield feedback, during the life of a design, to increase yield in early processes in such a way that hierarchy is preserved. The invention removes the need to involve designers in improving yield where new technologies such as maskless fabrication are implemented.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Two step post-deposition treatment of ILD layer for a lower dielectric constant and improved mechanical properties
InactiveUS7250370B2Increase resistanceImprove the immunityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMechanical propertyMoisture
A method of lowering the dielectric constant of an organosilicon low k dielectric layer while improving the hardness and thermal stability is provided. A deposited layer of carbon doped oxide, HSQ, or MSQ is cured and treated with a He plasma which improves hardness for a subsequent CMP step and lowers the dielectric constant. There is no loss of H2O or CH4 during the He treatment. The low k dielectric layer is then treated with a H2 plasma which converts some of the Si—O and Si—CH3 bonds near the surface to Si—H bonds, thereby further lowering the dielectric constant and increasing thermal stability that improves breakdown resistance. Moisture uptake is also reduced. The method is especially useful for interconnect schemes with deep sub-micron ground rules. Surprisingly, the k value obtained from two different plasma treatments is lower than when two He treatments or two H2 treatment are performed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MASNUFACTURING
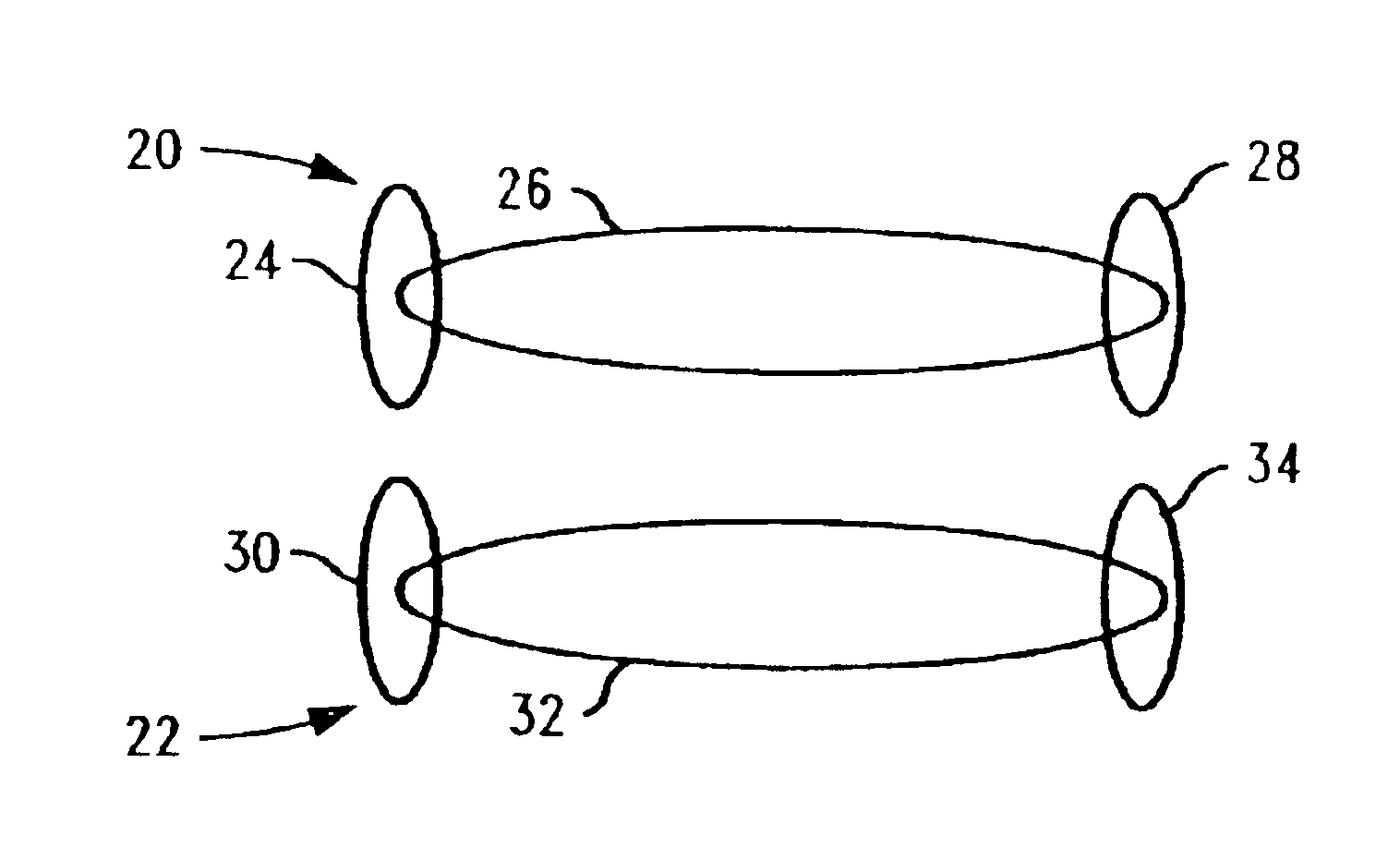
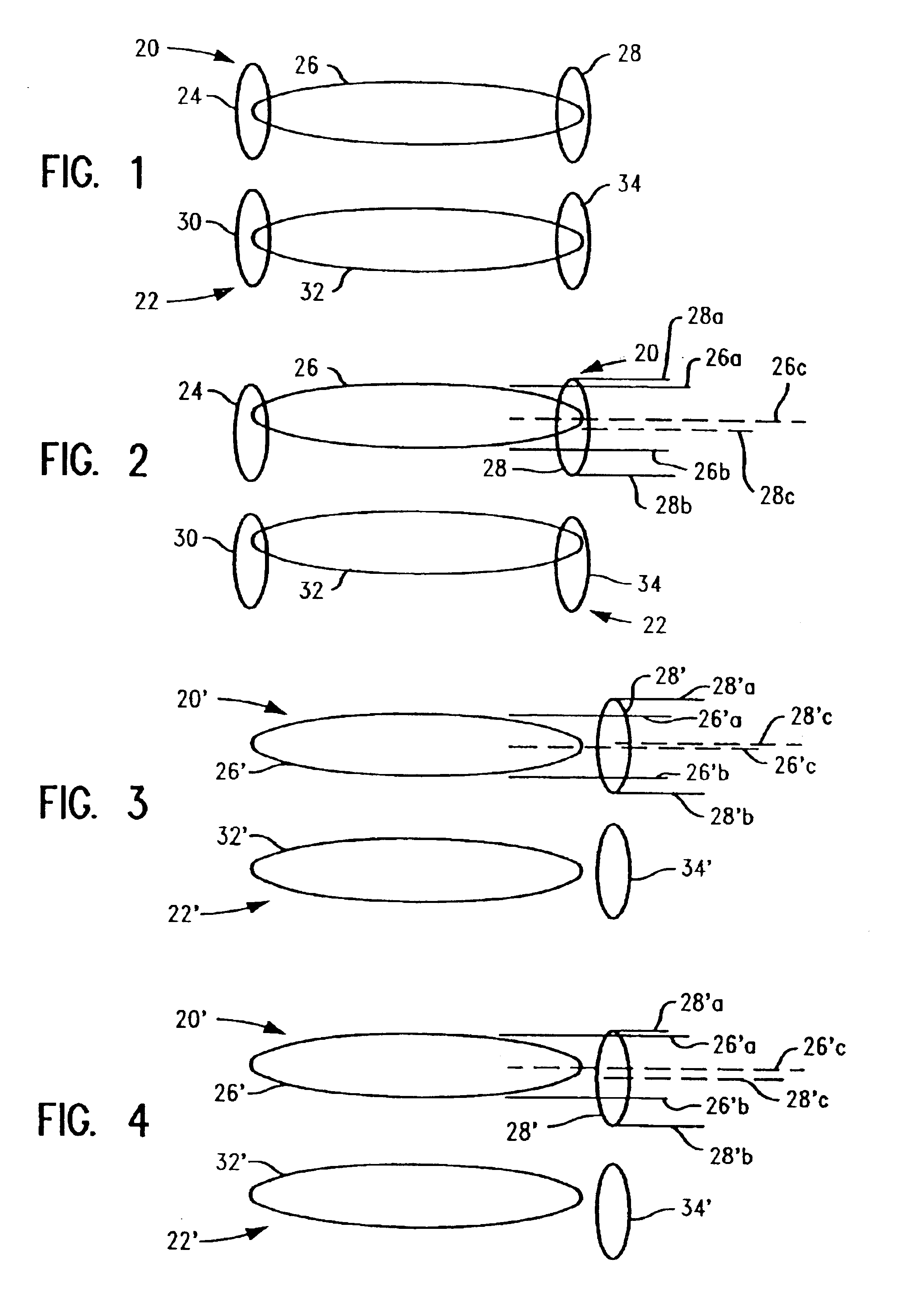
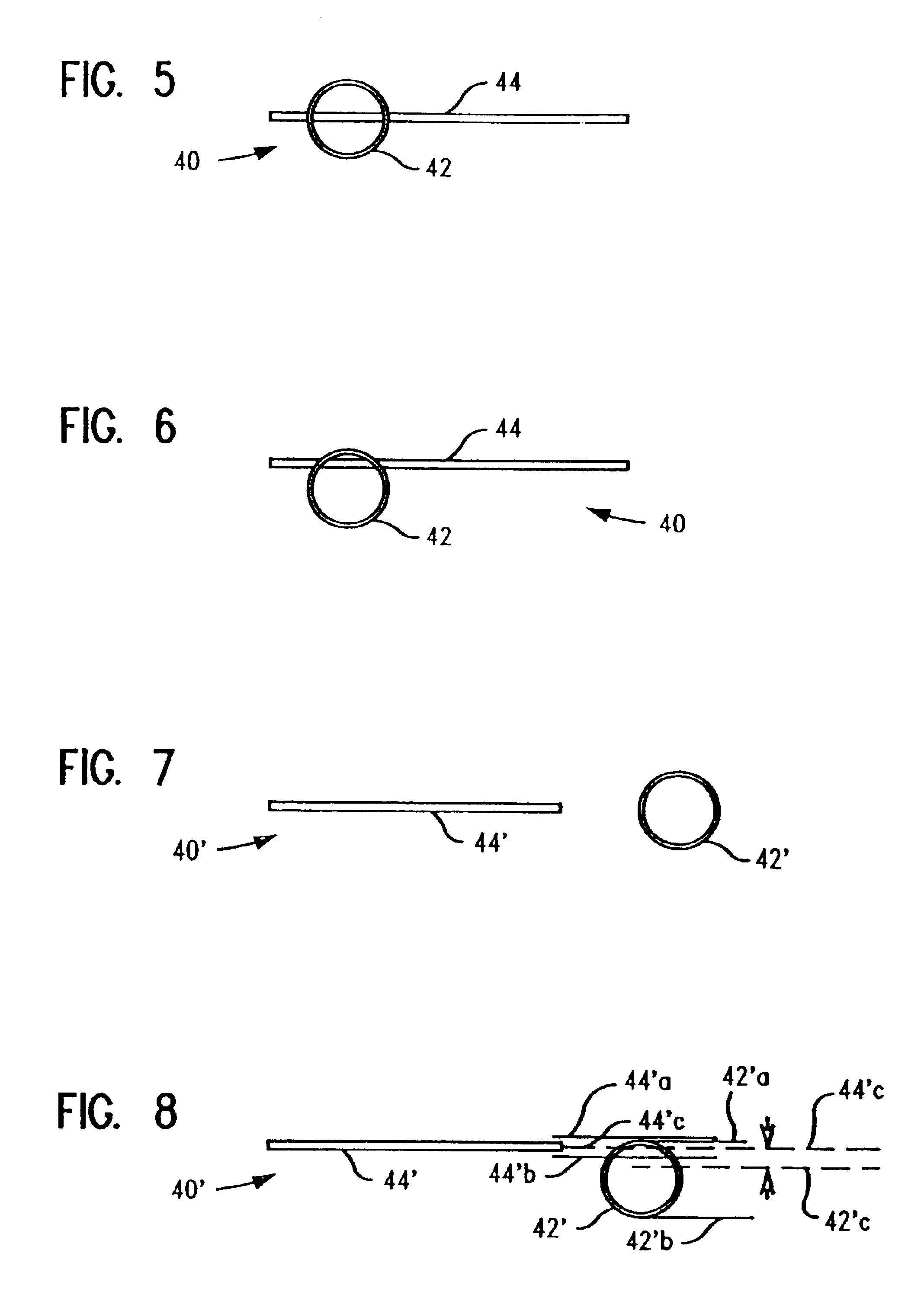
Method for determining semiconductor overlay on groundrule devices
InactiveUS6975398B2Easily identifiableSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsComputer scienceGround rule
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for determining semiconductor overlay on groundrule devices
InactiveUS20030071997A1Reduce the amount requiredEasily identifiableSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsComputer scienceGround rule
A method of determining overlay error comprises creating a first and second layers of an integrated circuit, each having an active circuit feature and an adjacent kerf area. Each kerf area includes a first measurement feature separated from and corresponding substantially to the layer's active circuit feature. The circuit and kerf areas of the layers are substantially superimposed. The distance of separation between the active circuit feature and the layer kerf measurement feature in each layer in the direction of overlay error is the same. The second layer kerf measurement feature is displaced from the first layer kerf measurement feature in a direction perpendicular to the direction that the overlay error is to be determined. Overlay error is determined by measuring distance of separation in the direction of overlay error between the common points of reference of each of the first and second layer kerf measurement features.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
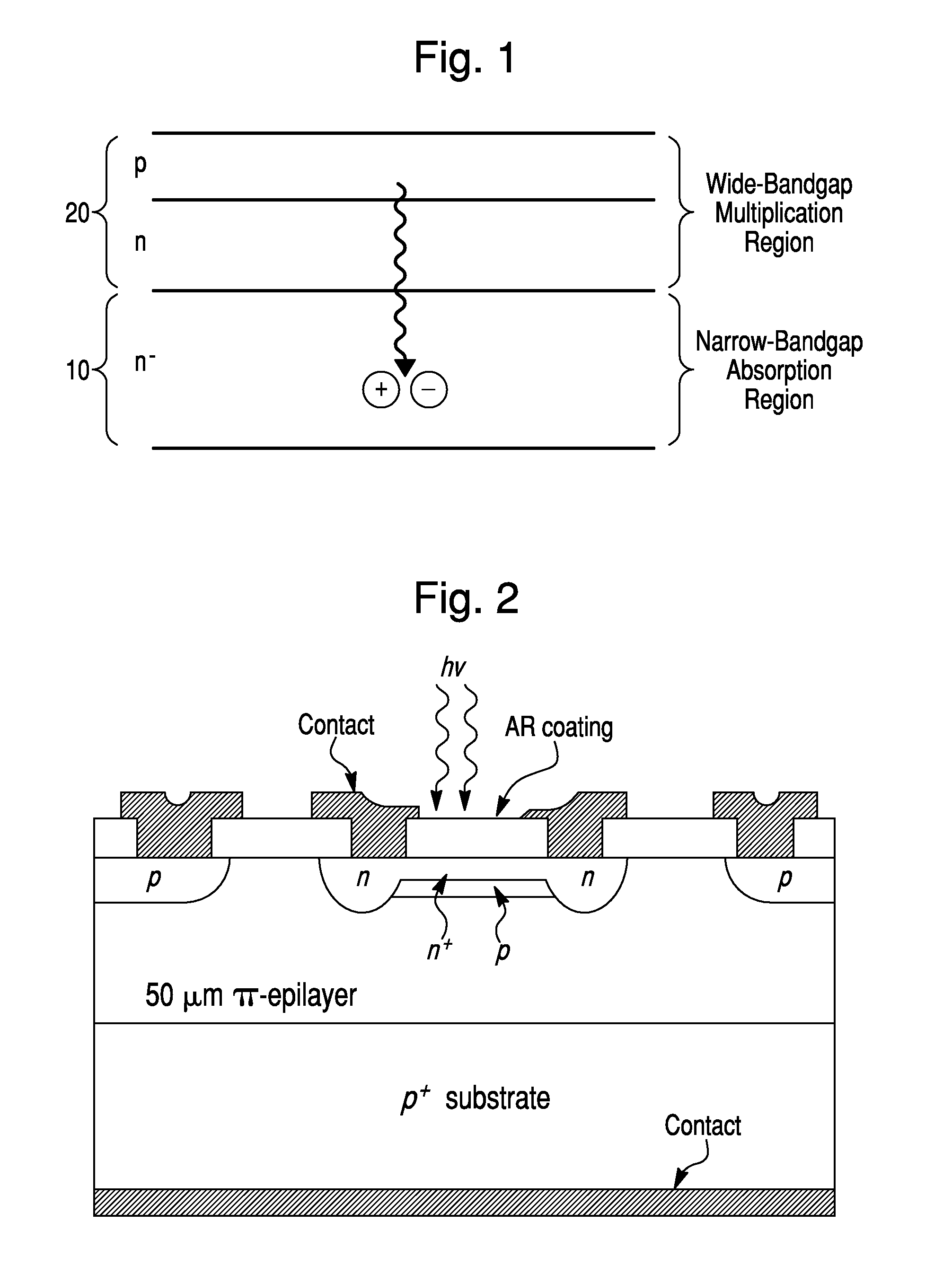
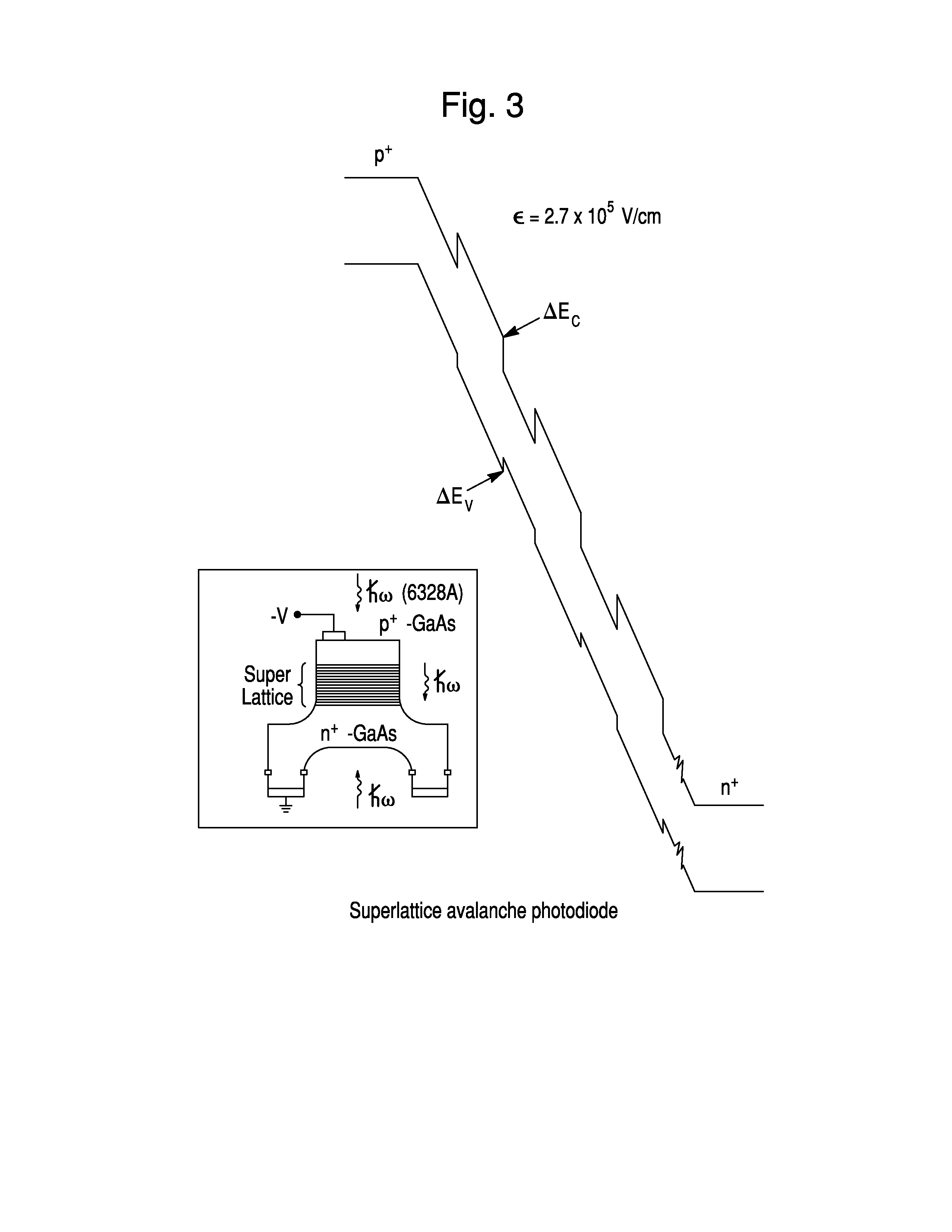
VIS-NIR plasmonic APD detectors
An avalanche photodiode (APD) electro-magnetic radiation (EMR) detector for visible to near infrared wavelengths is described. The detector includes an EMR absorption region, a voltage biasing element, and a charge multiplication region. The EMR absorption region includes a substantially regular array of silver or aluminum nanoparticles embedded in a matrix material. The voltage biasing element is configured to apply a bias voltage to the matrix material such that electrical current is directly generated in the EMR absorption region based on a cooperative plasmon effect in the detector material when electro-magnetic radiation in the visible to near infrared wavelength range is incident upon the detector material, where the dominant mechanism for decay in the cooperative plasmon effect is non-radiative. The charge multiplication region is arranged relative to the EMR absorption region to avalanche multiply the electrical current generated in the EMR absorption region.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
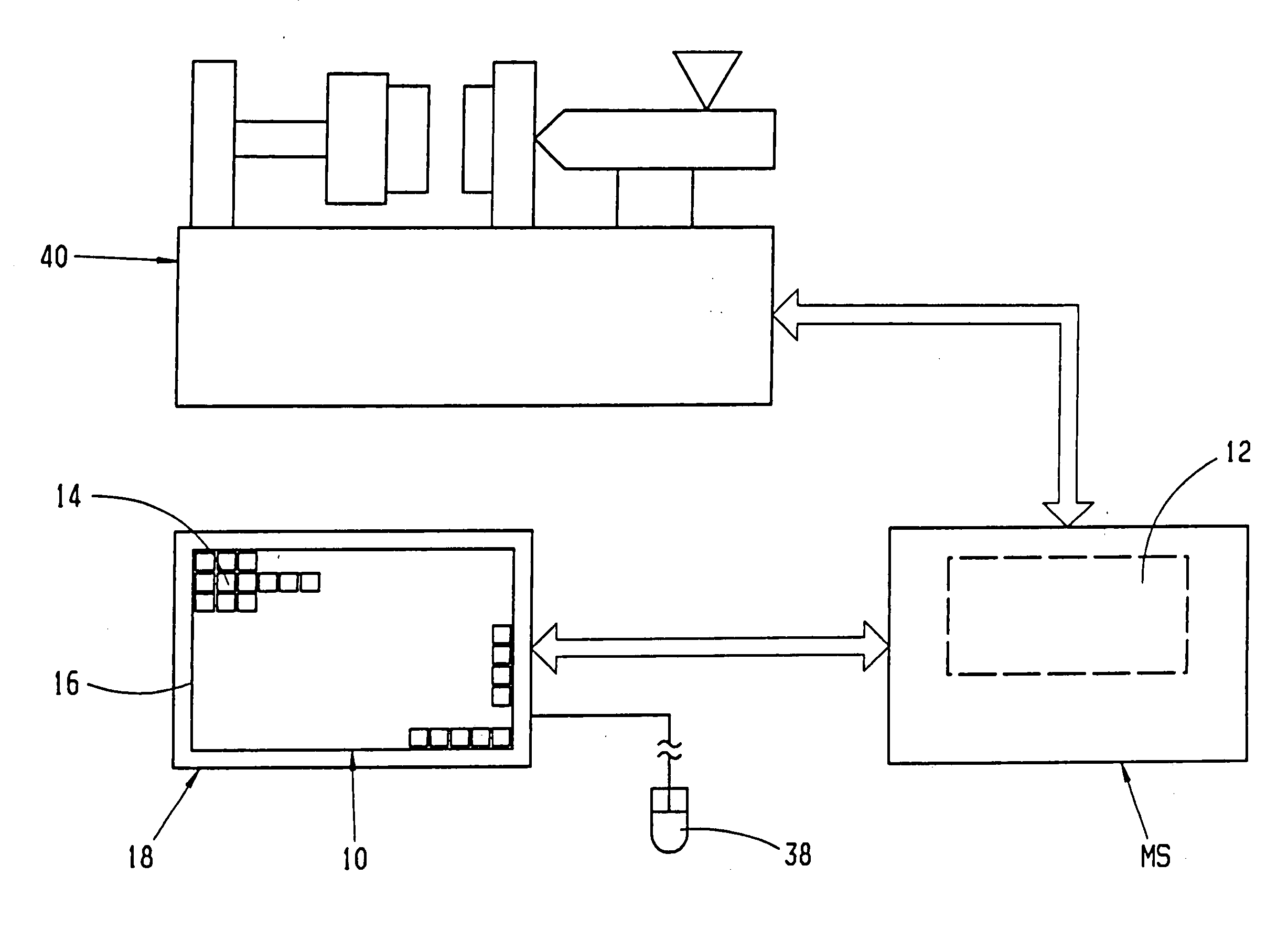
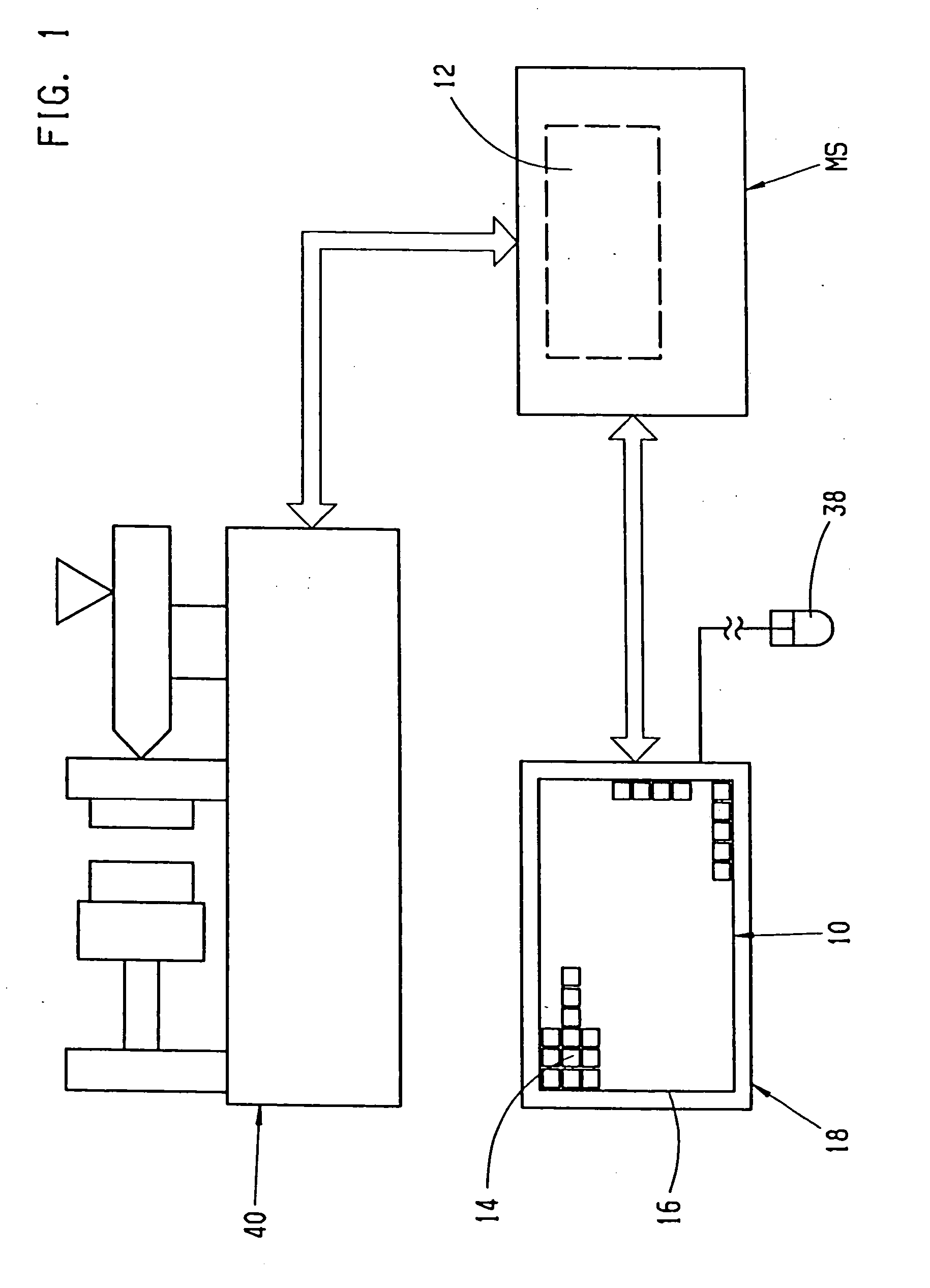
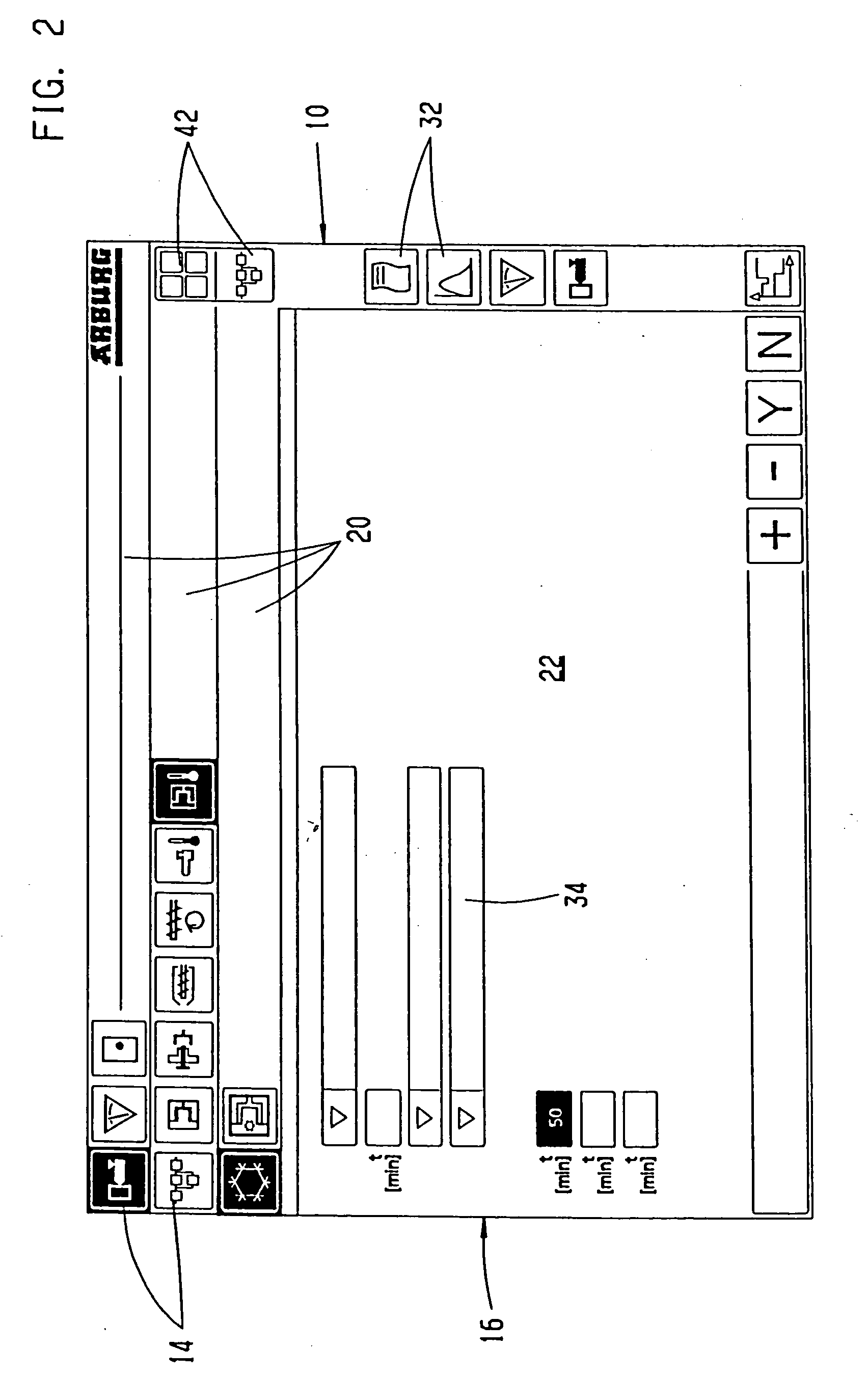
Method and device for interactive control of a machine
The invention relates to a method and a device for interactive control of a machine, whereby the operating parameters necessary for the working process of the machine are inputted into a data processing unit ( 12 ), for storing the operating parameters, using an input unit ( 10 ) with input fields in a form which guides the user. Working processes are thus carried out as a result of the inputs. A data set of the base rules for the working process of the machine is recorded in the data processing unit. A limited selection ( 11 ) of possible input choices is provided for the user by application of the data set based on the machine configuration and machine environment, which further comprise compatible parts for addition to the extant parts of a working process. Operator guidance is facilitated, whereby the user is provided with a limited selection ( 11 ), corresponding to the further parts of the process, on operating fields, by the input unit ( 10 ) on the surface ( 16 ) for manual input and / or for input using a manipulator ( 38 ).
Owner:卡尔‧赫尔
Integrated circuit selective scaling
InactiveUS7363601B2Increase productionHierarchy is preservedCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringGround rule
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and device for interactive control of a machine
ActiveUS20060157880A1Simplify sequenceSimplify creationAuxillary shaping apparatusInput/output processes for data processingData setManipulator
The invention relates to a method and a device for interactive control of a machine, whereby the operating parameters necessary for the working process of the machine are inputted into a data processing unit (12), for storing the operating parameters, using an input unit (10) with input fields in a form which guides the user. Working processes are thus carried out as a result of the inputs. A data set of the base rules for the working process of the machine is recorded in the data processing unit. A limited selection (11) of possible input choices is provided for the user by application of the data set based on the machine configuration and machine environment, which further comprise compatible parts for addition to the extant parts of a working process. Operator guidance is facilitated, whereby the user is provided with a limited selection (11), corresponding to the further parts of the process, on operating fields, by the input unit (10) on the surface (16) for manual input and / or for input using a manipulator (38).
Owner:HEHL KARL
VLSI artwork legalization for hierarchical designs with multiple grid constraints
ActiveUS7437691B2Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsLayout Versus Schematic
A system and method are disclosed for legalizing a flat or hierarchical VLSI layout to meet multiple grid constraints and conventional ground rules. Given a set of ground rules with multiple grid constraints and a VLSI layout (either hierarchical or flat) which is layout-versus-schematic (LVS) correct but may not be ground rule correct, the system and method provide a legalized layout which meets the multiple grid constraints while maintaining LVS correctness and fixing the ground rule errors as much as possible with minimum layout perturbation from the input design. The system and method support multiple grid pitch constraints for hierarchical design, and provide for LVS correctness to be maintained while an on-grid solution possibly with some spacing violations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Technology migration for integrated circuits with radical design restrictions
InactiveUS7257783B2CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
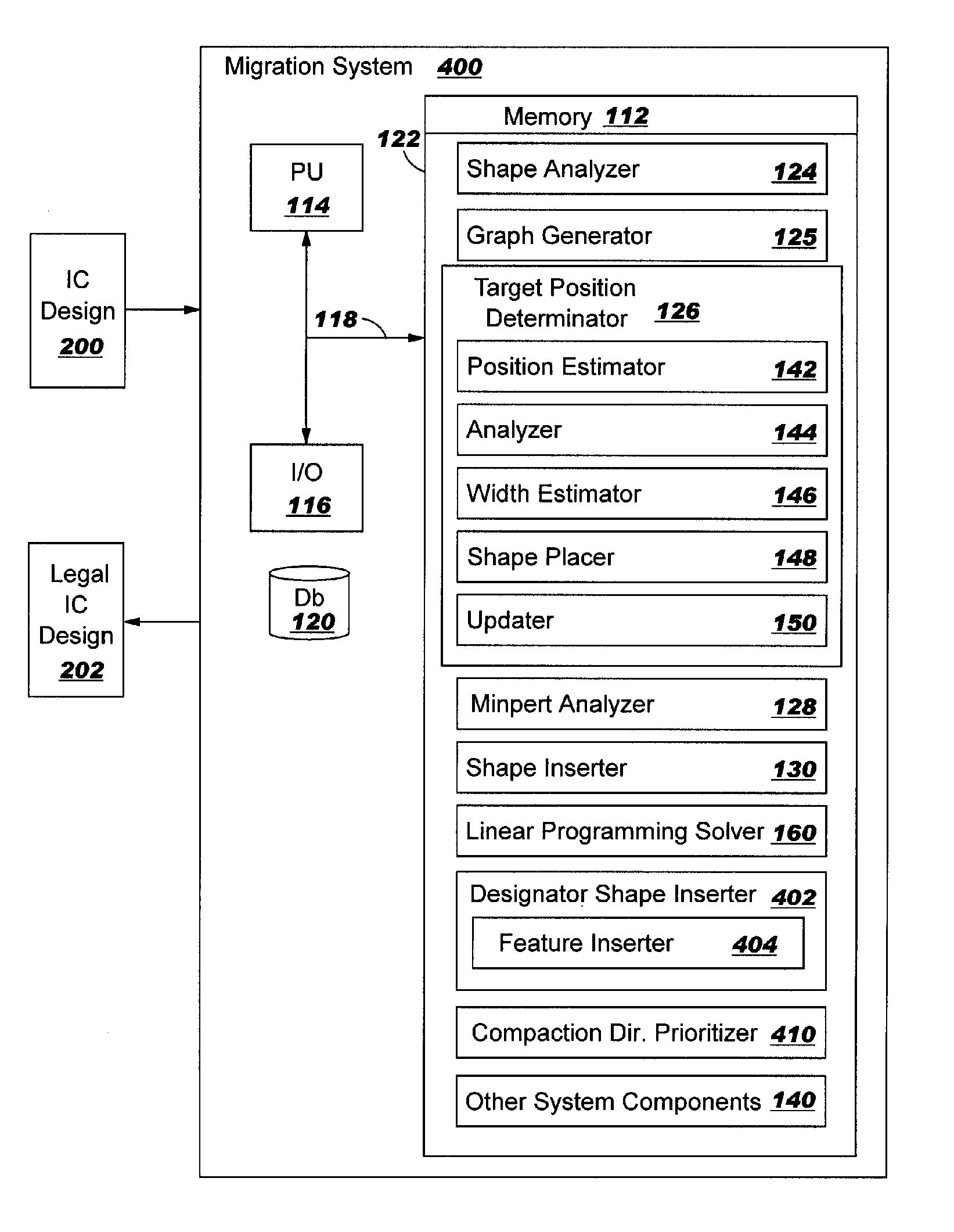
A method, system and program product for migrating an integrated circuit (IC) design from a source technology without radical design restrictions (RDR) to a target technology with RDR, are disclosed. Also, a method, system and program product for migrating an integrated circuit design from a source technology without RDR to a target technology with RDR in which space may be reserved for late insertion of a feature and in which migration first occurs in a primary compaction direction having less tolerant ground rules.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method, apparatus and computer program product for optimizing an integrated circuit layout
InactiveUS7454721B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureIntegrated circuit layout
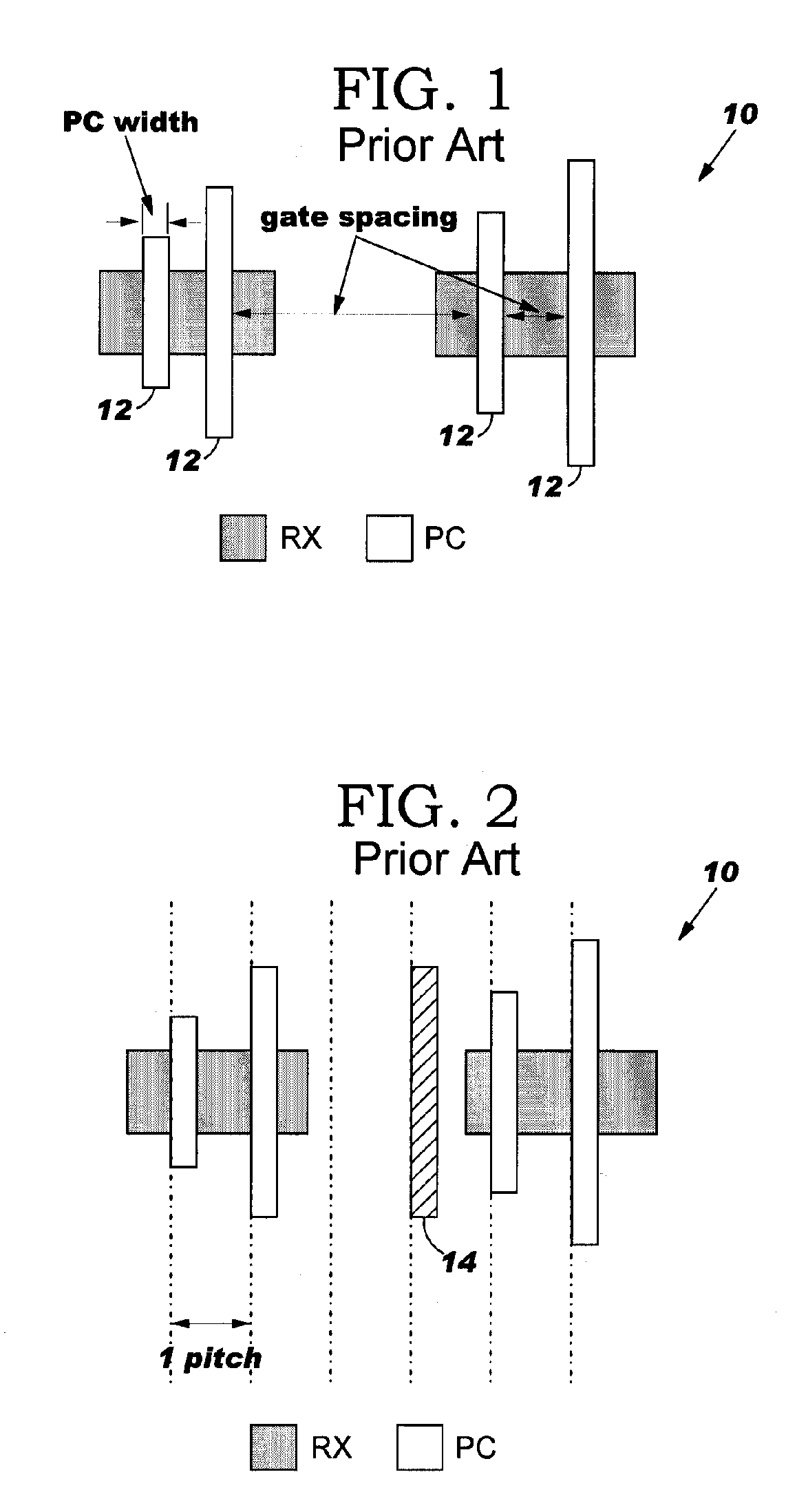
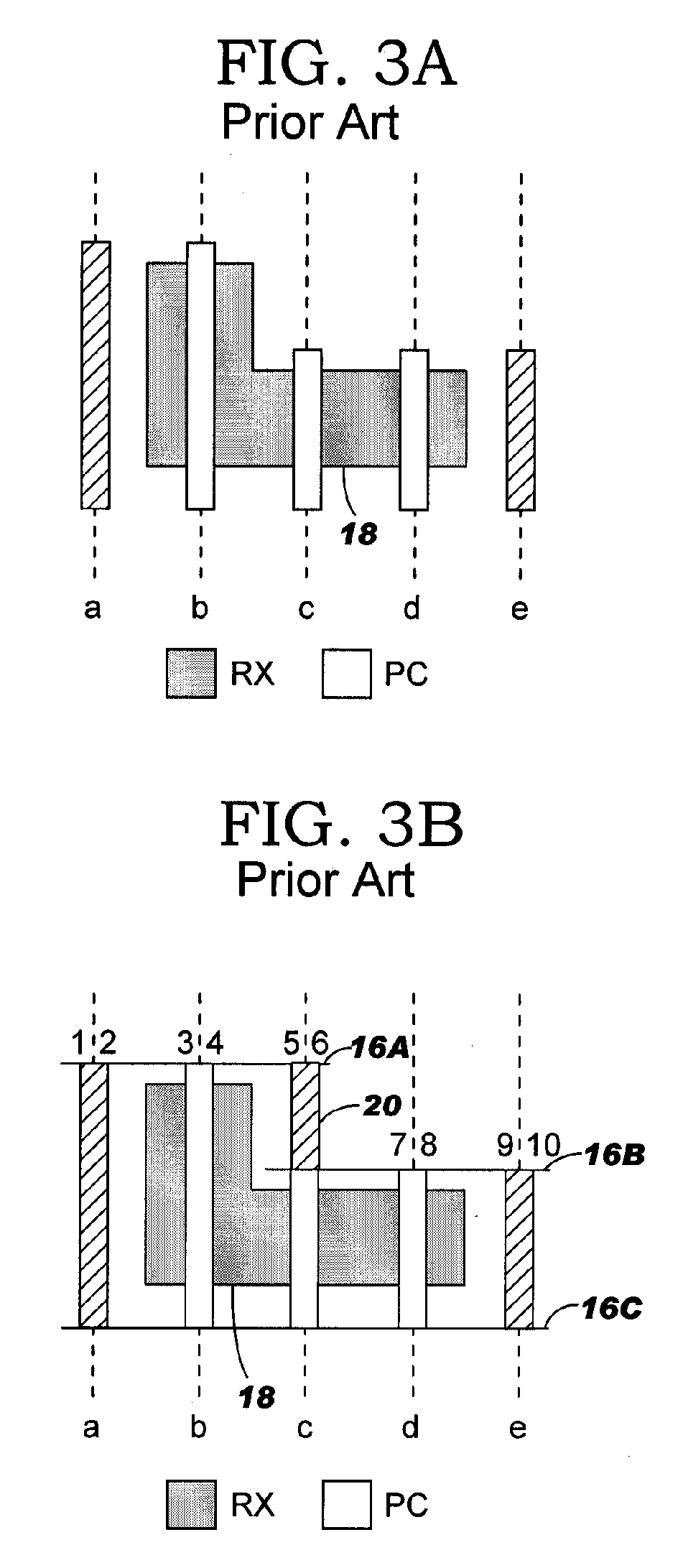
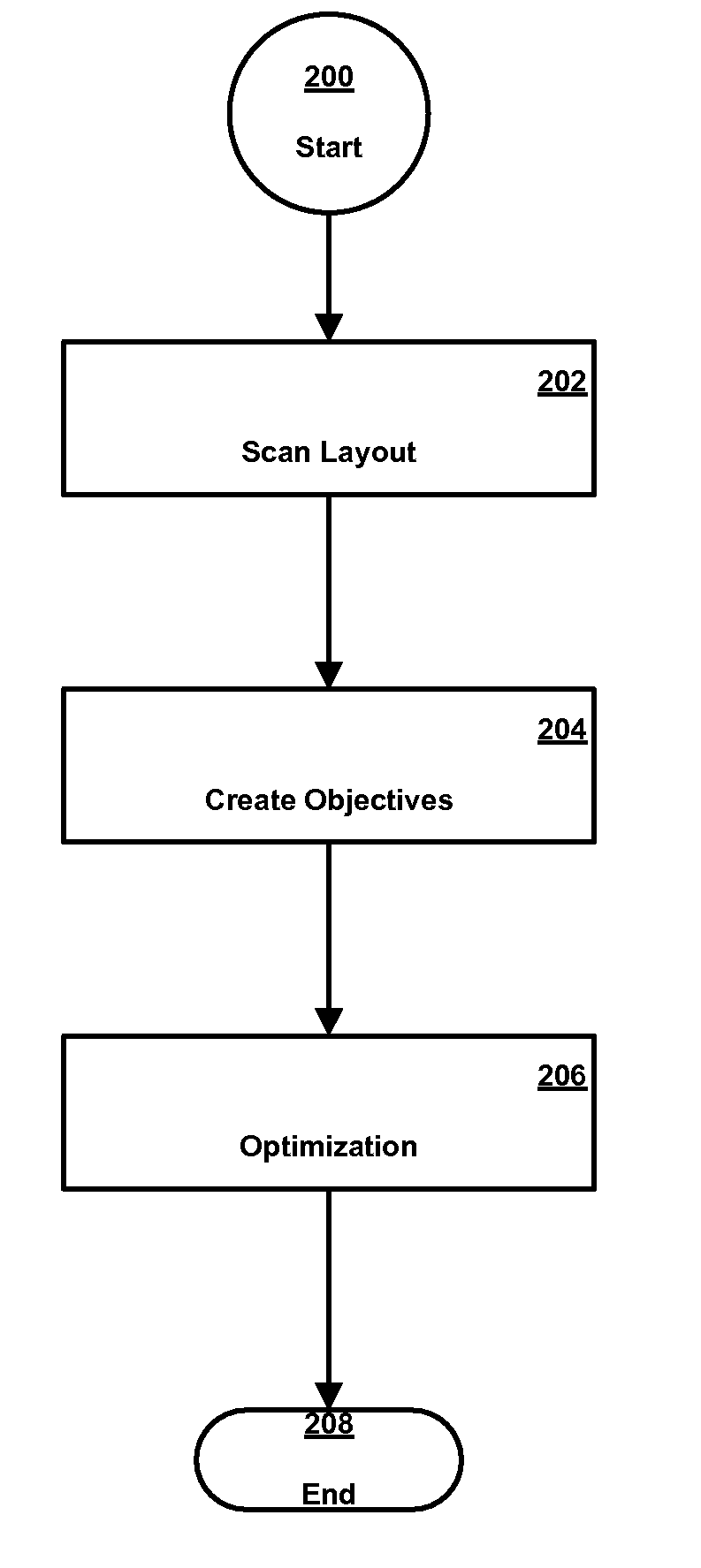
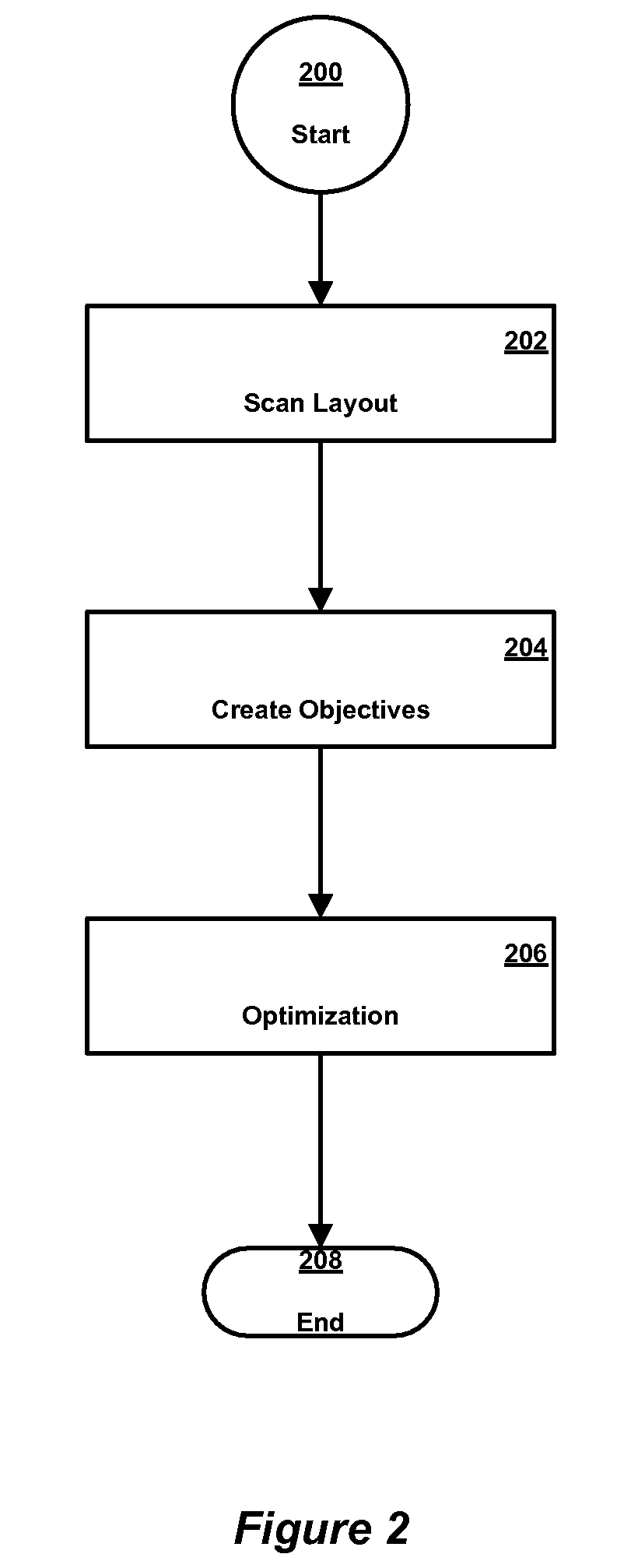
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for optimizing the layout of an integrated circuit design. Base ground rules and recommended ground rules are prioritized according to the impact they have on the yield of the integrated circuit design. The layout is optimized according to the prioritized base ground rules and recommended ground rules.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for improving yield of a layout and recording medium having the layout
InactiveUS7818697B2Increase productionPhotomechanical apparatusCAD circuit designData miningGround rule
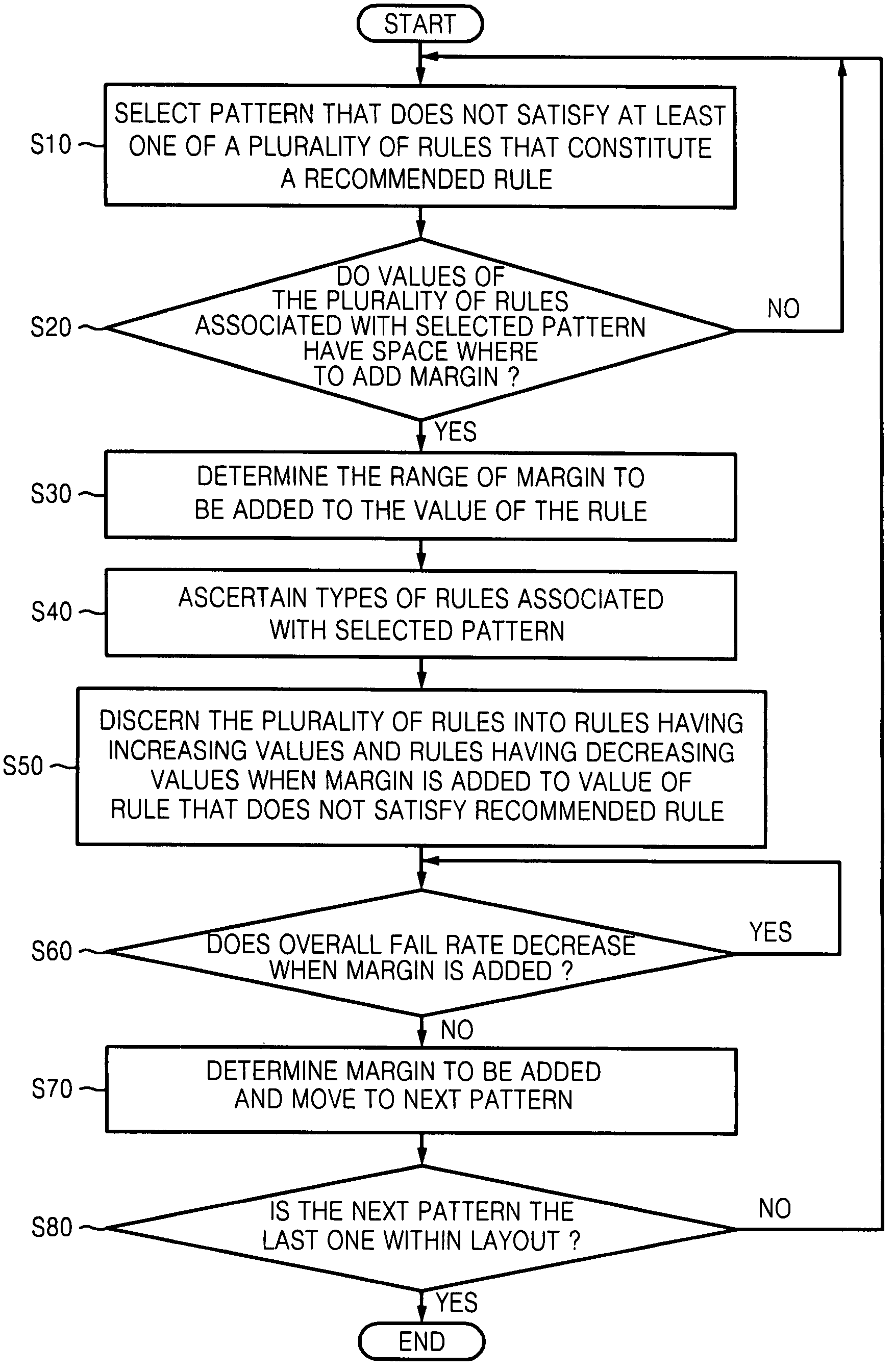
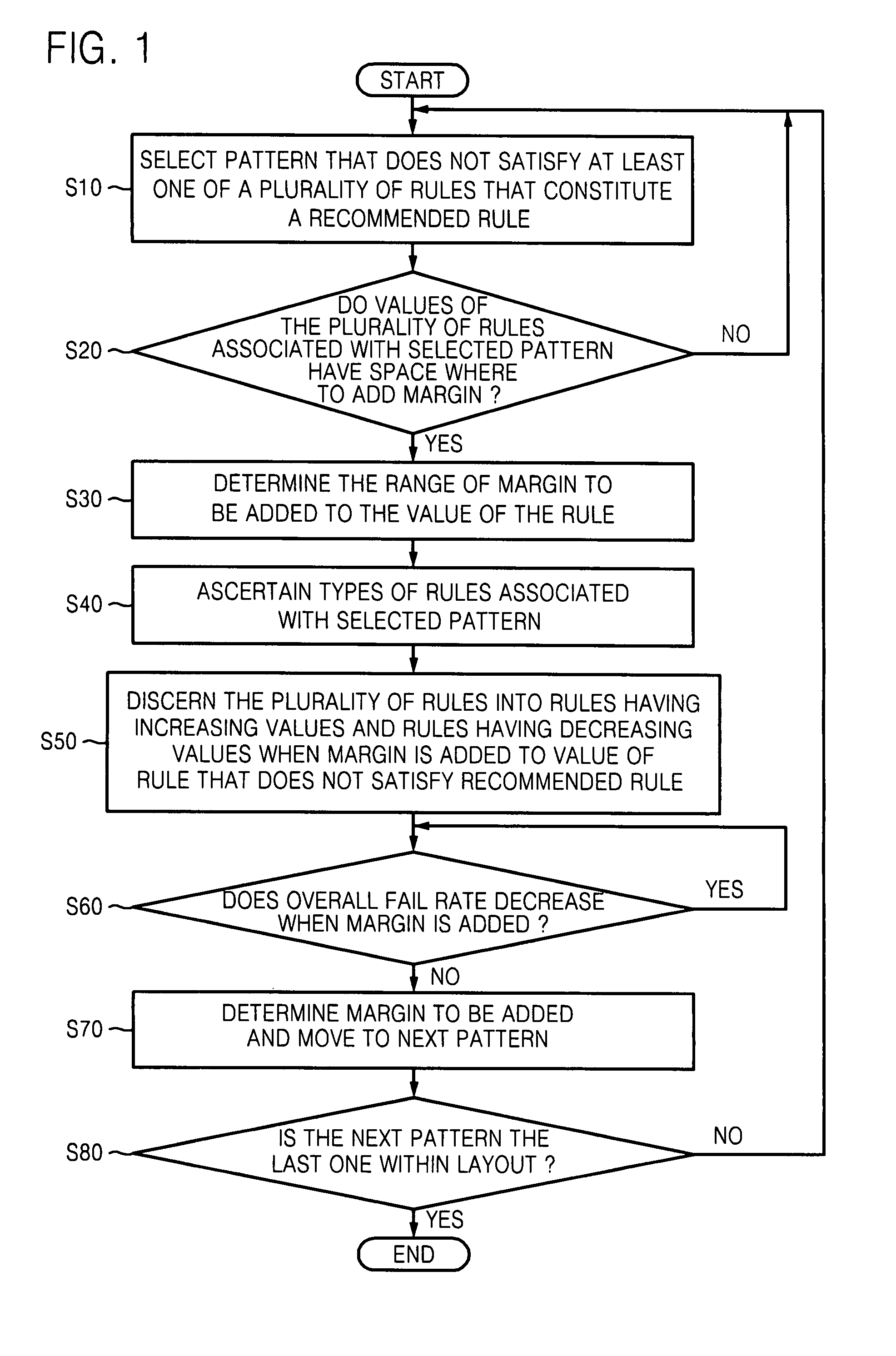
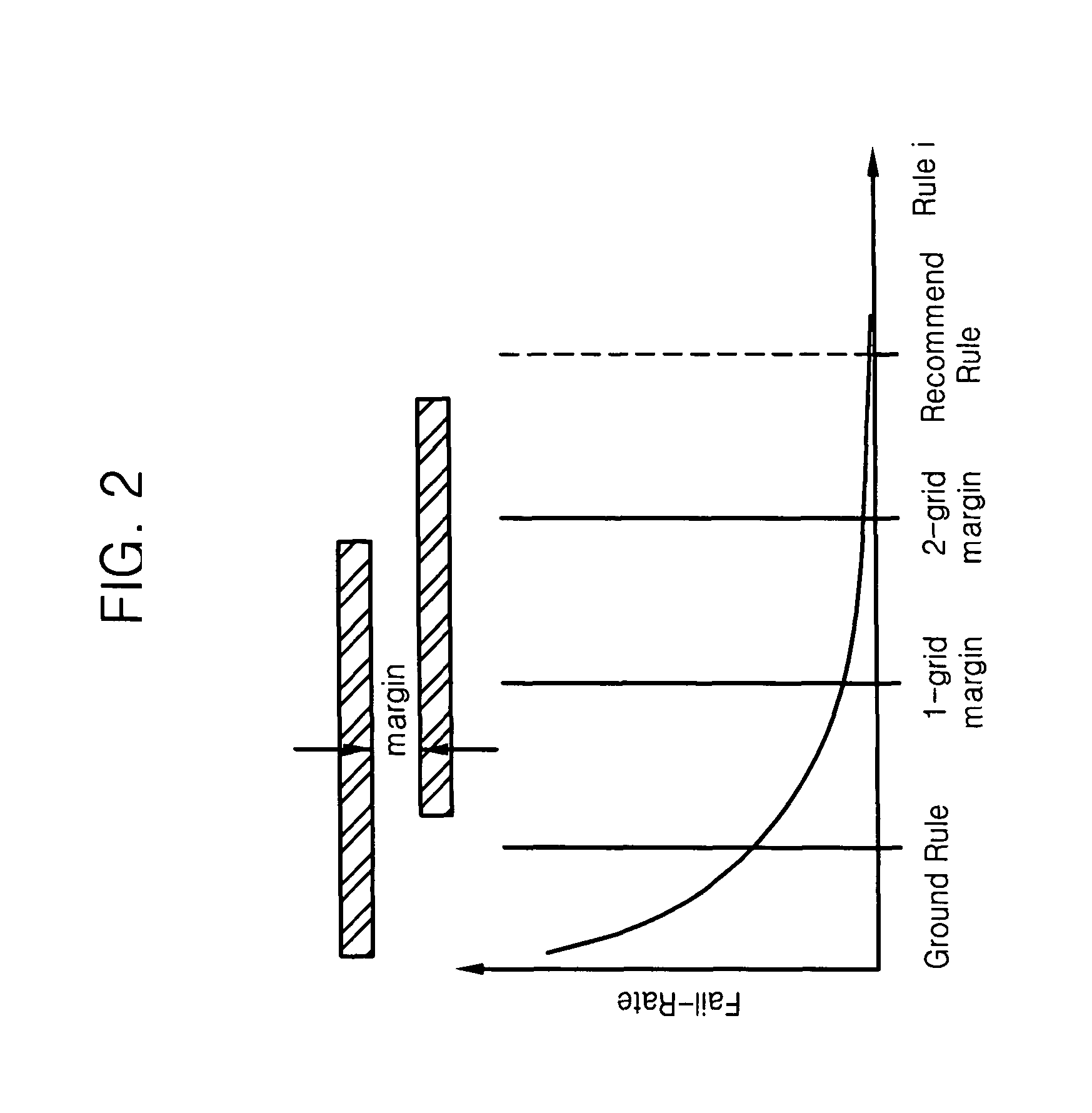
A yield of a semiconductor layout may be improved by selecting a pattern that does not satisfy at least one of multiple rules within the layout, adding a margin to a predetermined value of the at least one of the rules associated with selected pattern, based on a ground rule and a recommended rule of each of the rules, calculating an overall fail rate of at least one of the rules that varies according to the addition of the margin, and determining an adjusted margin to be added based on the calculated overall fail rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
The use of a layout-optimization tool to increase the yield and reliability of VLSI designs
InactiveUS20050050500A1Easy to placeIncrease the number ofComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designGround ruleIntegrated circuit design
The invention provides a method and structure for optimizing placement of redundant vias within an integrated circuit design. The invention first locates target vias by determining which vias do not have a redundant via. Then, the invention draws marker shapes on or adjacent to the target vias. The marker shapes are only drawn in a horizontal or vertical direction from each of the target vias. Next, the invention simultaneously expands all of the marker shapes in the first direction to a predetermined length or until the marker shapes reach the limits of a ground rule. During the expanding, different marker shapes will be expanded to different lengths. The invention determines which of the marker shapes were expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via to produce a first set of potential redundant vias and the invention eliminates marker shapes that could not be expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via. The invention repeats the foregoing processing in the direction perpendicular to the first. The invention can also be used to eliminate certain undesirable structures such as stacked vias or can be used to fix other problems such as insufficient via-to-via spacing. The invention then adds the redundant vias to the integrated circuit design, according to output produced by the optimizer.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY INC
Pitcher-shaped active area for field effect transistor and method of forming same
InactiveUS6960514B2Increase in transistor on-currentDecrease in serial resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesLithographic artistEngineering
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
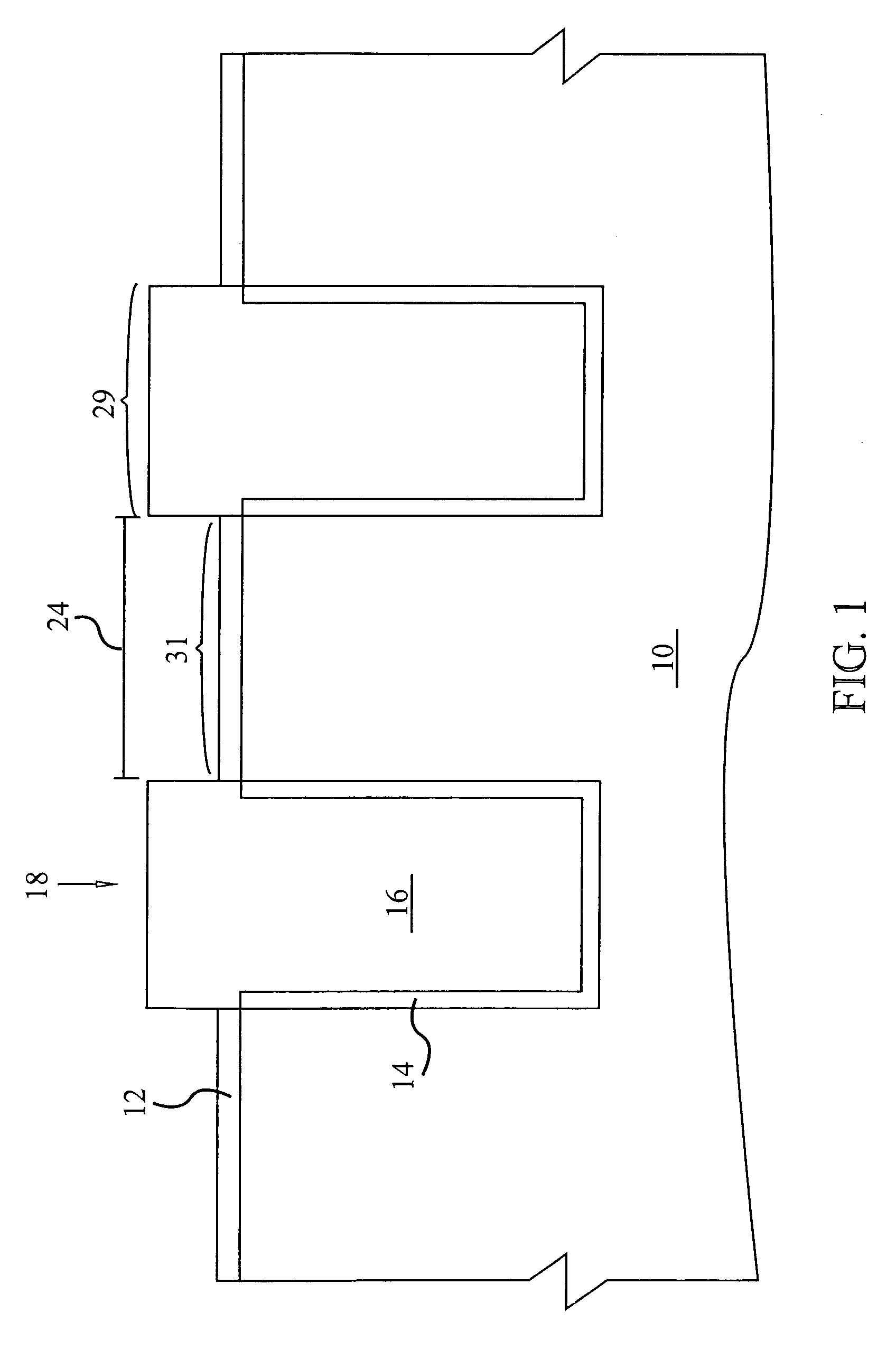
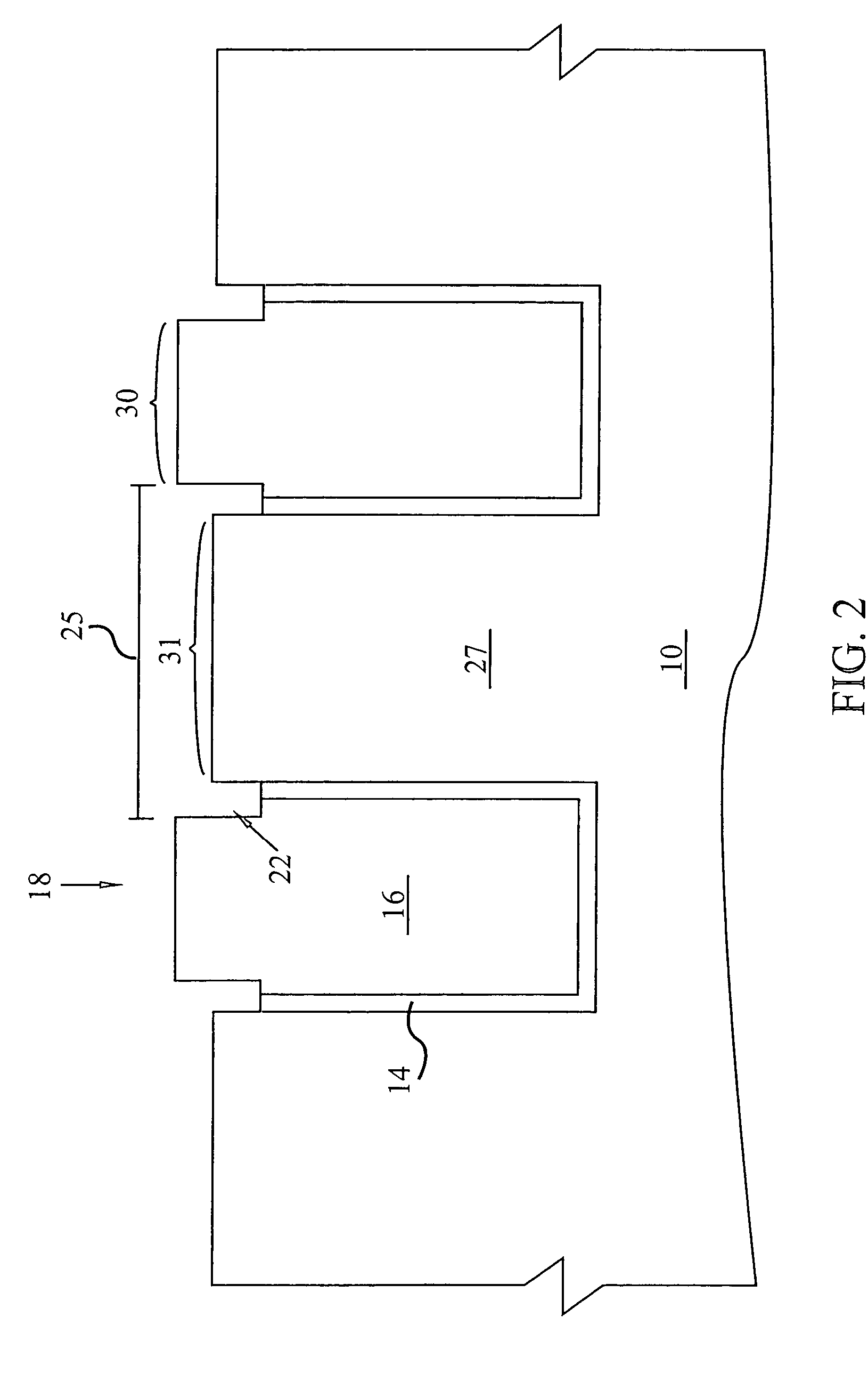
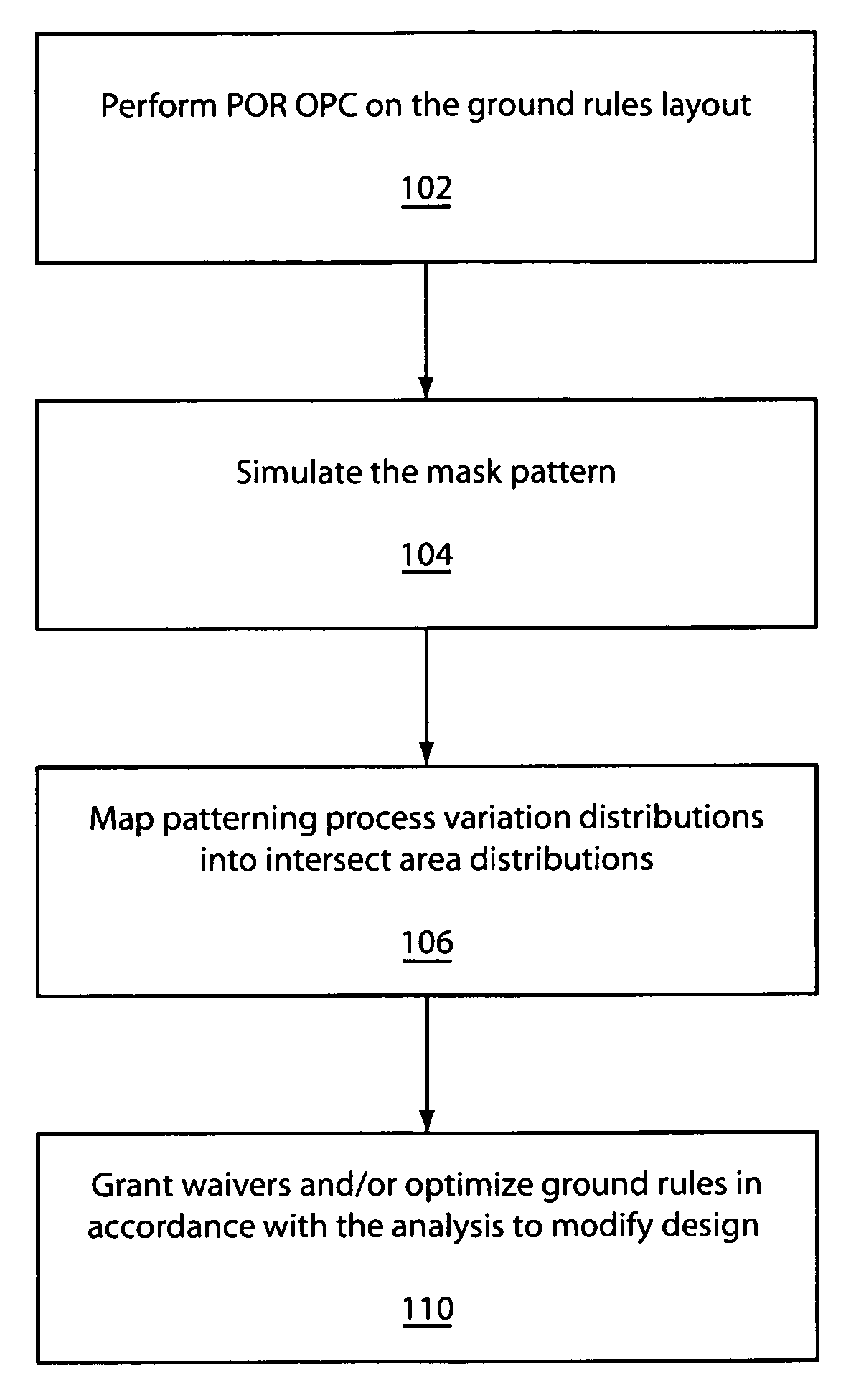
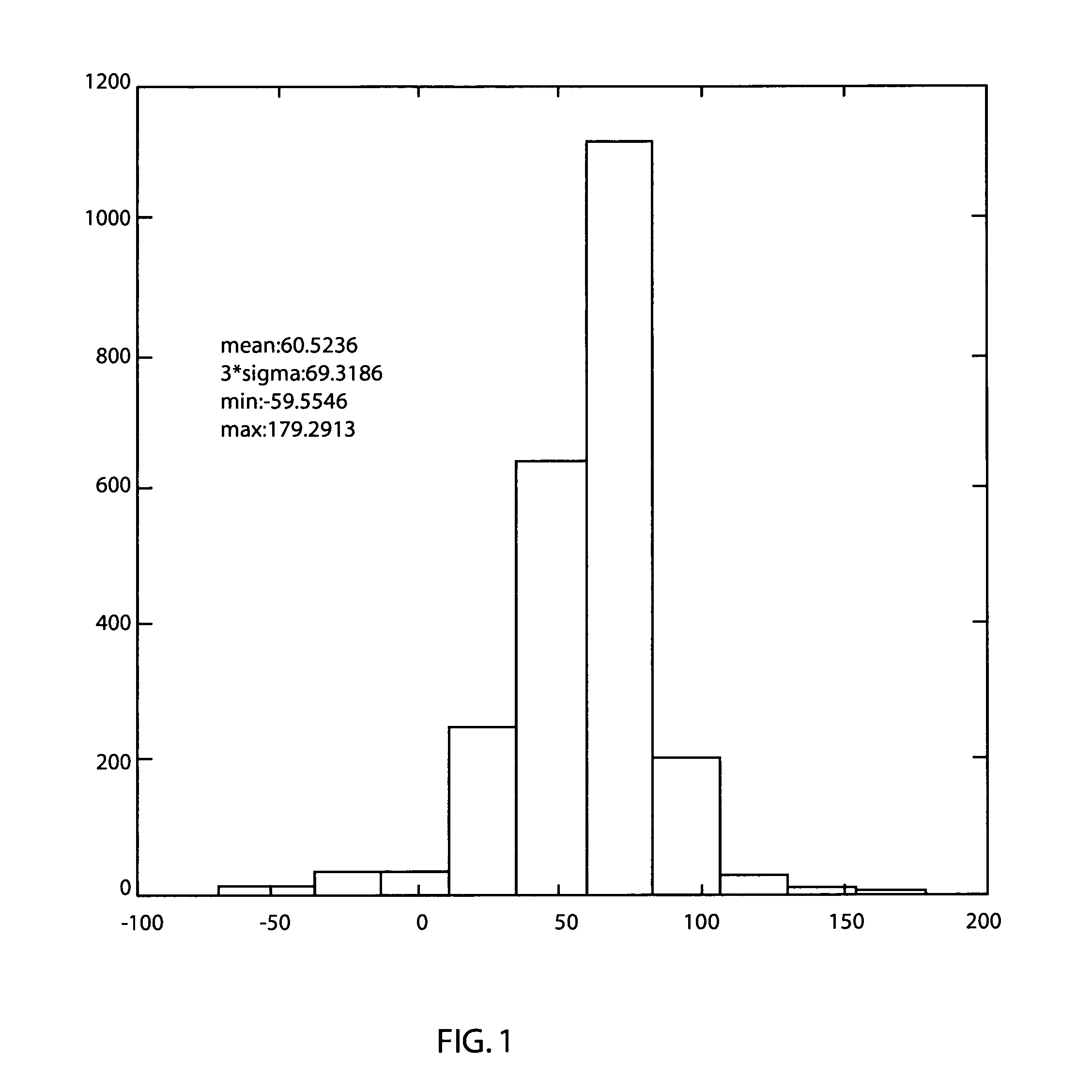
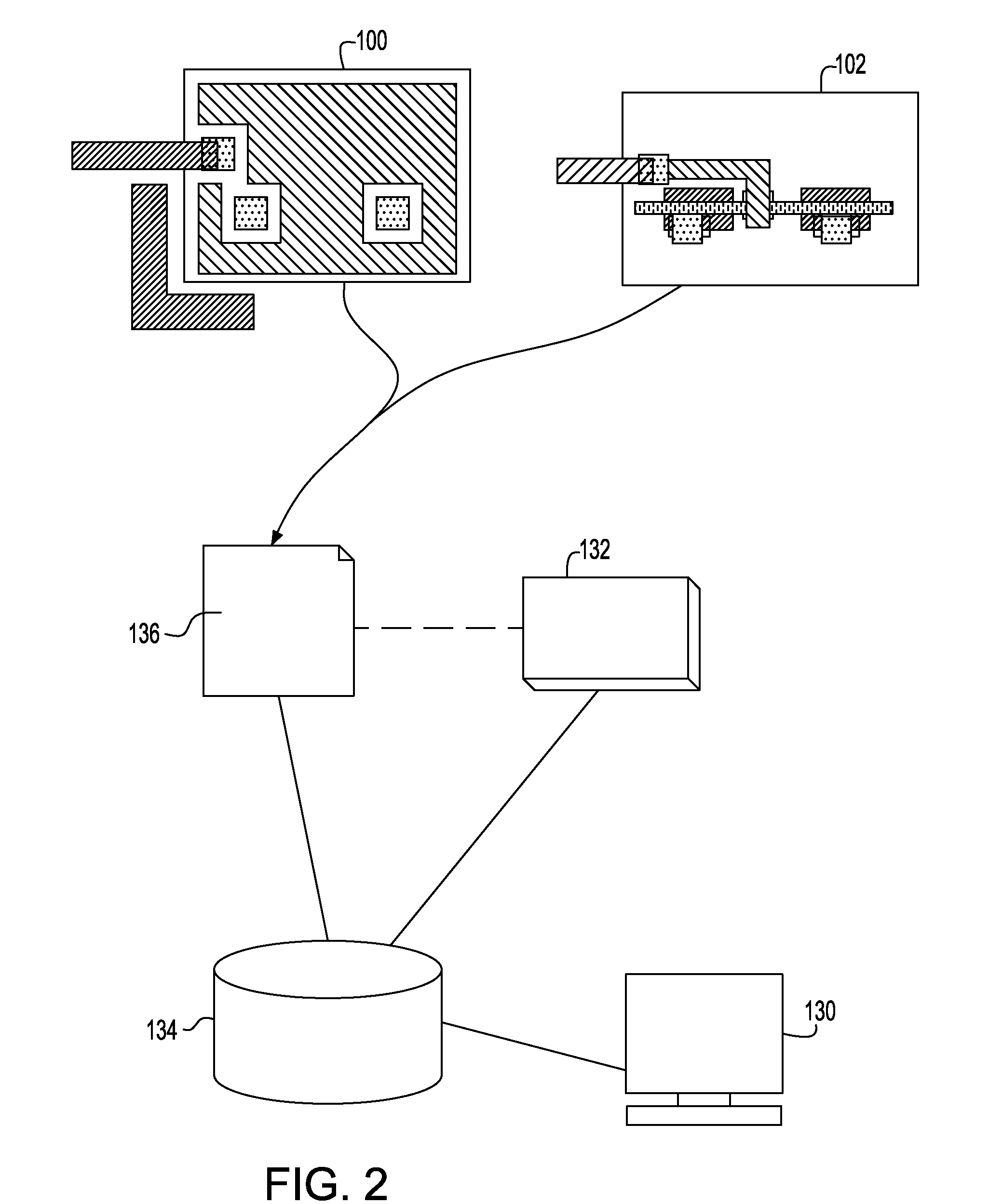
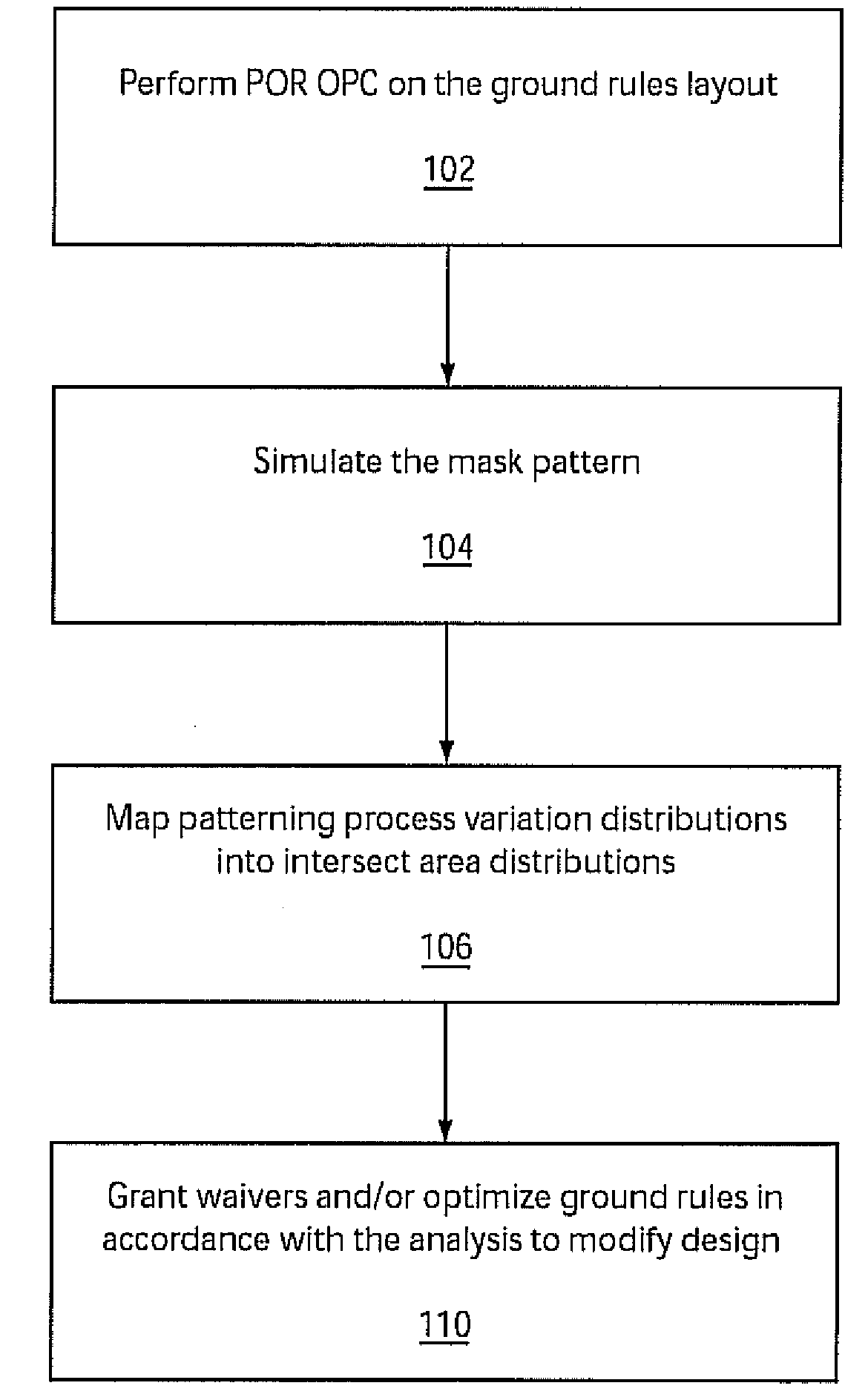
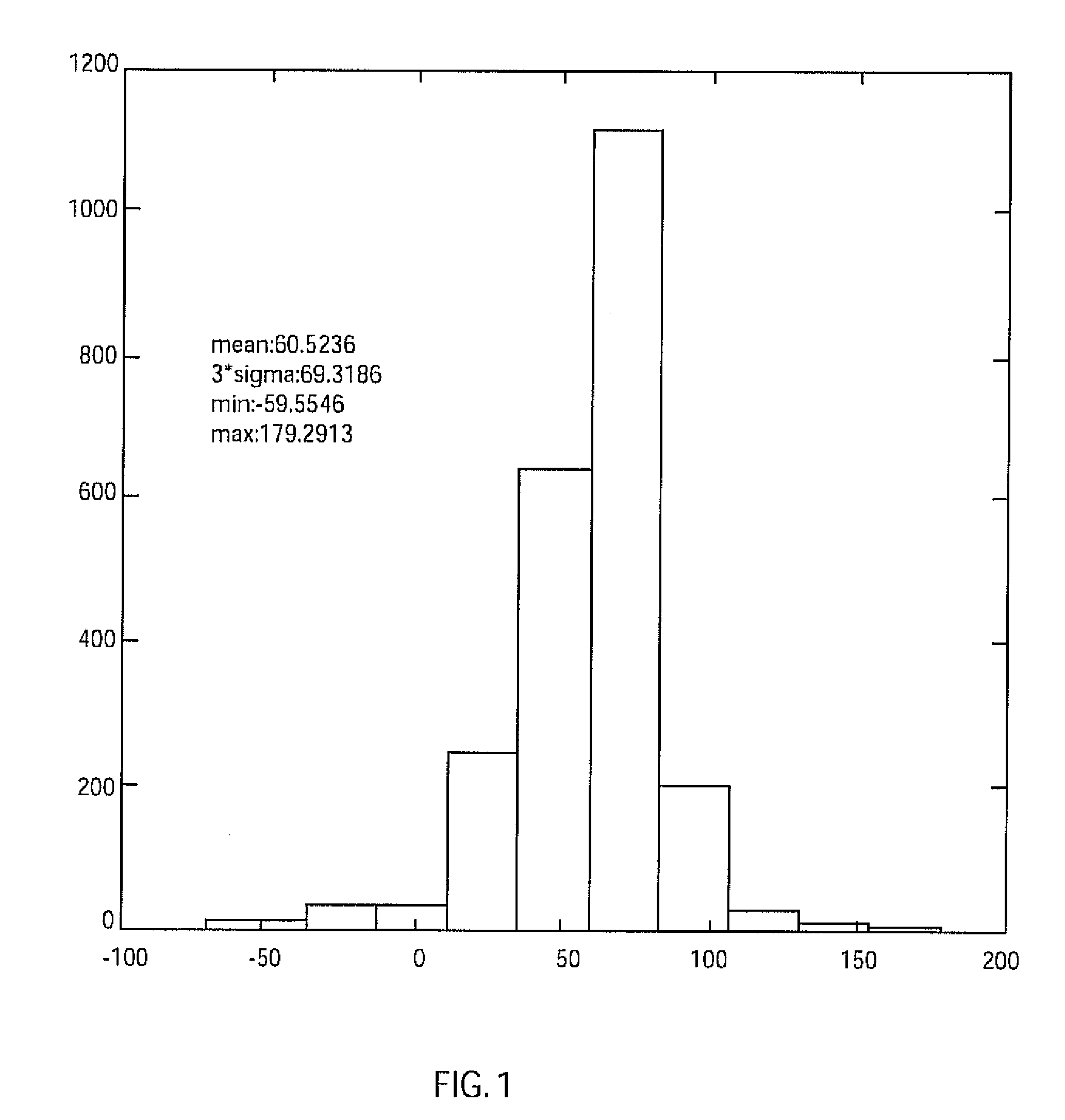
System and method for employing patterning process statistics for ground rules waivers and optimization
InactiveUS20080066047A1Improve complianceNatural language data processingCAD circuit designAlgorithmGround rule
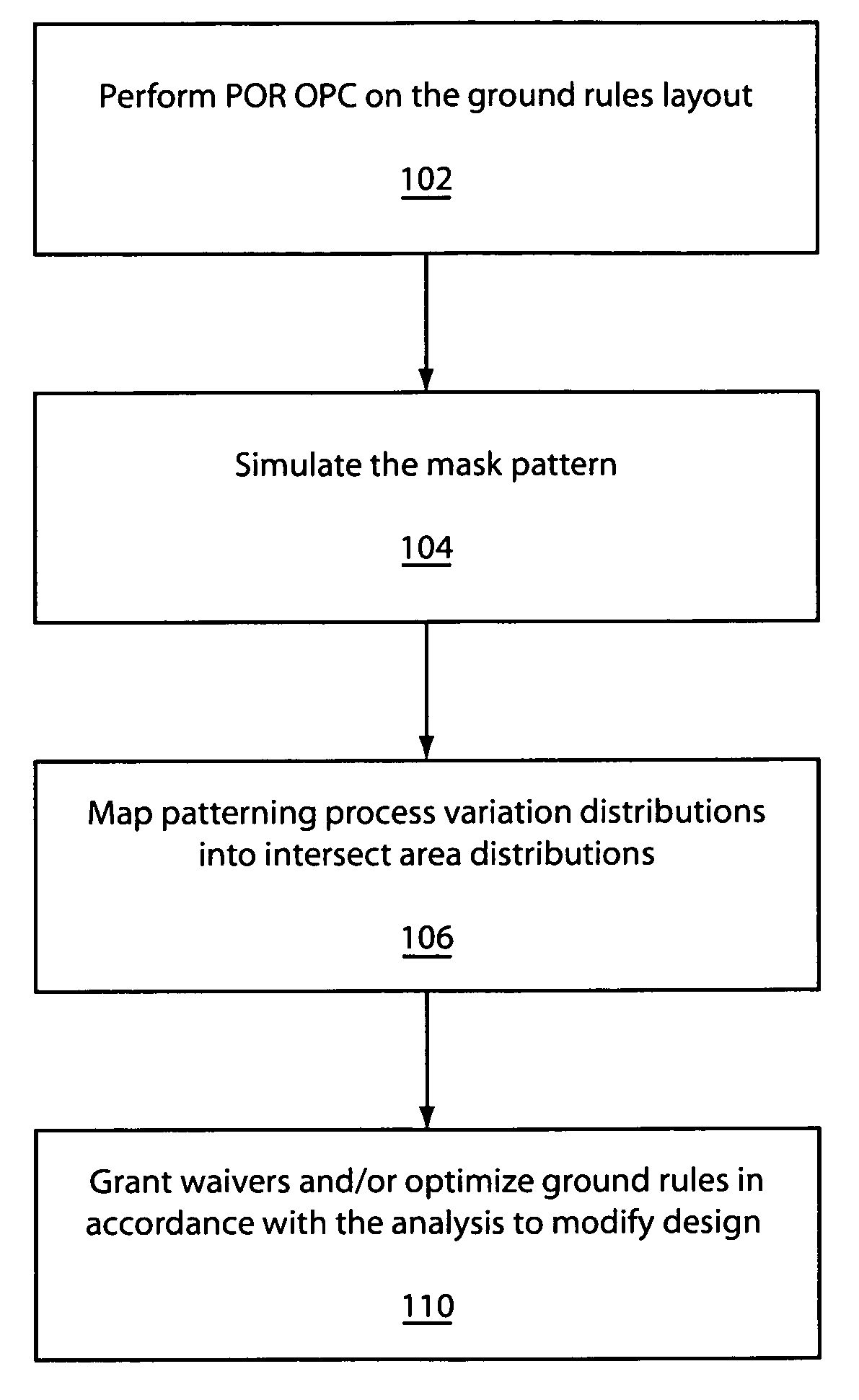
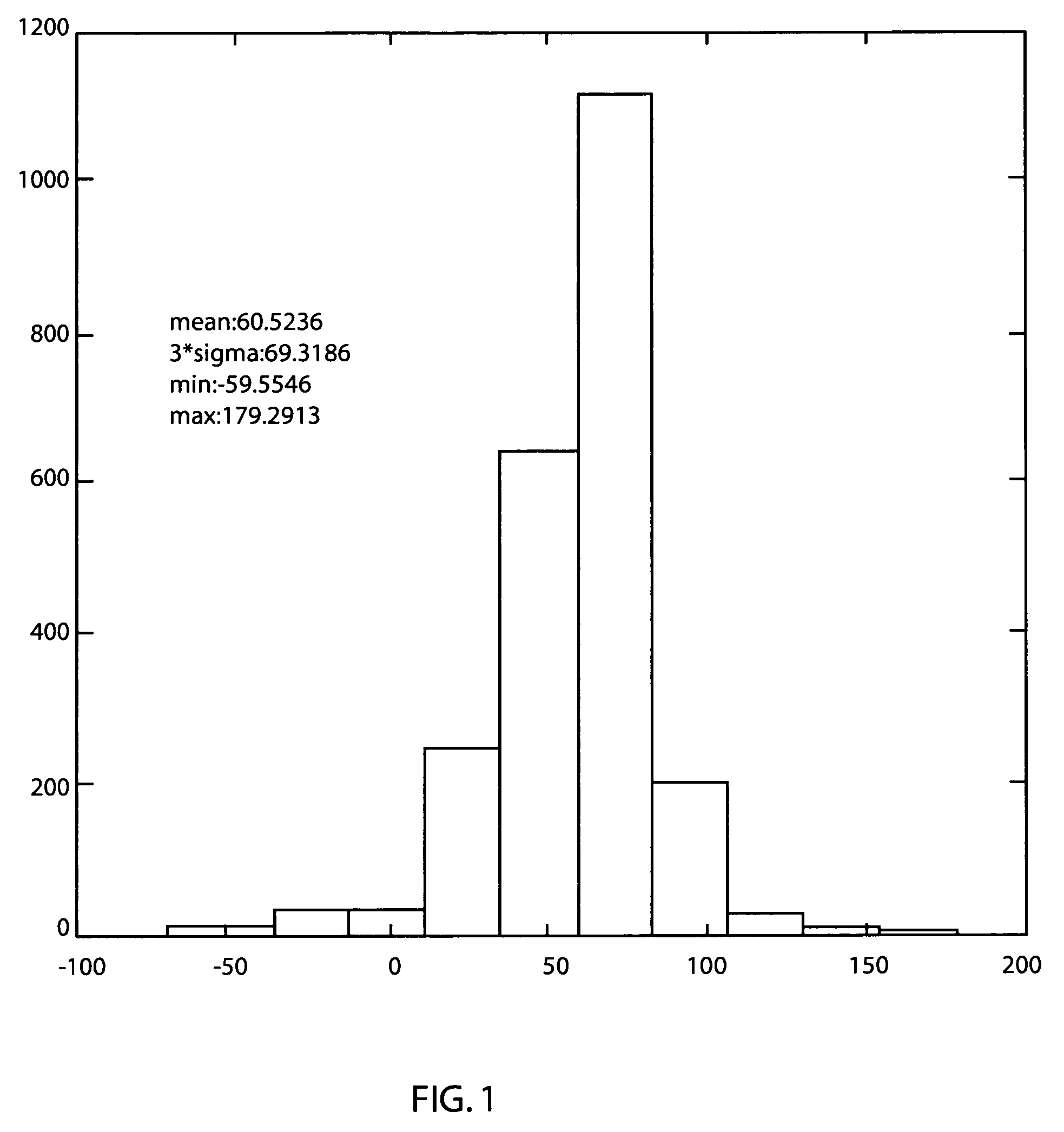
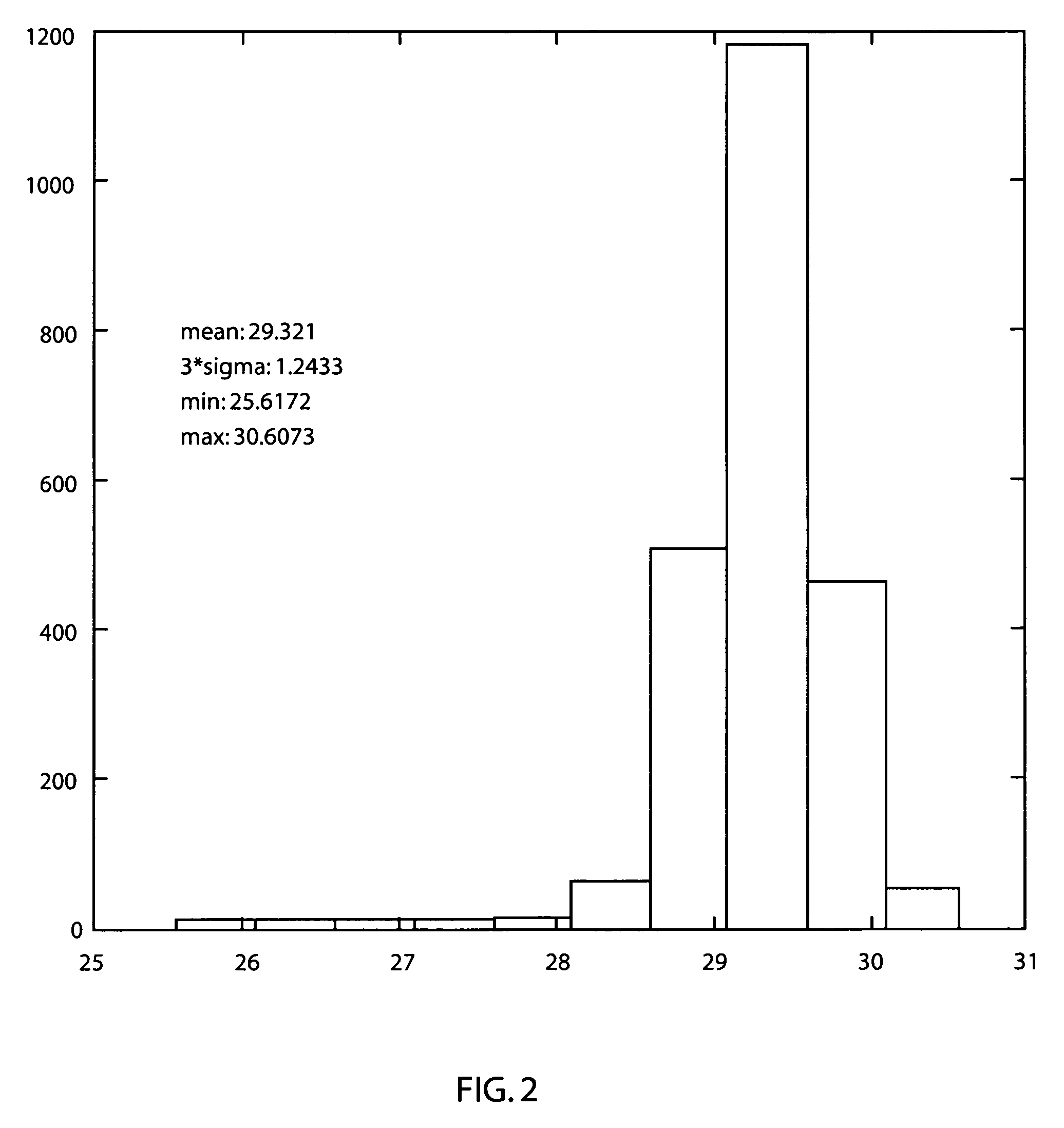
A system and method of employing patterning process statistics to evaluate layouts for intersect area analysis includes applying Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) to the layout, simulating images formed by the mask and applying patterning process variation distributions to influence and determine corrective actions taken to improve and optimize the rules for compliance by the layout. The process variation distributions are mapped to an intersect area distribution by creating a histogram based upon a plurality of processes for an intersect area. The intersect area is analyzed using the histogram to provide ground rule waivers and optimization.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
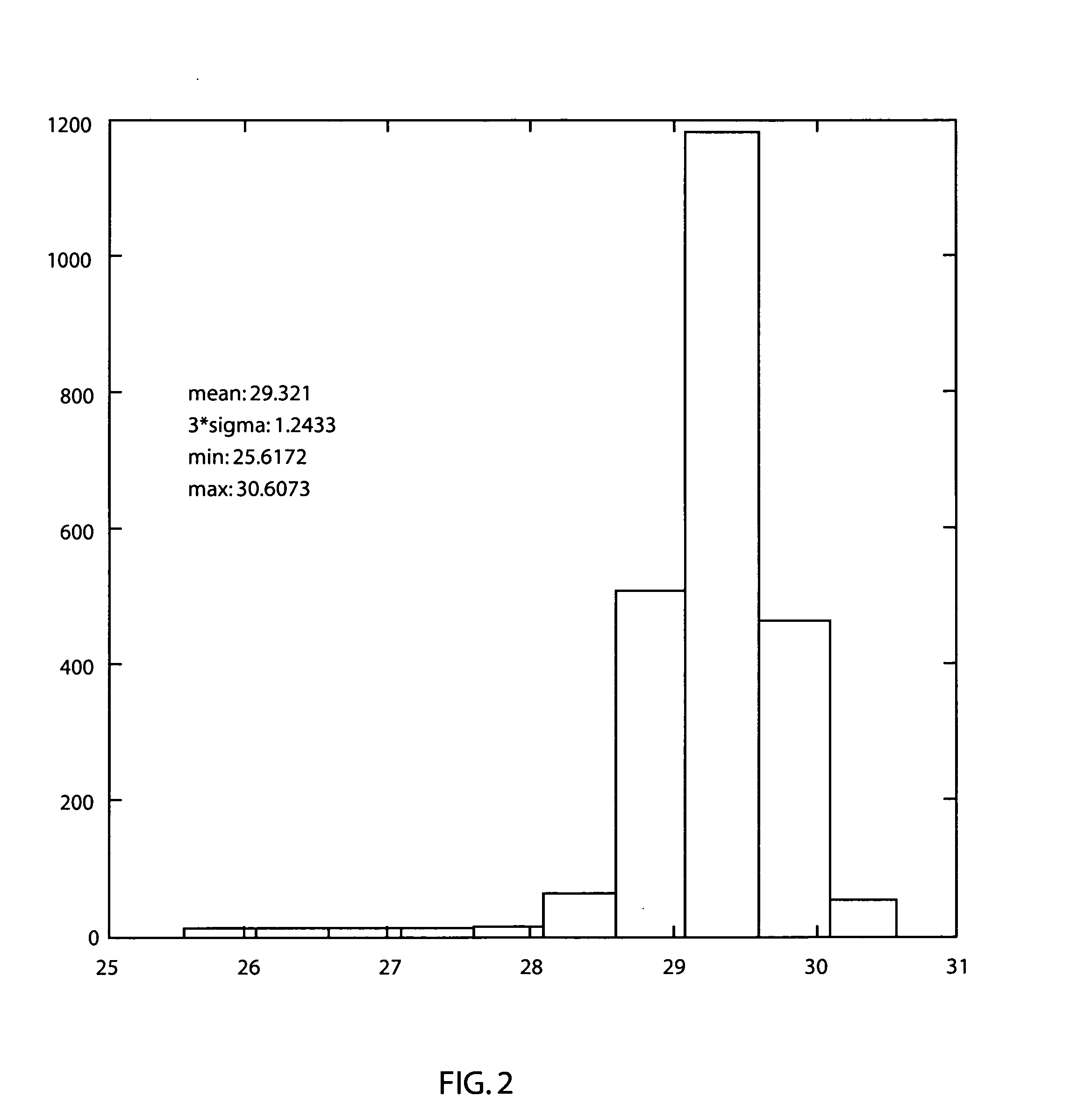
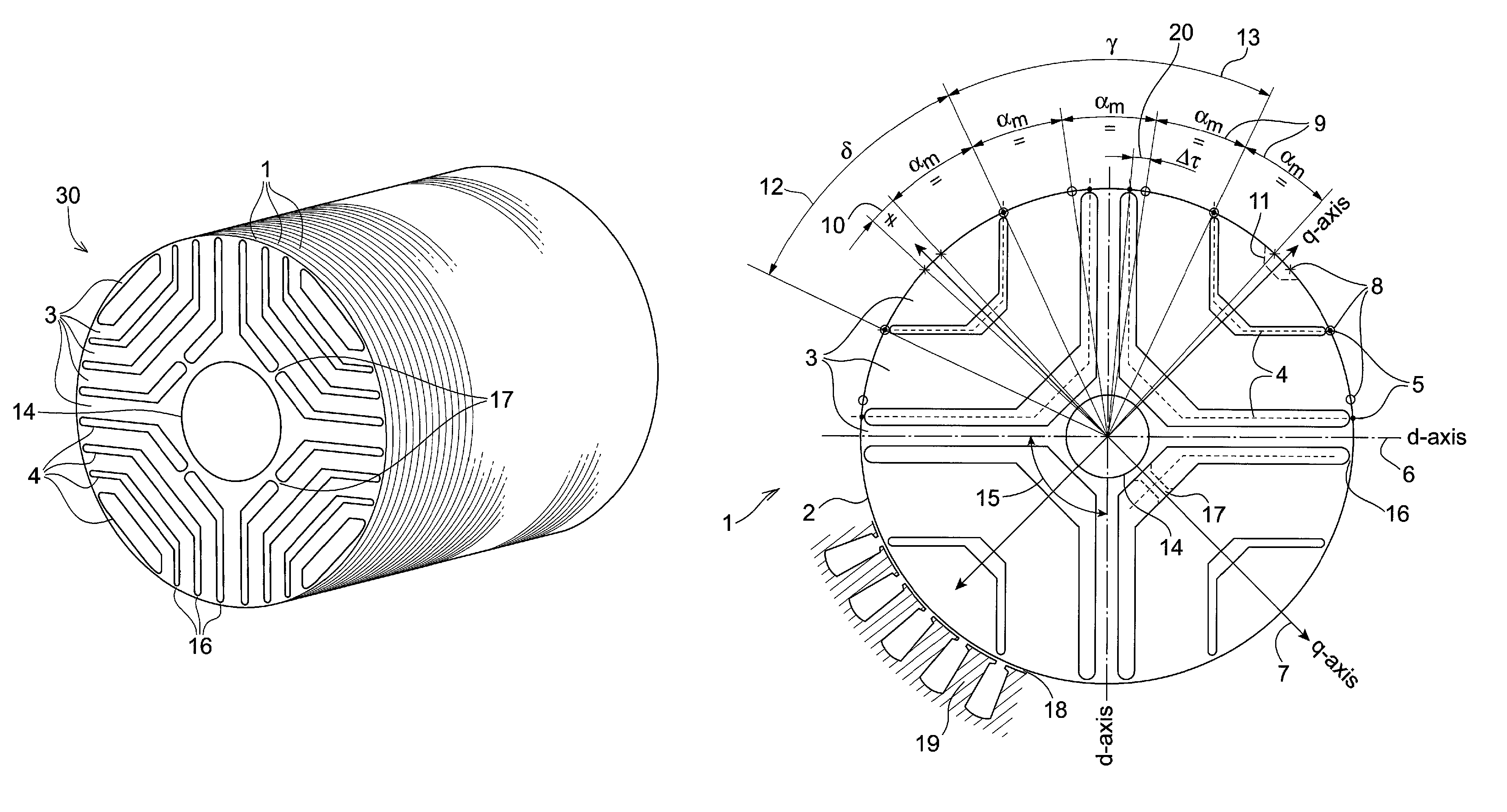
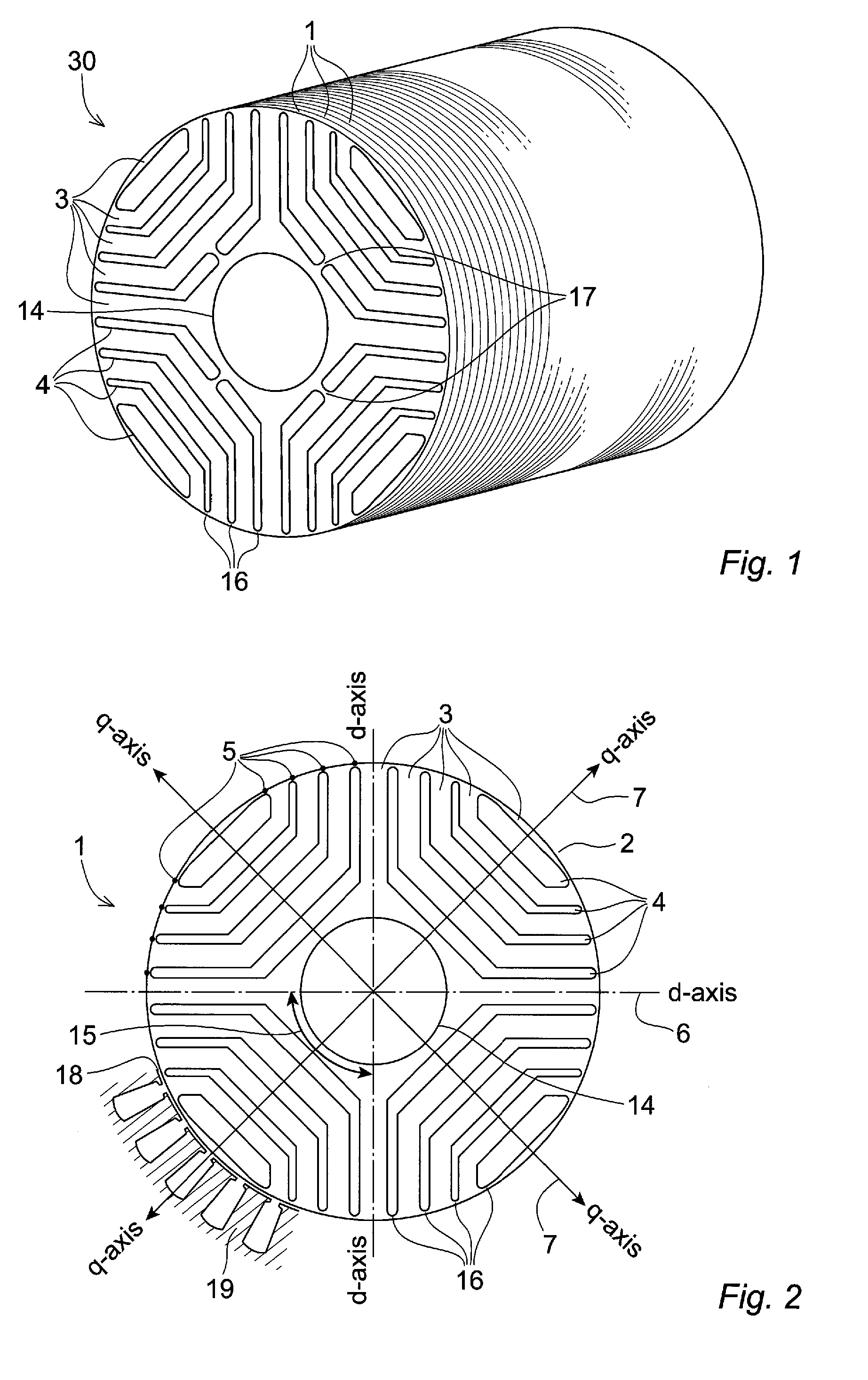
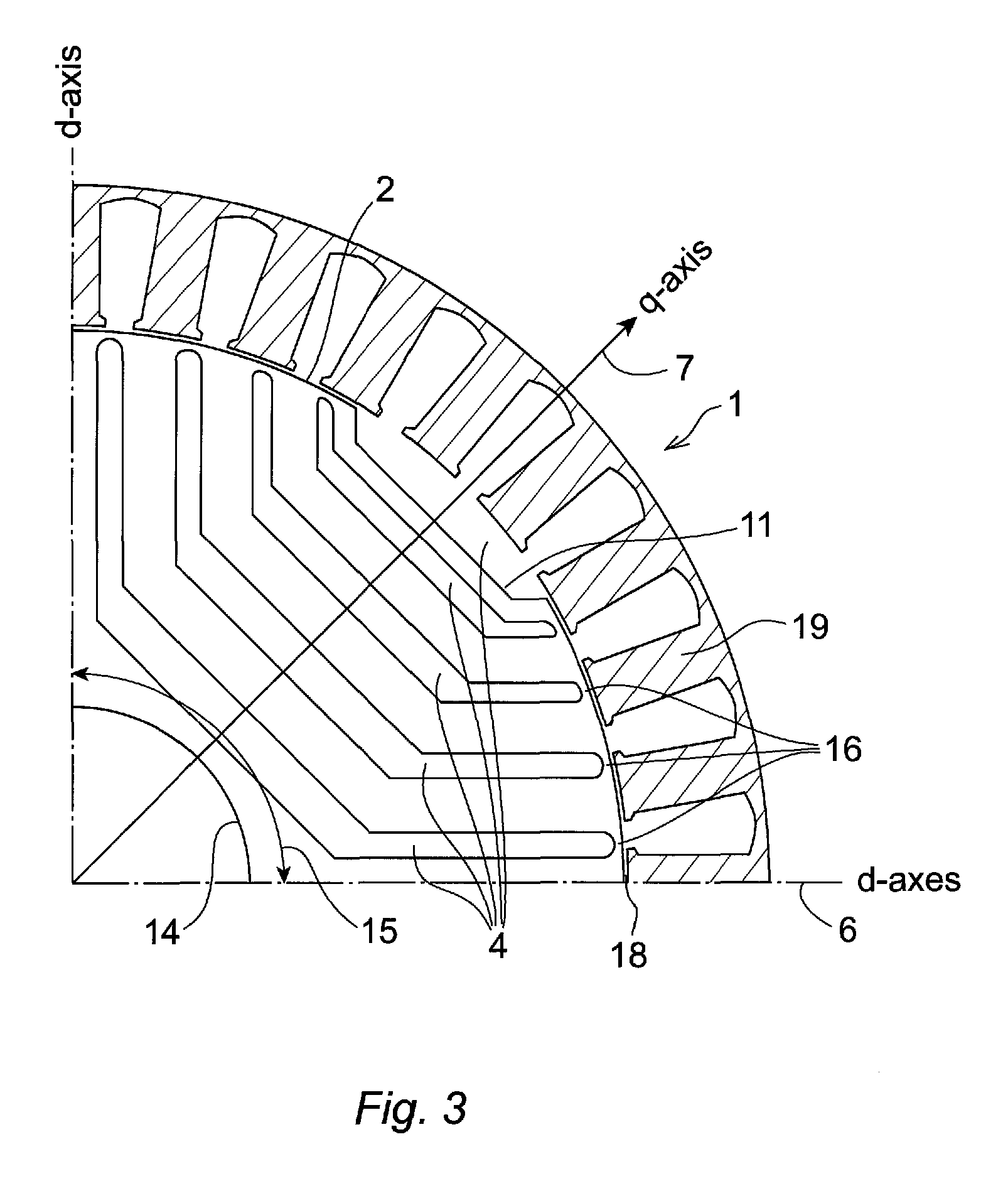
Rotor for a synchronous reluctance machine
ActiveUS8638012B2Efficient use ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsSynchronous reluctance motorHigh torque
A rotor for a synchronous reluctance machine wherein a torque ripple behaviour of the machine is optimized by altering the geometry of insulating barriers of the rotor. A q-axis pitch angle is used as a design variable instead of setting its value equal to the rest of the rotor slot pitches or binding its value to the stator slot pitch. The resulting rotor has a non-regular slot pitch across the q-axis and substantially regular slot pitch otherwise. Synchronous reluctance machines that employ rotor discs and rotor assemblies in accordance with the present invention may exhibit low torque ripple without sacrificing high torque values.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
System and method for employing patterning process statistics for ground rules waivers and optimization
A system and method of employing patterning process statistics to evaluate layouts for intersect area analysis includes applying Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) to the layout, simulating images formed by the mask and applying patterning process variation distributions to influence and determine corrective actions taken to improve and optimize the rules for compliance by the layout. The process variation distributions are mapped to an intersect area distribution by creating a histogram based upon a plurality of processes for an intersect area. The intersect area is analyzed using the histogram to provide ground rule waivers and optimization.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Intersect area based ground rule for semiconductor design
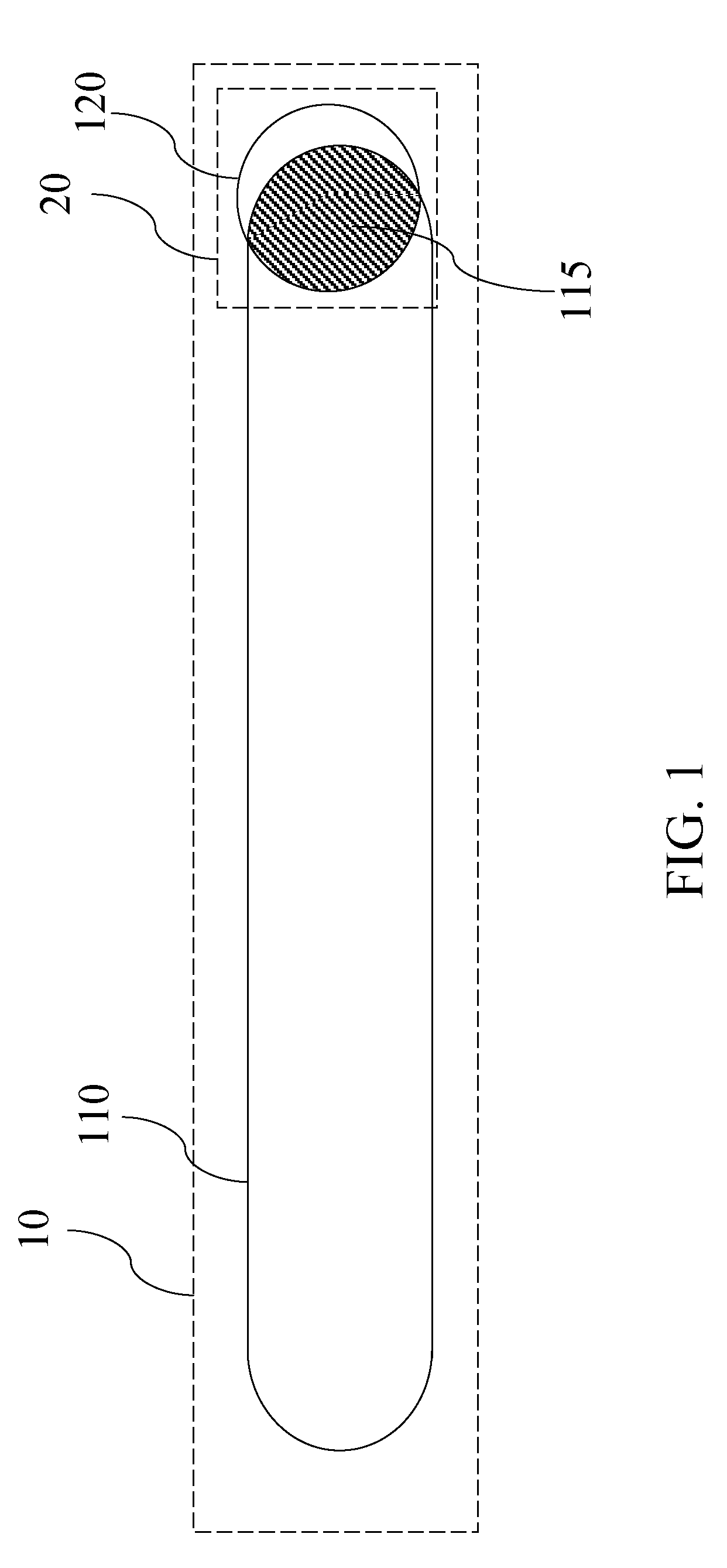
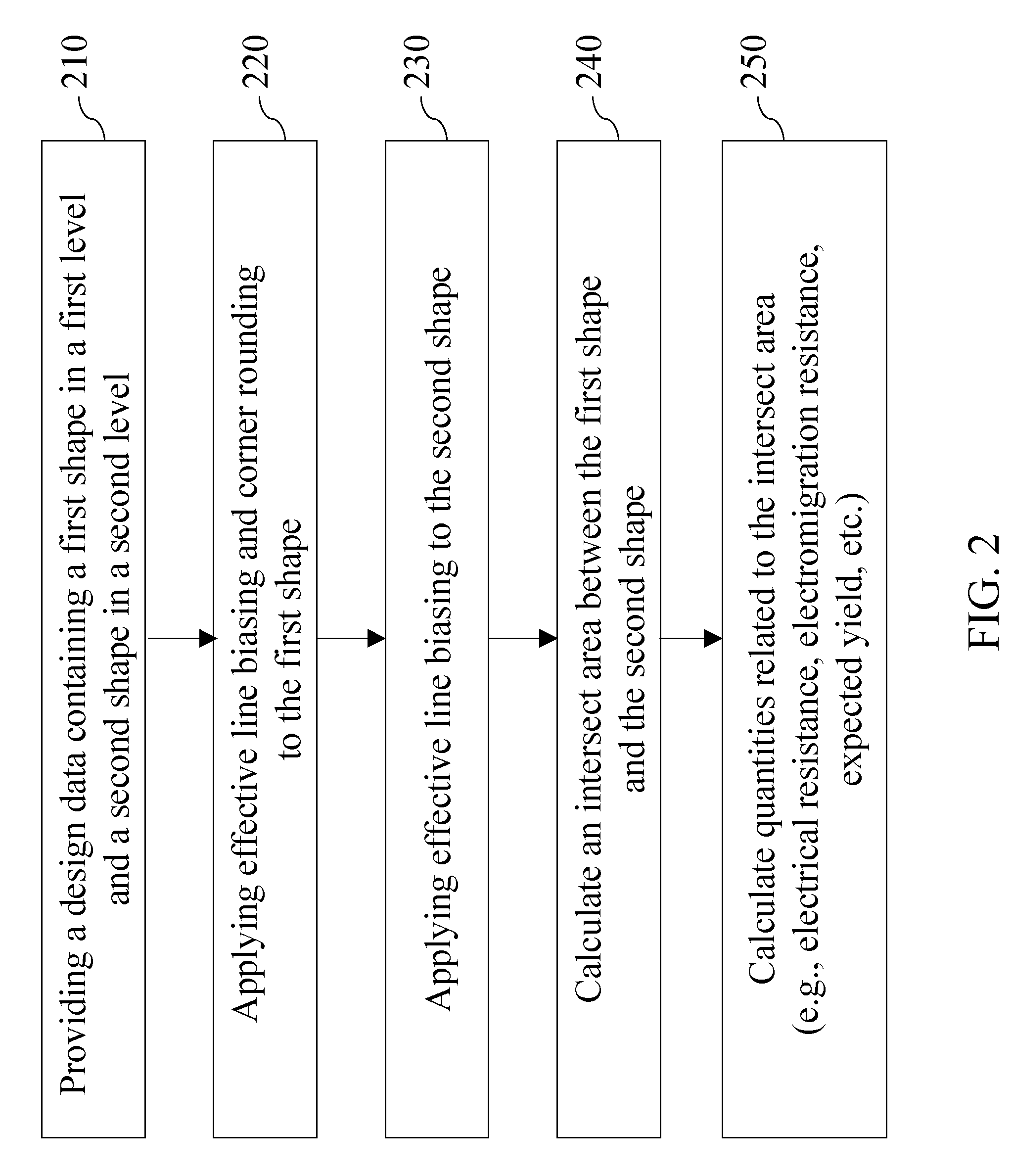
ActiveUS20090265673A1Optimize design dataAccurate estimateOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor chip
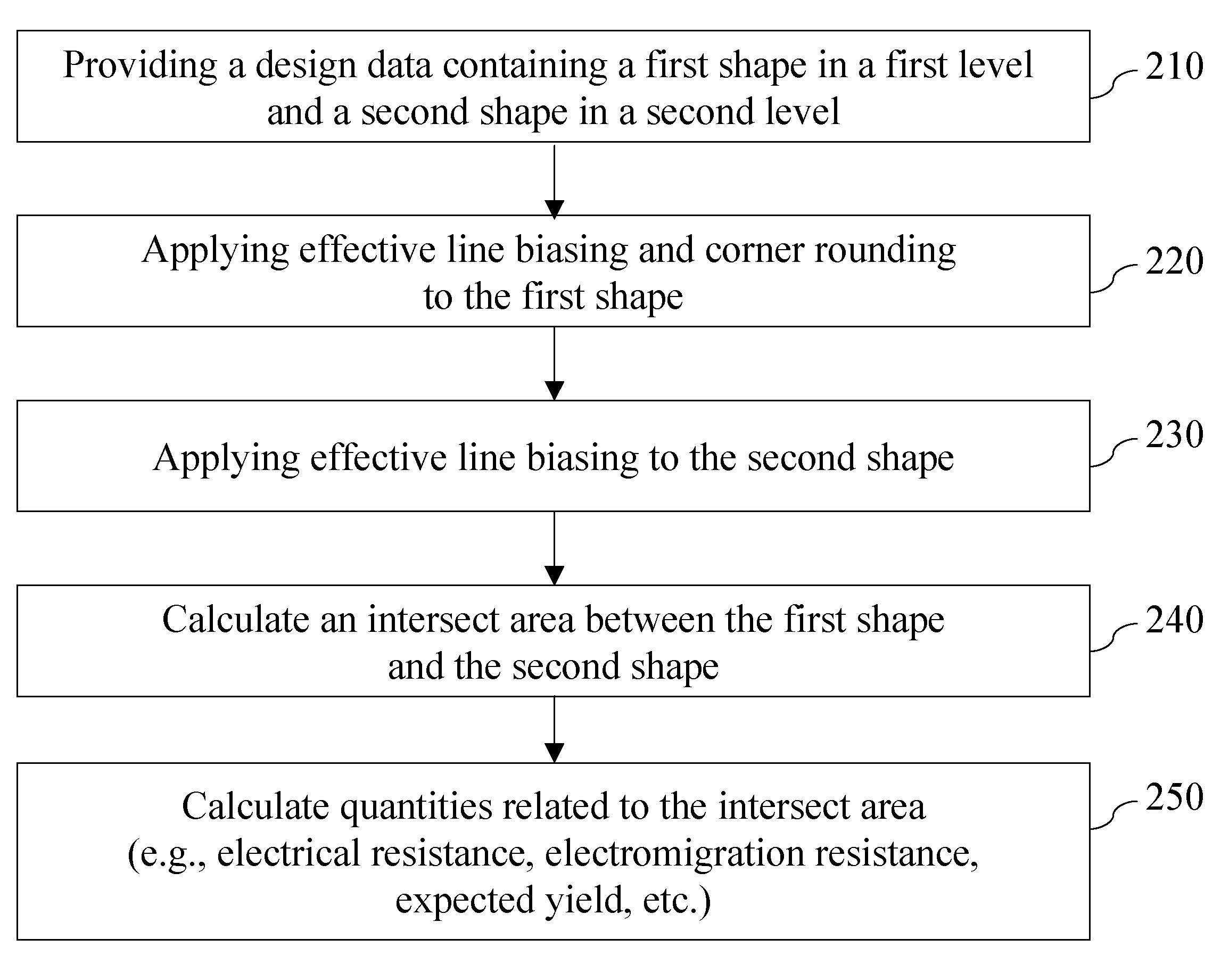
A design rule that determines a degree of overlap between two design elements in two adjoining levels by estimating a physical overlap area, or an “intersect area,” of corresponding structures in a semiconductor chip is provided. The estimation of the physical intersect area may factor in line edge biasing, critical dimension tolerance, overlay tolerance, and corner rounding to provide an accurate estimate of a physical area for each of the structures corresponding to the two design elements. The intersect area is employed as a metric to determine compliance with a ground rule, i.e., the ground rule is specified in terms of the intersect region. Other derived quantities such as electrical resistance, electromigration resistance, expected yield may be calculated from the intersect area, and may be advantageously employed to optimize the design data.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Integrated circuit (IC) design method, system and program product
InactiveUS7900178B2Low costReduce riskCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureACCESS PIN
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System and method for employing patterning process statistics for ground rules waivers and optimization
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
The use of a layout-optimization tool to increase the yield and reliability of VLSI designs
InactiveUS20050050501A1Easy to placeIncrease the number ofCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGround ruleCircuit design
The invention provides a method and structure for optimizing placement of redundant vias within an integrated circuit design. The invention first locates target vias by determining which vias do not have a redundant via. Then, the invention draws marker shapes on or adjacent to the target vias. The marker shapes are only drawn in a horizontal or vertical direction from each of the target vias. Next, the invention simultaneously expands all of the marker shapes in the first direction to a predetermined length or until the marker shapes reach the limits of a ground rule. During the expanding, different marker shapes will be expanded to different lengths. The invention determines which of the marker shapes were expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via to produce a first set of potential redundant vias and the invention eliminates marker shapes that could not be expanded sufficiently to form a valid redundant via. The invention repeats the foregoing processing in the direction perpendicular to the first. The invention can also be used to eliminate certain undesirable structures such as stacked vias or can be used to fix other problems such as insufficient via-to-via spacing. The invention then adds the redundant vias to the integrated circuit design, according to output produced by the optimizer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Circuit area minimization using scaling
InactiveUS7117456B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designGround ruleComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
High density butted junction CMOS inverter, and making and layout of same
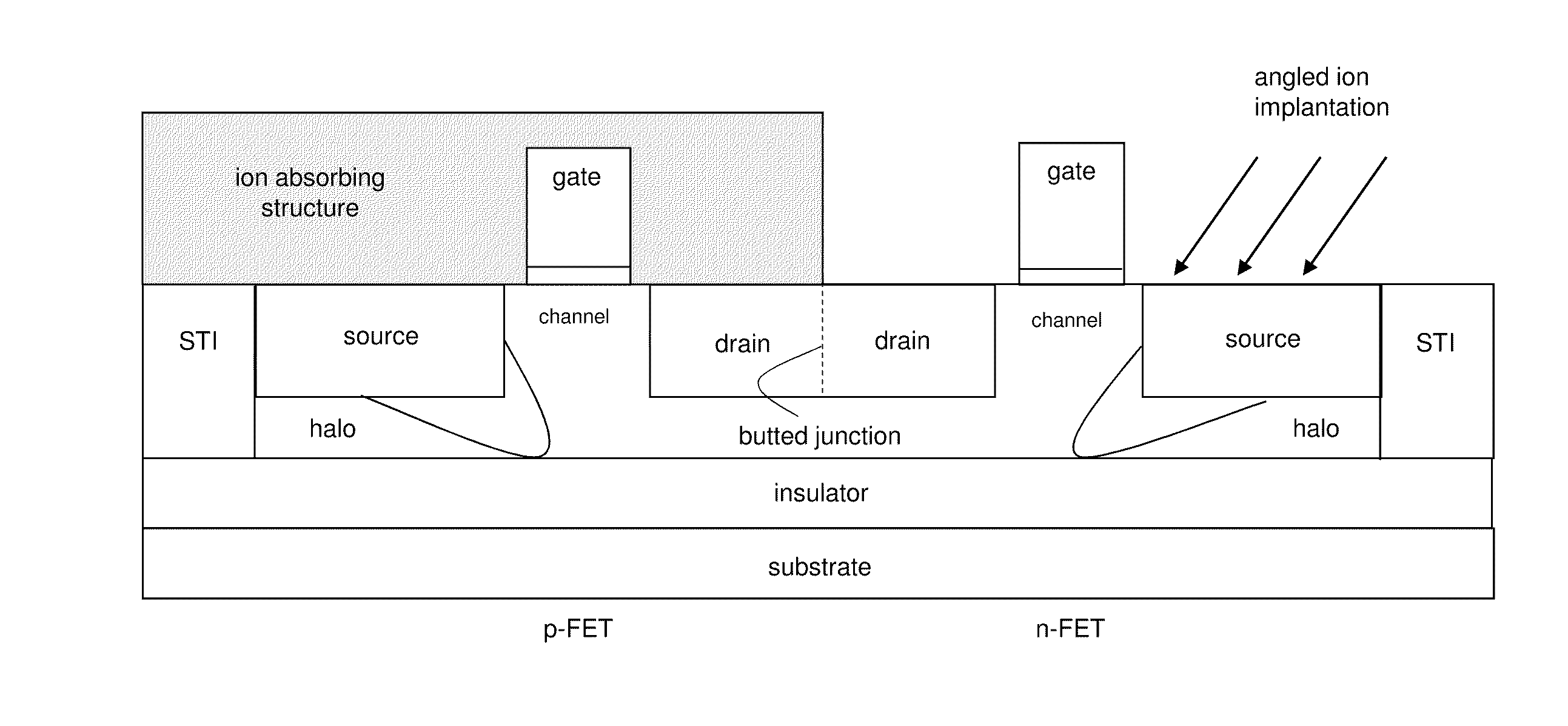
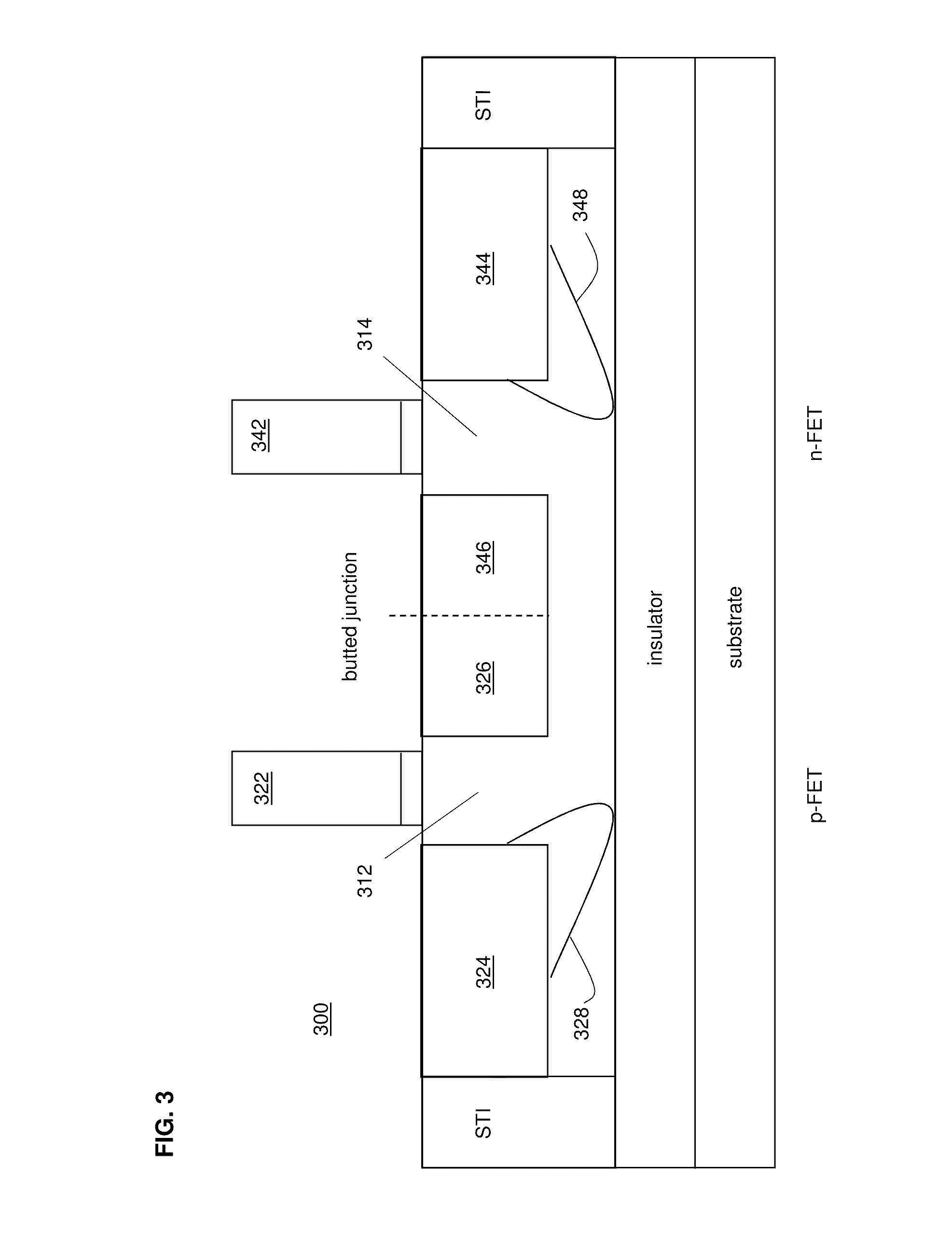
InactiveUS20110291193A1High circuit densityDensity of circuitry usingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSHigh density
A high density, asymmetric, butted junction CMOS inverter, formed on an SOI substrate, may include: an asymmetric p-FET that includes a halo implant on only a source side of the p-FET; an asymmetric n-FET that includes a halo implant on only a source side of the n-FET; and a butted junction comprising an area of said SOI substrate where a drain region of the asymmetric n-FET and a drain region of the asymmetric p-FET are in direct physical contact. Asymmetric halo implants may be formed by a sequential process of covering a first FET of the CMOS inverter with an ion-absorbing structure and applying angled ion radiation to only the source side of the second FET, removing the ion-absorbing structure, covering the first FET with a second ion-absorbing structure, and applying angled ion radiation to only the source side of the second FET. A layout display of CMOS integrated circuit may require one ground rule for the high density, asymmetric butted junction CMOS inverter and another ground rule for other CMOS circuits.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for fixing pin mismatch in layout migration
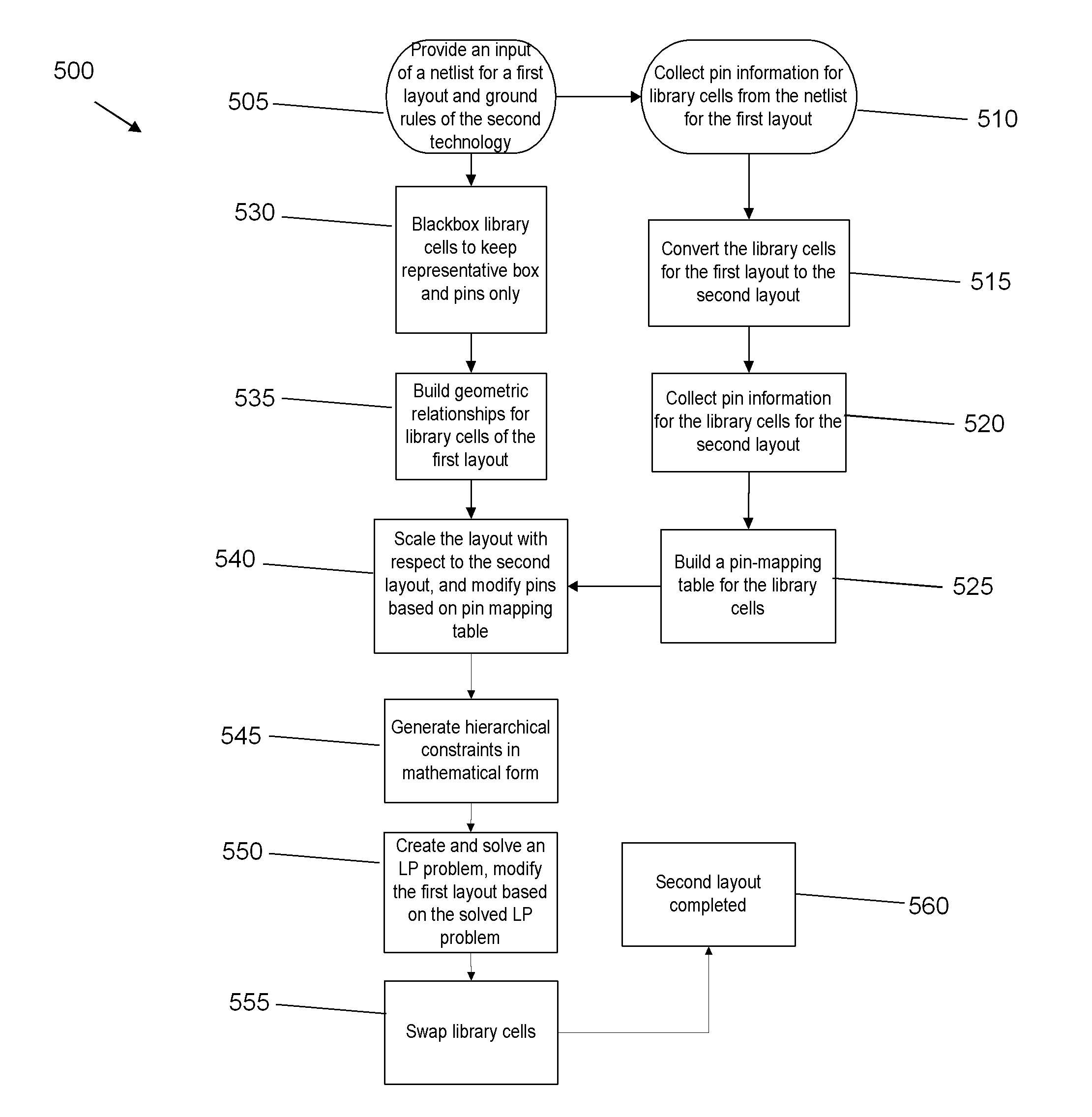
ActiveUS8627247B1Low costComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringGround rule
Approaches are provided for fixing pin mismatches from swapping library cells in layout migration. Specifically, a method is provided that includes collecting information about a first technology pin from a library cell in a first technology. The method further includes swapping the library cell in the first technology with a library cell in a second technology. The method further includes collecting information about a second technology pin from the library cell in the second technology. The method further includes building a pin-mapping table that is configured to map the first technology pin to the second technology pin. The method further includes scaling a layout from the first technology to the second technology. The method further includes modifying the layout based on the pin-mapping table to match the at least one first technology pin to the at least one second technology pin while satisfying ground rules of the second technology.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Methods for self-aligned self-assembled patterning enhancement
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com