Mark Reader Configured to Prioritize Images
a reader and image technology, applied in the field of mark or symbology readers, can solve the problems of large variation in the overall trigger-to-decode time, unsatisfactory both of these methods, and difficulty in detecting or decoding images within a limited number of images, so as to reduce the mean time to a successful decode and reduce the trigger-to-decode response time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
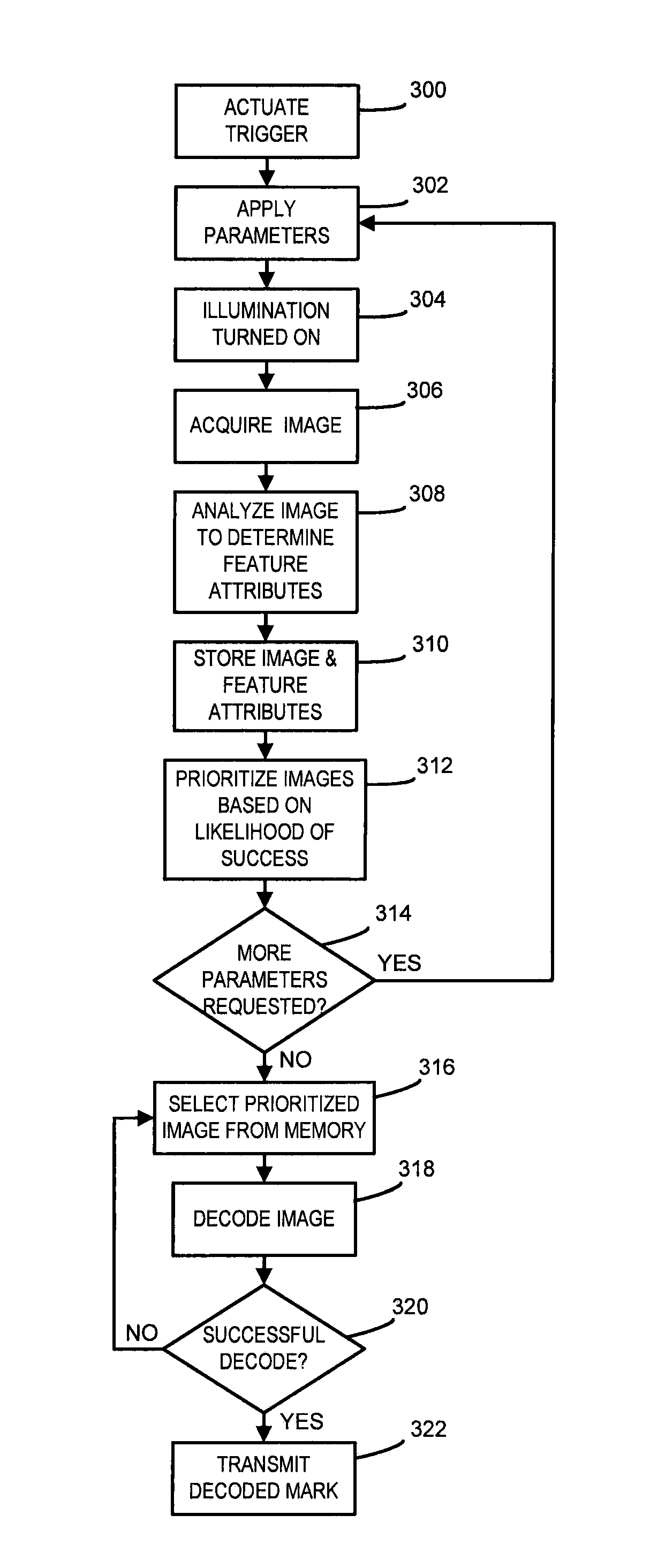
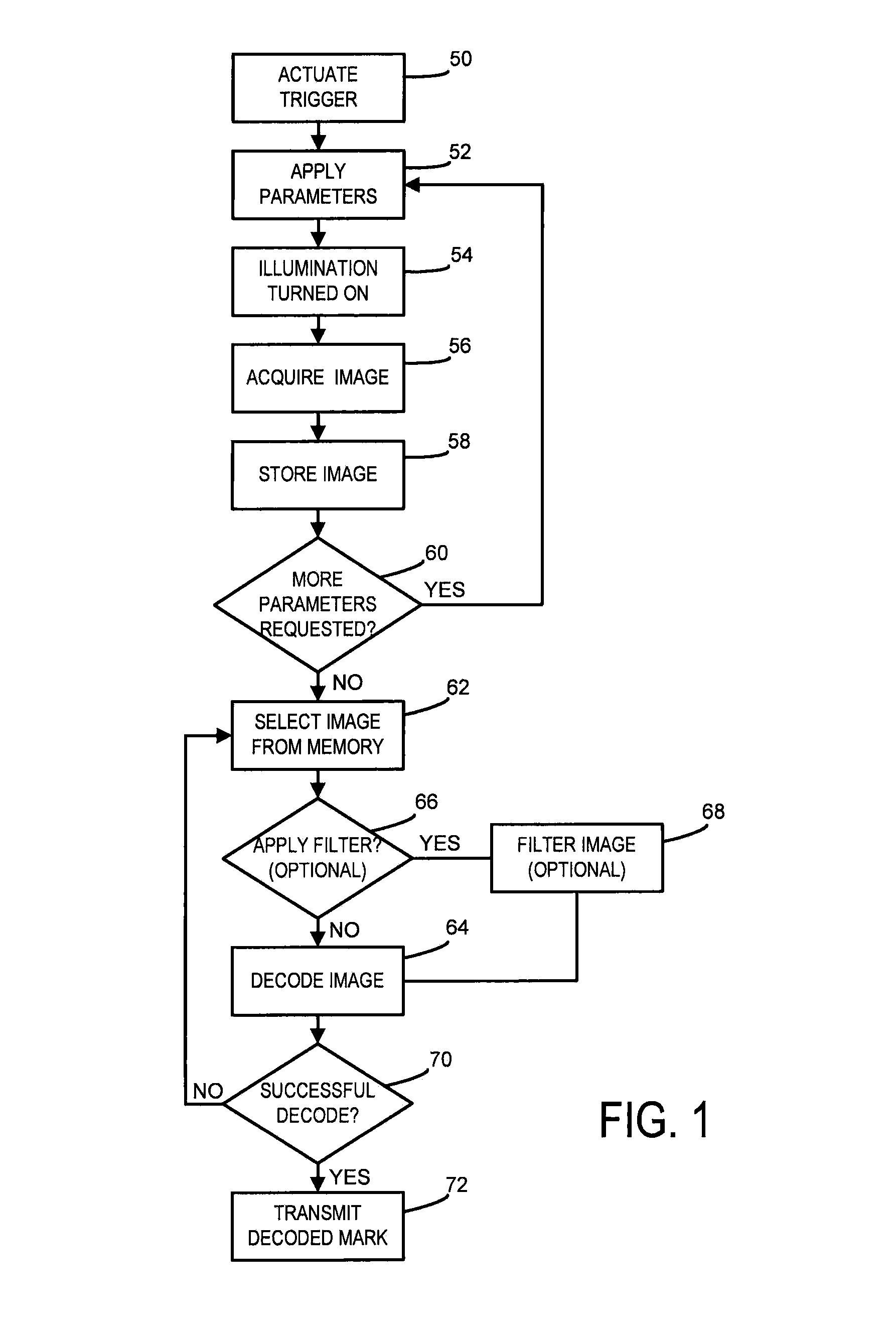
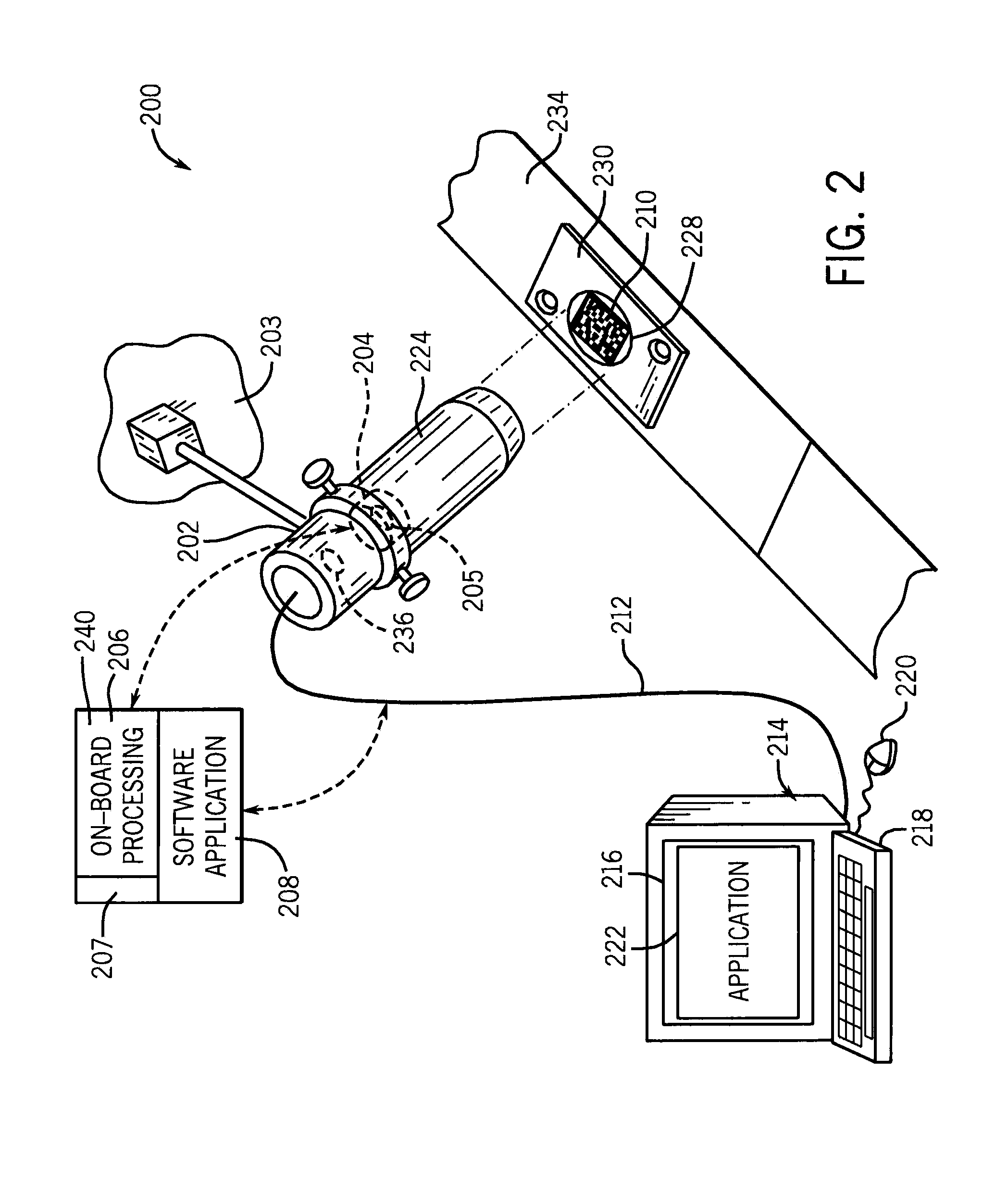
[0026]Referring to the drawings wherein like reference numerals correspond to similar elements throughout the views, and more specifically, referring to FIG. 2, the present embodiments are described in the context of an exemplary fixed mount mark reader system 200. The exemplary reader is provided with camera element 202 that is a conventional camera mounted on a fixed bracket 203. The camera element includes an image acquisition system 204, including a sensor 205, both shown in phantom, and is controlled to direct image data to a remote or an onboard embedded processor 206. This processor includes a software application 208 by which illumination is controlled, images are acquired and image data is interpreted into usable information derived from the marks (such as the depicted two-dimensional mark 210). Usable information includes, for example, alphanumeric strings, binary data, and binary data along with interpretation information, such as a flag to indicate the binary data is Kan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com