Garment, in particular a compression garment for medical use
a compression garment and medical technology, applied in the field of compression garments for medical use, can solve the problems of difficult reworking operation, difficult to solve, and relatively ineffective as medical compression stockings, and achieve the effect of avoiding any risk of strangulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
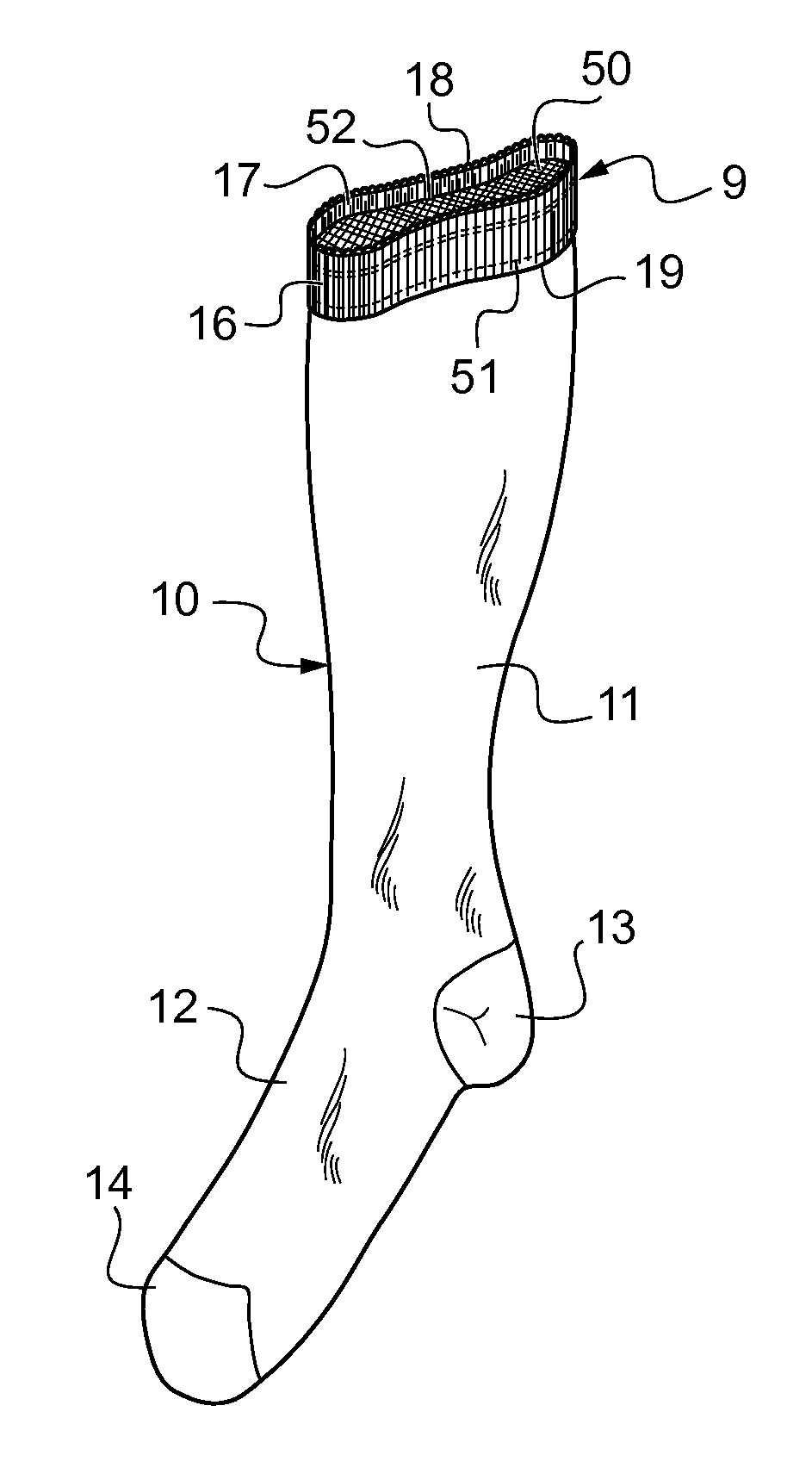
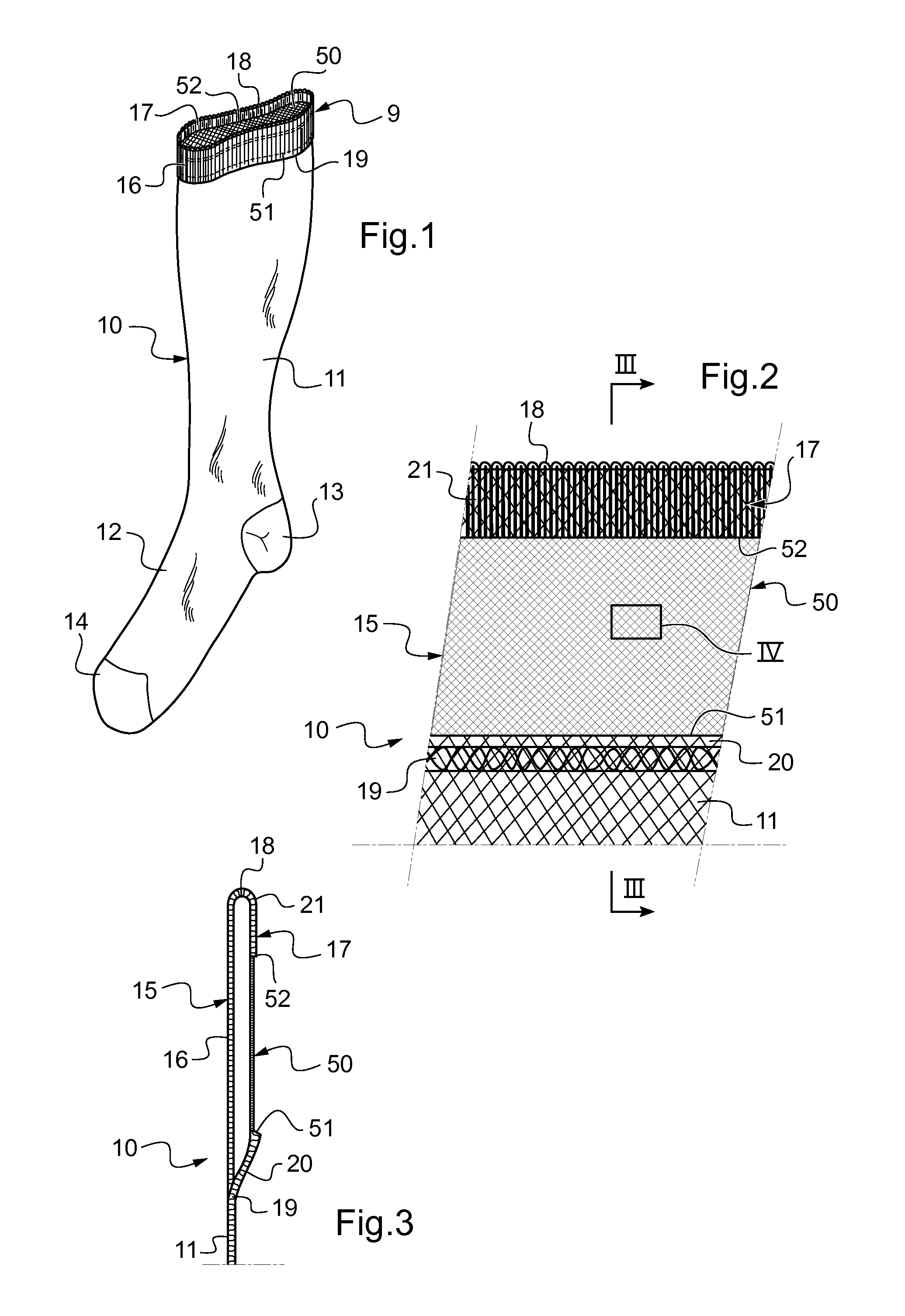
[0049]FIG. 1 shows a garment in accordance with the invention, here implemented in the form of a compression stocking or sock, referenced 10.
[0050]The compression garment 10 has a main portion 11 of elastic knit that serves to compress the portion of the leg on which the garment is positioned in order to treat lymphatic or venous insufficiency. The foot portion 12 has a heel 13 and a toe 14. The main portion 11 is also extended upwards by a welt portion also called here top portion referenced 9. The inner face of the top portion 9 in contact with the wearer's skin is conformed to provide an anti-slip effect promoting holding of the compression garment 10 in position. Of course, the inner face of the welt portion is also the inner face of the main portion.
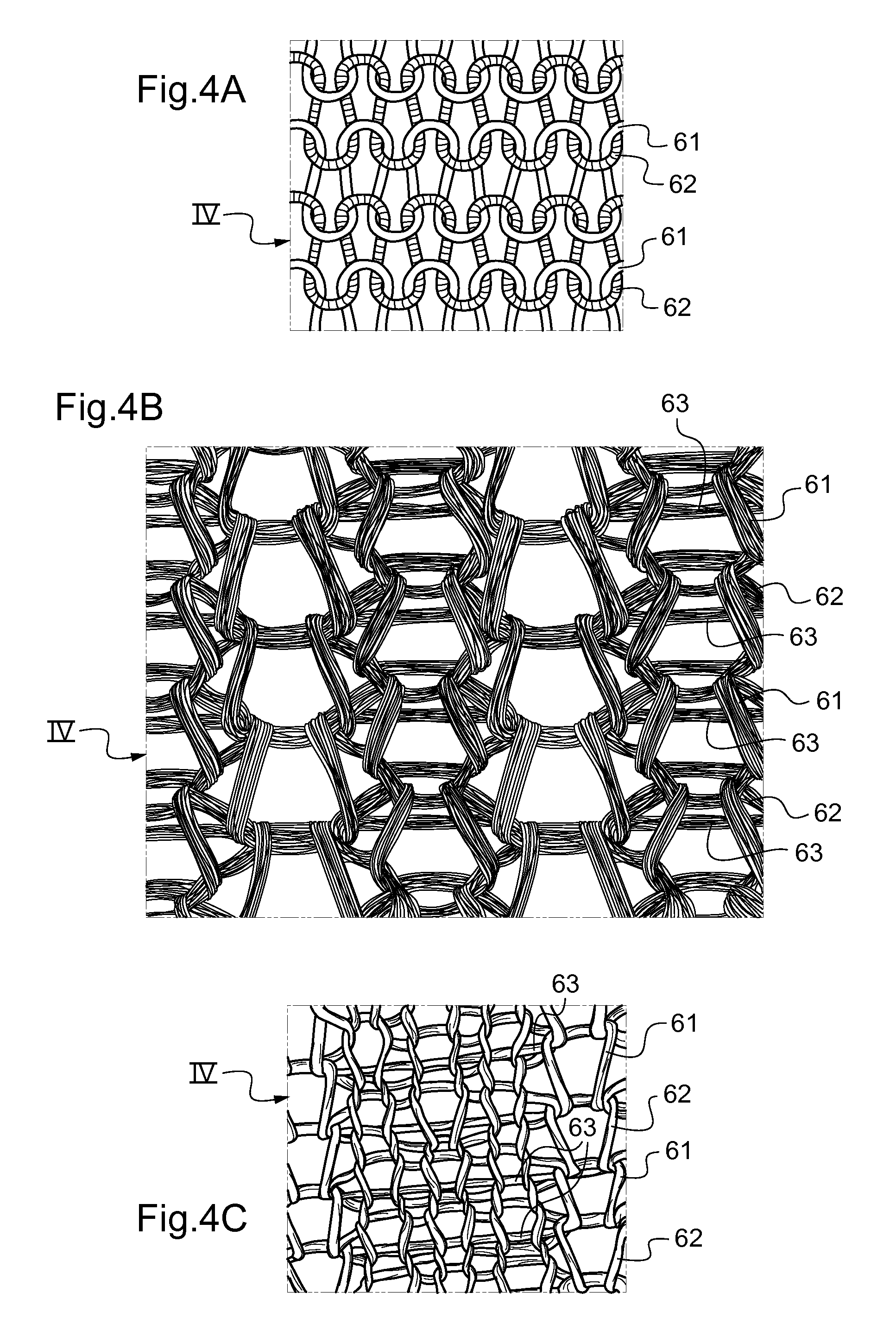
[0051]As shown in FIGS. 1 to 3, and in accordance with an essential characteristic of the invention, the top portion 9 of the compression garment 10 is folded so as to define a folded edge 15 with an outside welt 16 and an inside we...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| circumference | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com