Patents
Literature
51 results about "Layout Versus Schematic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
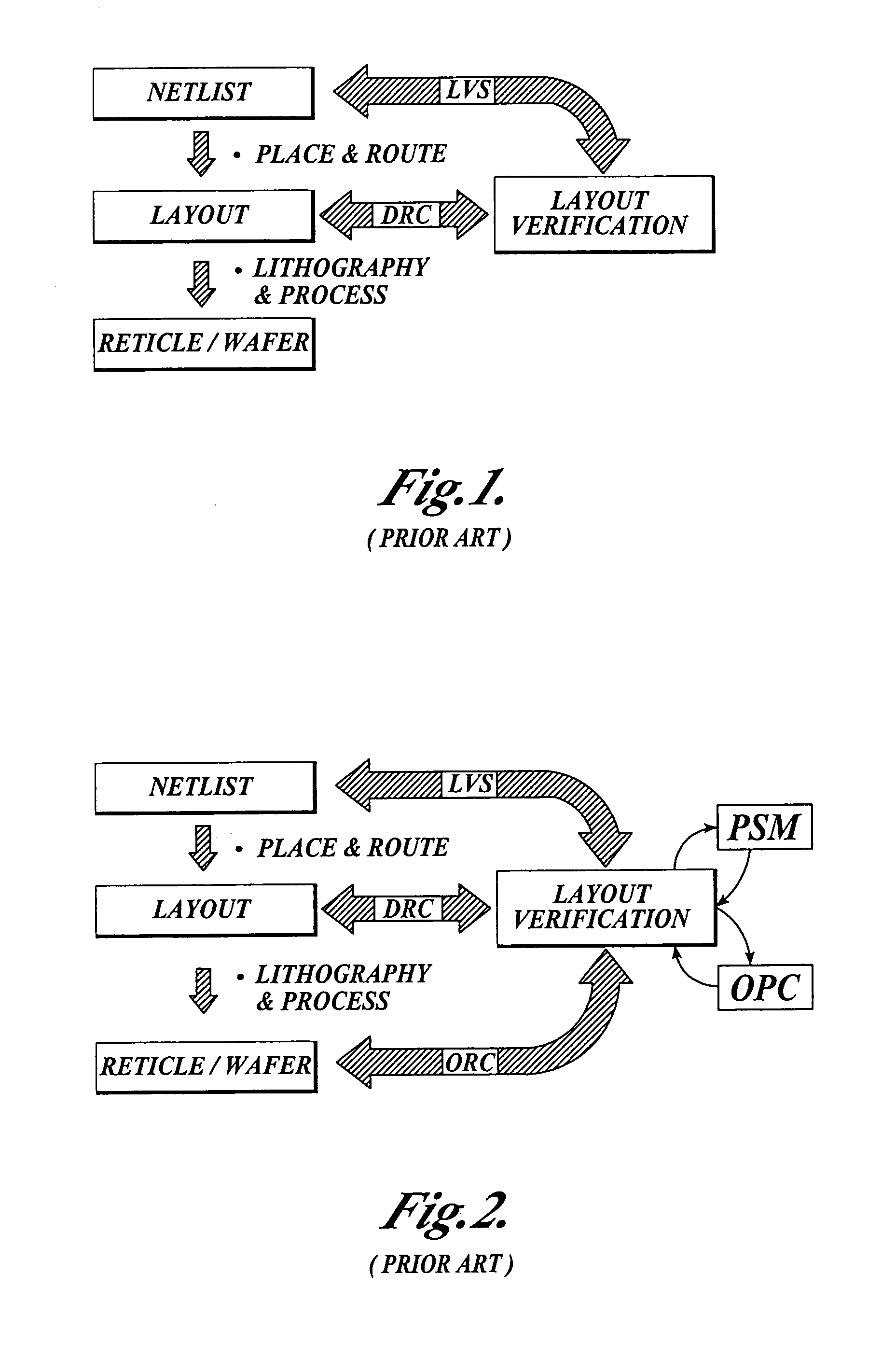
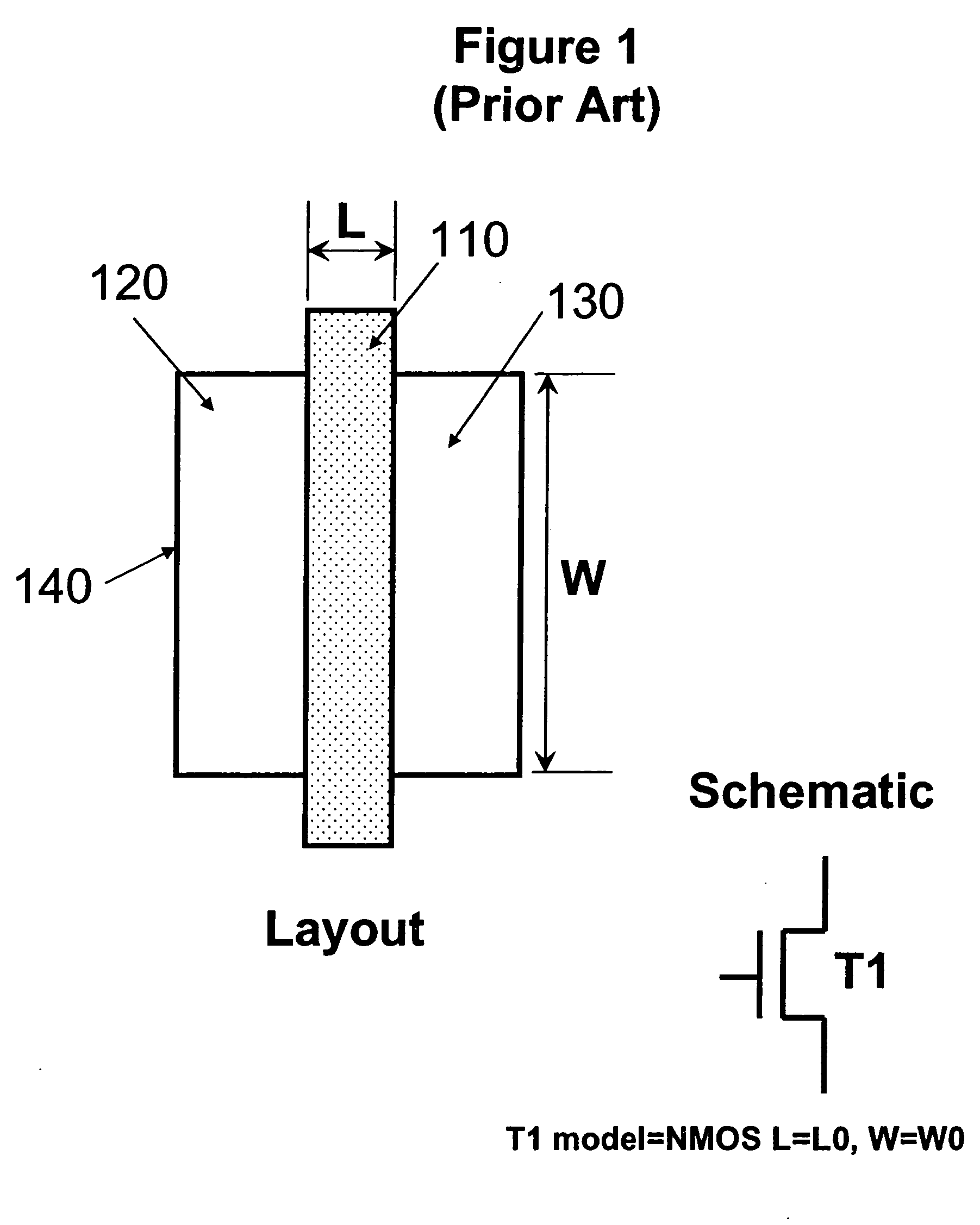
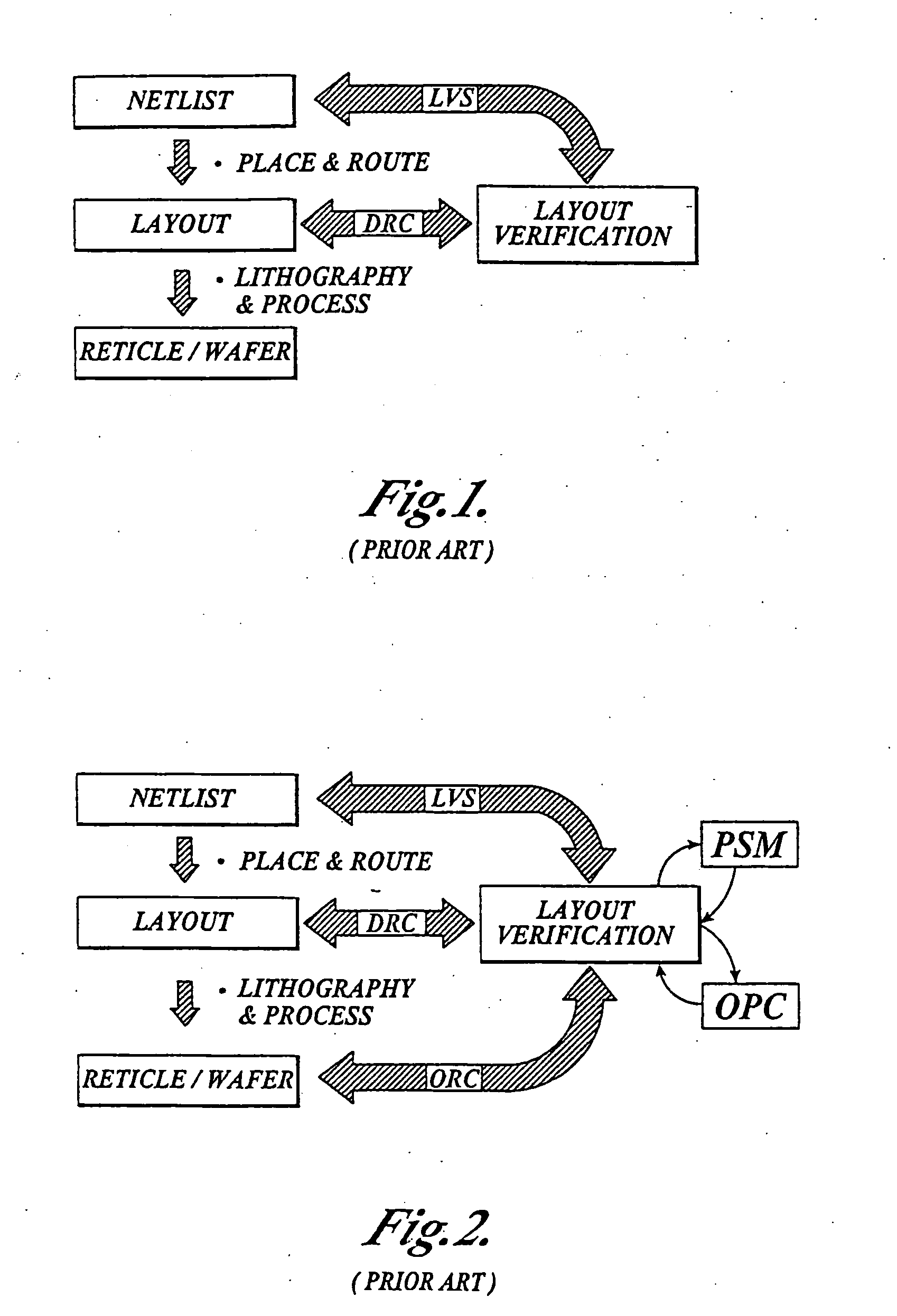
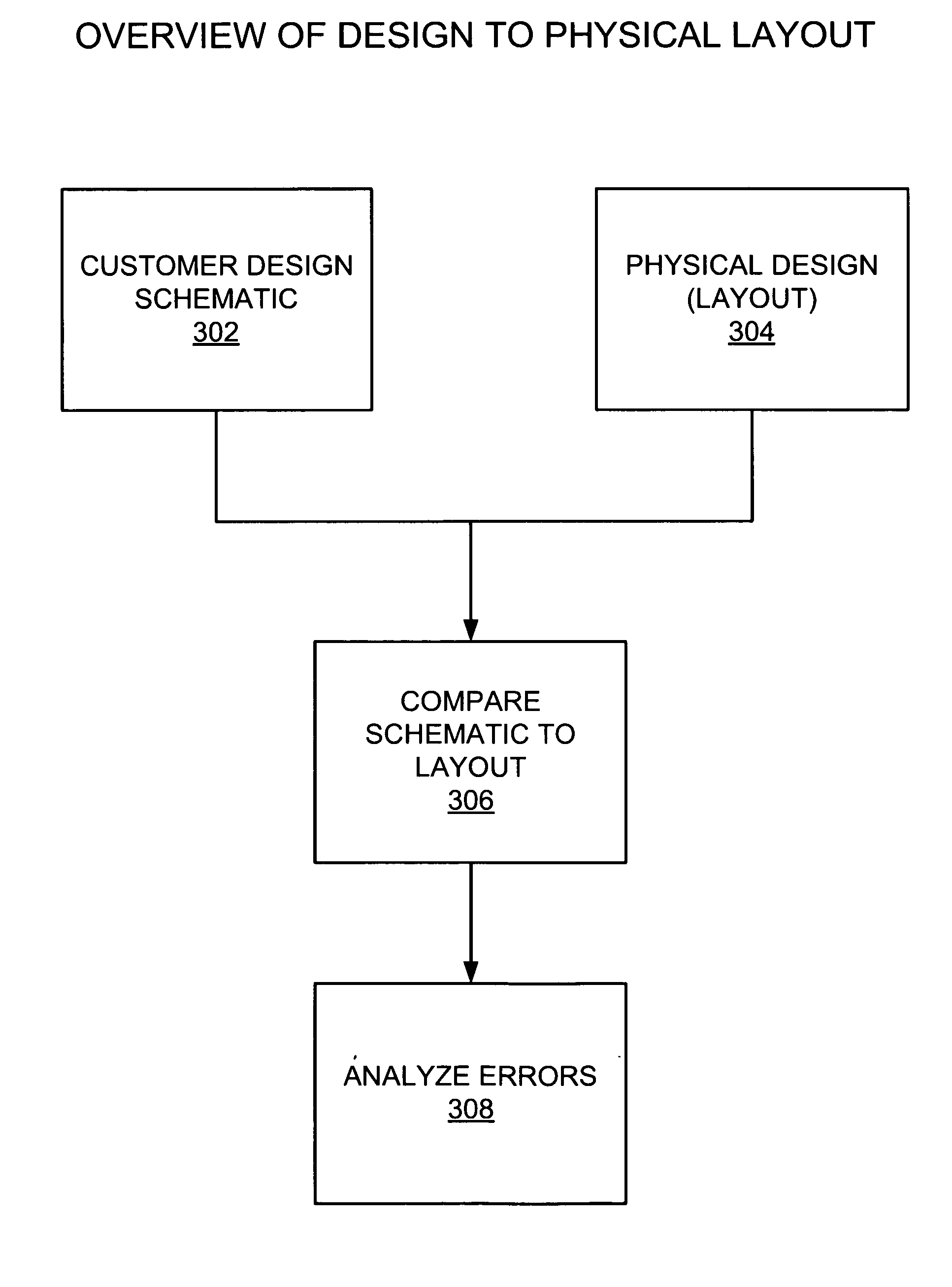
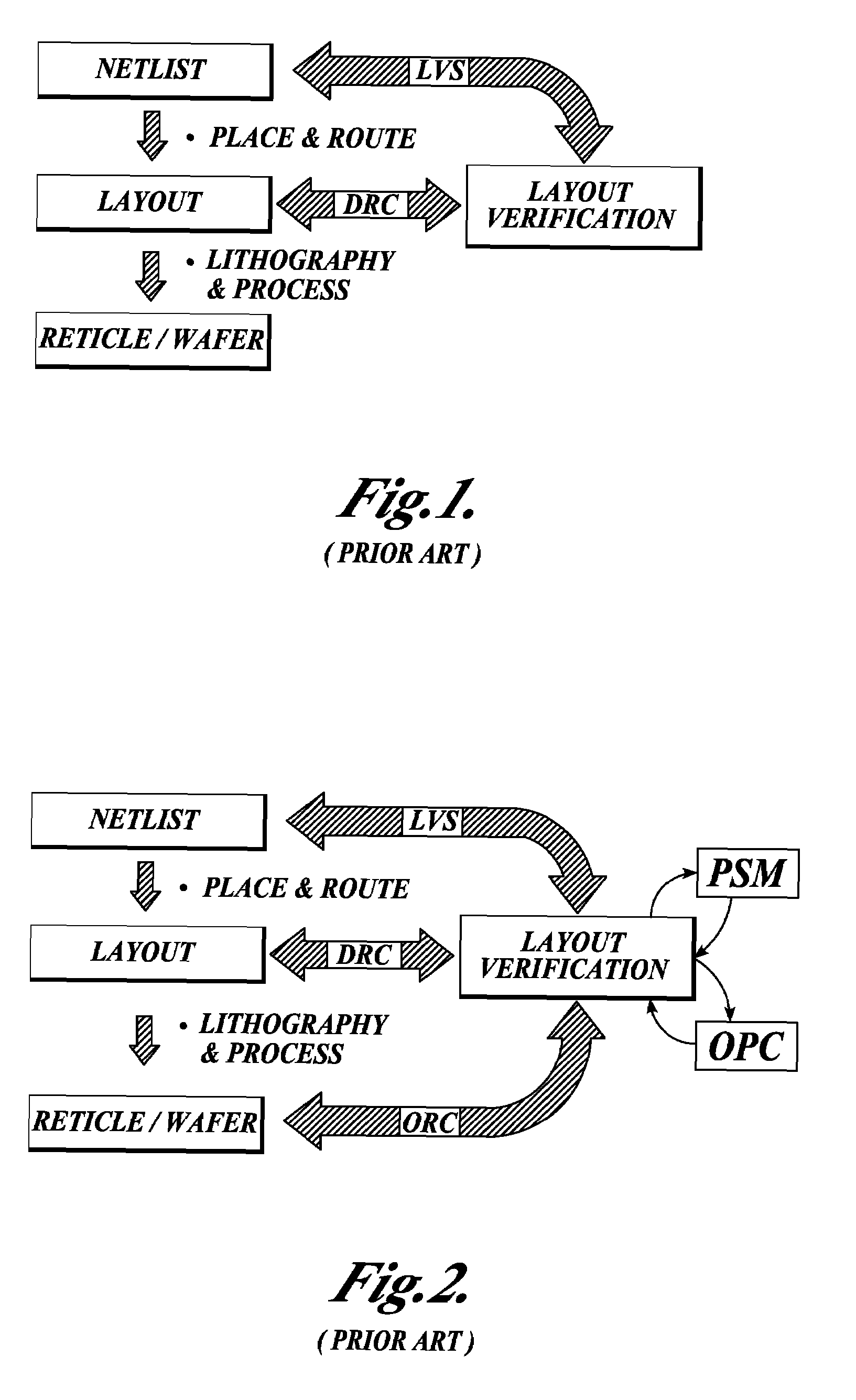
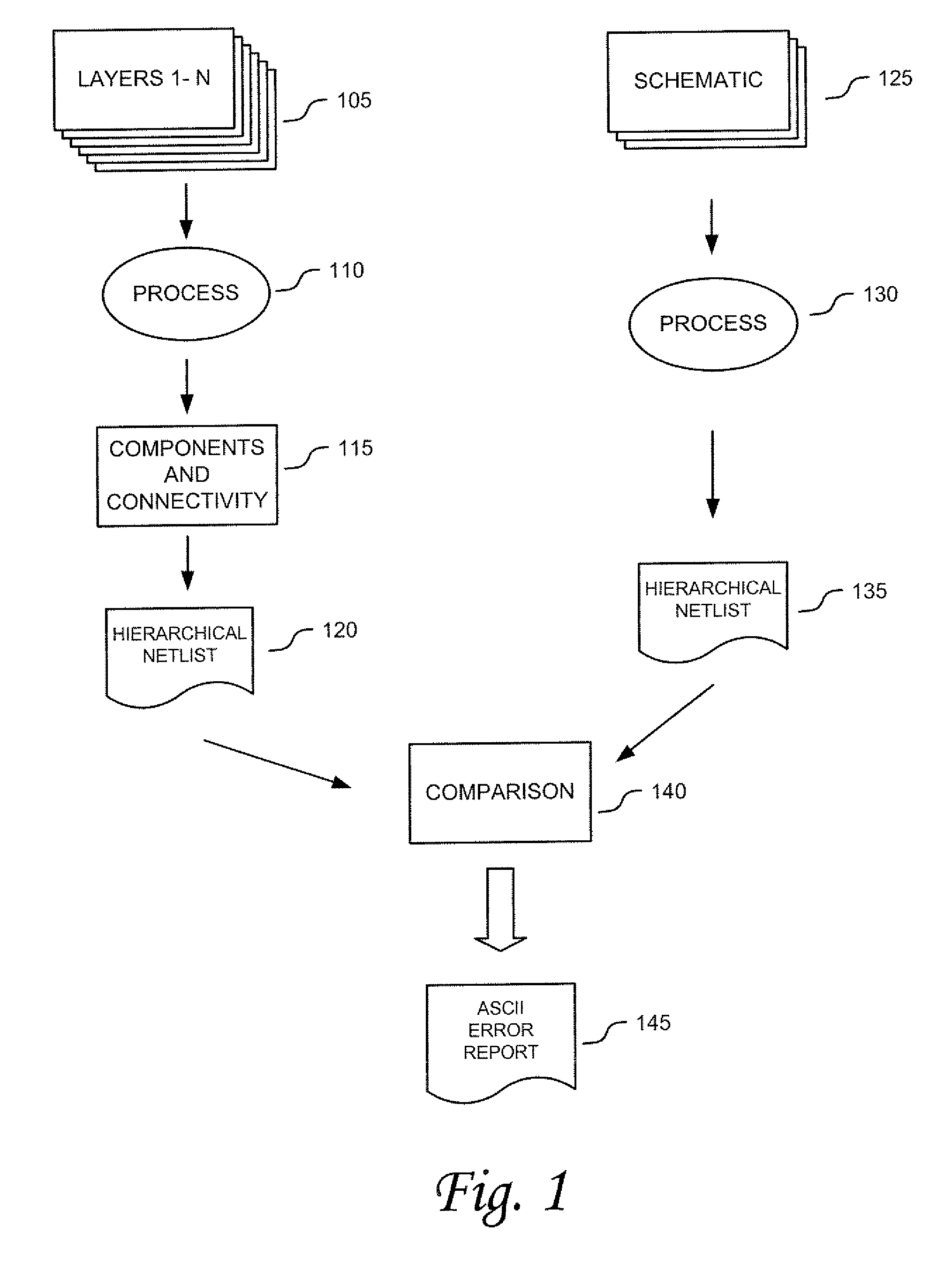
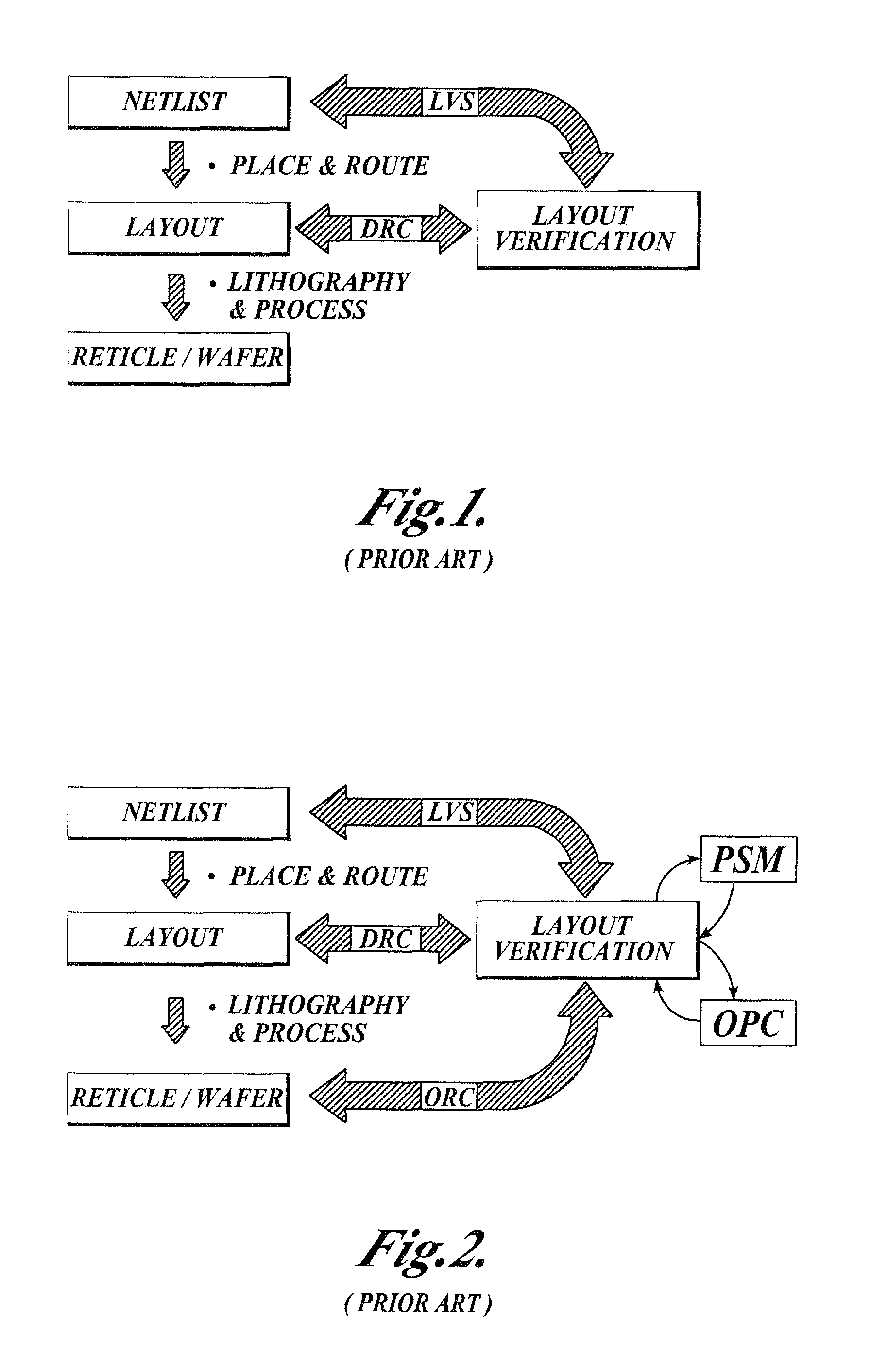
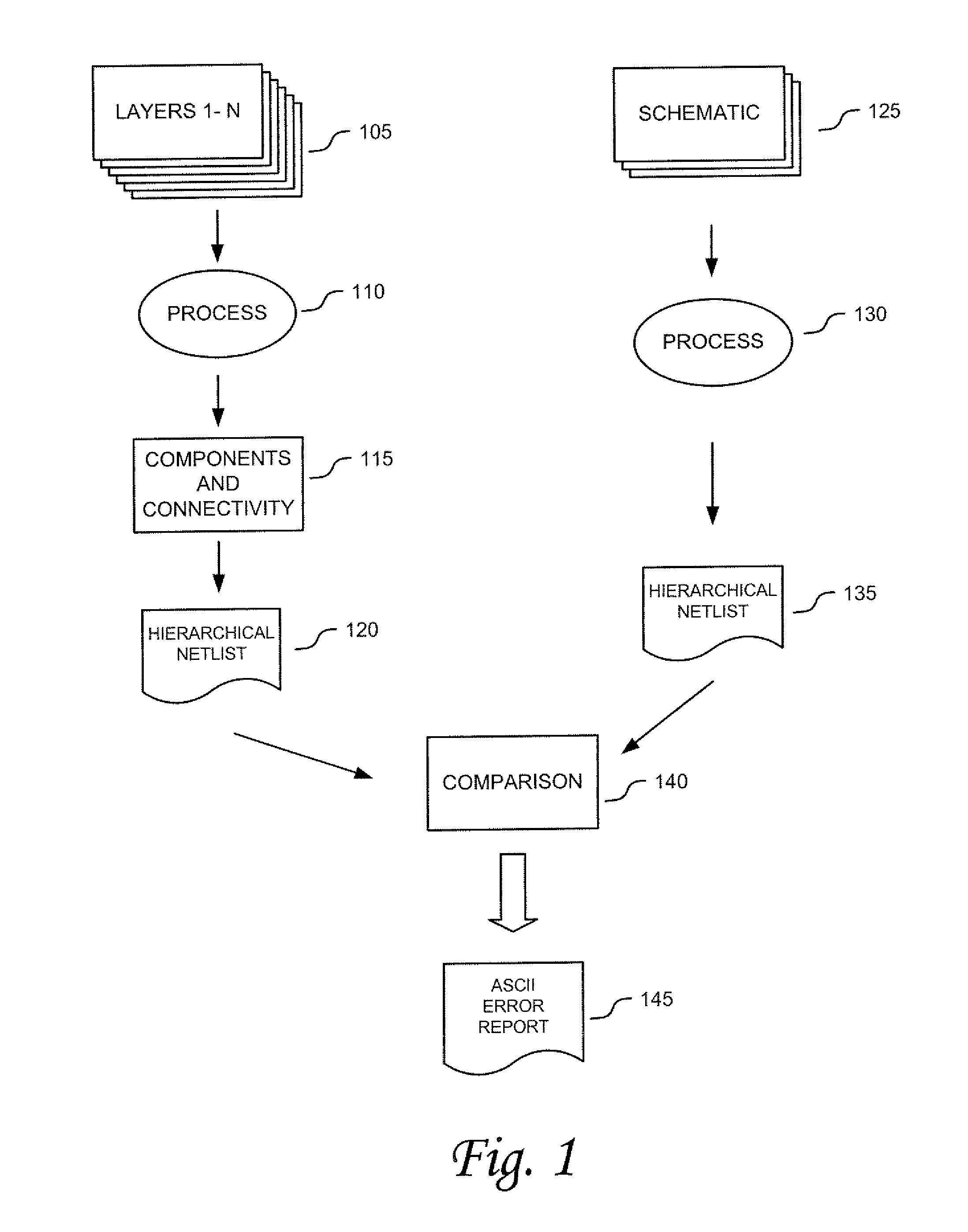
The Layout Versus Schematic (LVS) is the class of electronic design automation (EDA) verification software that determines whether a particular integrated circuit layout corresponds to the original schematic or circuit diagram of the design.
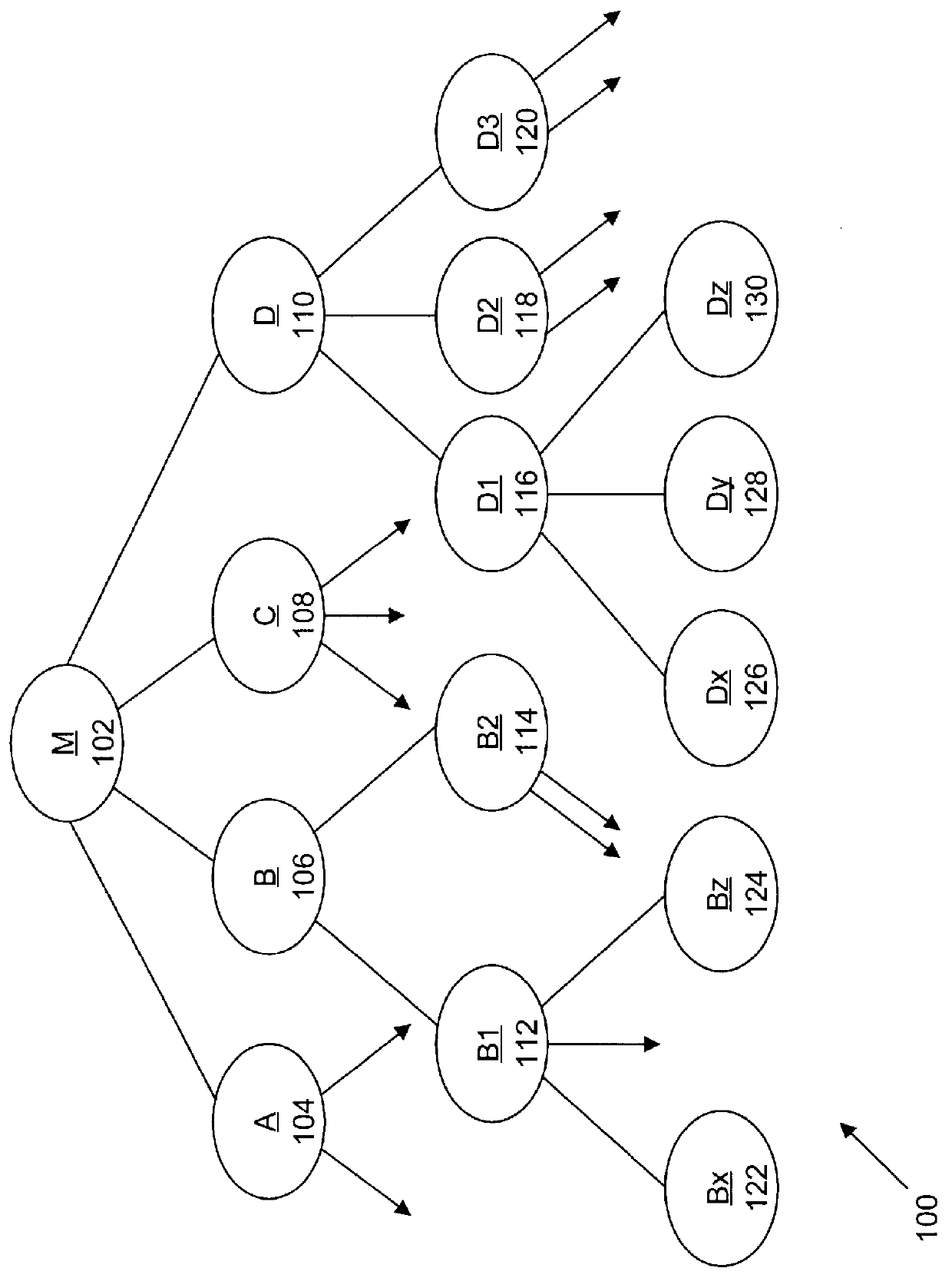
Layout overlap detection with selective flattening in computer implemented integrated circuit design
InactiveUS6011911AValid checkComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
The present invention relates to a method for efficiently performing hierarchical design rules checks (DRC) and layout versus schematic comparison (LVS) on layout areas of an integrated circuit where cells overlap or where a cell and local geometry overlap. With the present invention, a hierarchical tree describes the integrated circuit's layout data including cells having parent-child relationships and including local geometry. The present invention performs efficient layout verification by performing LVS and DRC checking on the new portions of an integrated circuit design and layout areas containing overlapping cells. When instances of cells overlap, the present invention determines the overlap area using predefined data structures that divide each cell into an array of spatial bins. Each bin of a parent is examined to determine if two or more cell instances reside therein or if a cell instance and local geometry reside therein. Once overlap is detected, the areas of the layout data corresponding to the overlap areas are selectively flattened prior to proceeding to DRC and LVS processing. During selective flattening of the overlap areas, the hierarchical tree is traversed from the top cell down through intermediate nodes to the leaf nodes. Each time geometry data is located during the traversal, it is pushes directly to the top cell without being stored in intermediate locations. This provides an effective mechanism for selective flattening.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
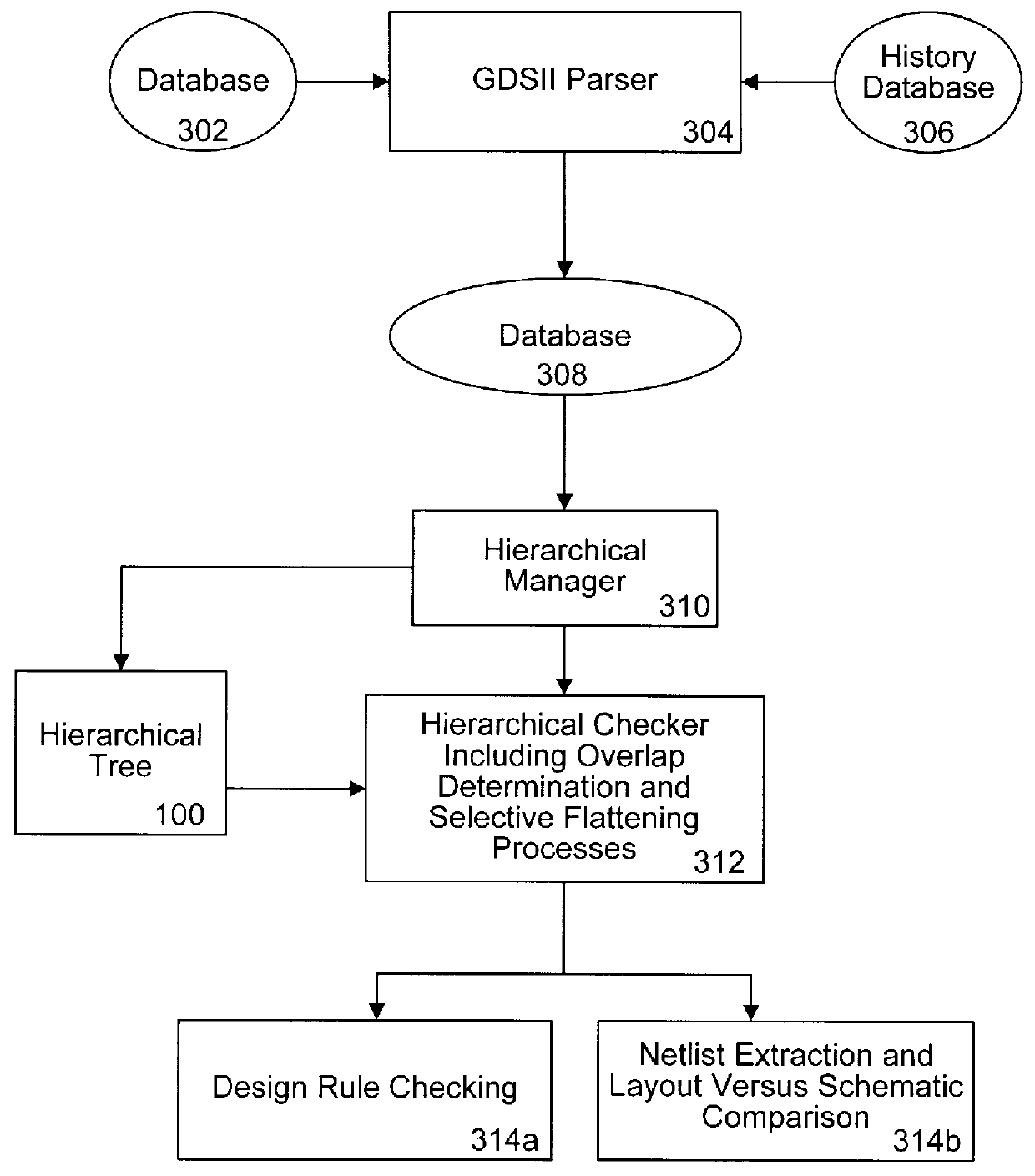
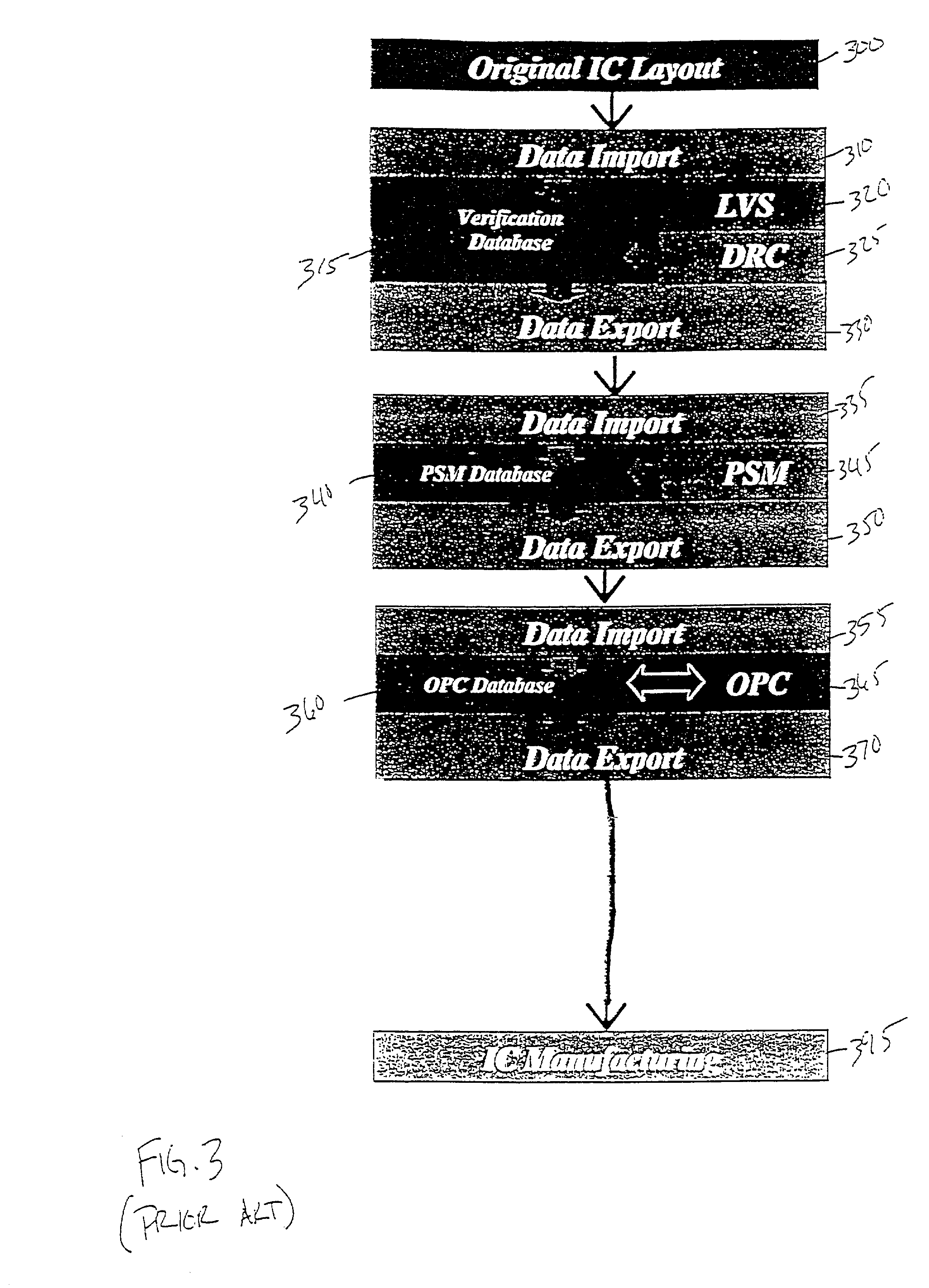
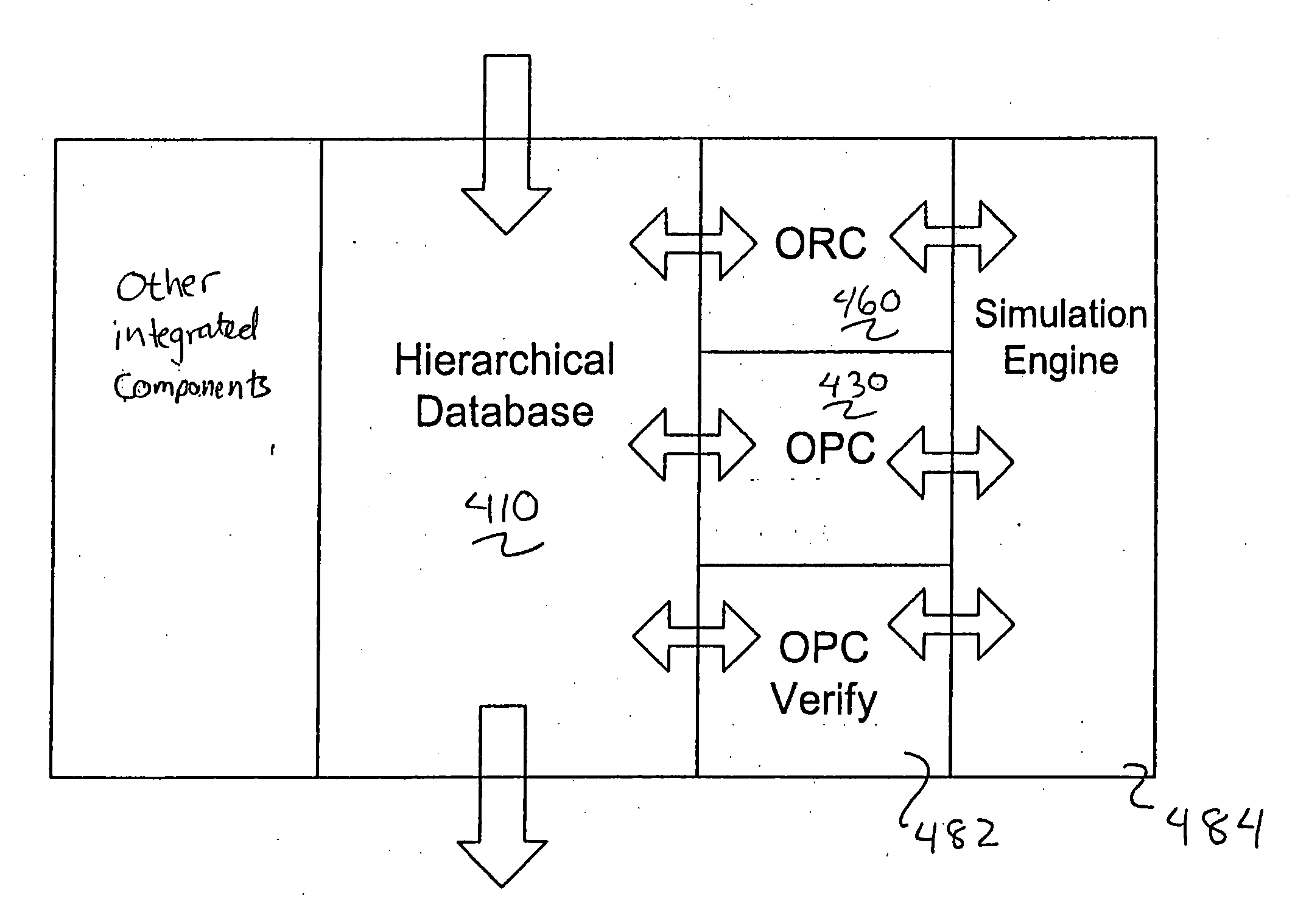
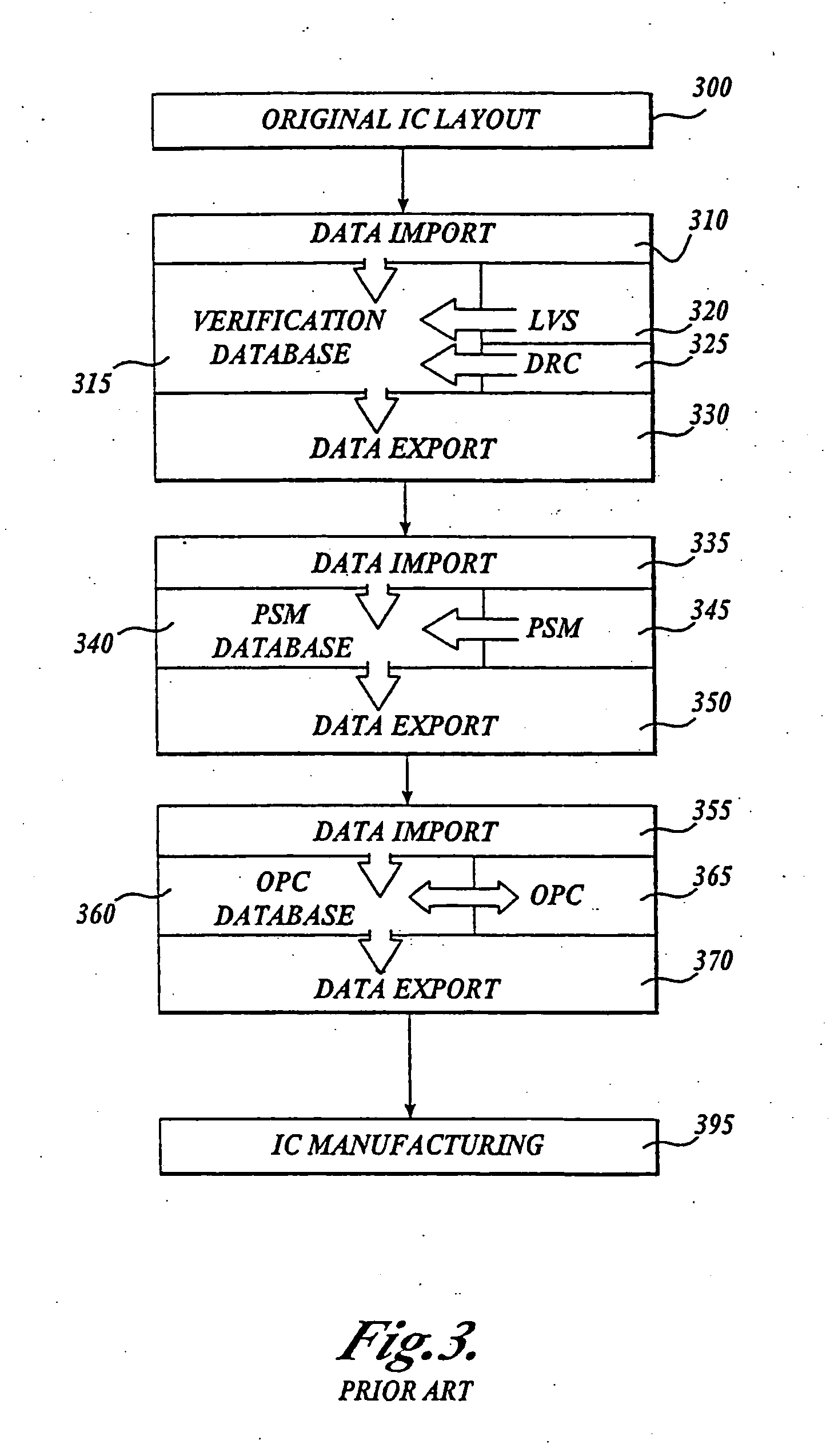
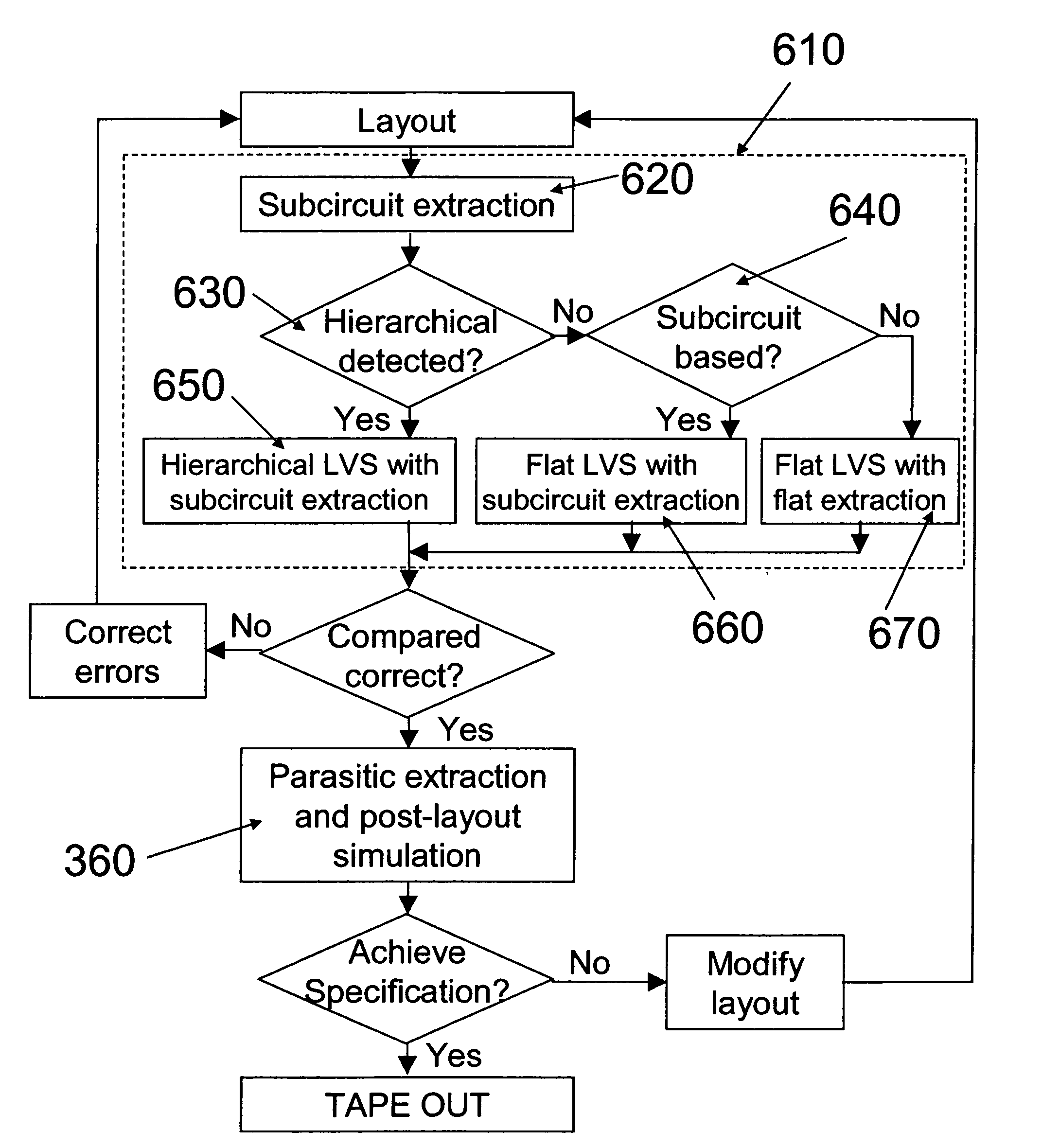
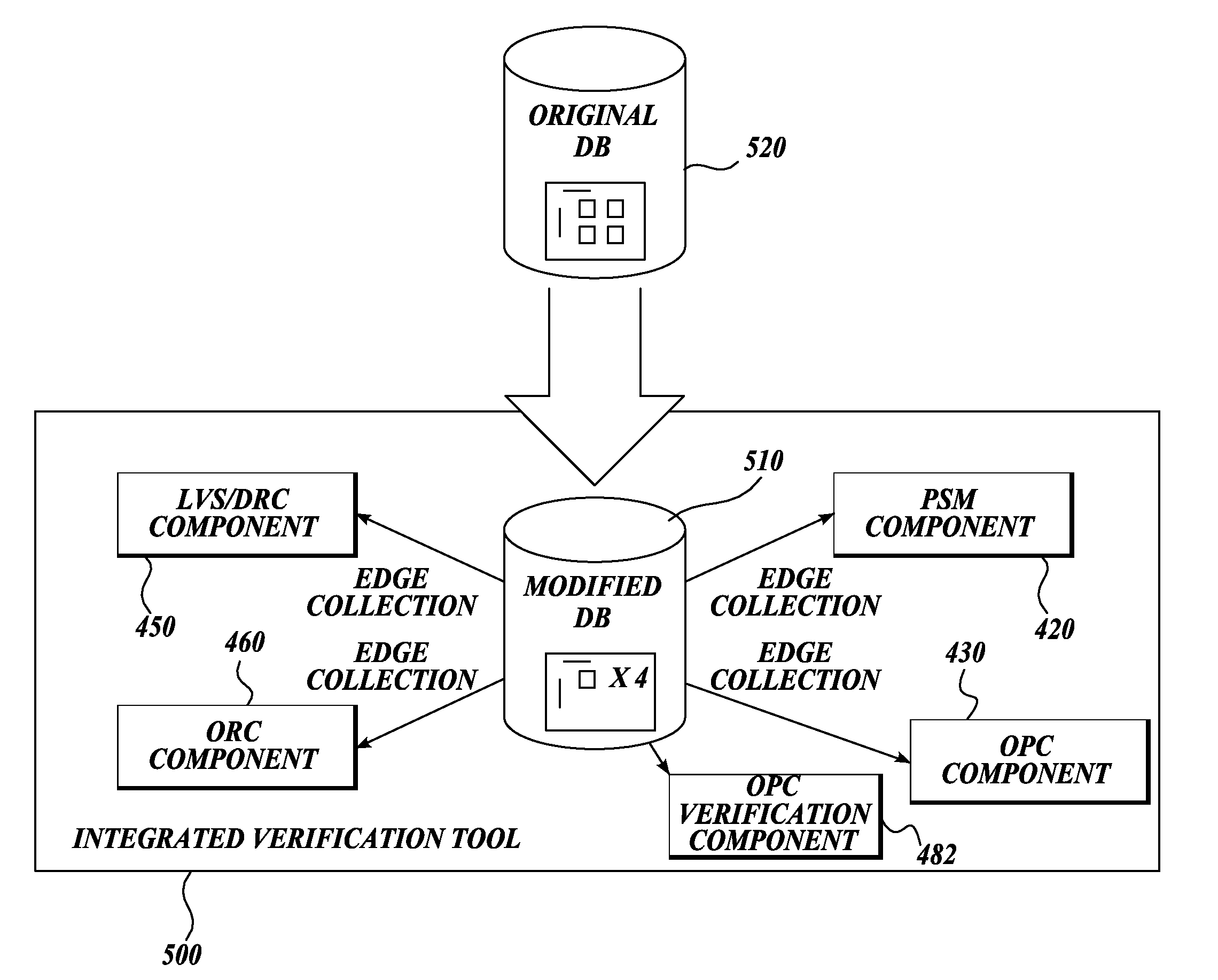
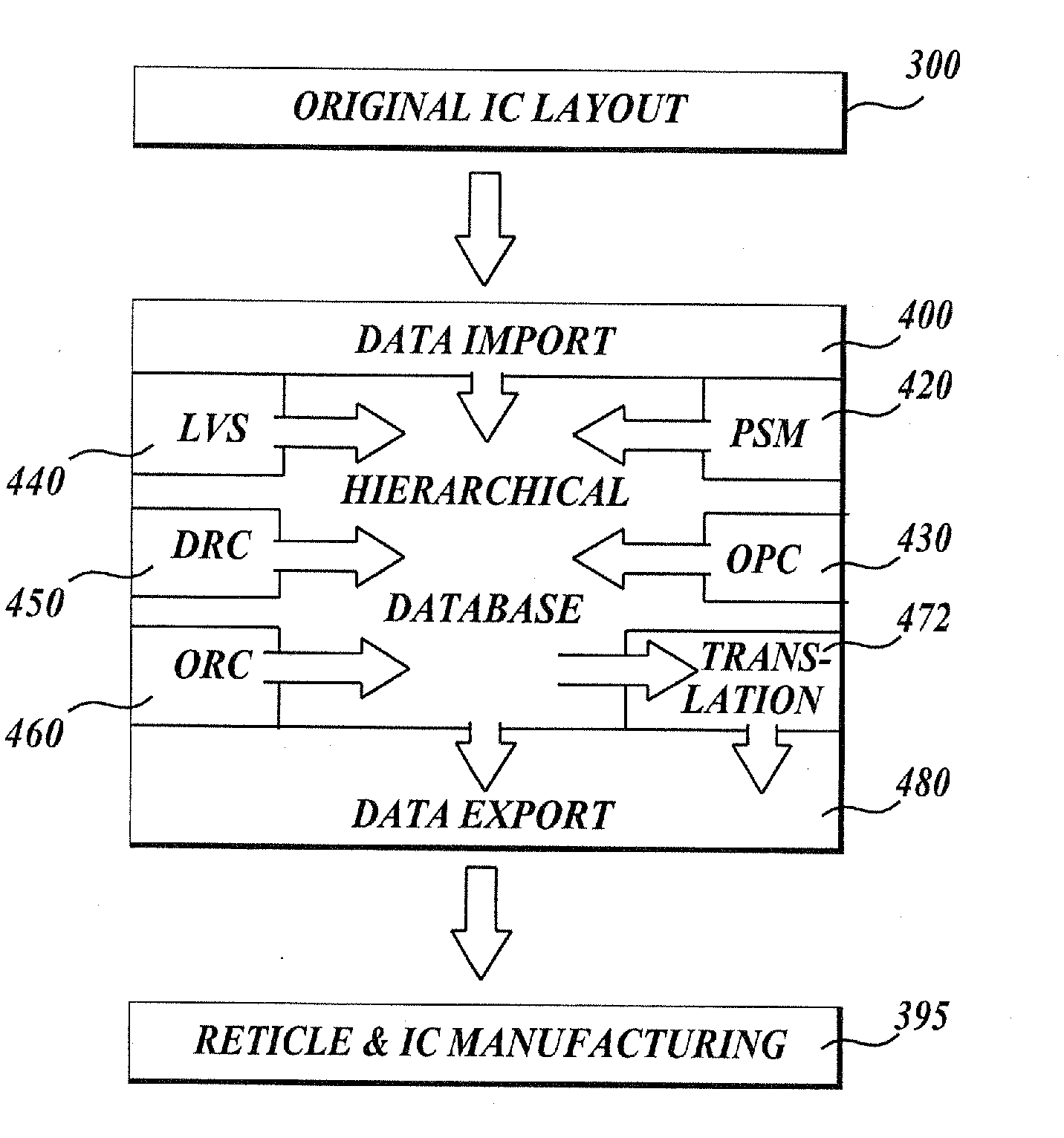
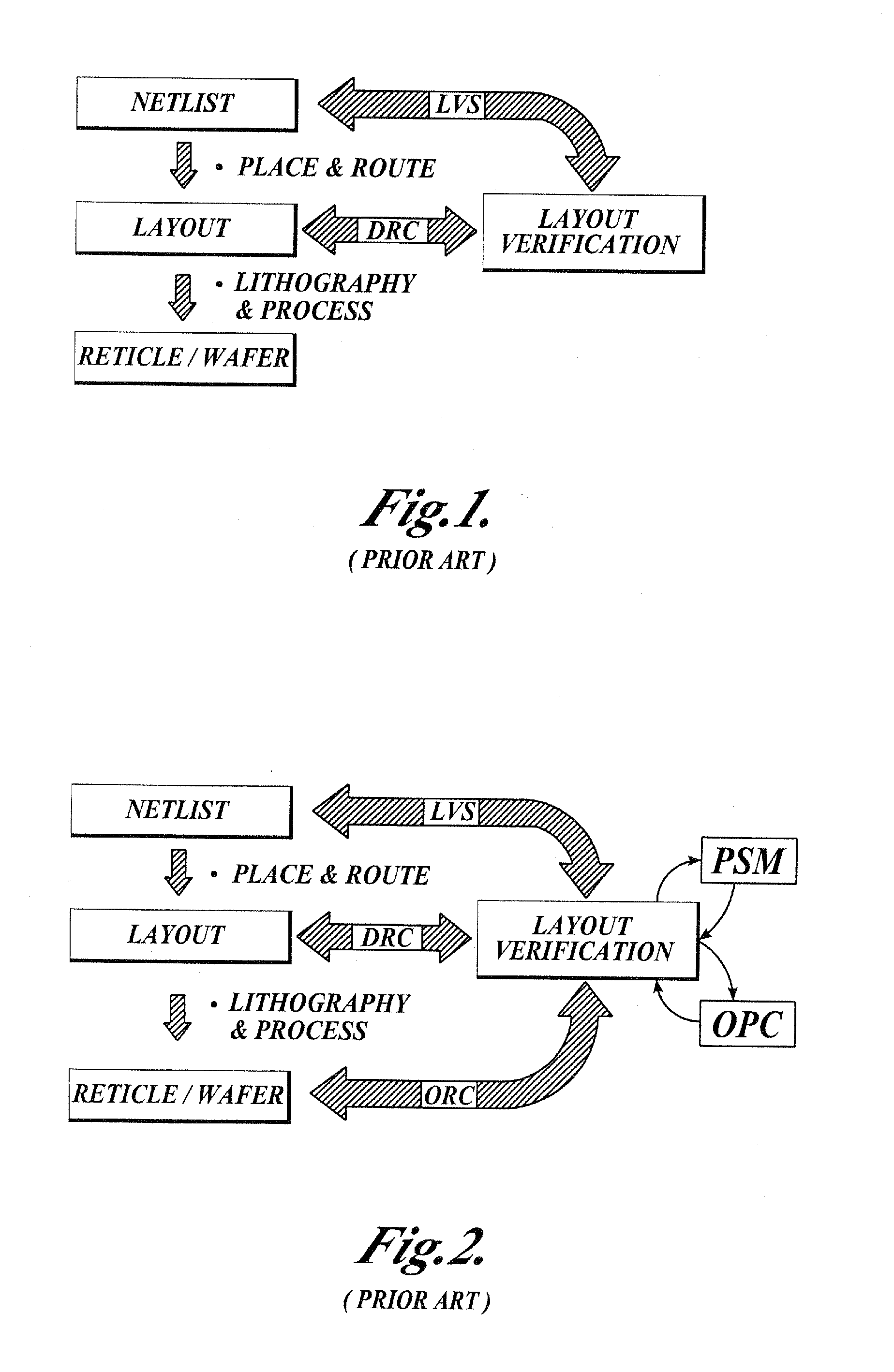
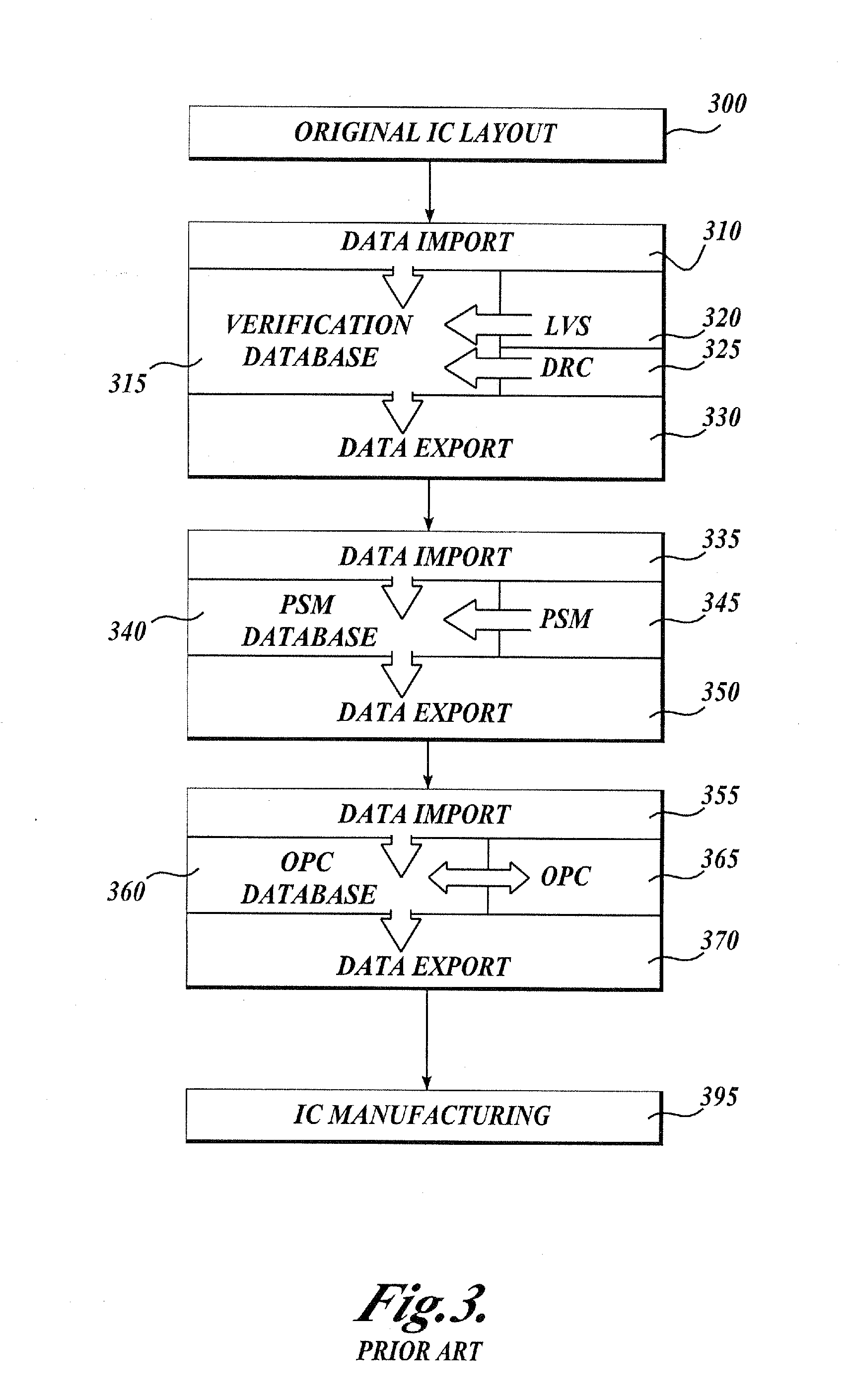
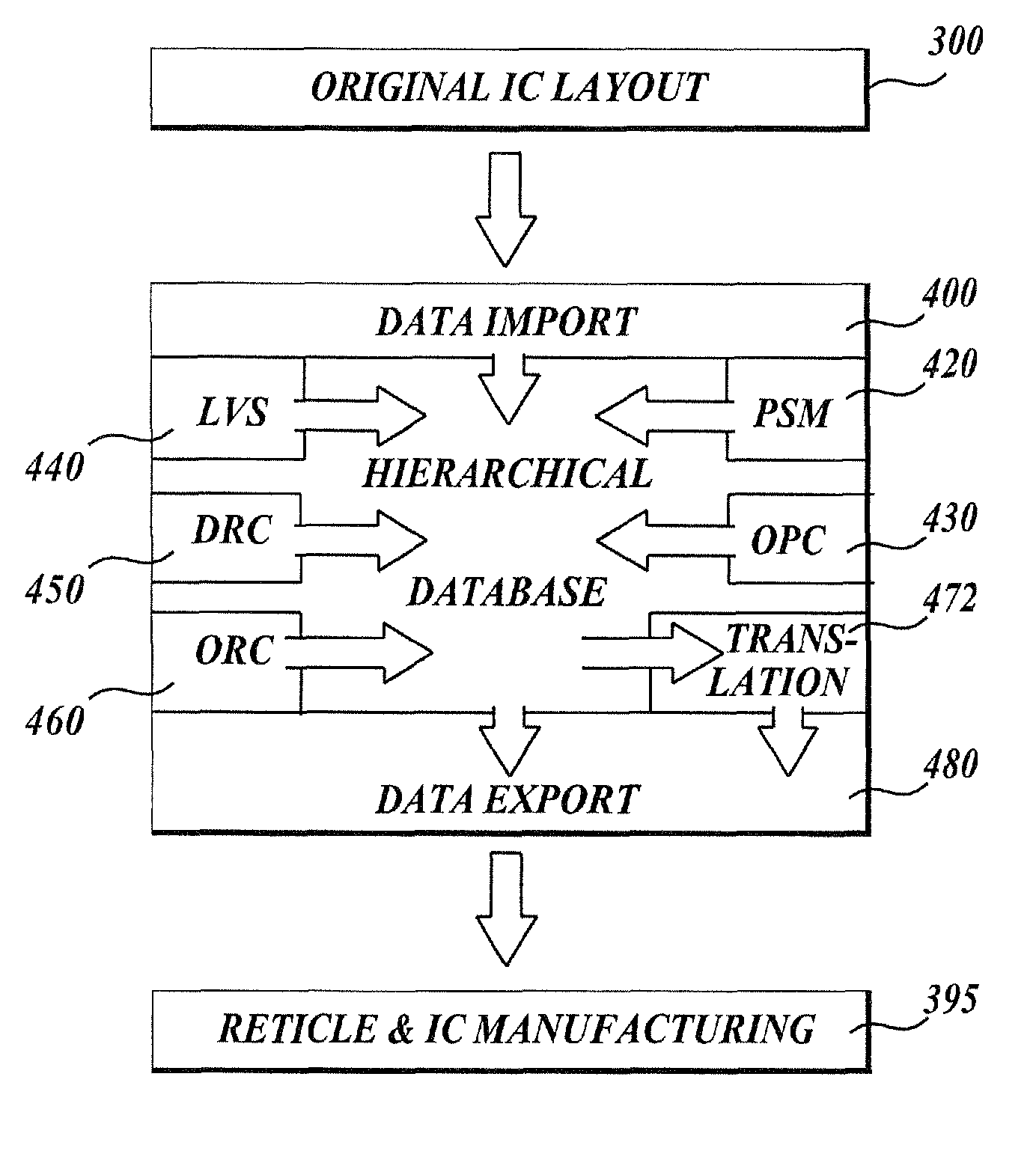
Integrated verification and manufacturability tool
InactiveUS7017141B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designComputer architectureInter layer
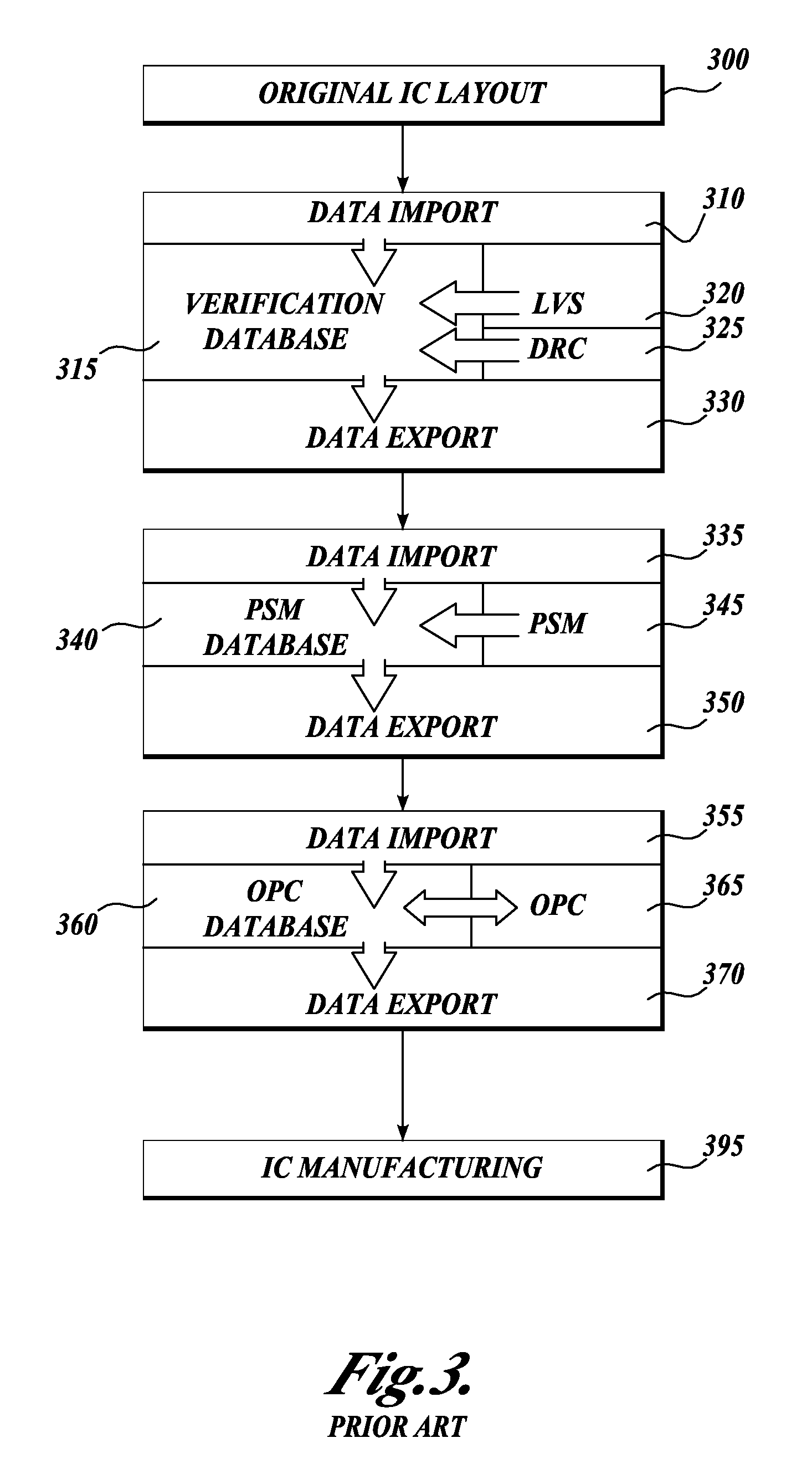
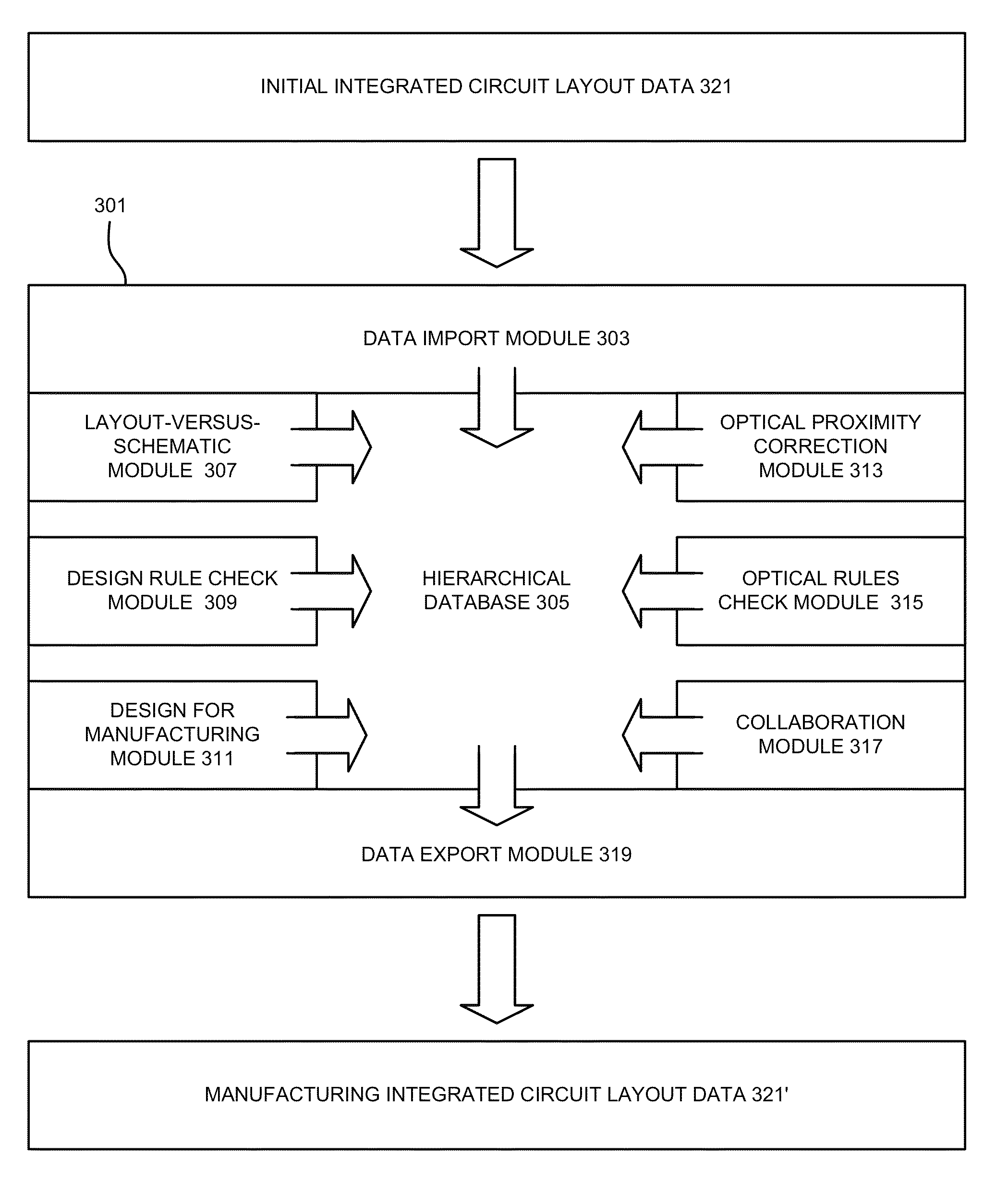
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification tools. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification tool components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification tool components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
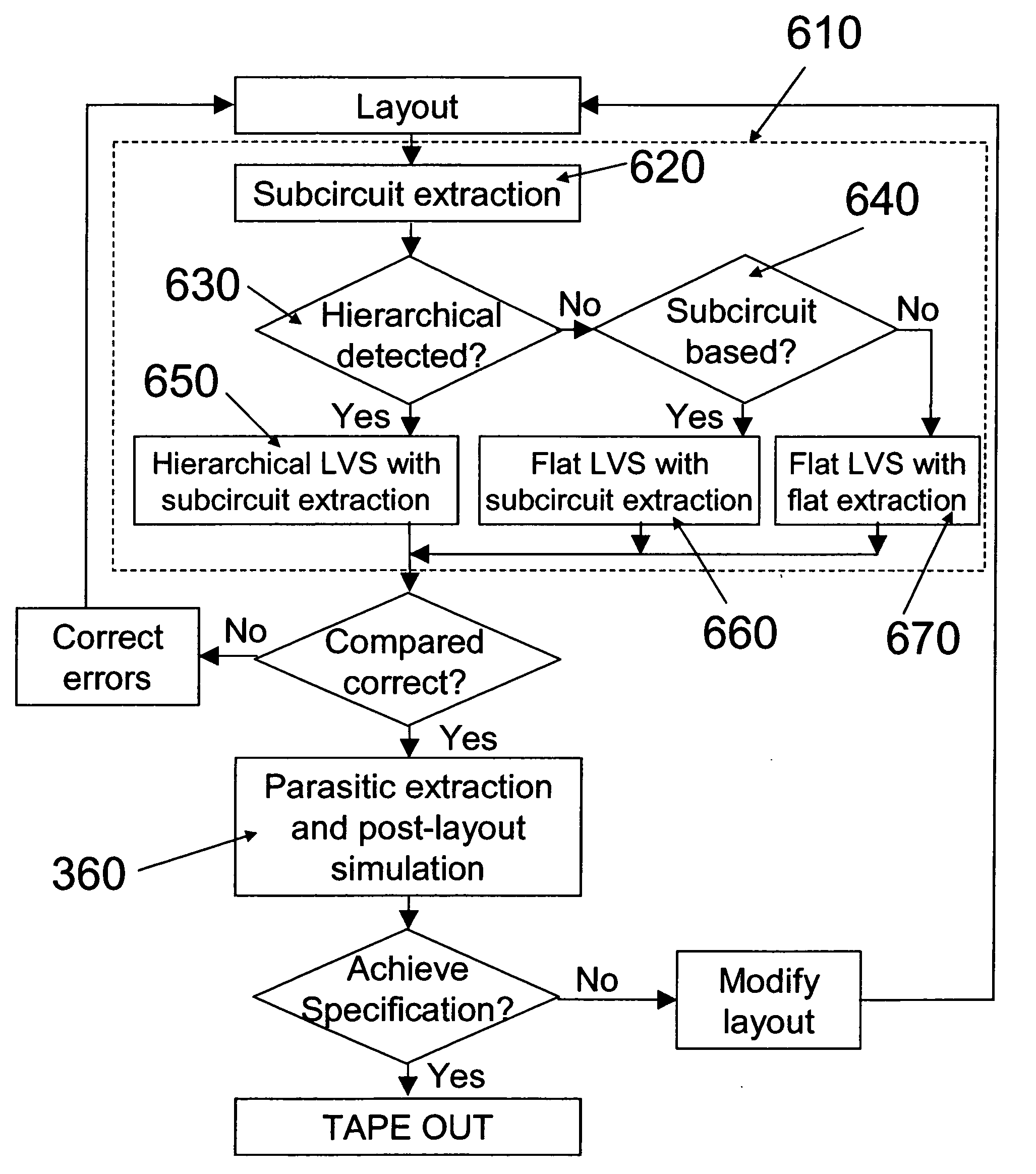
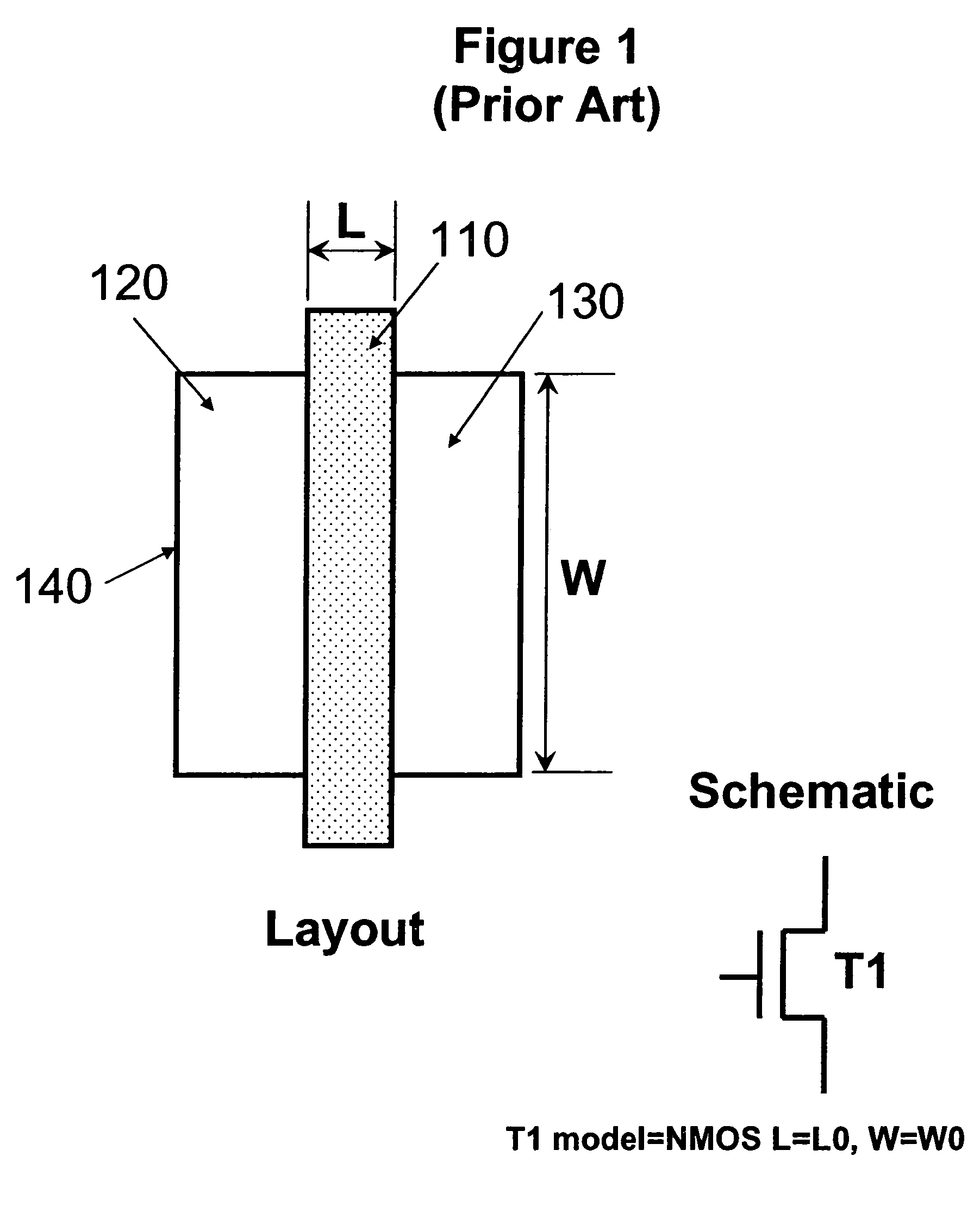
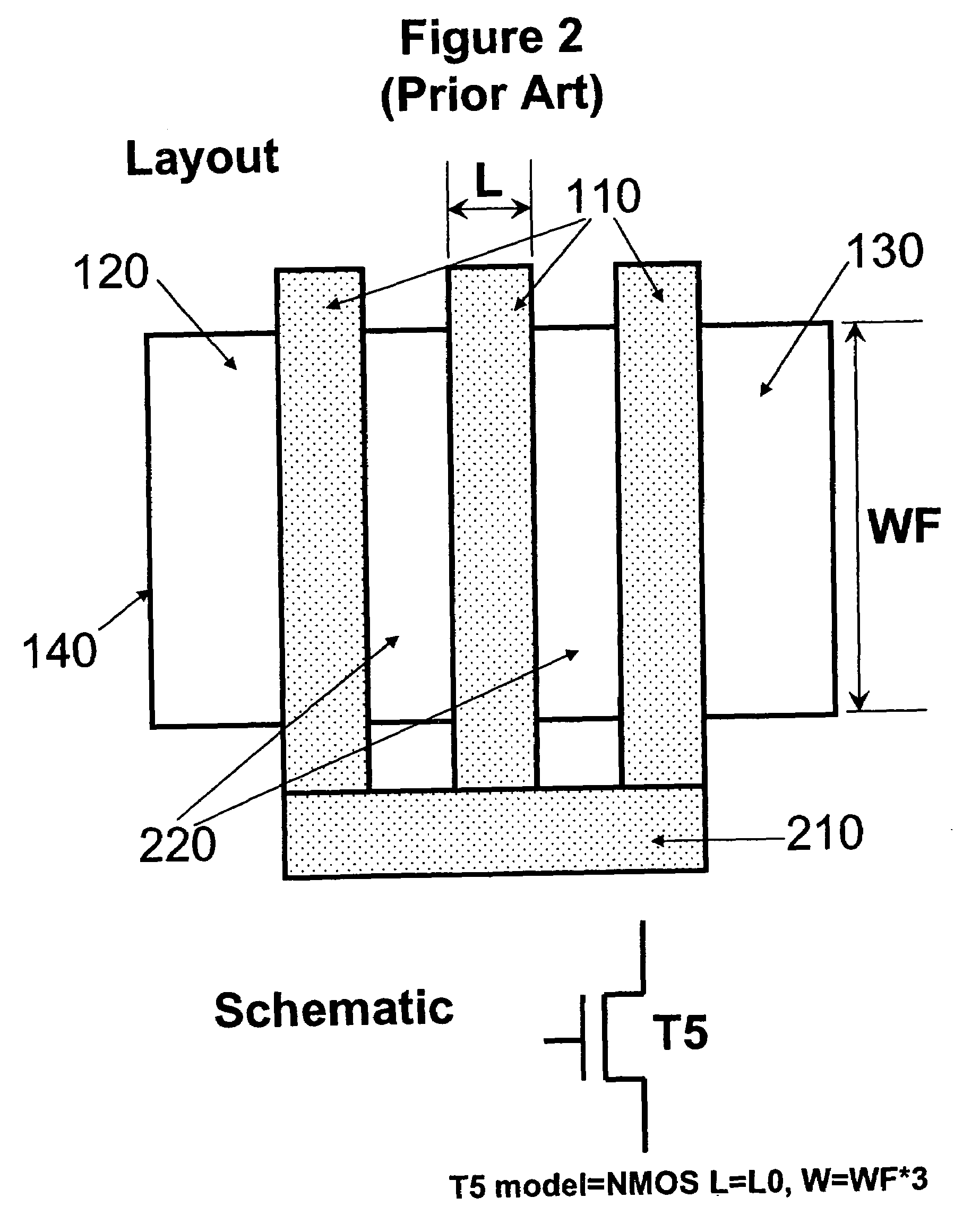
Method of checking the layout versus the schematic of multi-fingered MOS transistor layouts using a sub-circuit based extraction
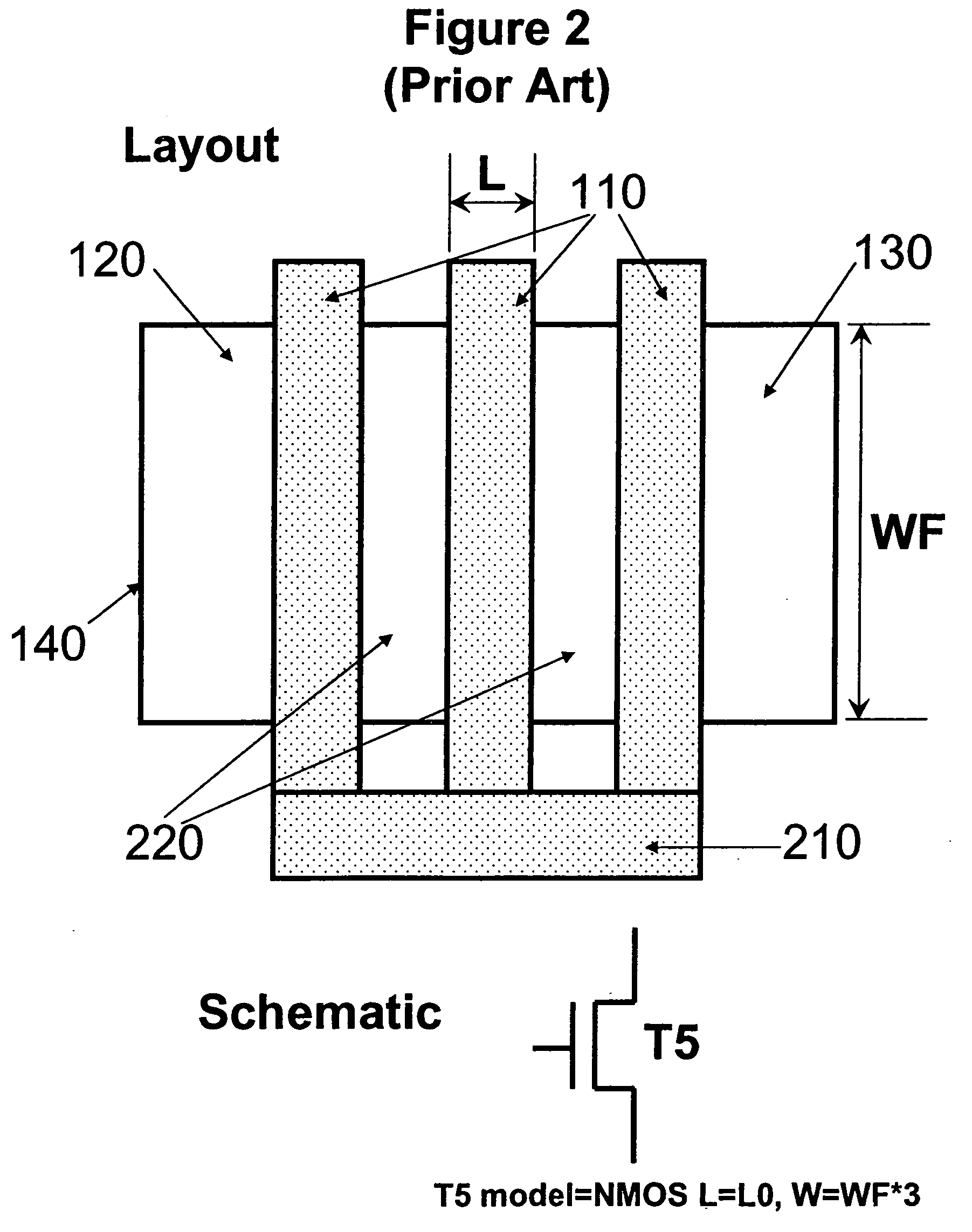
InactiveUS20050216873A1Improve trustEasy to identifyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDevice PropertiesComputer architecture
A sub-circuit based extraction method which extracts a multi-finger MOS transistor directly as a sub-circuit is described. By adding three marking layers, the method provides the layout extracted netlist with a complete list of device geometric parameters corresponding to the device properties as presented in the sub-circuit model based schematic netlist. By performing a layout-versus-schematic comparison based on all geometric parameters extracted, the layout checking is performed in a complete and accurate way where each device parameter is checked against the corresponding design schematic. This complete and accurate geometric parameter comparison enhances the confidence level of the layout physical verification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Integrated OPC verification tool
InactiveUS20060005154A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
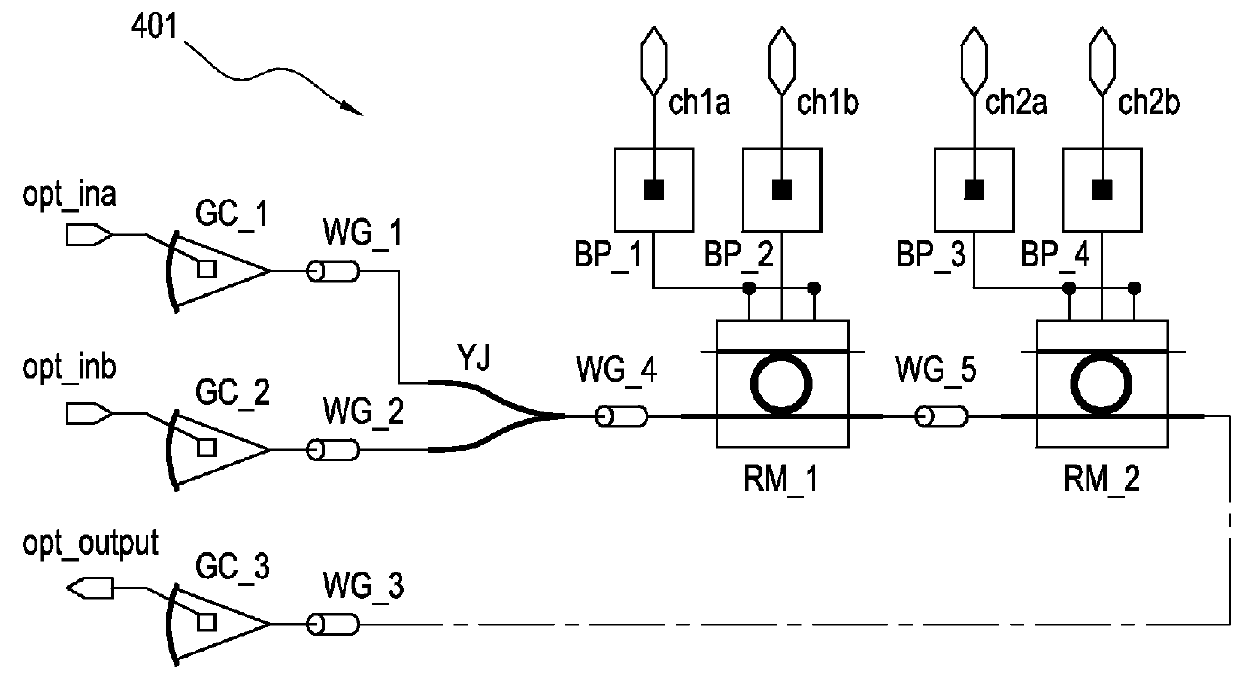
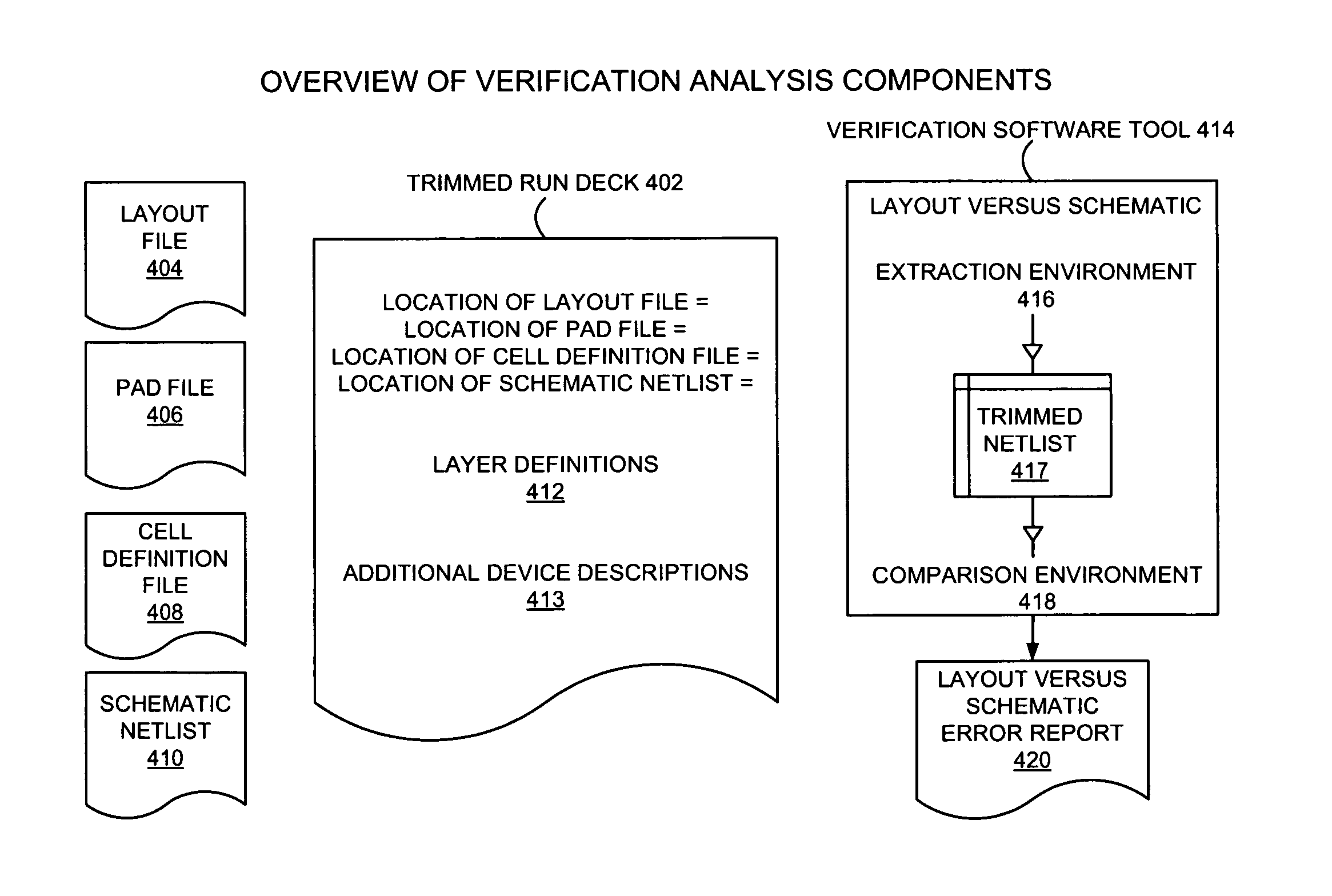
Method and computer program product for trimming the analysis of physical layout versus schematic design comparison
InactiveUS20070157140A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
A method, a computer program product, and an apparatus for performing a trimmed verification analysis comprising selecting layers of interest for a trimmed analysis, eliminating layer definitions for unselected layers to create a trimmed rundeck, and performing a layout versus schematic verification comparison to generate a trimmed error report for the selected layers of interest.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
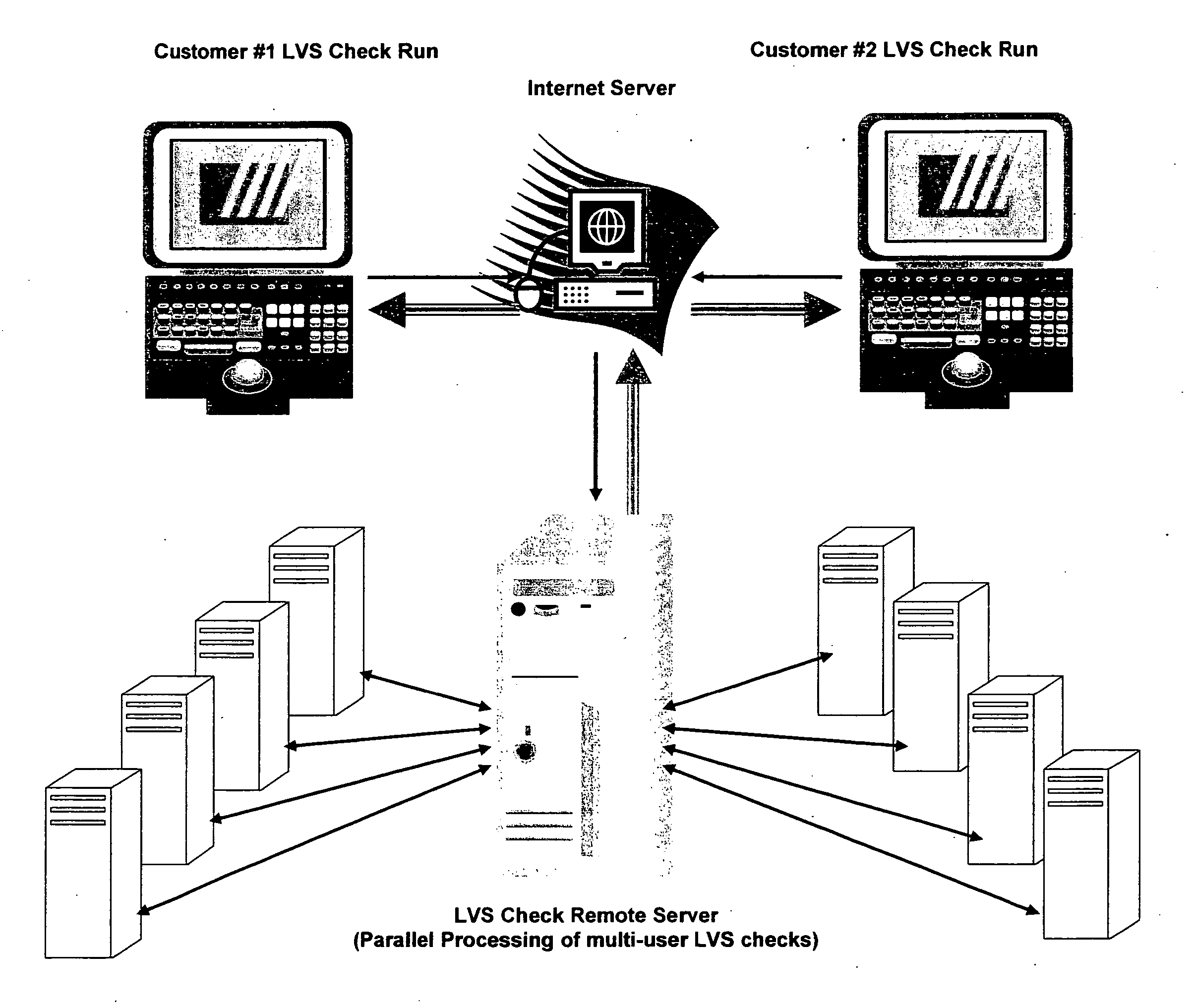
Connectivity verification of IC (integrated circuit) mask layout database versus IC schematic; LVS check, (LVS: IC layout versus IC schematic) via the internet method and computer software
InactiveUS20060200789A1Avoid repetitive drawingShorten the timeCAD network environmentCAD circuit designThe InternetLayout Versus Schematic
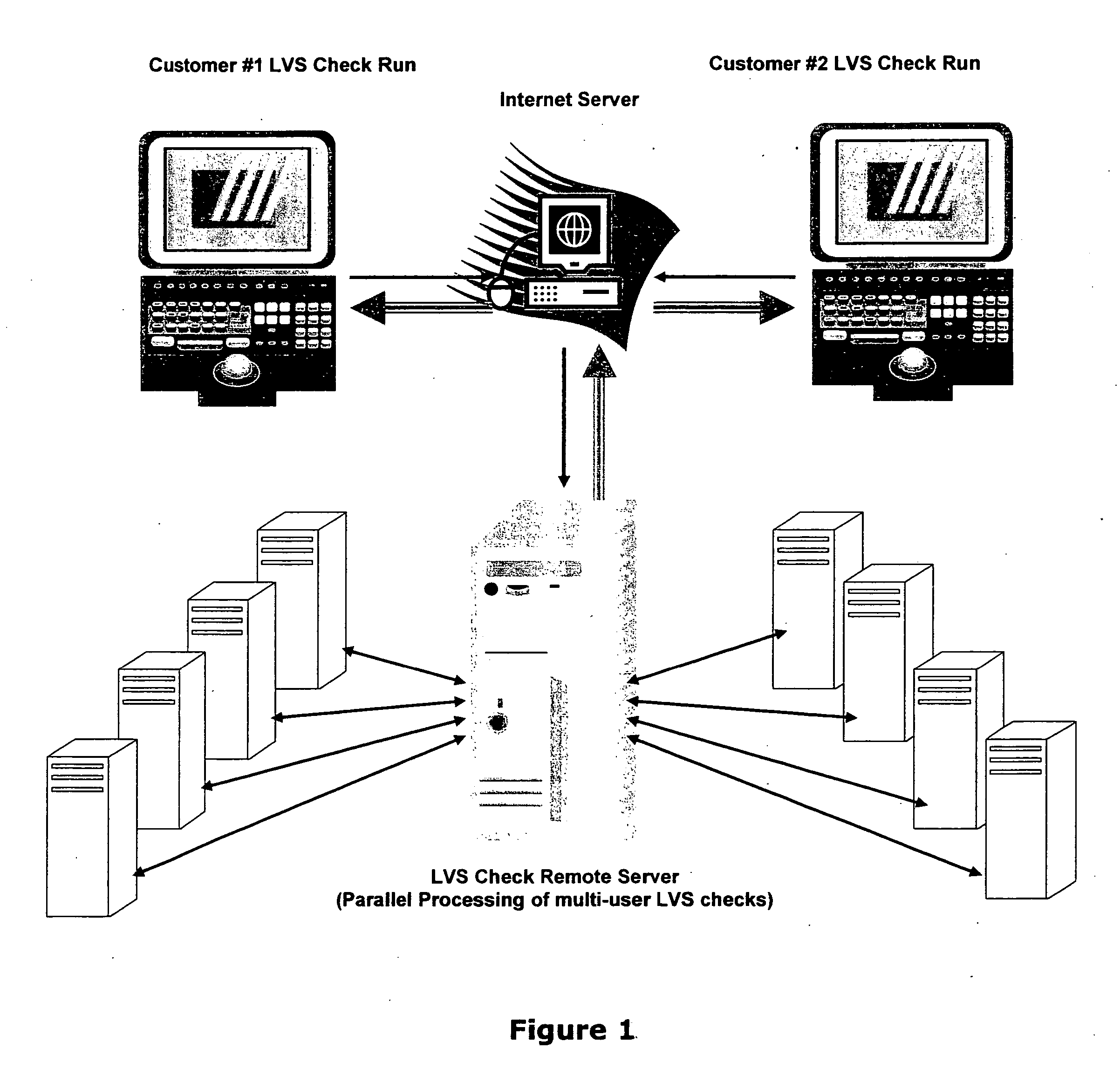
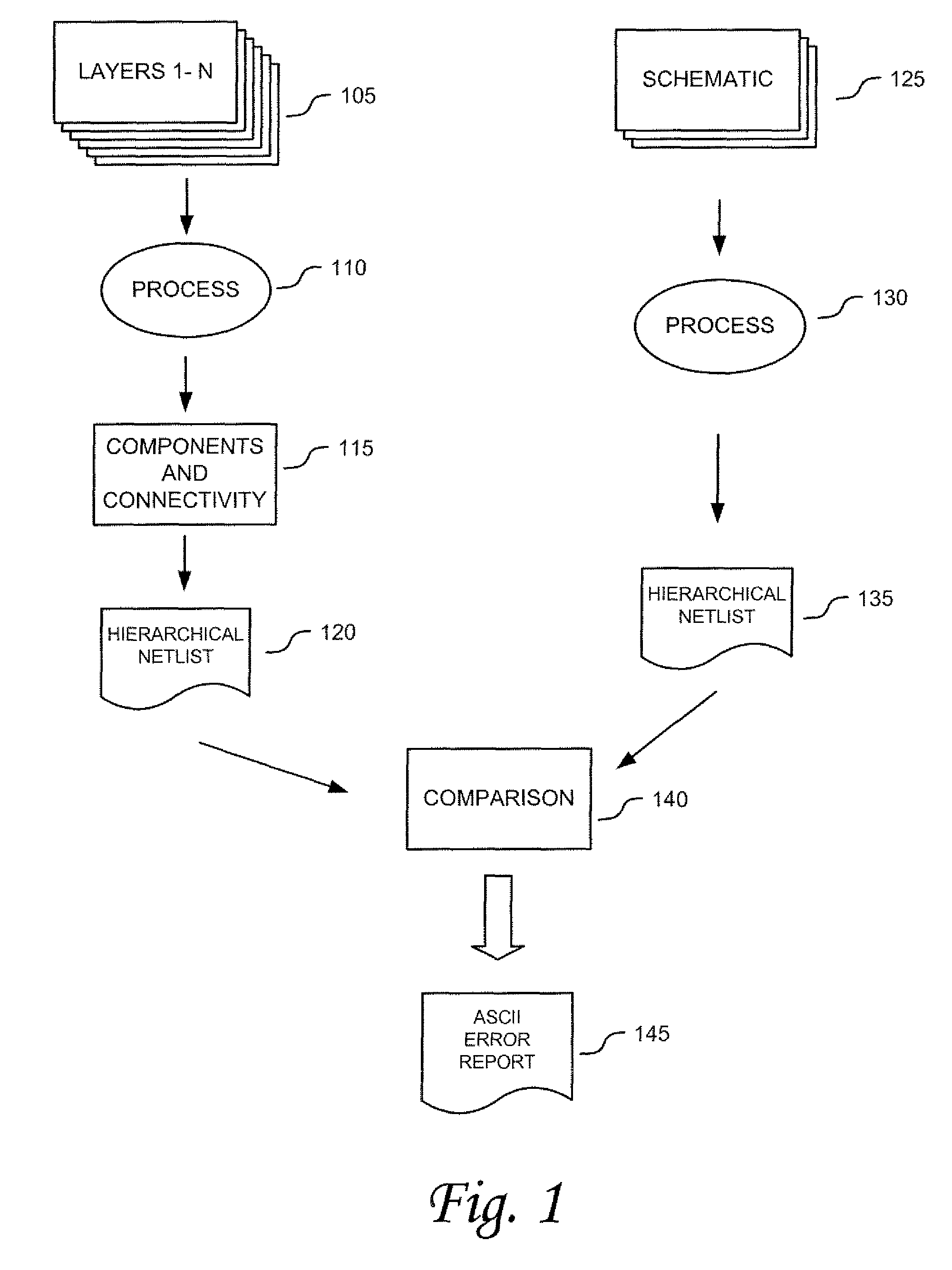
This paper describes an EDA (Electronic Data Automation) method and computer software invention for connectivity verification of IC mask Layout database versus IC Schematic; LVS Check (LVS: IC Layout versus IC Schematic) over the internet. The technique takes advantage of a unique algorithm to check the mask layout database connectivity, compare it with its corresponding schematic diagram for any mismatches in the mask layout polygons connections. The input of the tool is a mask layout database blocks (i.e.: IC layout) that were made manually and / or automatically using synthesized tools. These blocks may have some connectivity mismatches that need to be fixed in order to match the corresponding integrated circuit (IC) schematic diagrams. The output of the software tool is a text based descriptive log file and errors markers pointers that may be read into the mask layout database in order to point any connectivity mismatches of the mask layout database, comparing it to its corresponding schematic diagram. The end result is a mask layout set of markers and a text format log file that describes any mismatched connections in the mask layout database, comparing it to its corresponded schematic diagram. The software performs on individual mask layout blocks and / or on hierarchical structure of mask layout blocks. The system works hierarchically and / or flat. System also checks mask layout database incrementally, means only blocks that have been changed are checked. The system can be run via the internet using our secured protocol. The system offer a web based control panel to execute all necessary setups for submitting LVS check over the internet. The system offers the option to run on a local machine (user's computer) or on the main server over the internet. (Inventor's computer) The system also offers a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) interface to launch LVS runs via industry's standard PDA's. The procedure is fully secured by 128 bit security protocol. All necessary file including mask layout GDSII (or GDSIII) file, netlist and technology file are securely encrypted using 128 bit protocol and send to the remote server. These files are decrypted and submitted for LVS check on the remote servers. The main remote server is distributing the task among other computer system for advanced parallel processing to achieve fast results. All results log files are encrypted using 128 bit security protocol and available for download by the user. In case of local LVS check the results files are available on the user's local machine.
Owner:RITTMAN DAN
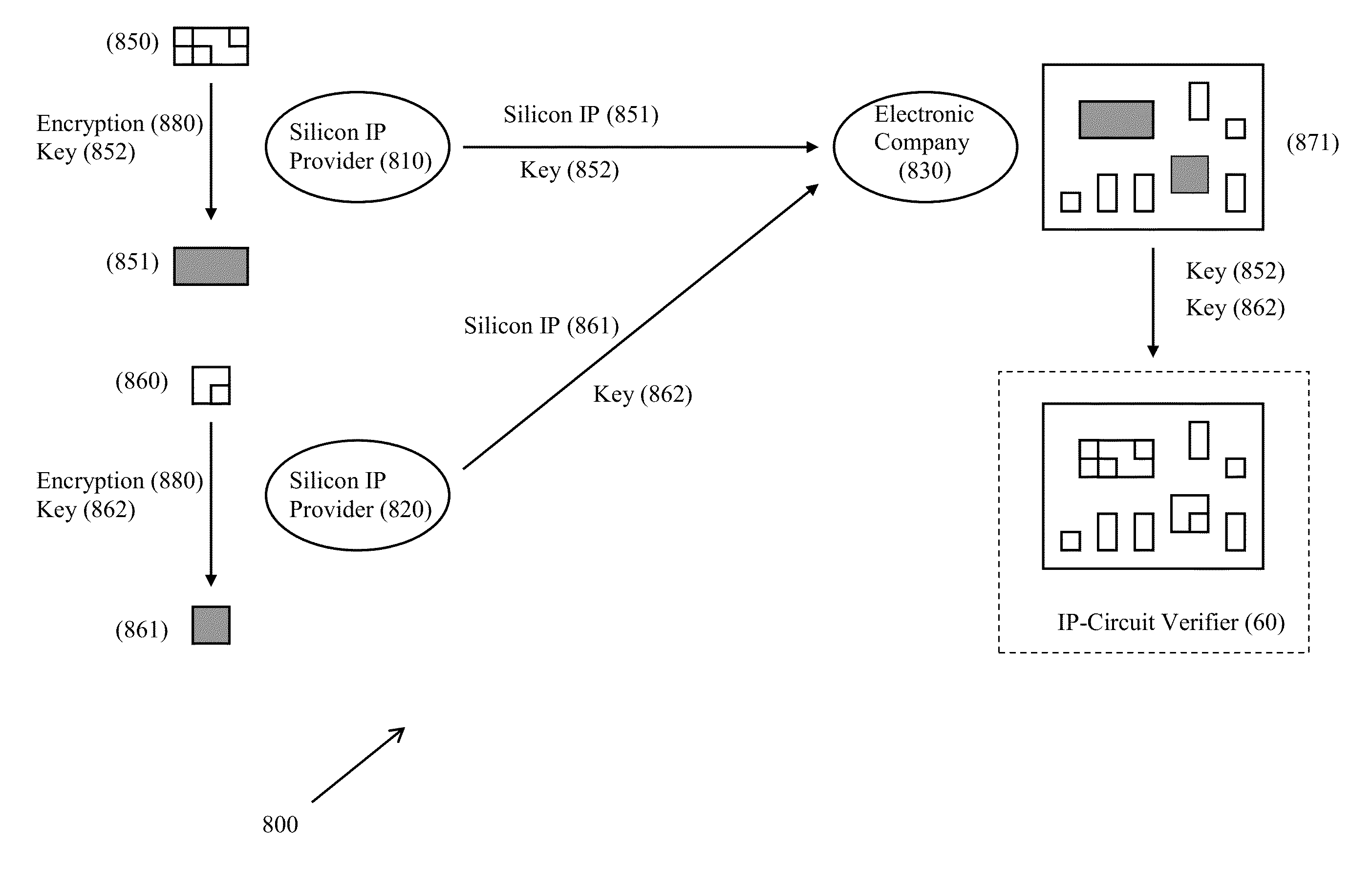
Validation of Integrated Circuit Designs Built With Encrypted Silicon IP Blocks
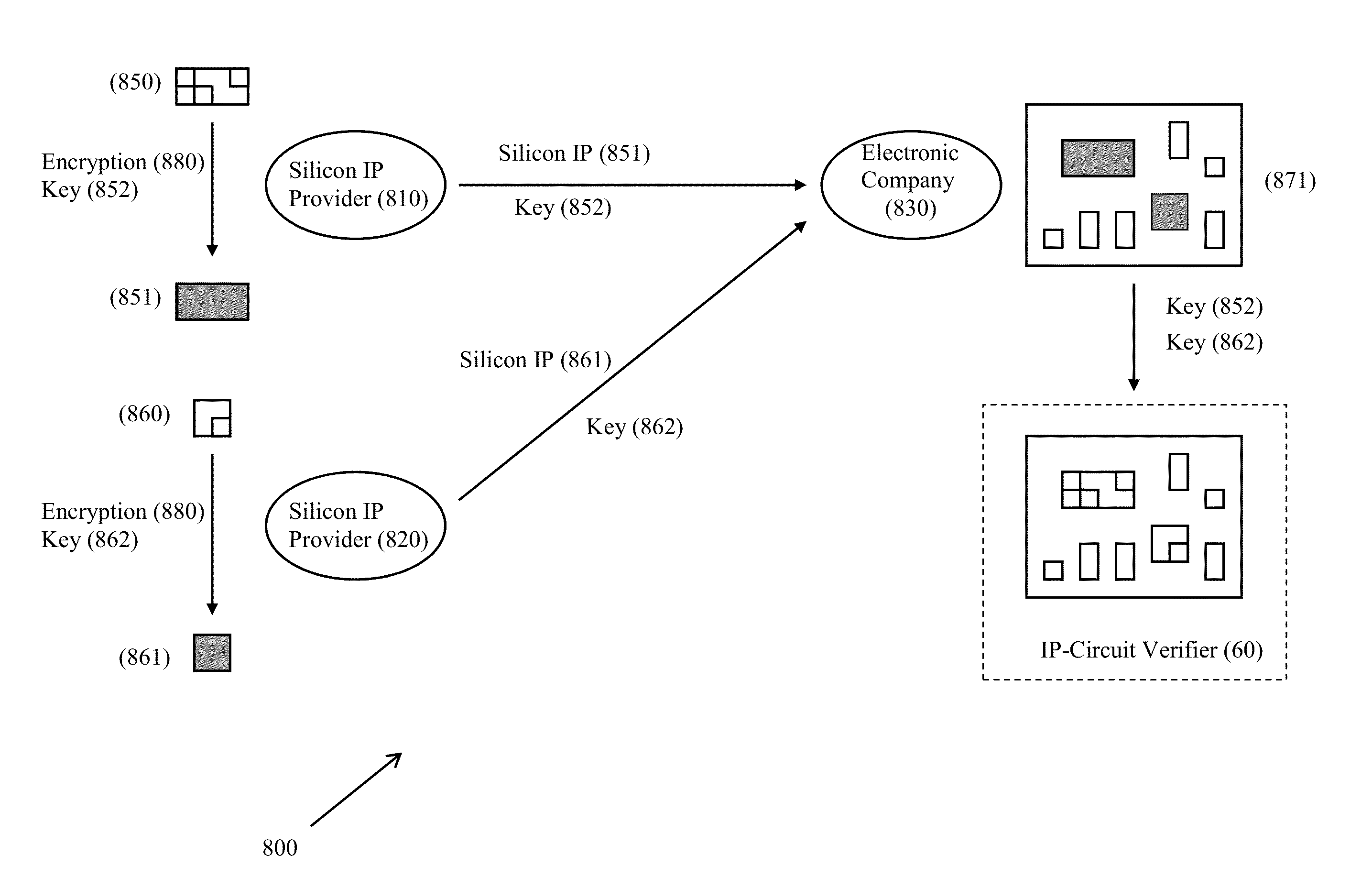
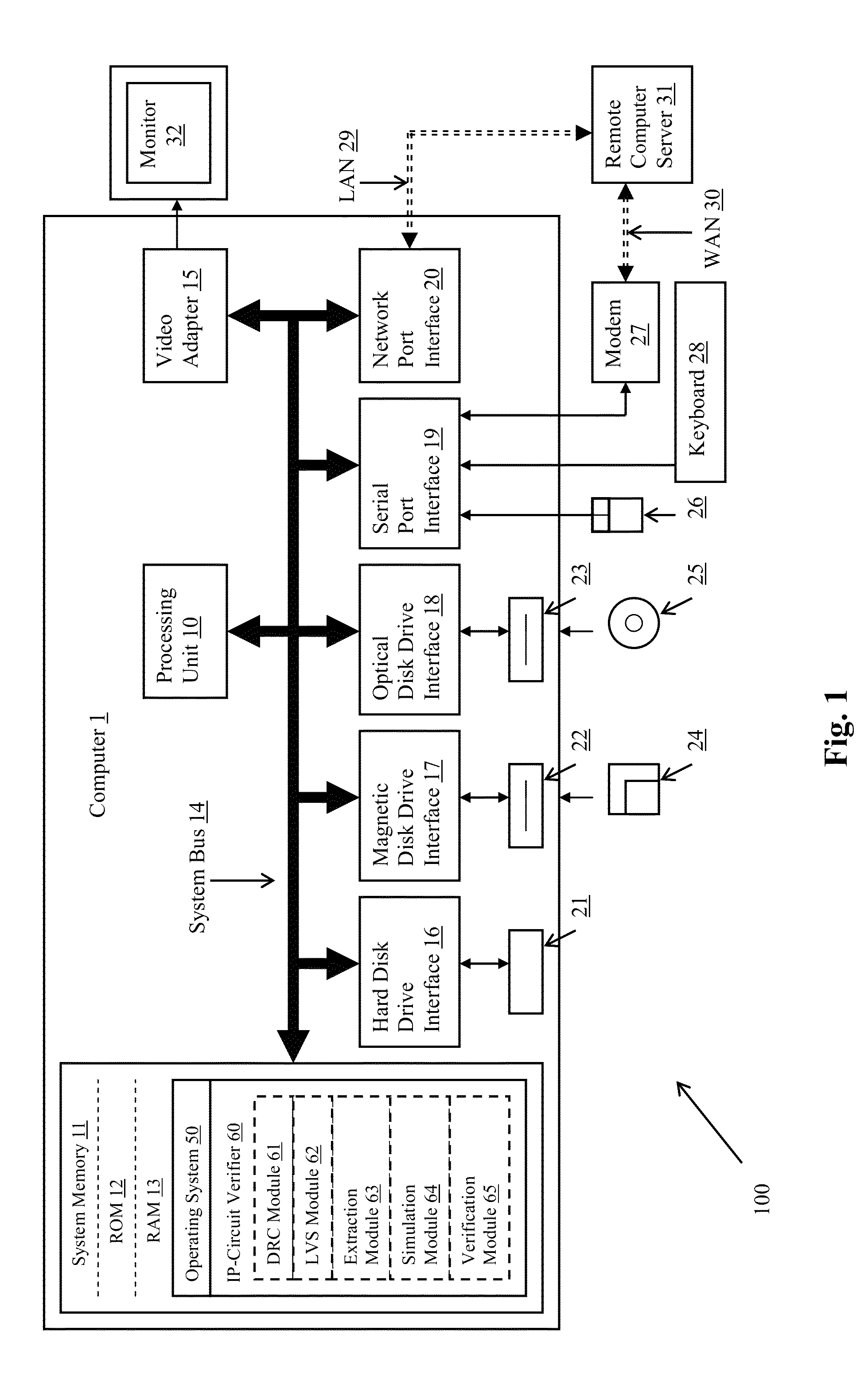
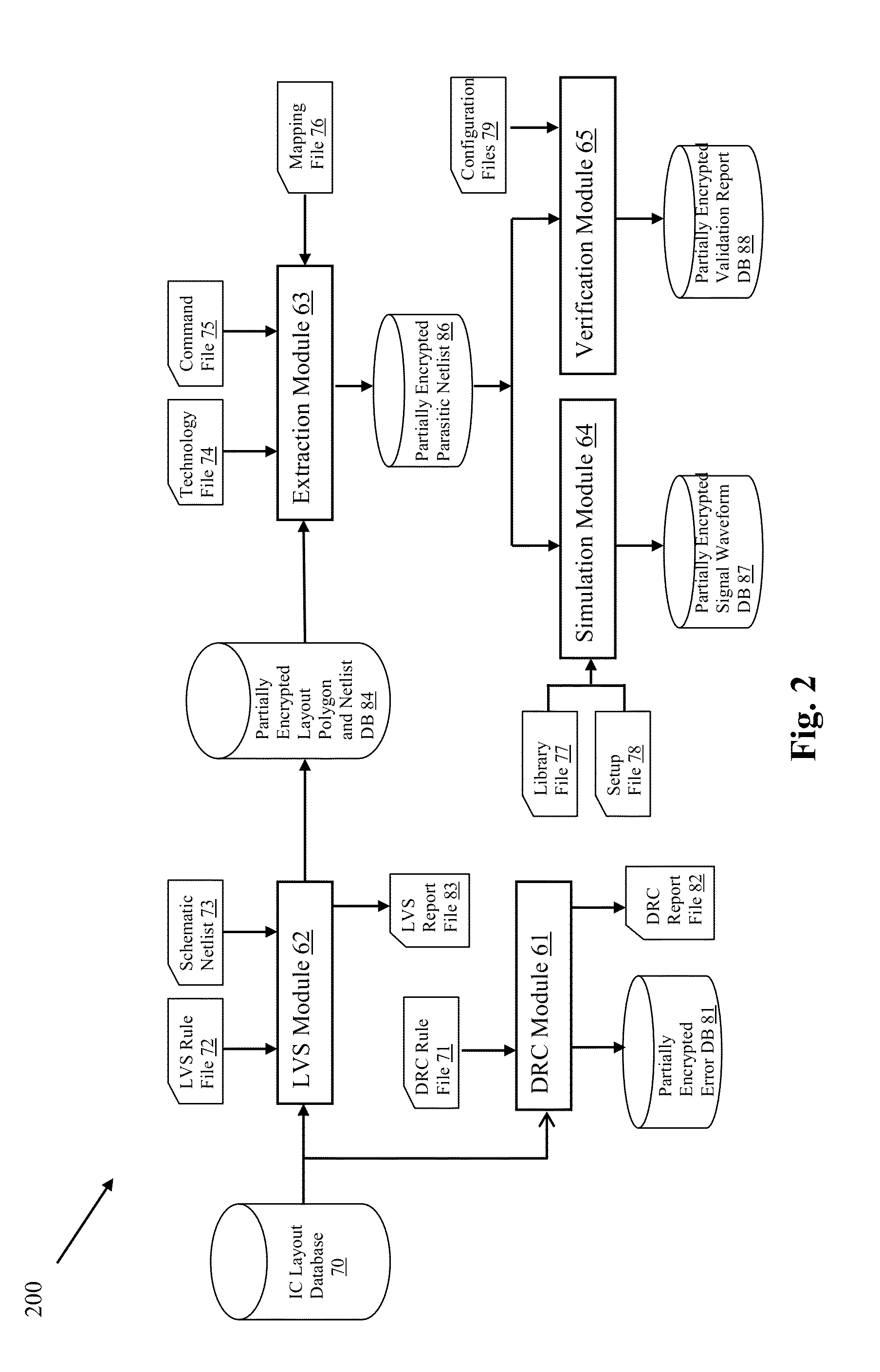
A method and system for validating integrated circuit designs that are built with encrypted silicon IP blocks decrypts the encrypted silicon IP blocks in the integrated circuit designs with the keys from IP providers. After decryption, various validation checks on the integrated circuit designs are done, such as design rule check (DRC), layout versus schematic (LVS) check, parasitic resistor capacitor (RC) extraction, circuit simulation, signal electro migration (EM) and voltage drop check, signal integrity (SI) check and static timing check, etc. After validation, any confidential data from the checking results related to the encrypted silicon IP blocks are themselves encrypted to protect the proprietary silicon IP blocks. The method and system work with silicon IP encryption technology to establish a low cost silicon IP usage and verification platform, and to enable a more cost efficient silicon IP business model.
Owner:ENCRIP
Method of checking the layout versus the schematic of multi-fingered MOS transistor layouts using a sub-circuit based extraction
InactiveUS7139990B2Improve trustEasy to identifyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureDevice Properties
A sub-circuit based extraction method which extracts a multi-finger MOS transistor directly as a sub-circuit is described. By adding three marking layers, the method provides the layout extracted netlist with a complete list of device geometric parameters corresponding to the device properties as presented in the sub-circuit model based schematic netlist. By performing a layout-versus-schematic comparison based on all geometric parameters extracted, the layout checking is performed in a complete and accurate way where each device parameter is checked against the corresponding design schematic. This complete and accurate geometric parameter comparison enhances the confidence level of the layout physical verification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Integrated OPC verification tool
InactiveUS7412676B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
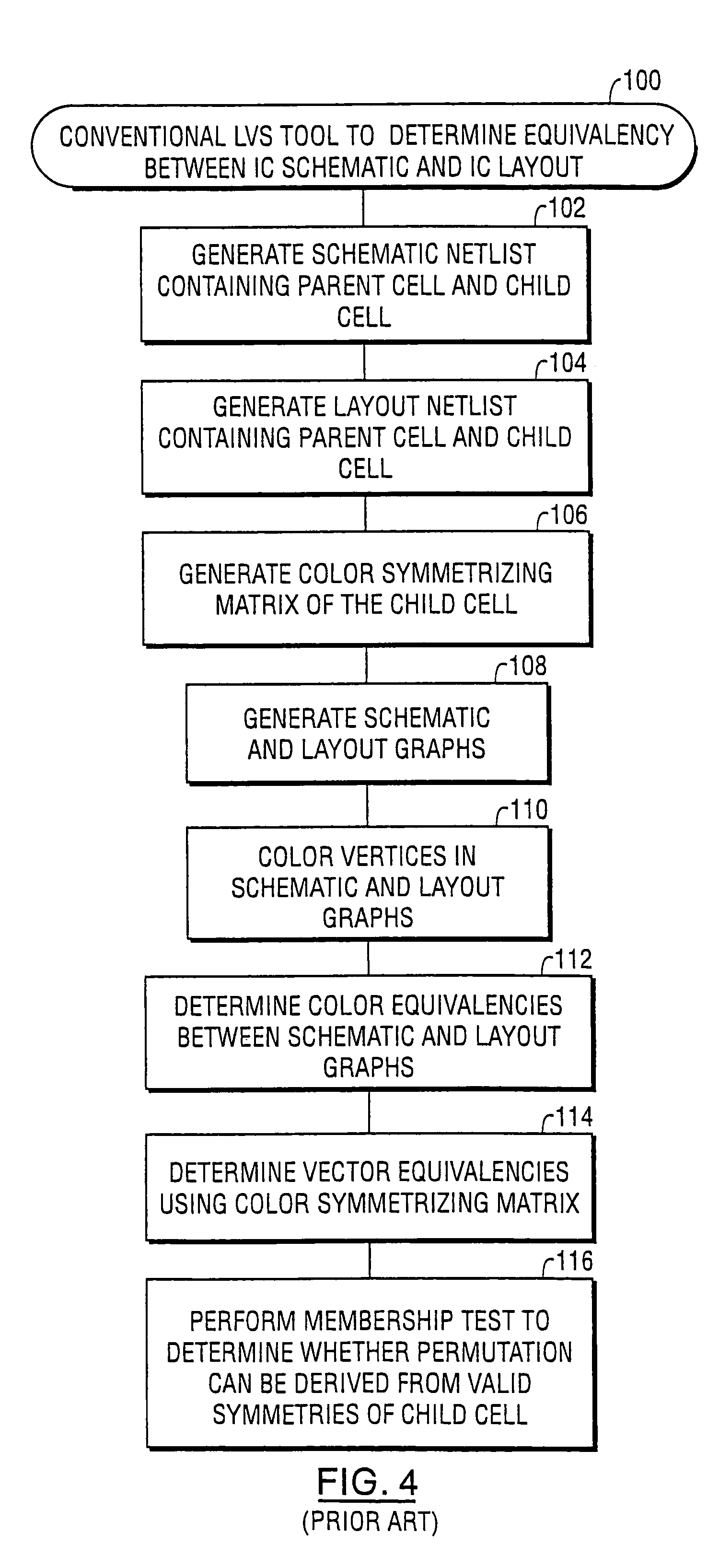
Methods, apparatus and computer program products that perform layout versus schematic comparison of integrated circuits using advanced pin coloring operations
InactiveUS6988253B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLayout Versus SchematicEngineering
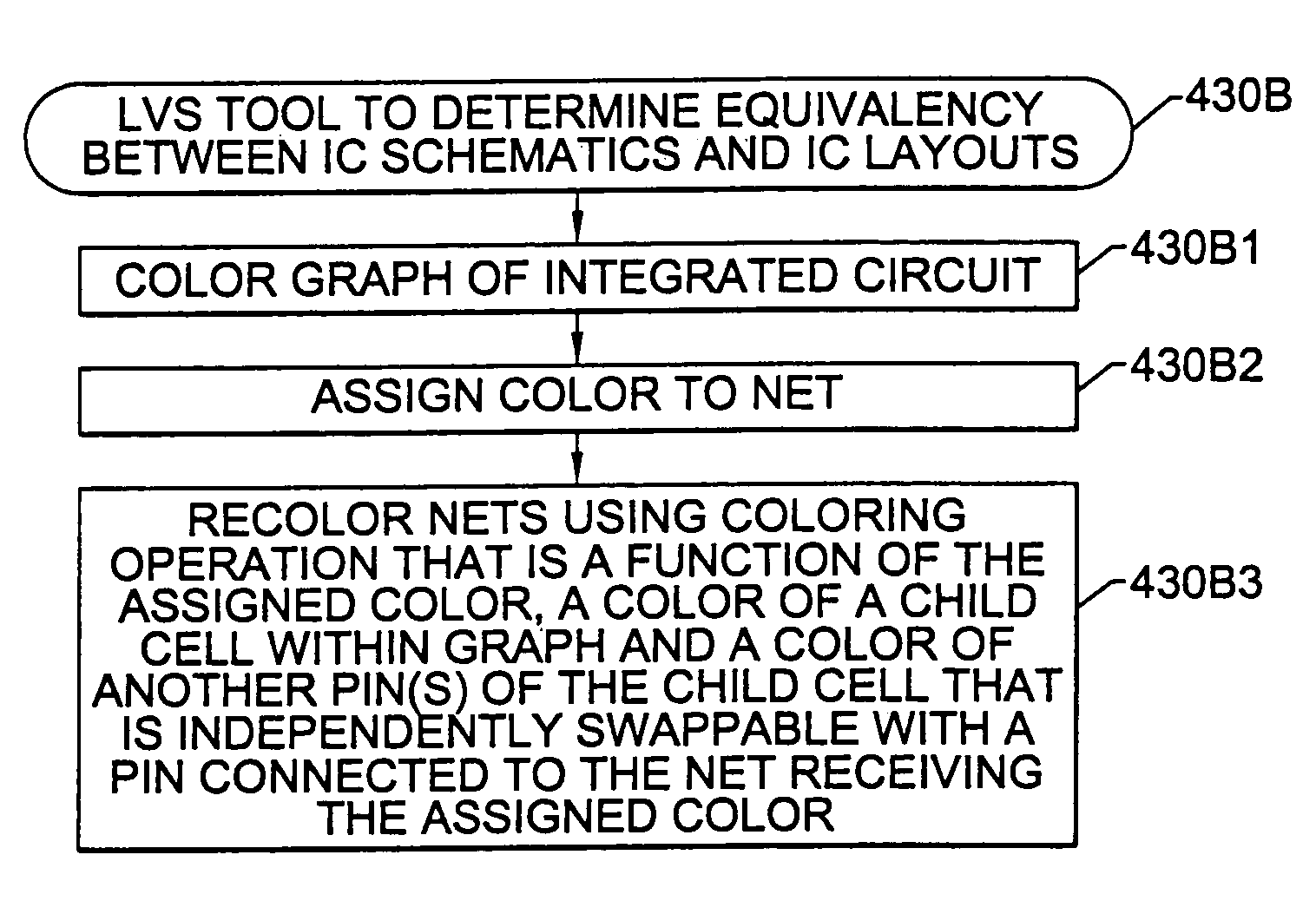
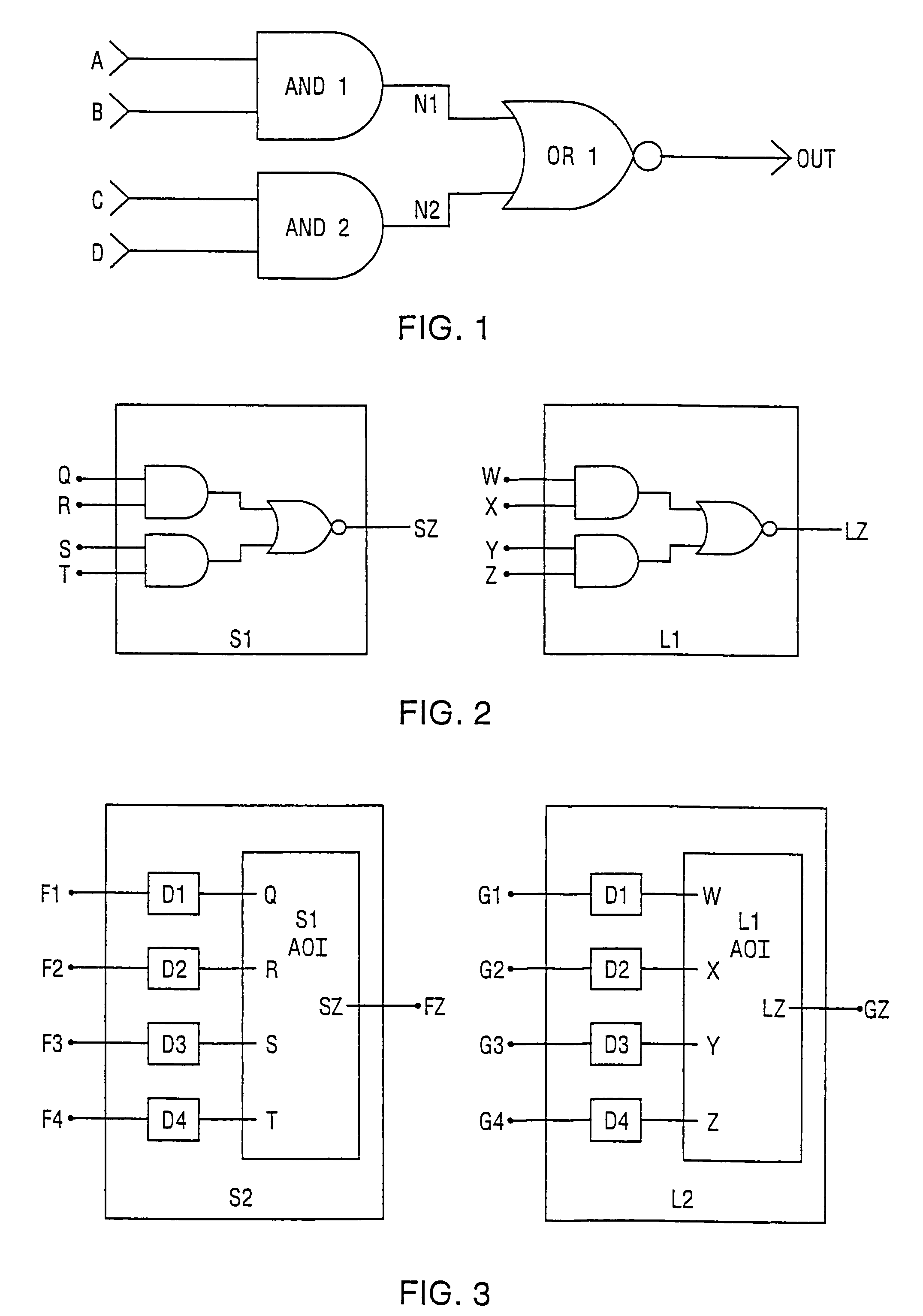
A layout versus schematic (LVS) comparison tool determines one-to-one equivalency between an integrated circuit schematic and an integrated circuit layout by performing operations to color a schematic graph of a parent cell to an equilibrium state. An operation is then performed to recolor nets connected to first and second child cells having the same device value within the parent cell, using a net coloring operation that recolors a first plurality of symmetric pins of the first child cell and recolors a second plurality of symmetric pins of the second child cell. Distinct device values are then generated for the first and second child cells by determining a first product of the colors of the recolored first plurality of symmetric pins and a second product of the colors of the recolored second plurality of symmetric pins. The operations to recolor the nets preferably include coloring a first pin of a child cell within a parent cell using a pin coloring operation that is a function of a device value of the child cell and a color of each of the pins of the child cell that are independently swappable with the first pin, but is independent of a color of a second pin of the child cell that is dependently swappable with the first pin.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Integrated opc verification tool
InactiveUS20080256500A1Digital data processing detailsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentInter layerComputer architecture
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
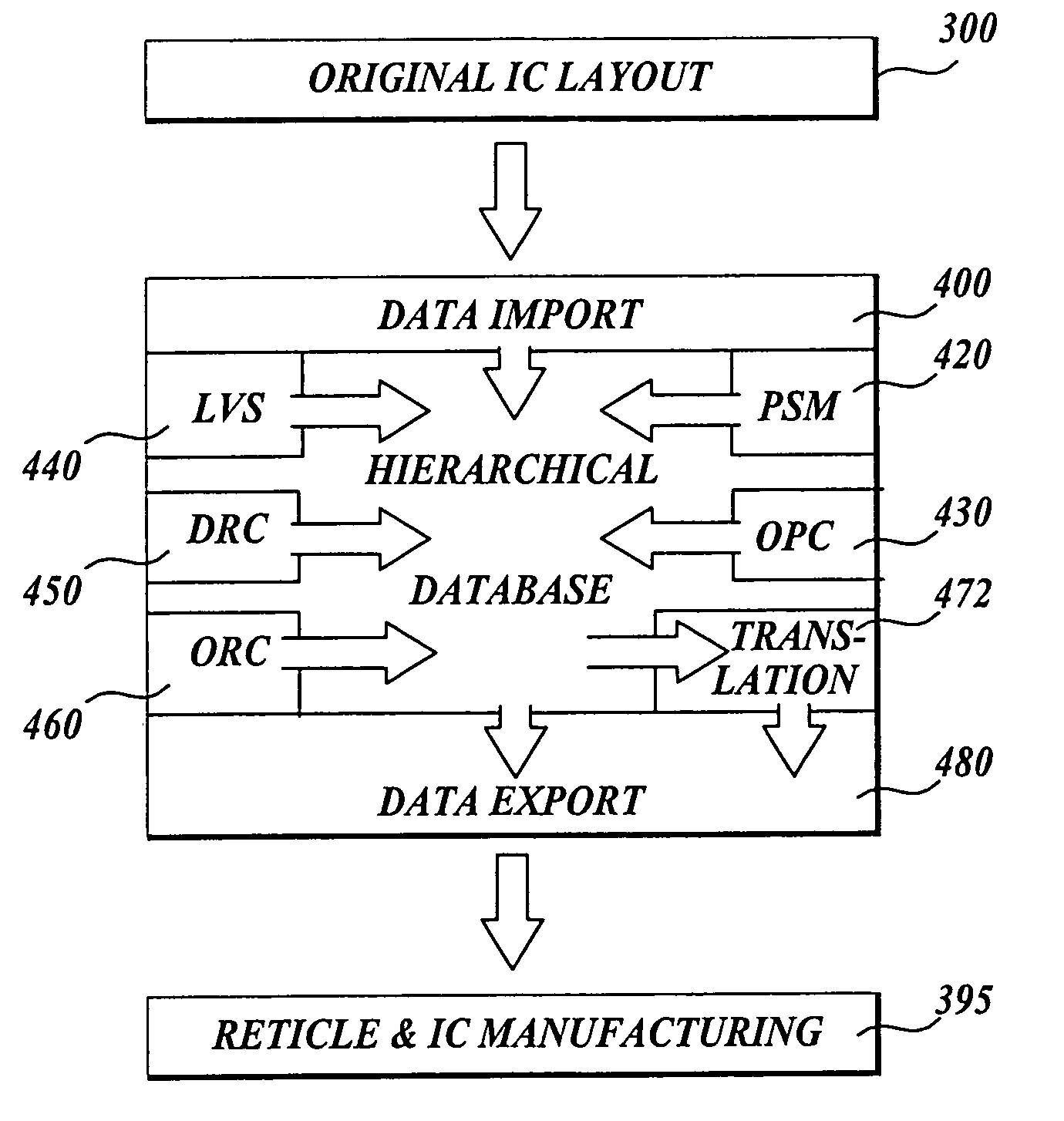
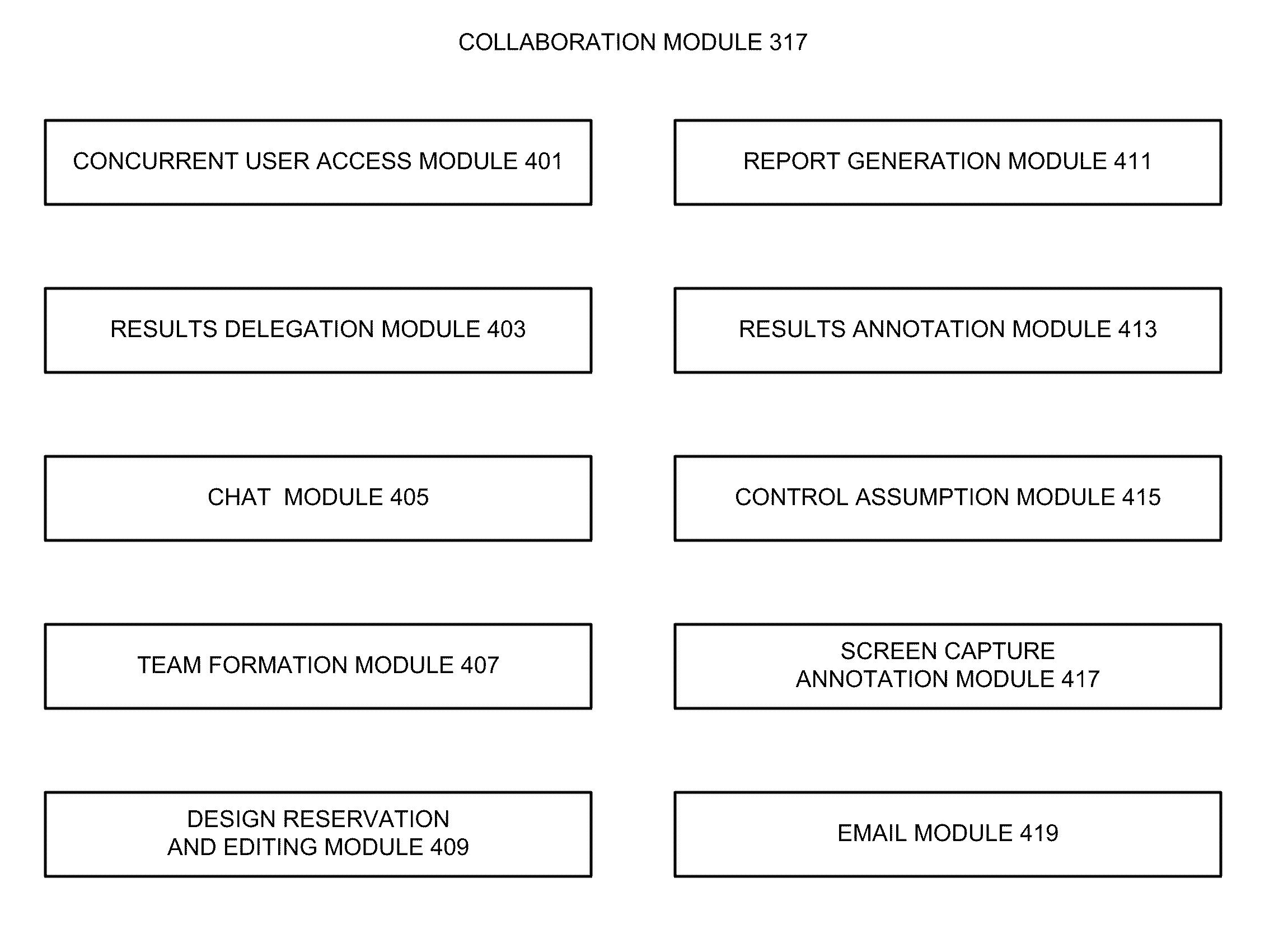
Collaborative environment for physical verification of microdevice designs
A collaborative environment for performing physical verification processes on integrated circuit designs. Multiple physical verification results may be stored in a “unified” results database / directory (e.g., unified at least from a user's perspective), where results from various verification processes, such as Design-Rule-Check (DRC) processes, Layout-Versus-Schematic comparison (LVS) processes, Design-For-Manufacturing (DFM) processes Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) processes, and Optical Rule Check (ORC) processes are accessible from the same style of user interface, which may be a graphical user interface. The basic abilities for design team-based interactions can be equally available to each process involved in the physical verification of an integrated circuit design.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
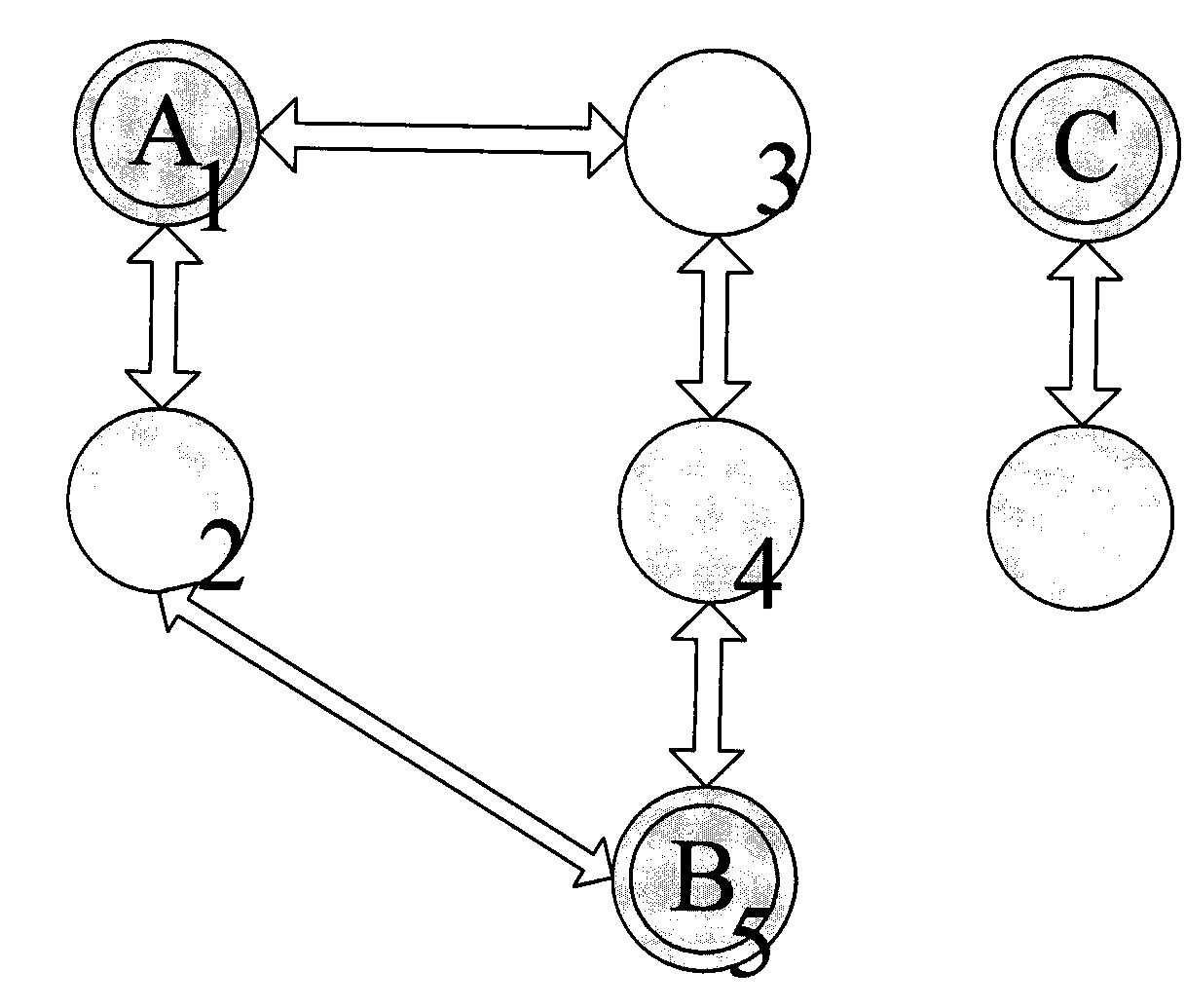
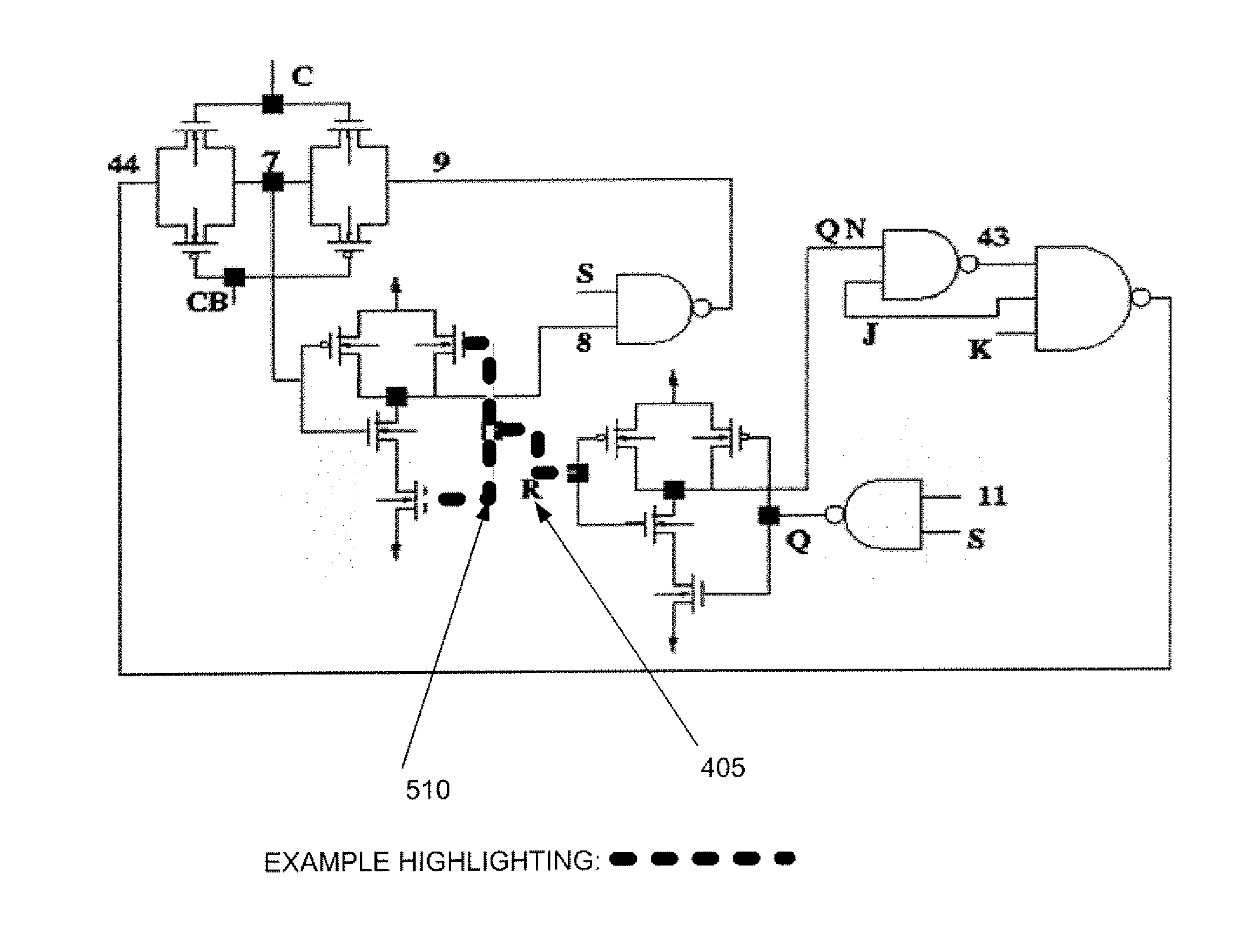
Layout versus schematic error system and method
InactiveUS20090064077A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designGraphicsComputer architecture
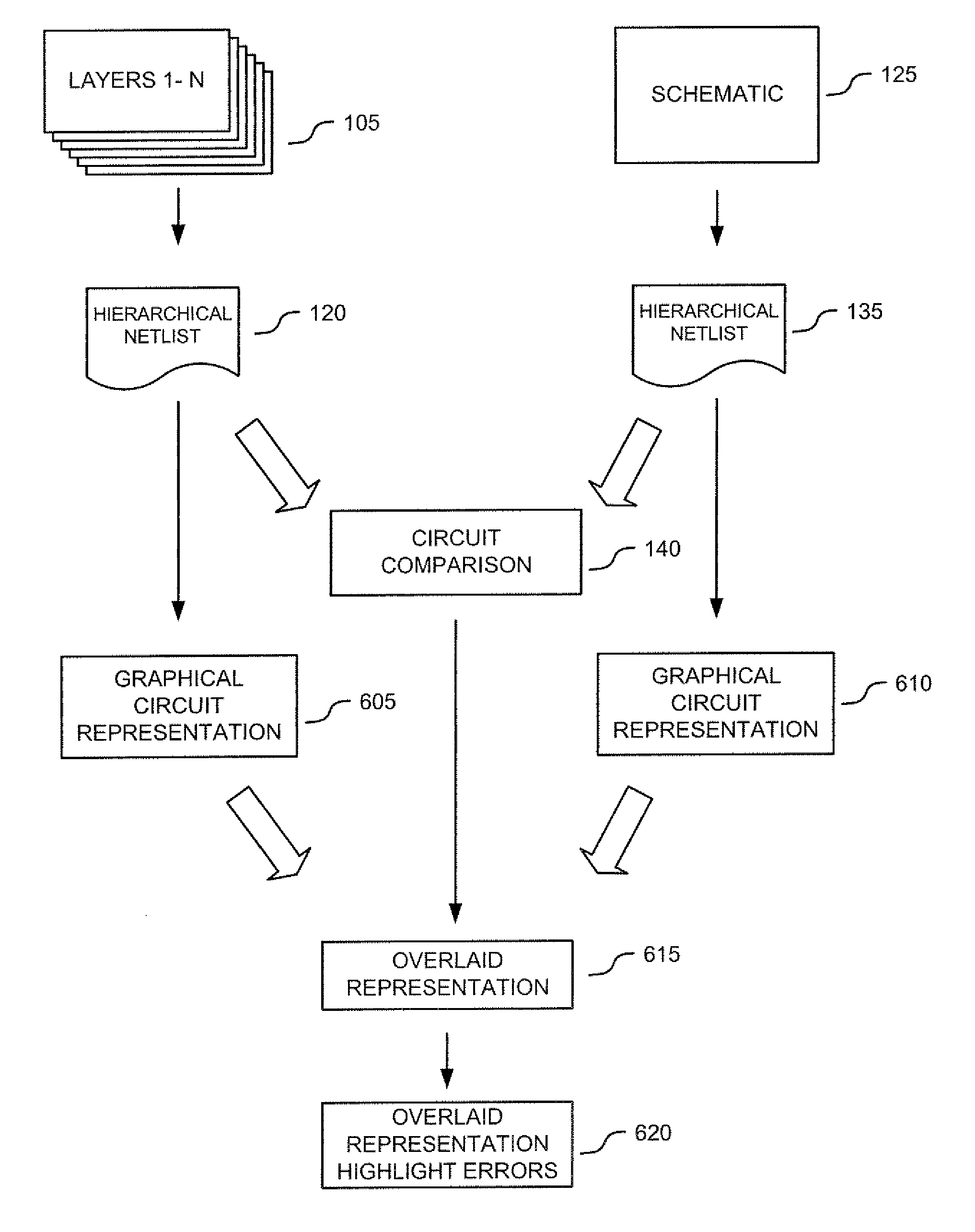
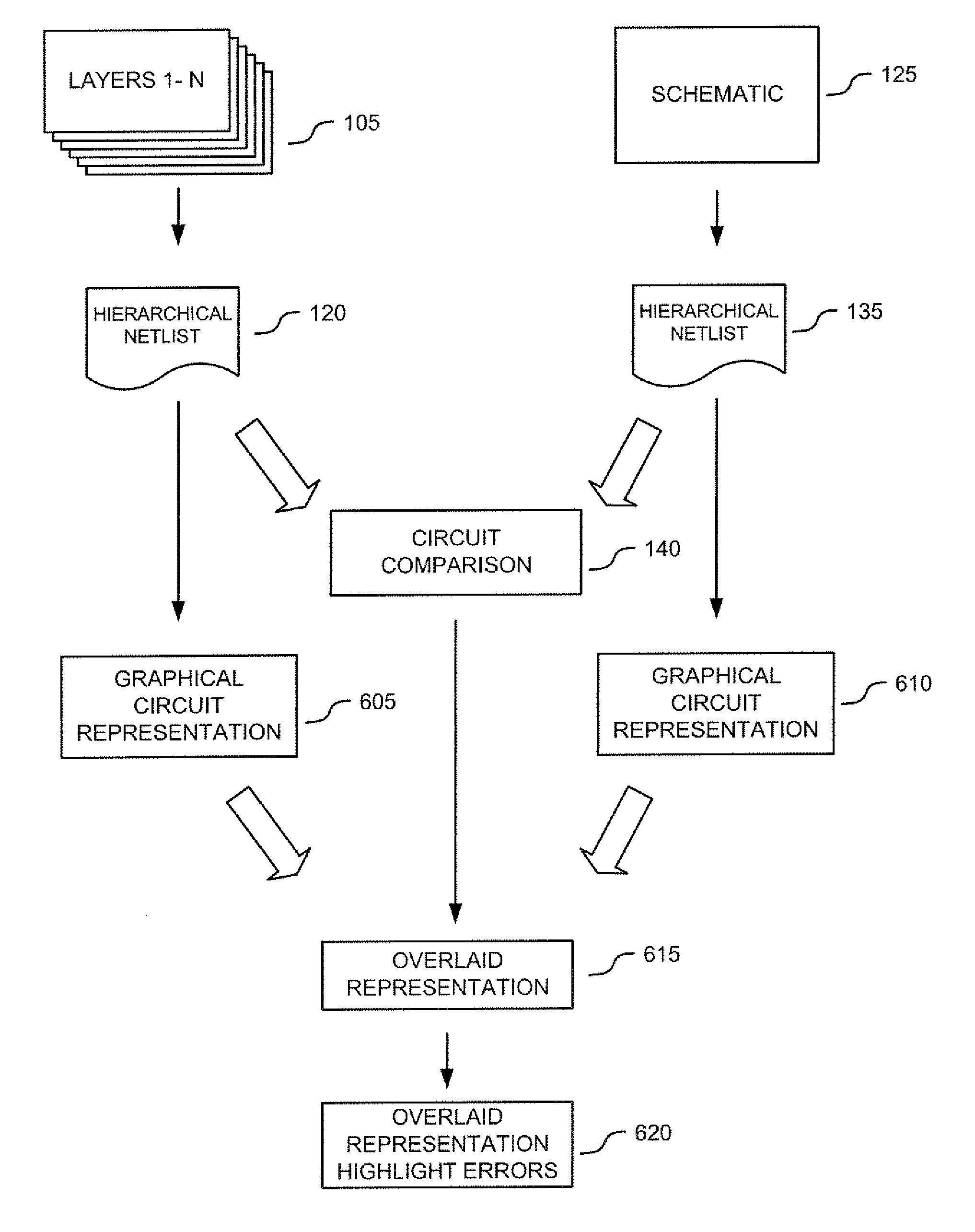
According to various embodiments of the invention, systems and methods for presenting Layout Versus Schematic (LVS) errors within a layout using a visual circuit representation of the design and highlighting is provided. One embodiment includes overlaying the layout circuit representation on the schematic circuit representation with highlighting that indicates the LVS errors. The method of such an embodiment compares a layout netlist against a schematic netlist in order to identify the layout-versus-schematic errors, generates a graphical representation of the layout netlist and a graphical representation of the schematic netlist, displays an overlay of the graphical representation of the layout netlist with the graphical representation of the schematic netlist and then, highlights the identified layout-versus-schematic errors that are present.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Layout verification method used for polysilicon cell edge structure in FinFET standard cells
The invention discloses a method for standard cells using an FinFET standard cell structure with polysilicon on OD edges. FinFET transistors are used to define the standard cells, and the standard cells comprise grid structures forming a transistor at a crossing point with a semiconductor fin. Polysilicon pseudo-structures are formed in active areas of the standard cells or edges of OD areas. In a design process, a pre-layout netlist schematic diagram for the standard cells includes a three-terminal MOS device corresponding to the polysilicon pseudo-structure at the edges of the standard cells. After automatic placement and routing processing, standard cells are employed to form a device layout, and a post-layout netlist is extracted. If two standard cells are contiguous, a single polysilicon pseudo-structure at the common boundary is formed. A layout-versus-schematic comparison is then performed in which the pre-layout netlist and the post-layout netlist are compared in order to verify the obtained layout. The invention also discloses a layout verification method used for a polysilicon cell edge structure in FinFET standard cells.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
IC layout physical verification method
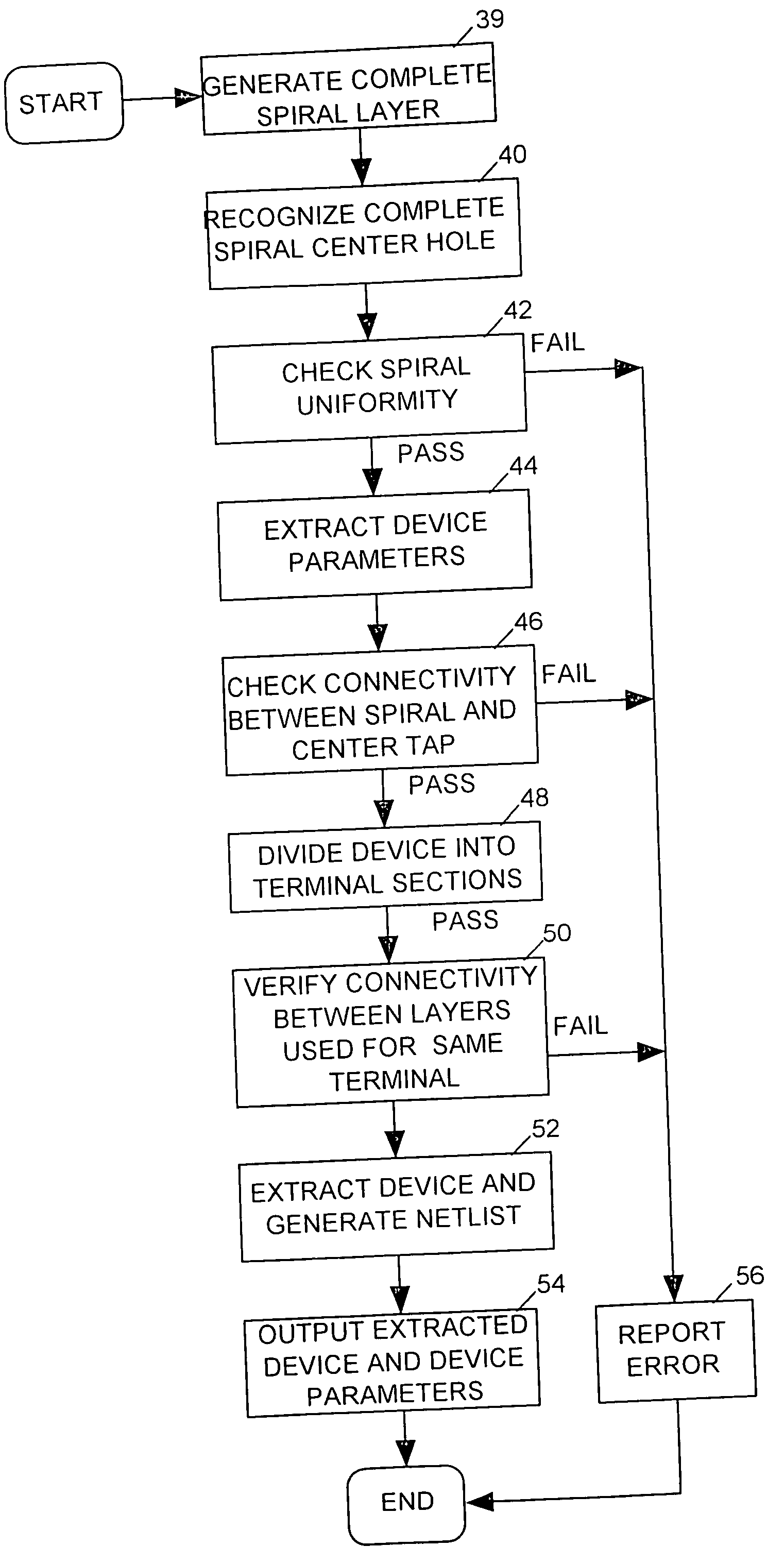
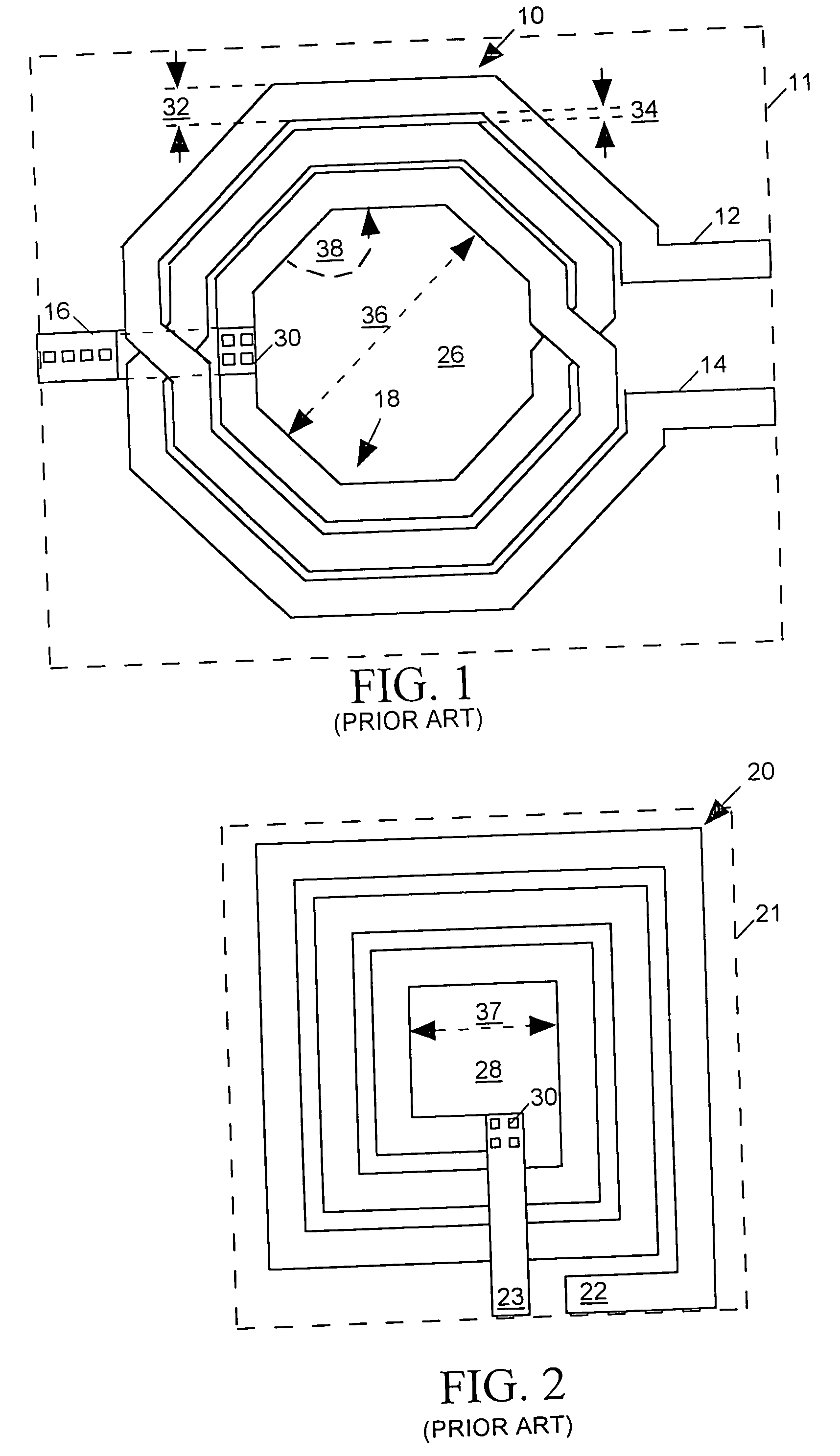
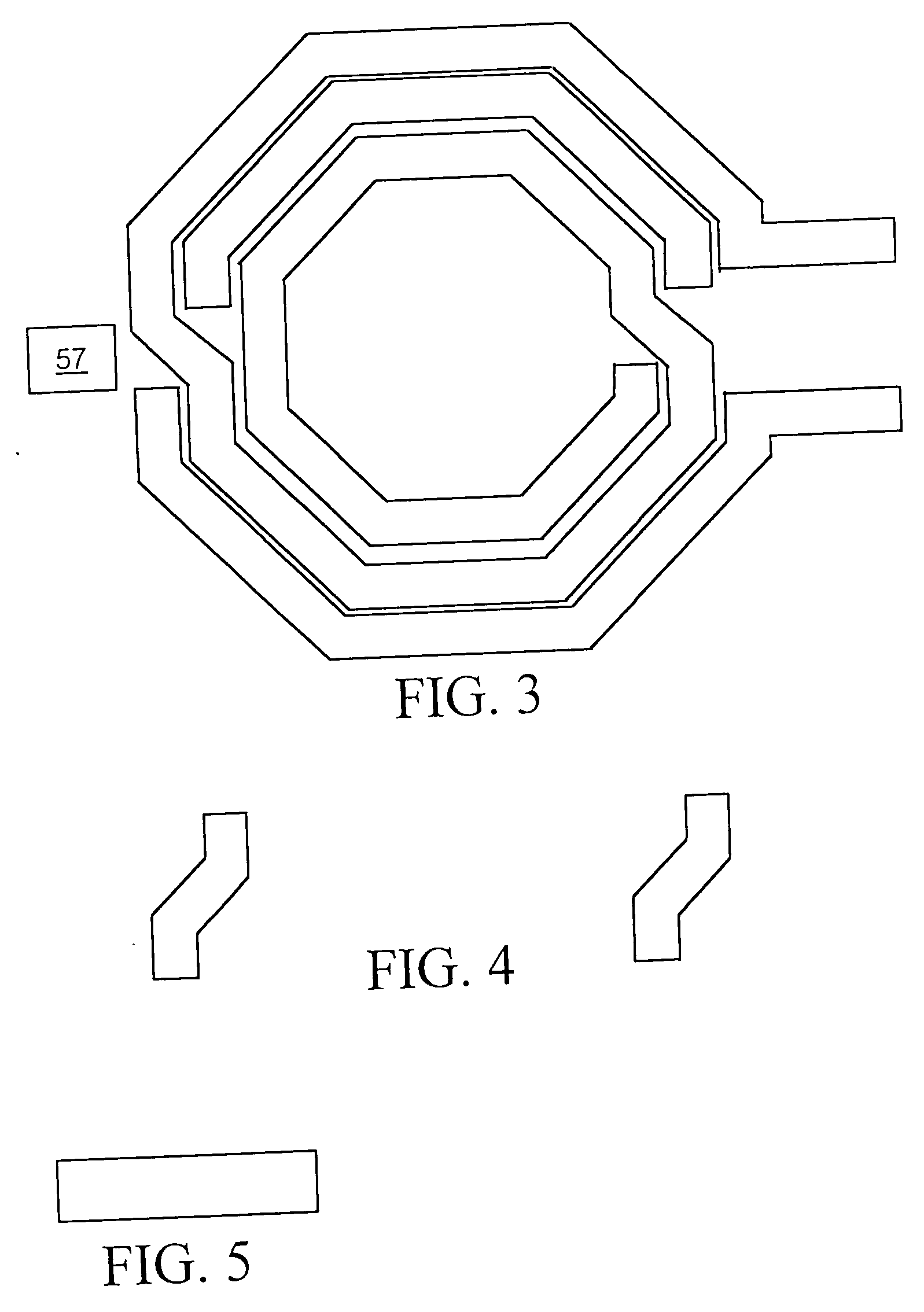
InactiveUS20050229126A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationHelical linePhysical verification
Responding to a single command, a layout versus schematic (LVS) tool processes layout data describing positions of conductors on layers of an IC to produce data representing a shape recognition layer depicting boundary shapes of spirals of drawn inductors. The boundary shape of a spiral is the shape of the spiral as viewed from above with all of the layers of conductive material forming the spiral superimposed. The LVS tool then processes the shape recognition layer data to identify the type and position of each drawn inductor, to determine whether each inductor's spiral turns are of uniform width and spacing, to detect connectivity violations, and to determine parameters relating to the shape of the spiral from which its inductance can be computed.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Collaborative Environment For Physical Verification Of Microdevice Designs
ActiveUS20110016444A1For easy referencePromote collaborationDetecting faulty computer hardwareOffice automationComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
A collaborative environment for performing physical verification processes on integrated circuit designs. Multiple physical verification results may be stored in a “unified” results database / directory (e.g., unified at least from a user's perspective), where results from various verification processes, such as Design-Rule-Check (DRC) processes, Layout-Versus-Schematic comparison (LVS) processes, Design-For-Manufacturing (DFM) processes Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) processes, and Optical Rule Check (ORC) processes are accessible from the same style of user interface, which may be a graphical user interface. The basic abilities for design team-based interactions can be equally available to each process involved in the physical verification of an integrated circuit design.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Verification Of Photonic Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20160055289A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLayout Versus SchematicAnalysis tools
Techniques and mechanisms for the use of layout-versus-schematic (LVS) design tools to validate photonic integrated circuit designs. Various implementations employ alternate analysis techniques with LVS analysis tools to perform one or more LVS analysis processes on photonic integrated circuits. These analysis processes may include curvilinear design validation and the associated flow implementations.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method and system for layout versus schematic validation of integrated circuit designs
InactiveUS7480878B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
A method and system for validating selected layers of an integrated circuit design. A rundeck is edited to include IC layers and device structures of interest that may require validation. In some embodiments the IC layer of interest may include only metal. A layout versus schematic (LVS) comparison is performed using the edited rundeck and an error report is generated.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
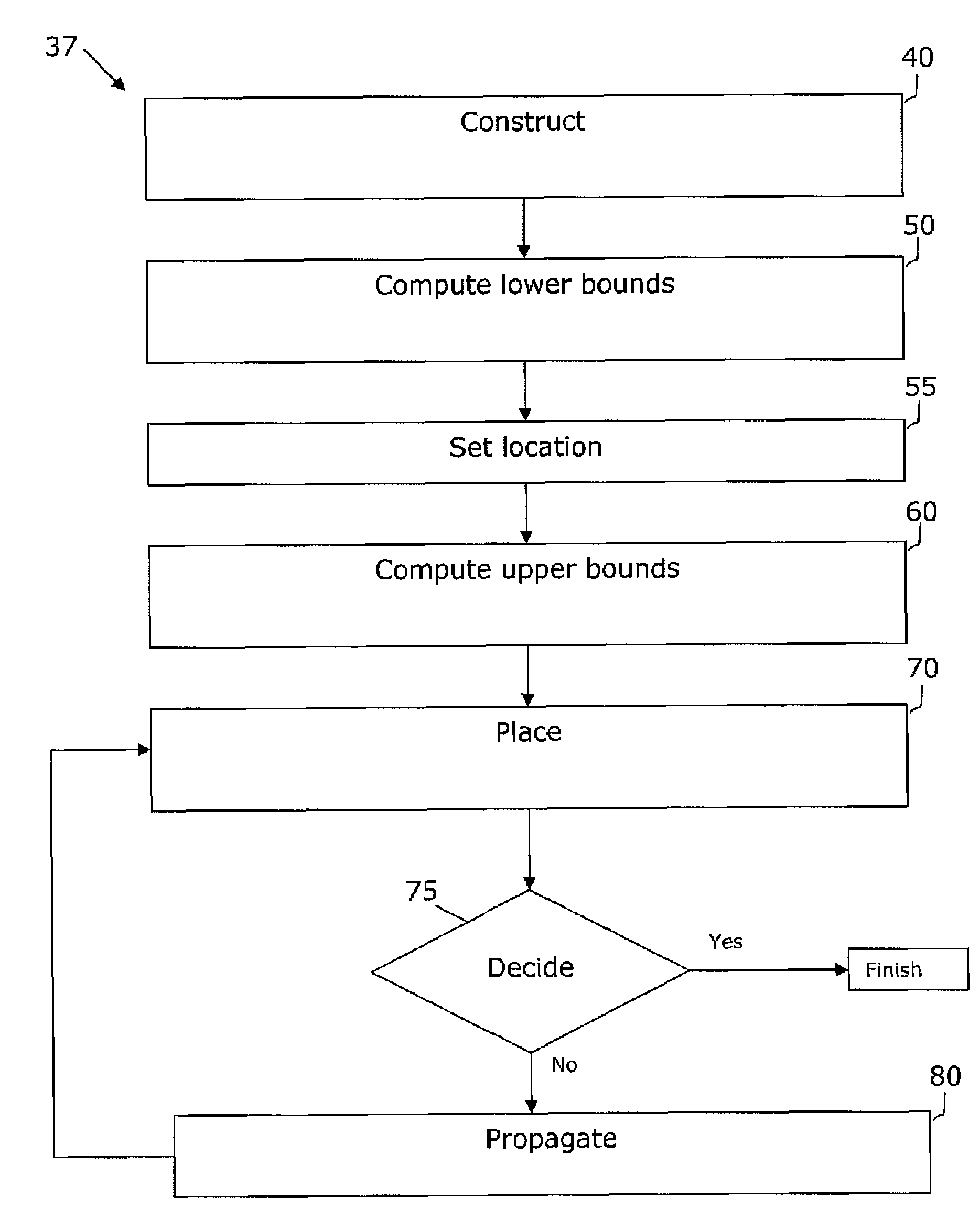
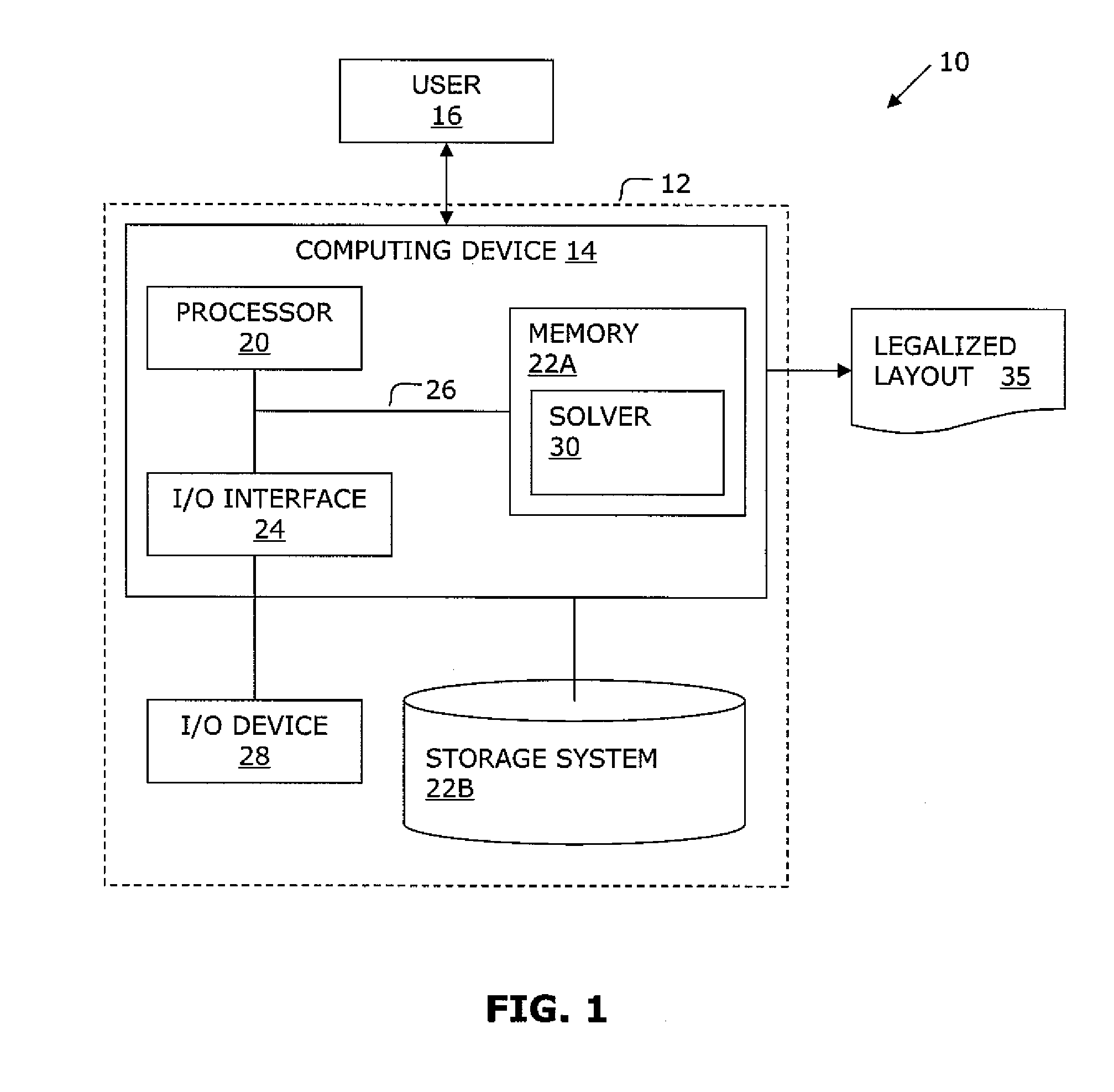
VLSI artwork legalization for hierarchical designs with multiple grid constraints
ActiveUS7437691B2Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsLayout Versus Schematic
A system and method are disclosed for legalizing a flat or hierarchical VLSI layout to meet multiple grid constraints and conventional ground rules. Given a set of ground rules with multiple grid constraints and a VLSI layout (either hierarchical or flat) which is layout-versus-schematic (LVS) correct but may not be ground rule correct, the system and method provide a legalized layout which meets the multiple grid constraints while maintaining LVS correctness and fixing the ground rule errors as much as possible with minimum layout perturbation from the input design. The system and method support multiple grid pitch constraints for hierarchical design, and provide for LVS correctness to be maintained while an on-grid solution possibly with some spacing violations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
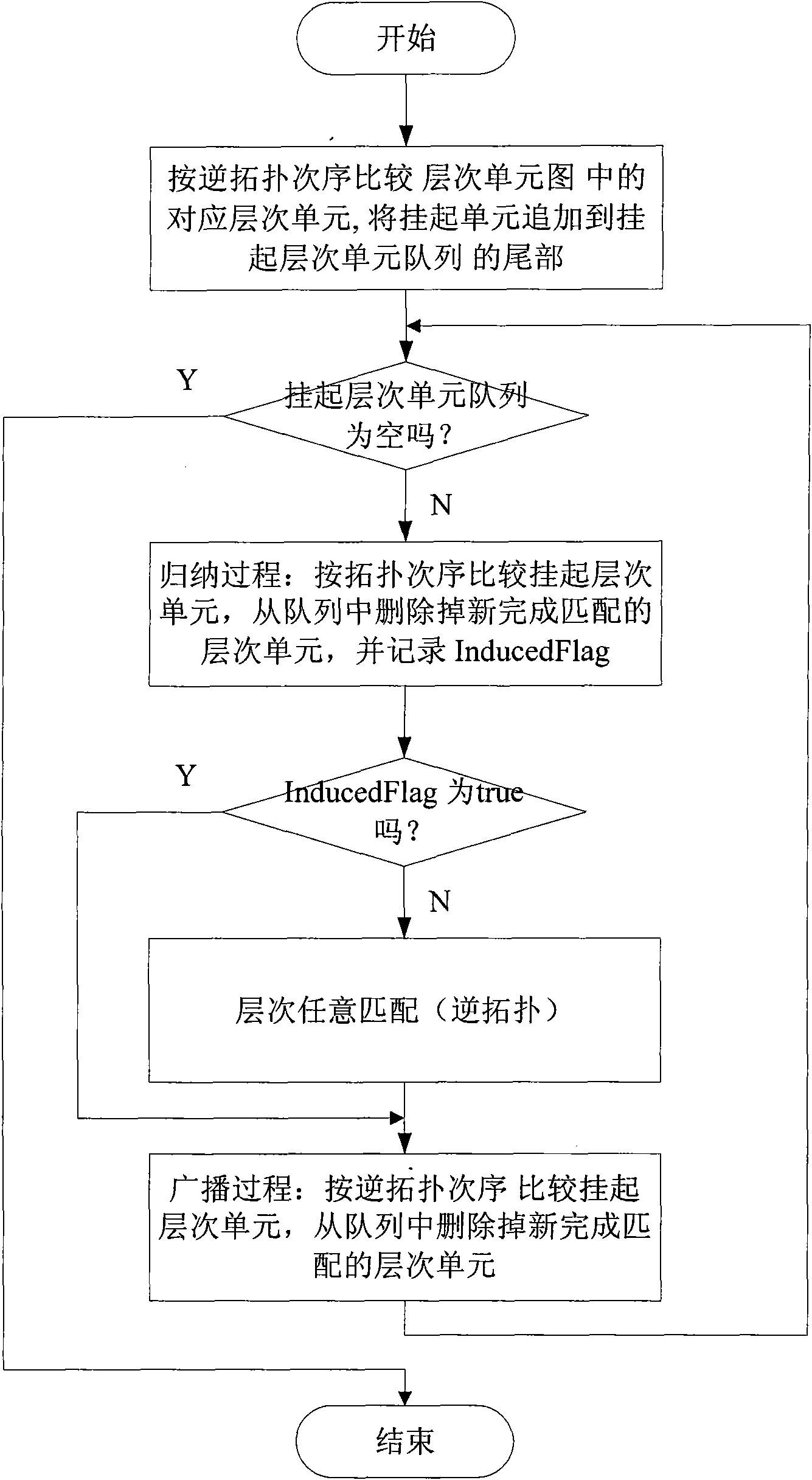
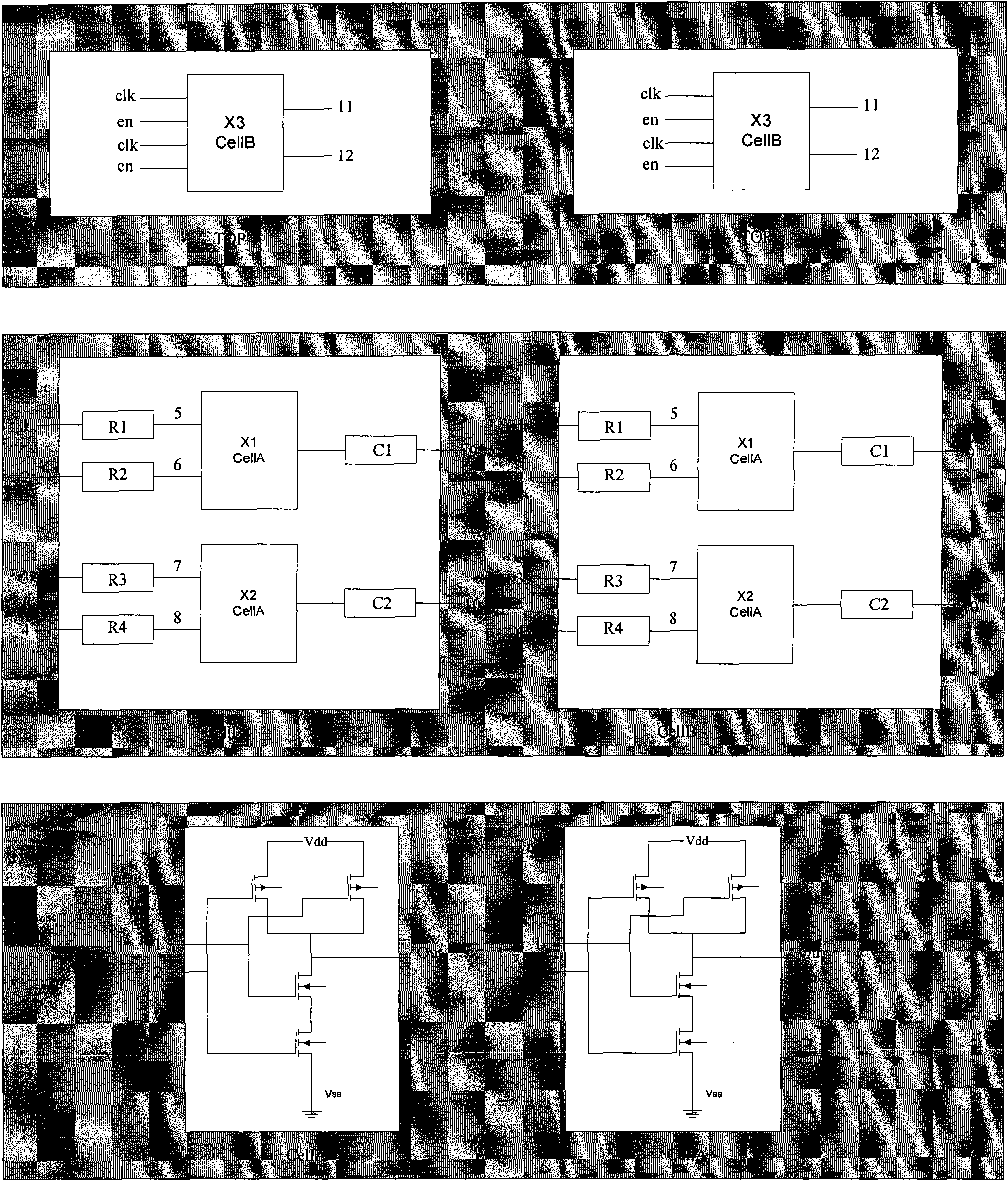
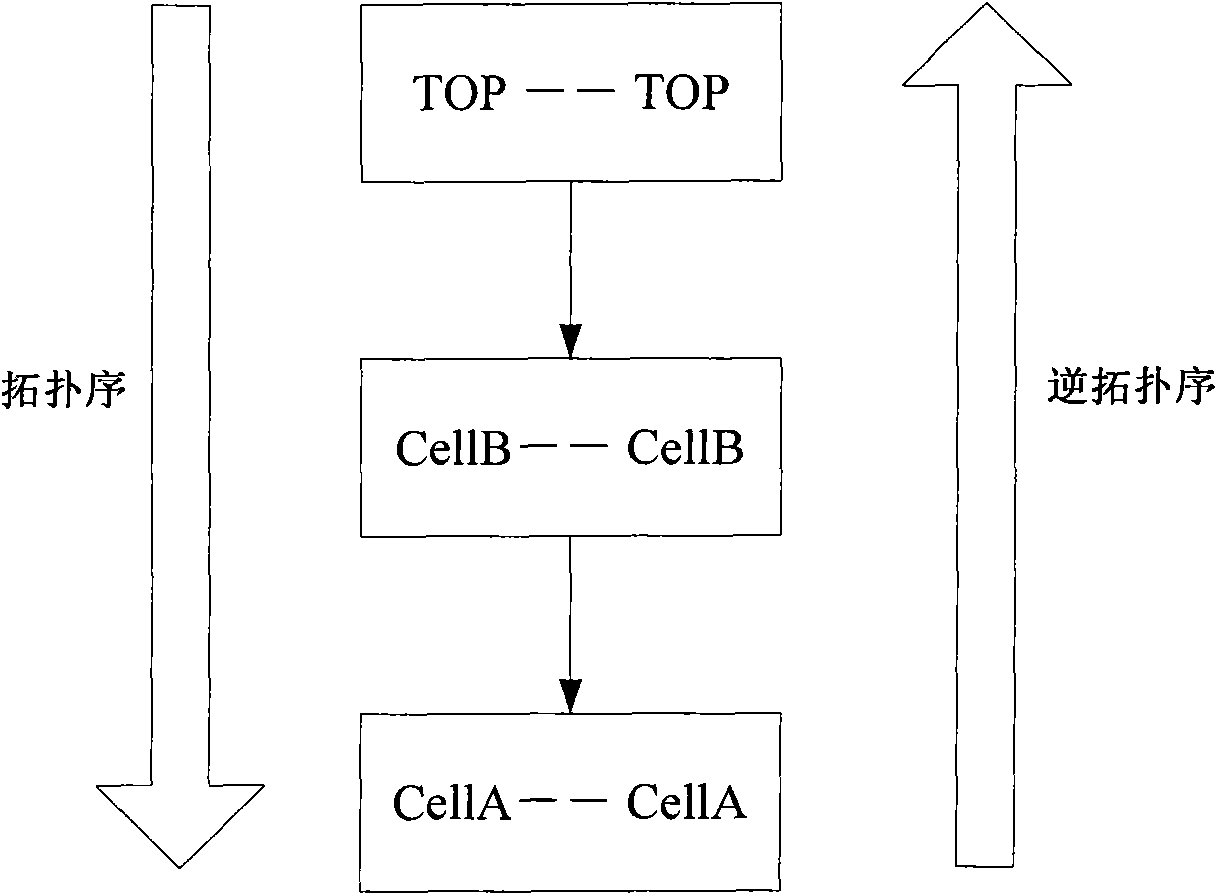
Method for comparing hierarchical net list of integrated circuit
The invention discloses a method for comparing a hierarchical net list of an integrated circuit, which belongs to the field of semiconductor integrated circuit design automation, and is mainly used for layout versus schematic consistency check during a rear-end layout design. Hierarchical units are compared by transmitting matching information of a port and a pin, and the iteration cycle of the rear-end layout design is shortened. The method is implemented by the following steps of: performing hierarchical preprocessing on the hierarchical net list, comparing the hierarchical units in turn according to a reverse topological sequence, and adding hierarchical units which cannot be completely matched in the comparison process to the tail part of a suspended queue; and processing the hierarchical units in the suspended queue by using a topological sequence induction method and a reverse topological sequence broadcasting method circularly, processing by a hierarchical random matching method when the induction method is ineffective to all suspended units, and repeating until the suspended queue is empty.
Owner:北京华大九天科技股份有限公司
Integrated OPC verification tool
InactiveUS7945871B2Digital data processing detailsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentInter layerComputer architecture
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method and system of linking on-chip parasitic coupling capacitance into distributed pre-layout passive models
InactiveUS8141013B2Accurately include post-layout parasiticsAccurate predictionDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
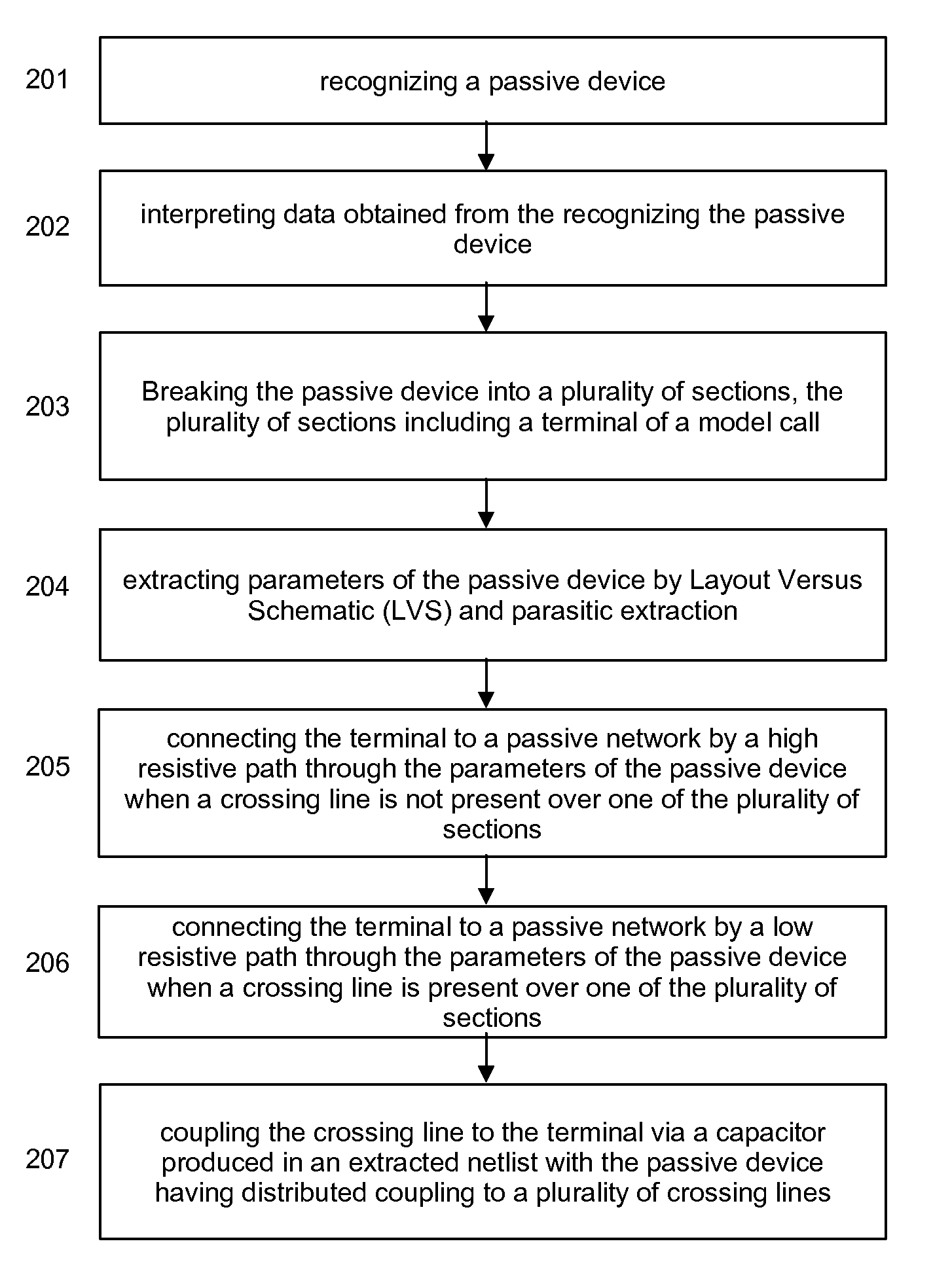
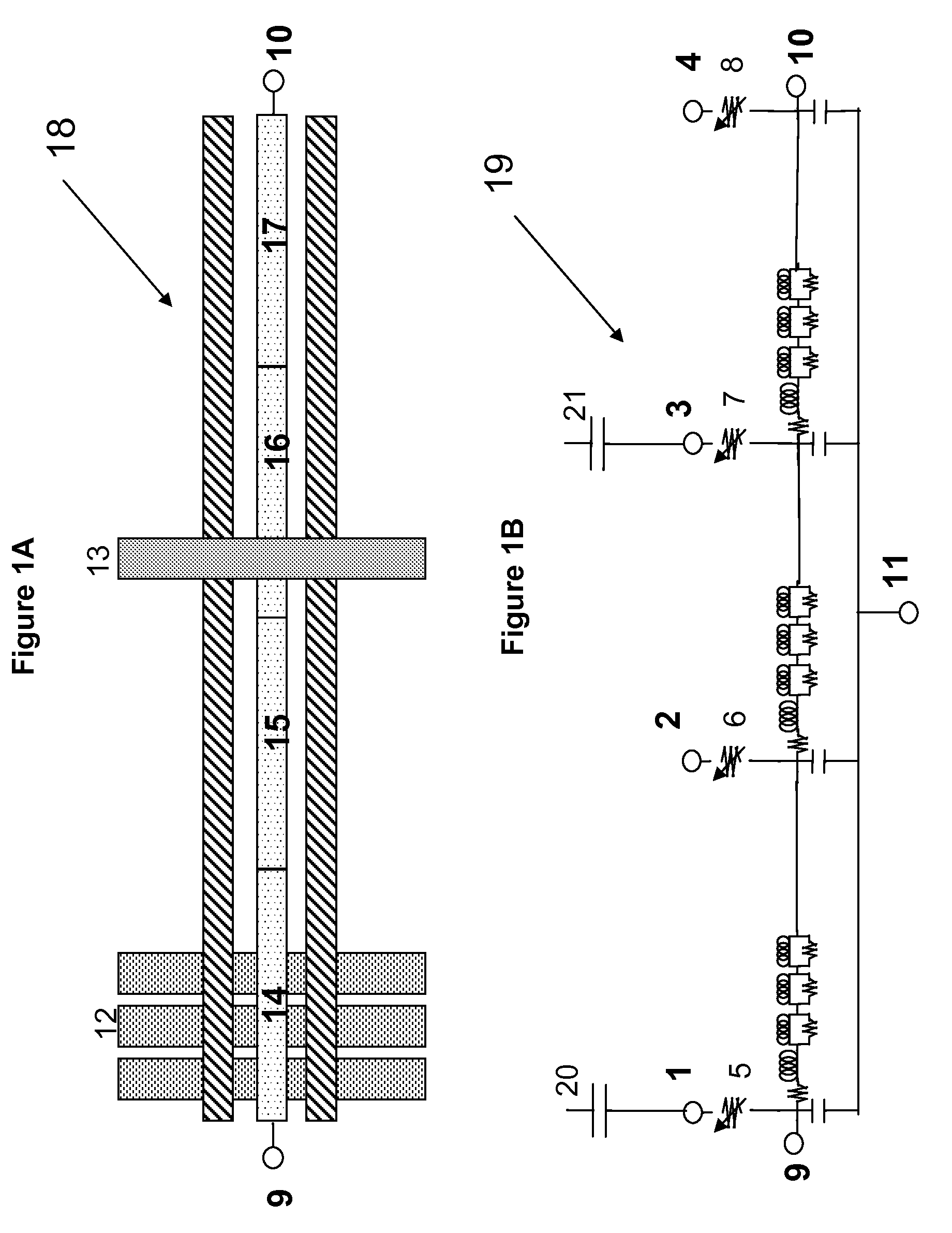
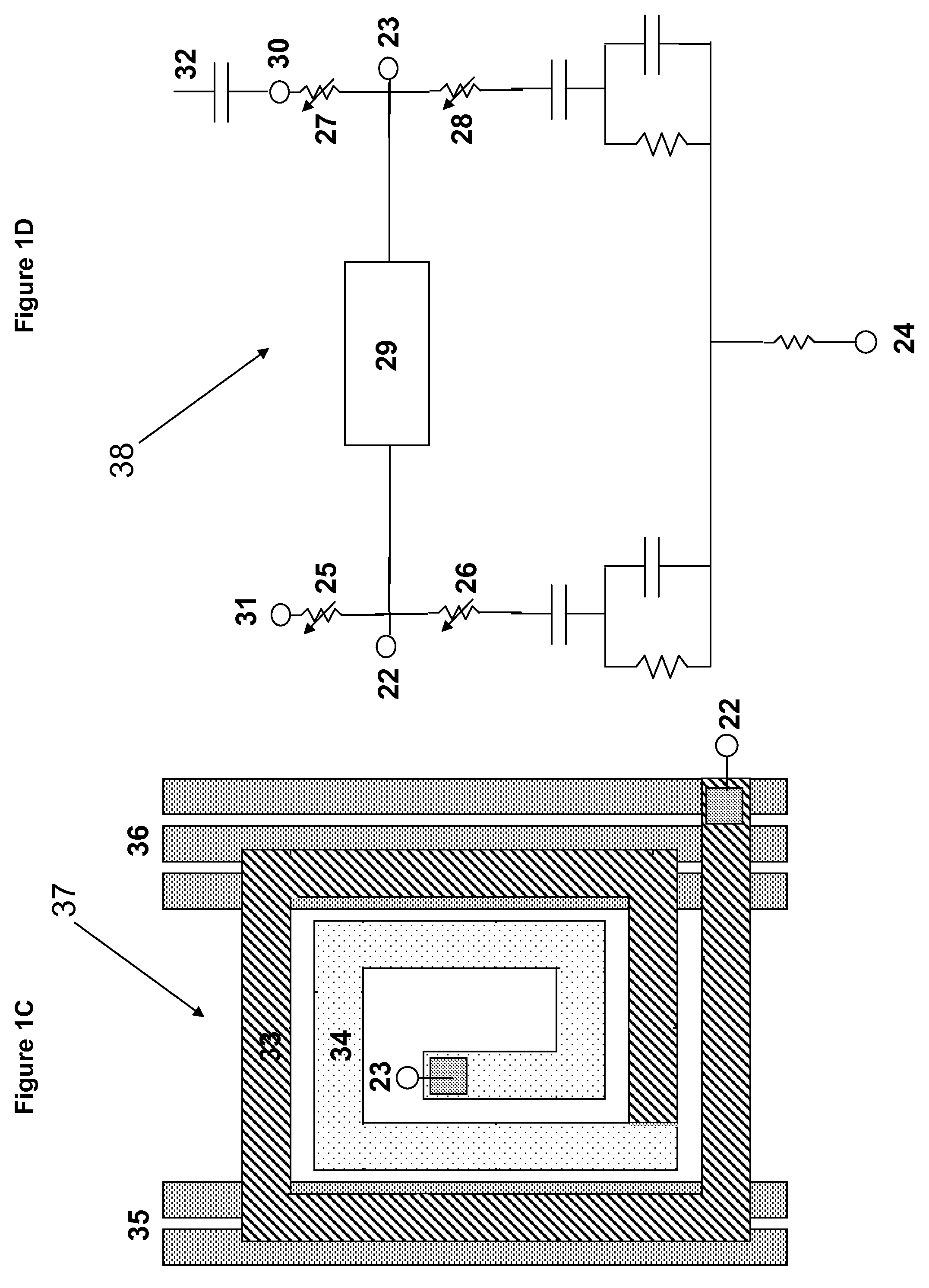
A method of linking on-chip parasitic coupling capacitance into distributed pre-layout passive models such as distributed transmission line models and on-chip spiral inductor models includes recognizing a passive device such as a distributed transmission line device and an on-chip spiral inductor device, interpreting data obtained from the recognizing the passive device, breaking the passive device into a plurality of sections, the plurality of sections including a terminal of a model call, extracting parameters of the passive device by Layout Versus Schematic (LVS) and parasitic extraction, connecting the terminal to a pre-layout passive network by selectively low and high resistive paths set by the parameters of the passive device depending on whether crossing lines are present or not present in one of the plurality of sections, connecting the terminal to a distributed passive model, and coupling the crossing lines to the terminal via capacitors produced in an extracted netlist with the passive device having distributed coupling to a plurality of crossing lines.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Graph optimization method for short-circuit path in integrated circuit layout verification
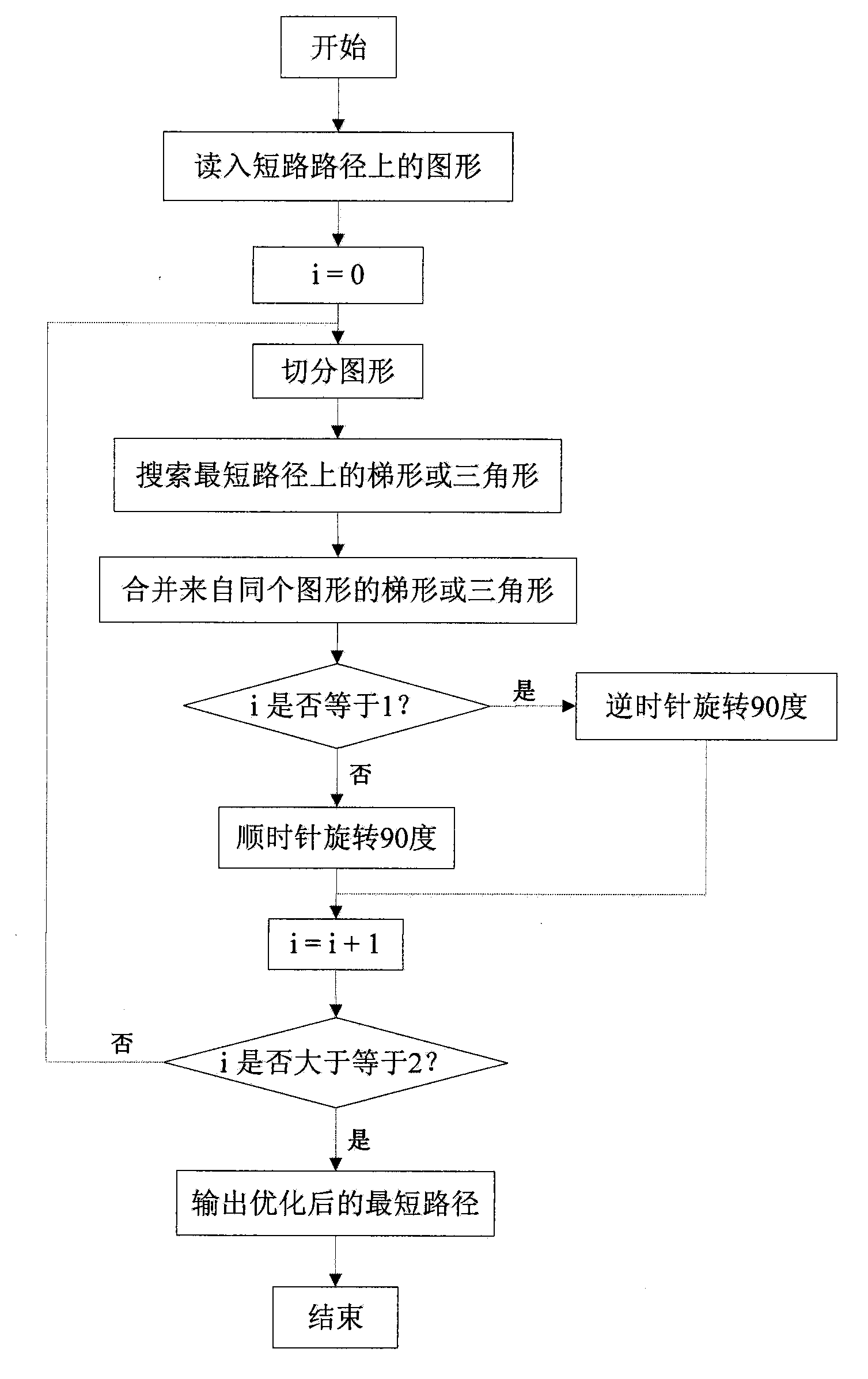
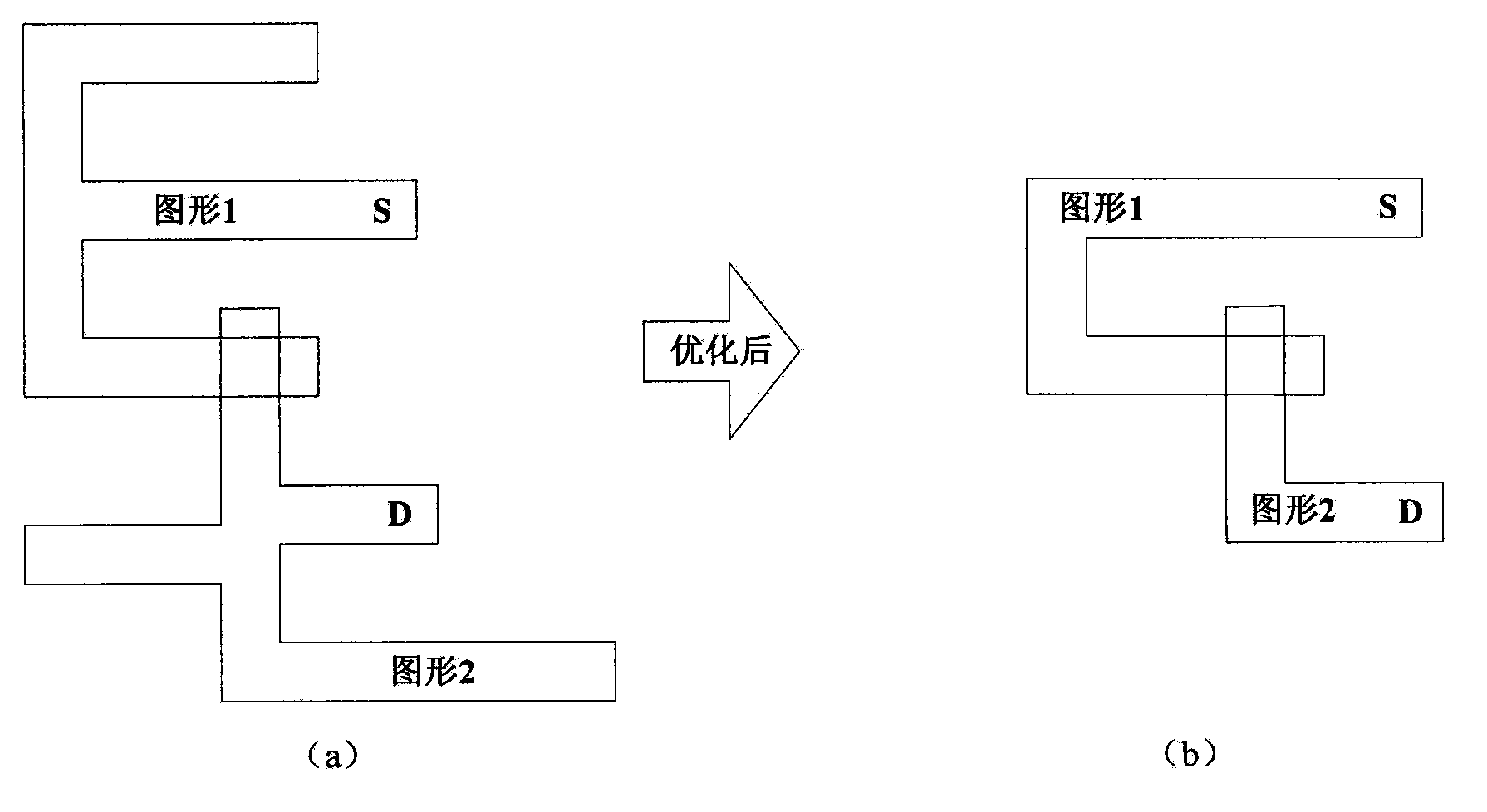
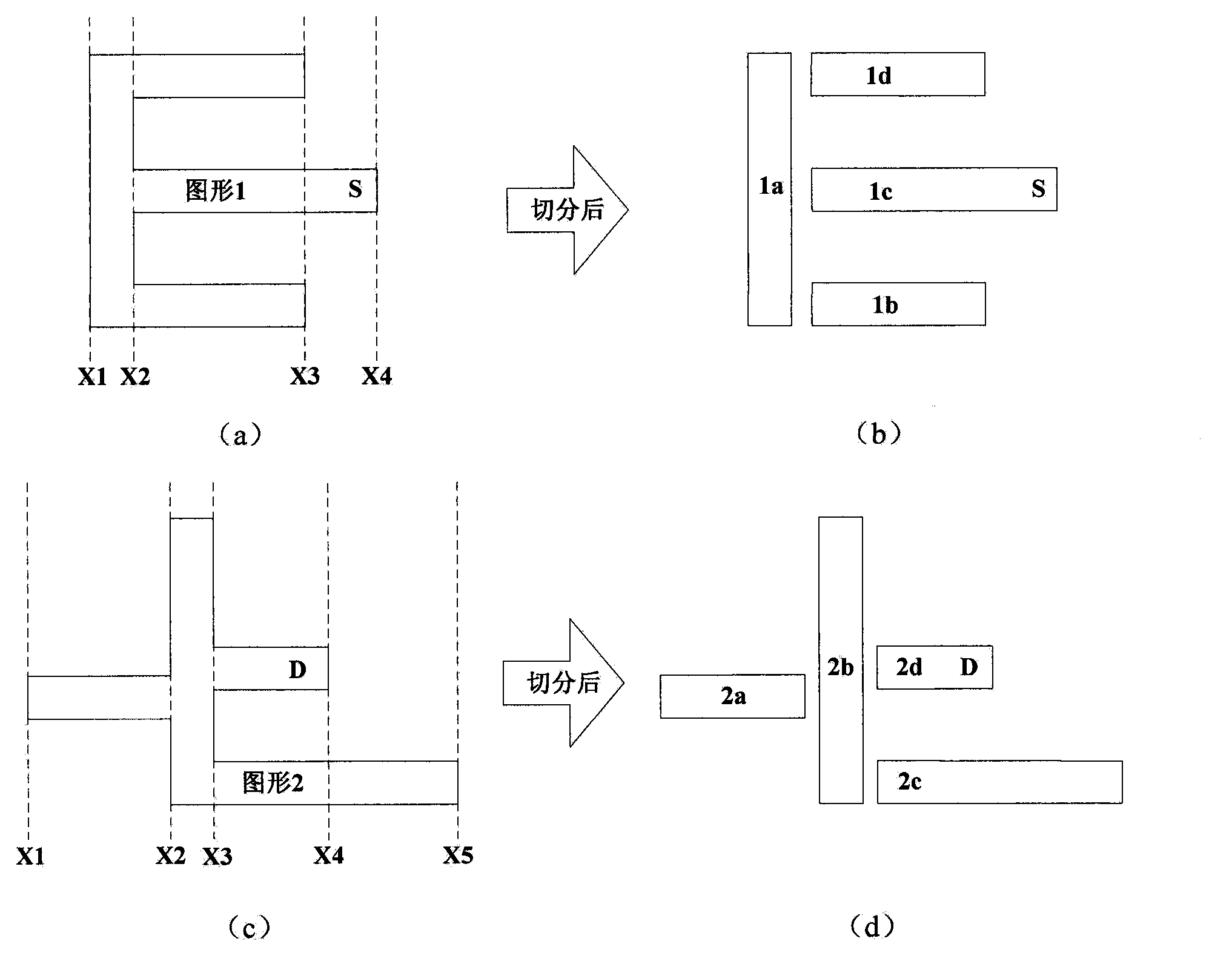
The invention discloses a graph optimization method for a short-circuit path in integrated circuit layout verification, which belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit computer-aided design, and particularly relates to the field of design rule checking (DRC) and layout versus schematic checking (LVS) for an integrated circuit layout. The graph optimization method disclosed by the invention refers to the following three key steps: step one, splitting graphs, specifically, splitting complex graphs into simple trapezoids or triangles by means of a scanning line method; step two, abstracting a problem to a path finding problem for an undirected graph, finding a path with the fewest graphs from a source point to an end point by virtue of breadth-first traversal; and step three, combining the trapezoids or triangles obtained by splitting the same graph by virtue of the characteristics of the split graphs. The presentation of the short-circuit path in a layout can be effectively optimized to be more intuitive and simpler by utilizing the method in the integrated circuit layout verification, thus facilitating design personnel to rapidly locate a short-circuit position.
Owner:北京华大九天科技股份有限公司
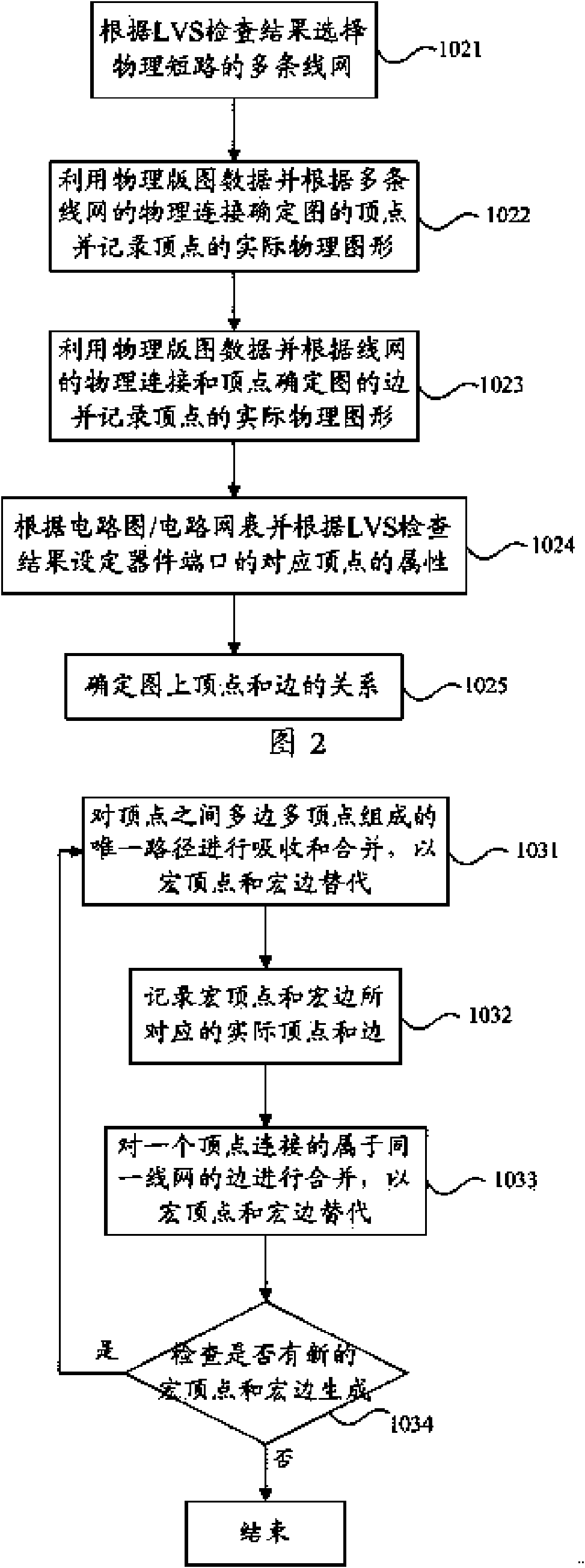
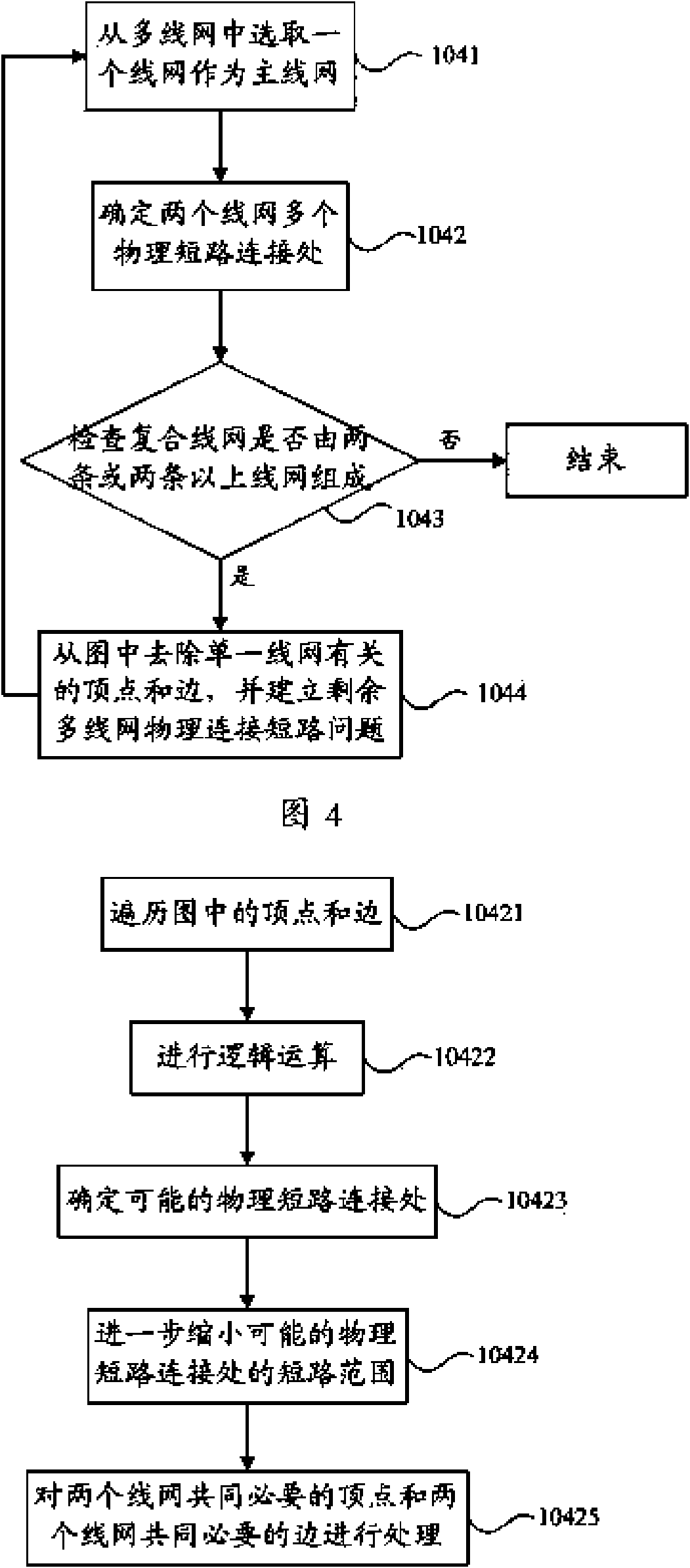
Automatic positioning method for physical short circuit positions among multiple line networks
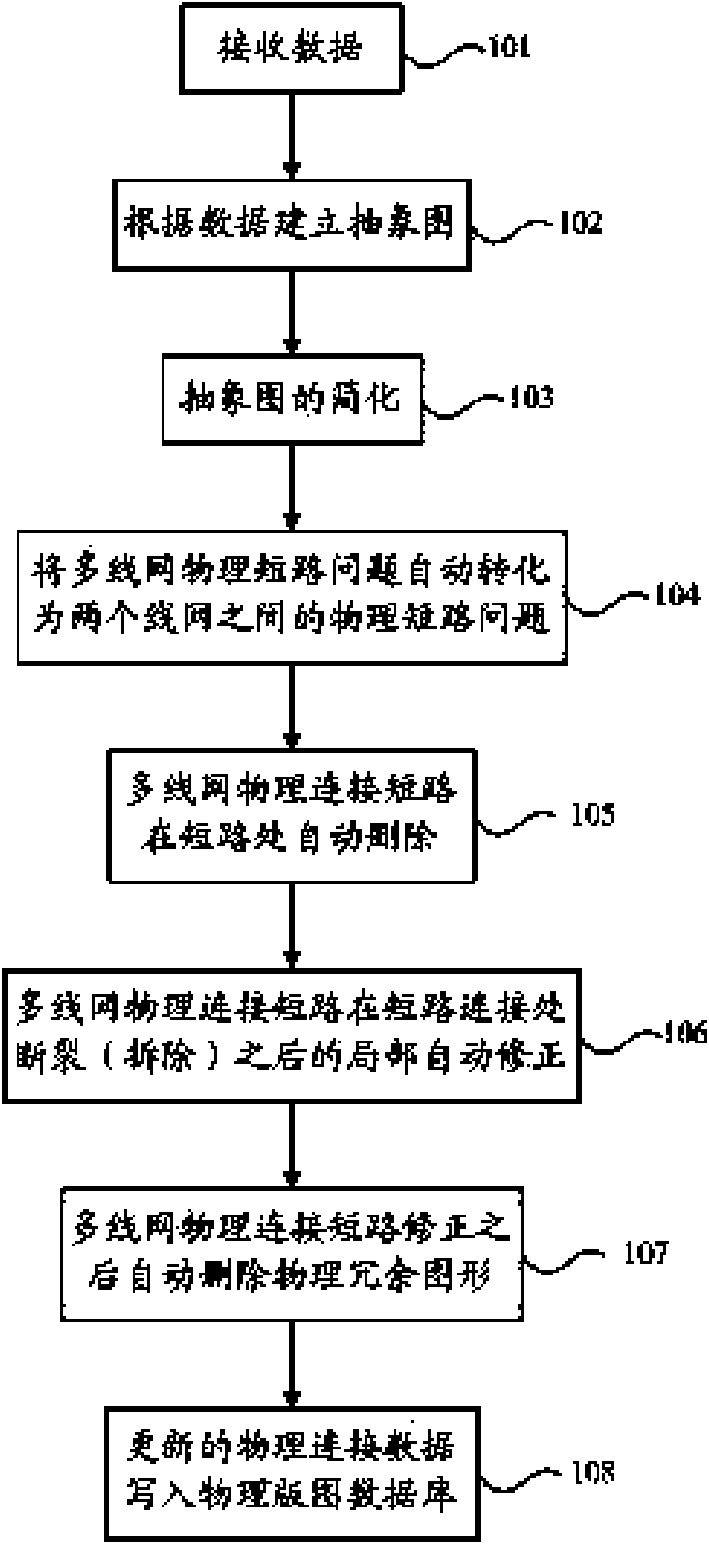
ActiveCN102117350AImprove design efficiencyAutomatically achieve automatic positioningSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureNetwork on
The invention discloses an automatic positioning method for physical short circuit positions among multiple line networks, and belongs to the technical field of electronic design automation. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a circuit diagram / circuit network table, physical layout data and layout versus schematic (LVS) result data; and establishing an abstract diagram according to the circuit diagram / circuit network table, the physical layout data and the LVS result data, and simplifying the abstract diagram so as to complete automatic positioning of physical connection short circuits of the multiple line networks on the simplified abstract diagram. By using the method, automatic positioning of the physical short circuits among the multiple line networks during integrated circuit physical layout design can be automatically realized to replace a designer to manually seek the physical short circuit positions on the physical layout, so that the design efficiency of the physical layout is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
3D inter-stratum connectivity robustness
There is provided a method for verifying inter-stratum connectivity for two or more strata to be combined into a 3D chip stack. Each of the two or more strata has 3D elements including active 3D elements, mechanical 3D elements, and dummy 3D elements. The method includes performing a respective 2D layout versus schematic verification on each of the two or more strata with respect to at least the 3D elements to pre-ensure an absence of shorts between the 3D elements when the two or more strata are subsequently stacked into the 3D chip stack. The method further includes checking inter-stratum interconnectivity between each adjacent pair of strata in the 3D chip stack.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
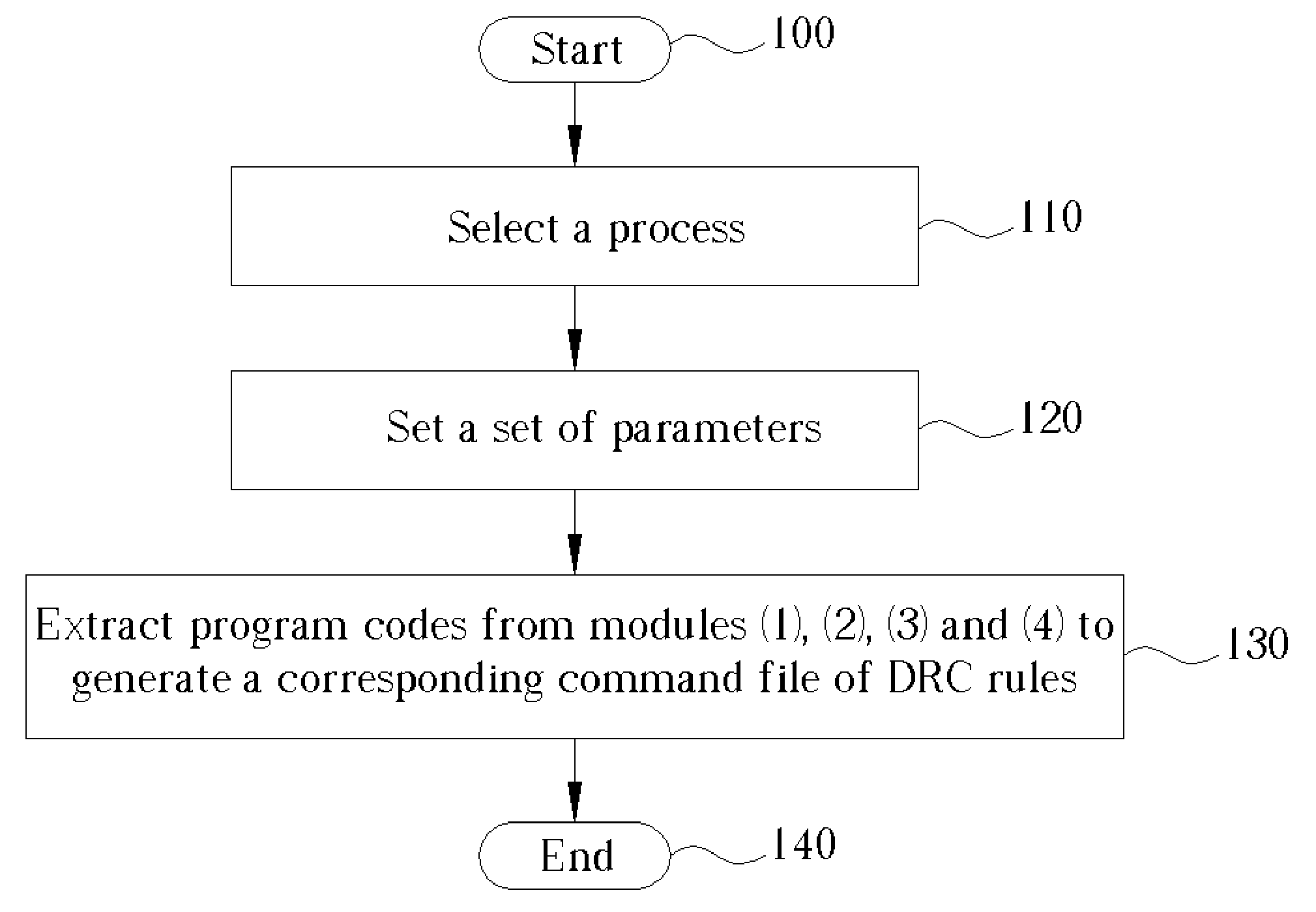
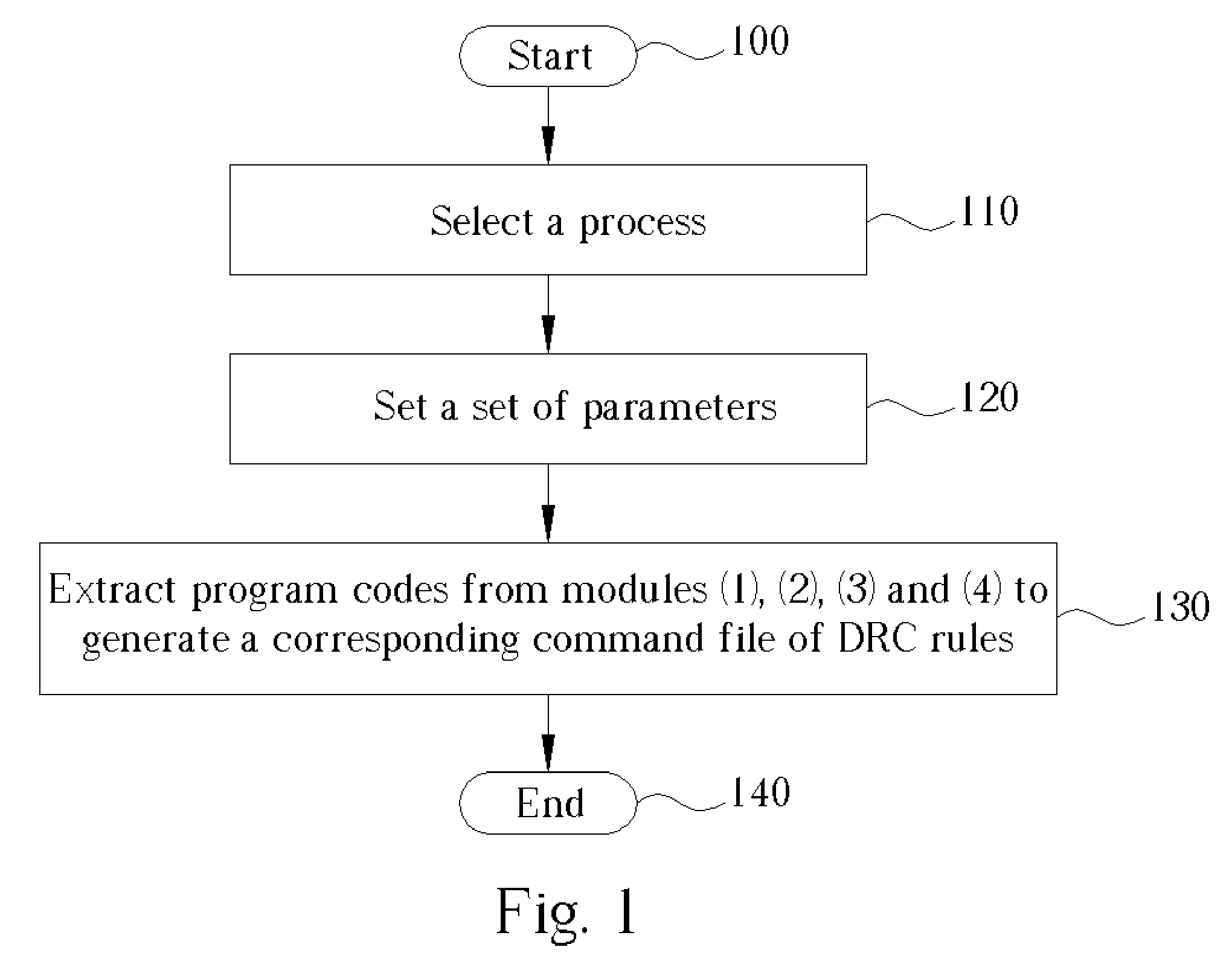
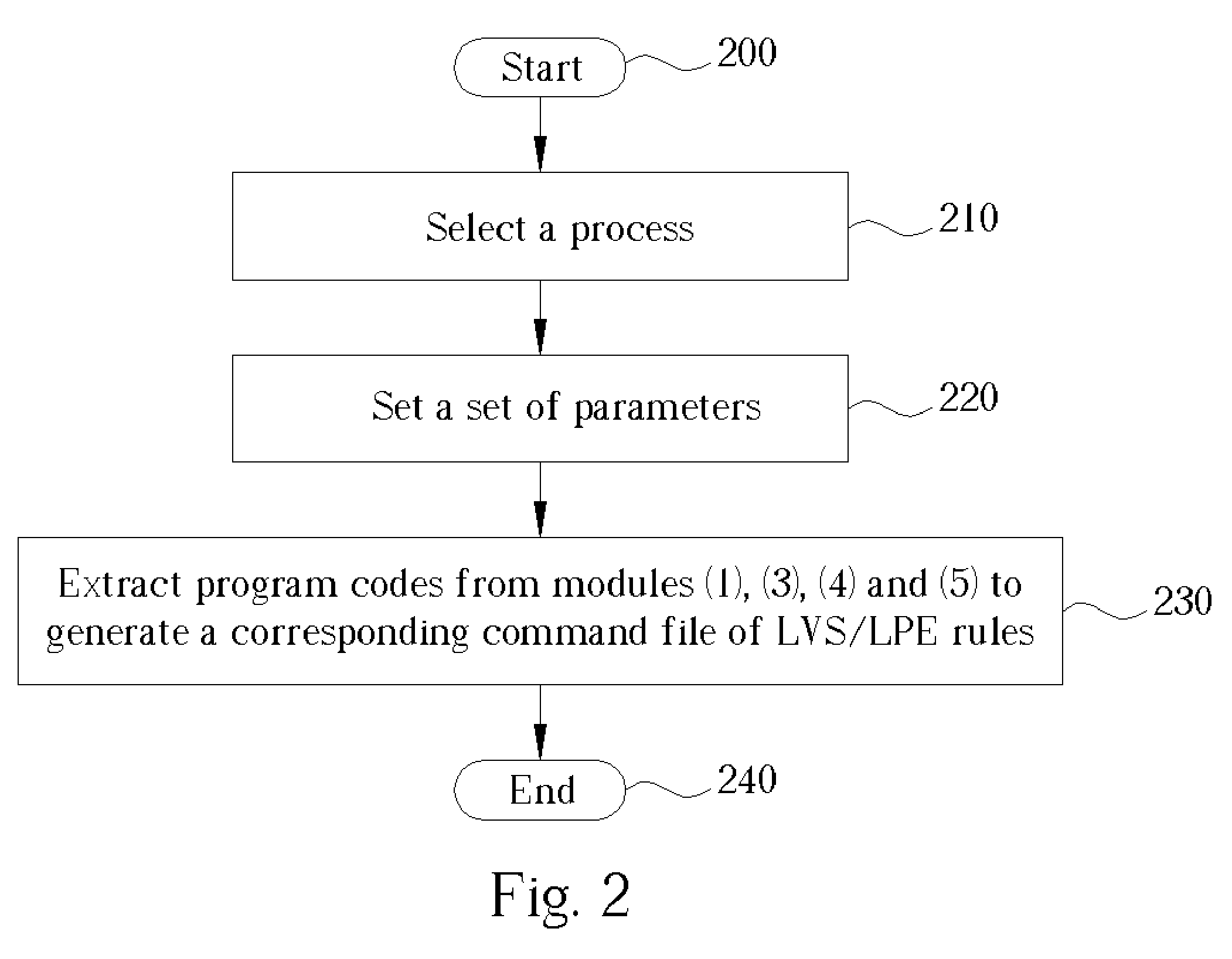
Method for generating a command file of a group of DRC rules and/or a command file of a group of LVS/LPE rules
InactiveUS7096441B2Efficient updateComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsLayout Versus SchematicParasitic extraction
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Method for identifying short-circuit path in integrated circuit layout verification process
InactiveCN103186690AReduce complexitySave storage spaceSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
The invention discloses a method for identifying a short-circuit path in an integrated circuit layout verification process, belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit computer aided design, and particularly relates to the field of integrated circuit layout design rule checking (DRC) and layout versus schematic (LVS). The invention aims at providing a method for quickly searching the short-circuit path in a layout database. The problem of searching the short-circuit path in the layout database is transformed into the problem of the shortest path between appointed top points in an undirected graph through abstract expression, and the solution space is divided into a plurality of subspaces independent of each other according to the connectivity characteristic of the undirected graph, so that the algorithm complexity of problem solving is lowered; and meanwhile, the multi-point breadth-first shortest path search algorithm is adopted according to the characteristics of large data volume and complex connection relation in integrated circuit design, so that the required storage space is smaller and the running efficiency is higher relative to the general search algorithm.
Owner:北京华大九天科技股份有限公司
Layout versus schematic error system and method
ActiveUS20120227024A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designGraphicsComputer architecture
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Validation of integrated circuit designs built with encrypted silicon IP blocks
ActiveUS8667450B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designLayout Versus SchematicCircuit design
A method and system for validating integrated circuit designs that are built with encrypted silicon IP blocks decrypts the encrypted silicon IP blocks in the integrated circuit designs with the keys from IP providers. After decryption, various validation checks on the integrated circuit designs are done, such as design rule check (DRC), layout versus schematic (LVS) check, parasitic resistor capacitor (RC) extraction, circuit simulation, signal electro migration (EM) and voltage drop check, signal integrity (SI) check and static timing check, etc. After validation, any confidential data from the checking results related to the encrypted silicon IP blocks are themselves encrypted to protect the proprietary silicon IP blocks. The method and system work with silicon IP encryption technology to establish a low cost silicon IP usage and verification platform, and to enable a more cost efficient silicon IP business model.
Owner:ENCRIP
Layout versus schematic error system and method
InactiveUS8181137B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designGraphicsComputer architecture
According to various embodiments of the invention, systems and methods for presenting Layout Versus Schematic (LVS) errors within a layout using a visual circuit representation of the design and highlighting is provided. One embodiment includes overlaying the layout circuit representation on the schematic circuit representation with highlighting that indicates the LVS errors. The method of such an embodiment compares a layout netlist against a schematic netlist in order to identify the layout-versus-schematic errors, generates a graphical representation of the layout netlist and a graphical representation of the schematic netlist, displays an overlay of the graphical representation of the layout netlist with the graphical representation of the schematic netlist and then, highlights the identified layout-versus-schematic errors that are present.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com