Fabric material
a technology of fabric and material, applied in the field of fabric materials, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of fabric, affecting the appearance of fabric, and affecting the appearance of fabric, and achieve the effects of inhibiting the irritation of the skin of users, reducing the risk of bacterial colonization, and reducing the risk of pressure ulcers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
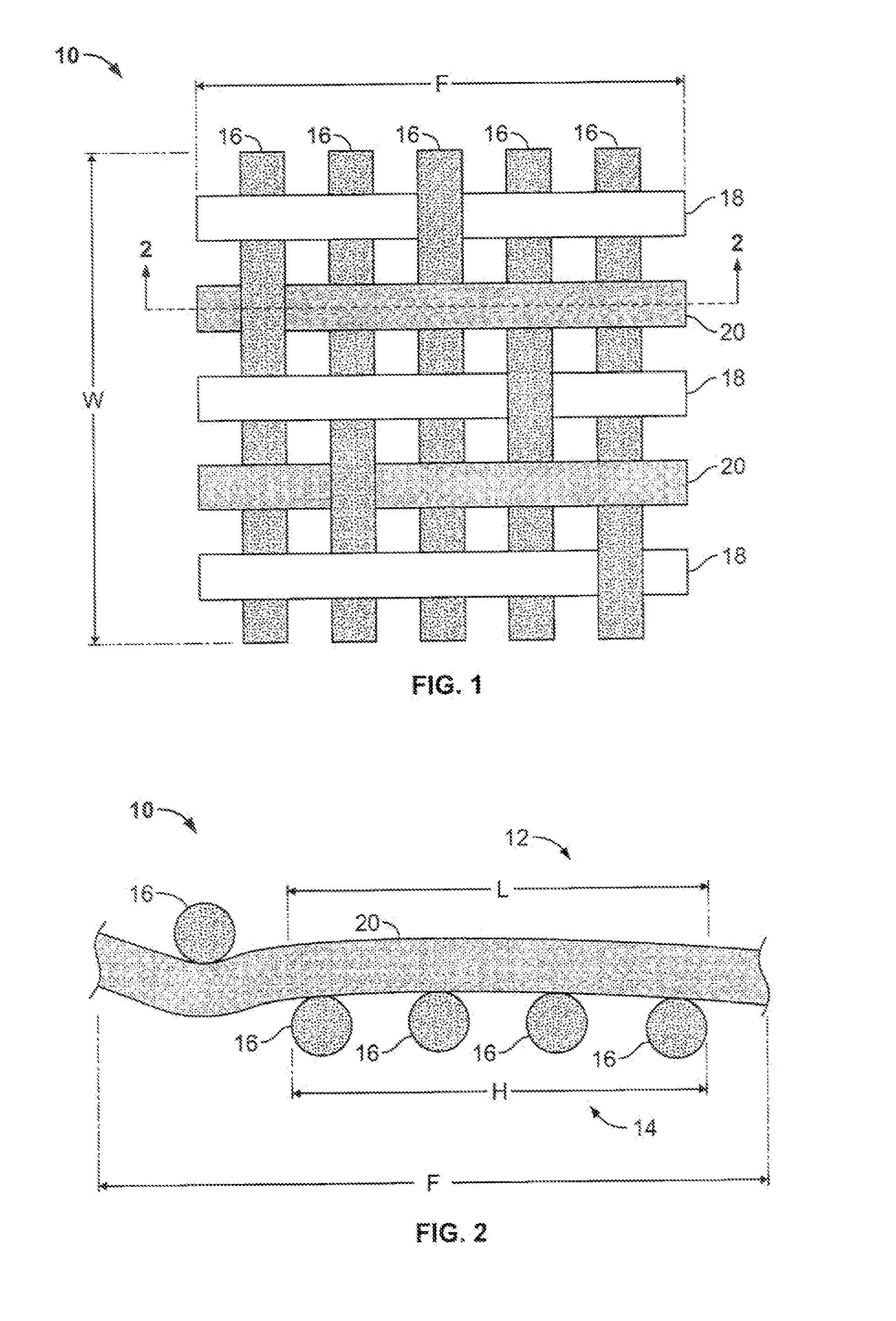
[0017]Although the present invention can be used in conjunction with a fabric material for use with any type of sleeping or resting facility, it is particularly suitable for bed sheets used in hospitals, medical facilities, and nursing homes. Accordingly, the present invention will be described hereinafter in connection with bed sheets used in hospitals, medical facilities, and nursing homes. It should be understood, however, that the following description is only meant to be illustrative of the present invention and is not meant to limit the scope of the present invention, which also has applicability in other facilities (e.g., hotels, etc.) or for other products, such as pillow cases, wearing apparel and clothing, boots and other footwear, elbow and knee pads, and other fabric protective guards and shields.
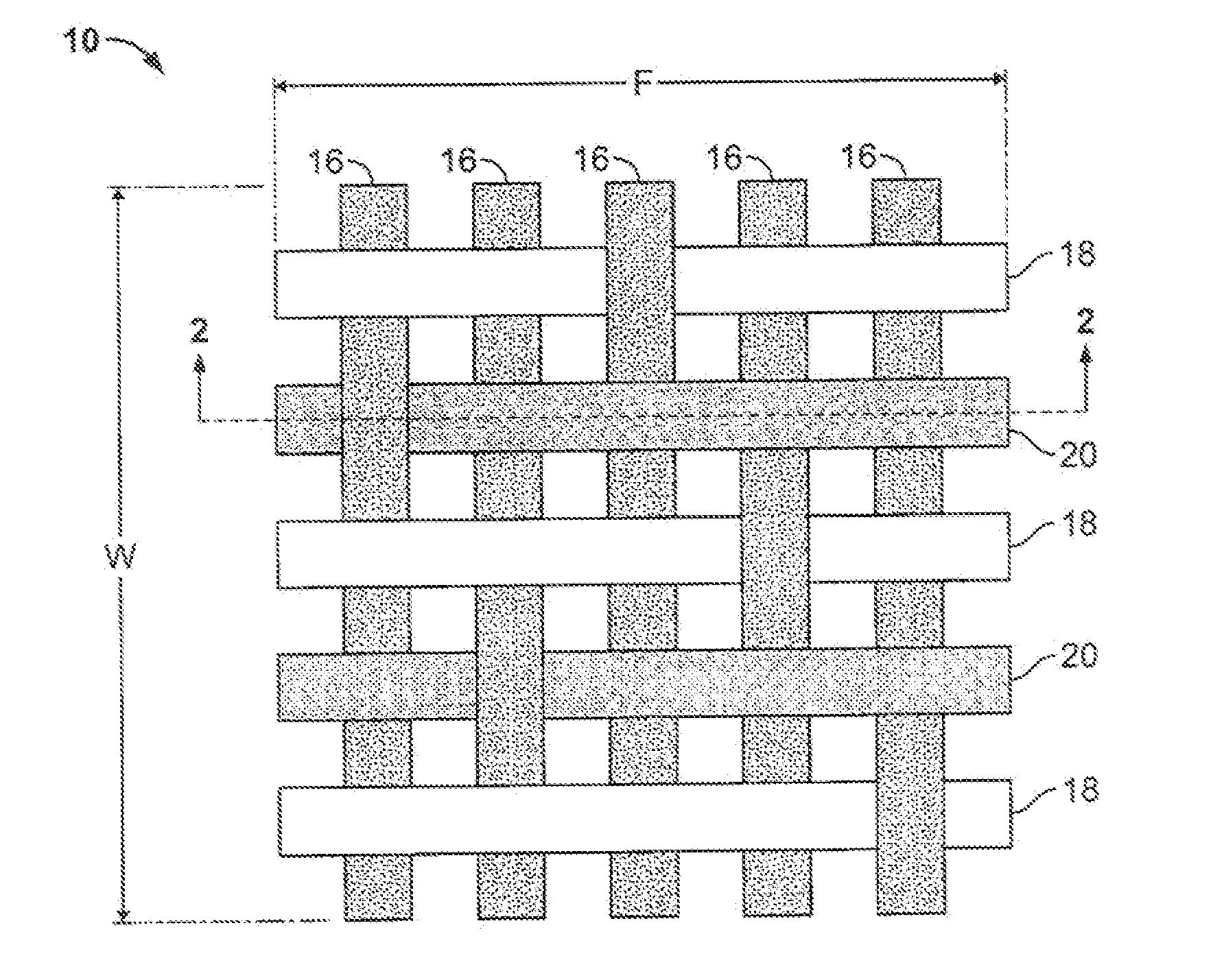
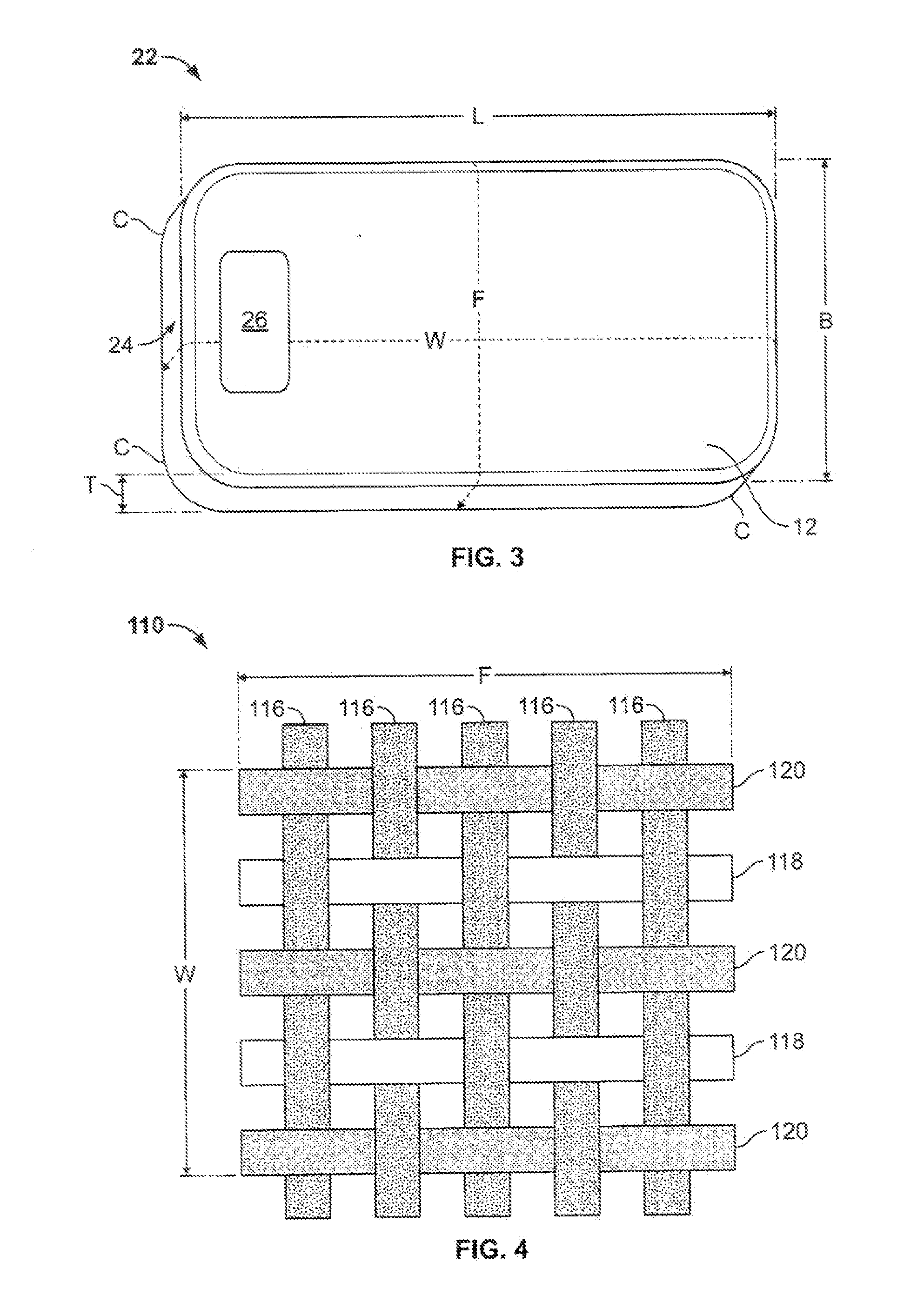
[0018]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate a portion of a fabric material 10 constructed in accordance with embodiment of the present invention. In embodiments to be described hereinbelow, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coefficient of friction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com