Shoe
a technology for shoes and soles, applied in the field of shoes, can solve the problems of not being designed to account for the actual location of the heel of a person, the soles and midsoles of the prior art shoes are not designed to account for the actual location of the toe area, and the transfer of load between, etc., to achieve the effect of facilitating the flexing of the shoe, and reducing the pronation ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
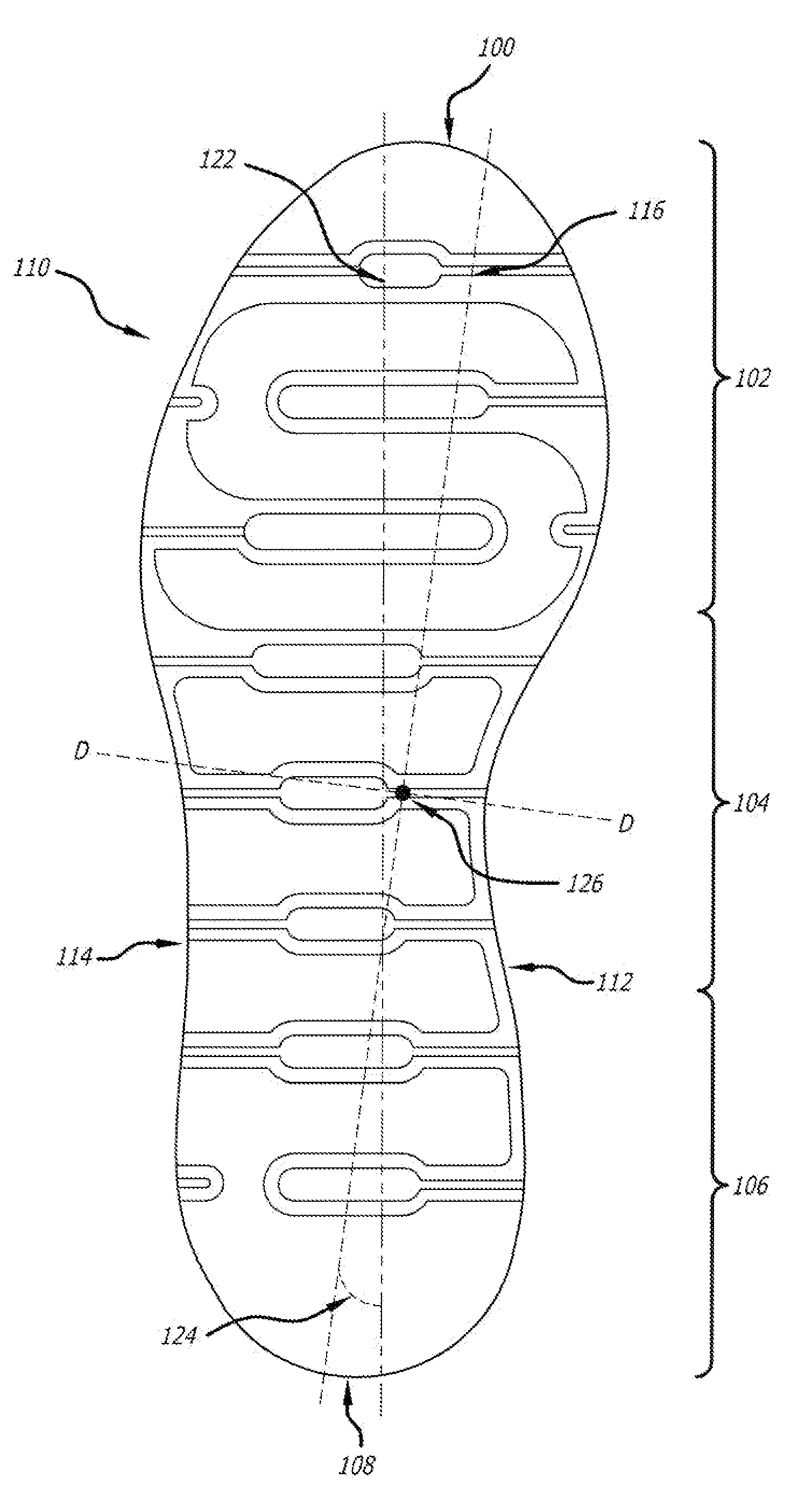
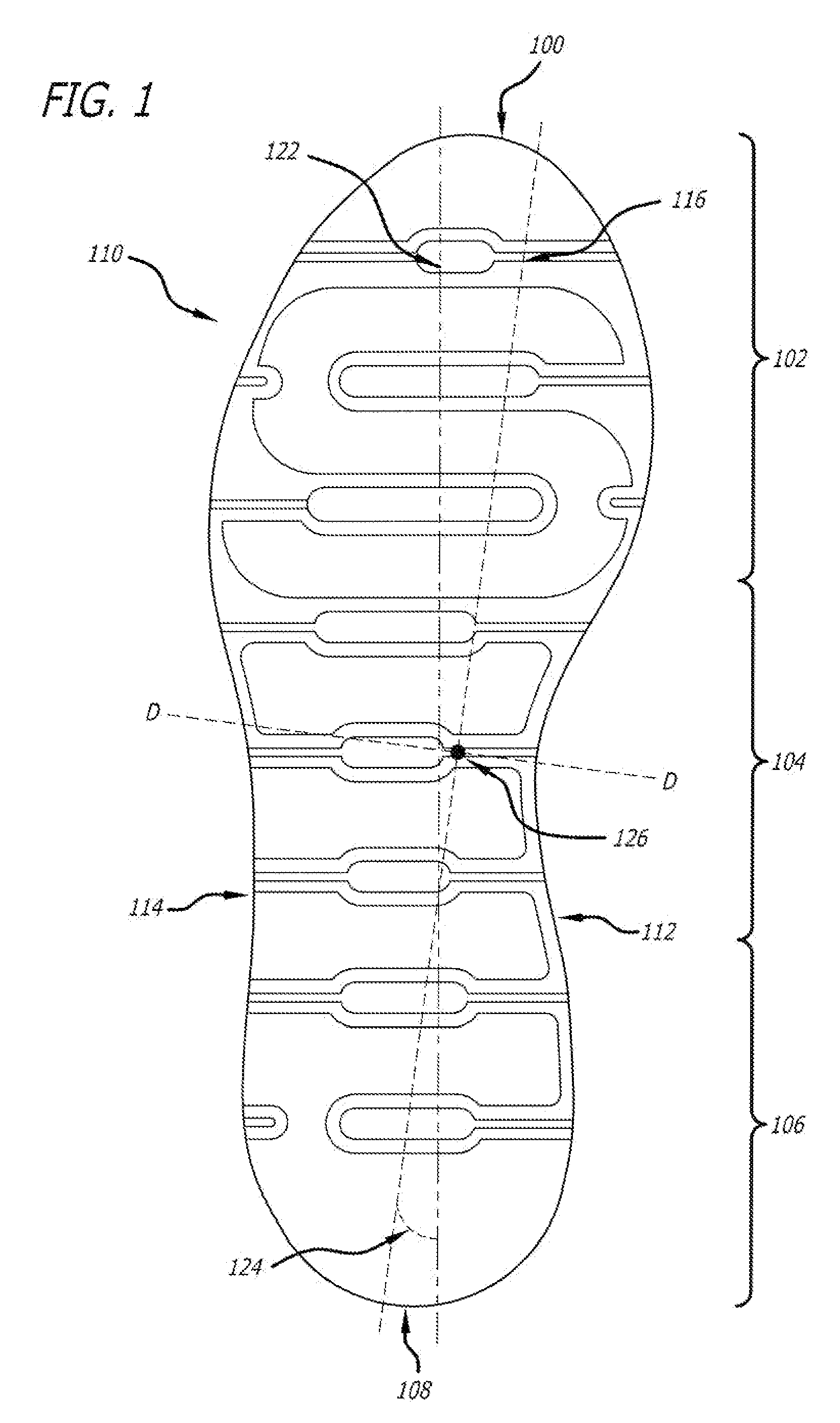
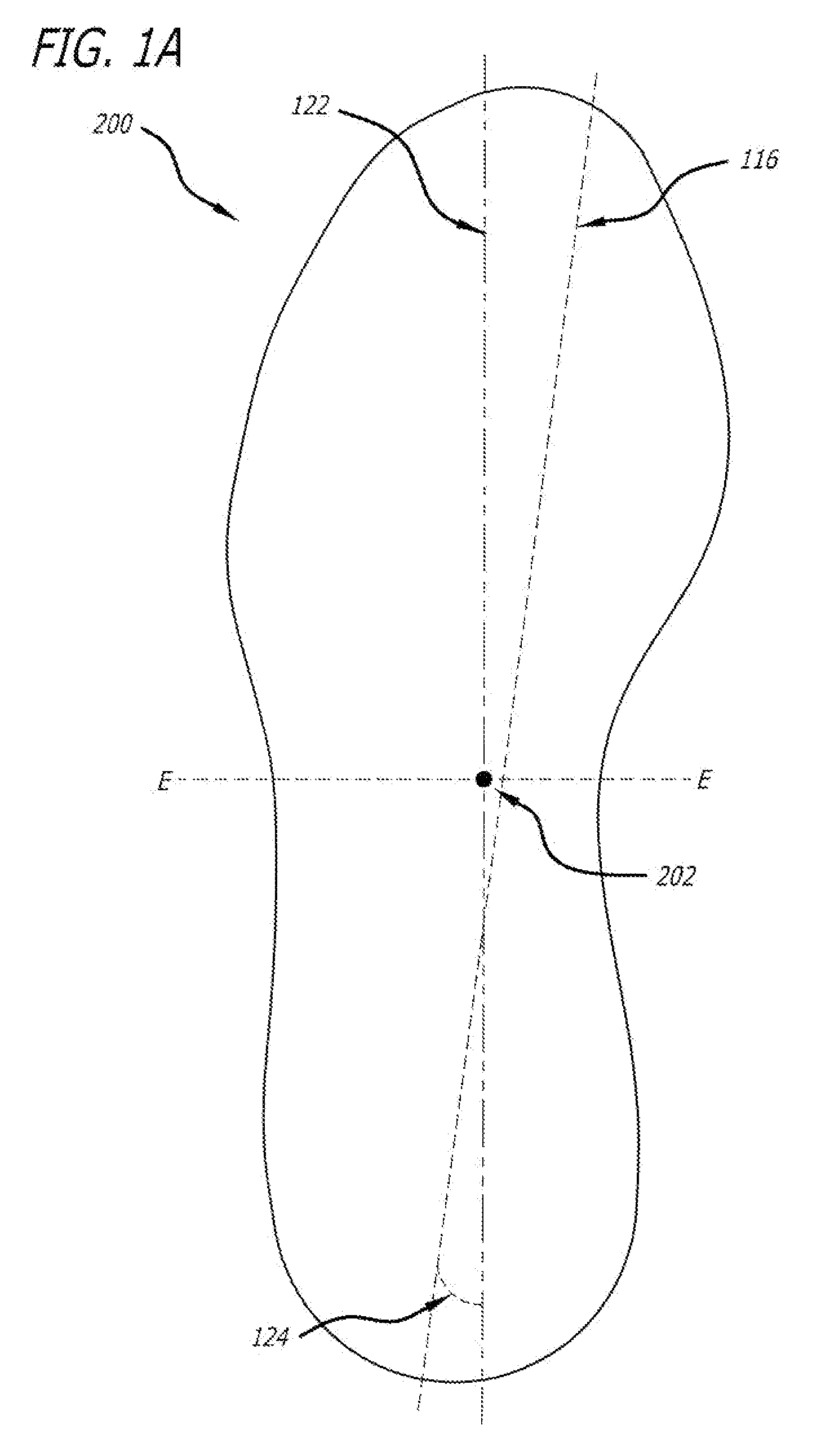
[0056]The invention will now be described with reference to the preferred embodiment shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 1 is a bottom plan view of an embodiment of the sole member 110 of a right shoe. The preferred embodiment of the shoe is comprised of an upper (not shown), a midsole and an outsole. In this preferred embodiment, the midsole and outsole are integrated and form a unitary piece, thus it is referred to as a sole member 110. A sole member may also alternatively be comprised of a combined separate outsole and separate midsole.
[0057]The sole member 110 has a front tip 100 that is located at the farthest forward point of the shoe when moving from the heel region 106 to the forefoot region 102. The shoe has a rear tip 108 that is located at the farthest rearward point of the shoe when moving from the forefoot region 102 to the heel region 106. In the preferred embodiment, the front tip 100 coincides with the frontmost point of the sole member 110 while the rear tip 108 coincides with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com