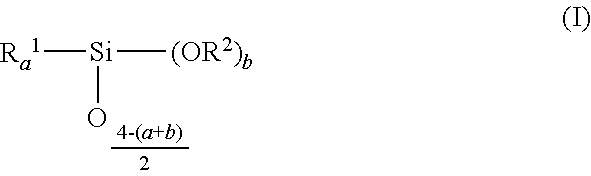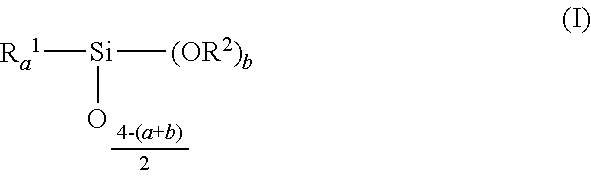Reactive liquid ceramic binder resin
a liquid ceramic and resin technology, applied in the field of reactive liquid ceramic binder, can solve the problems of high firing temperature, inability to obtain sufficient high green strength of ceramic products molded from ceramic particles, and insufficient production of homogenous mixtures with ceramic materials, so as to reduce nox emission, reduce energy consumption in the production of ceramic products, and reduce the effect of green strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Binding Strength in Corundum Bricks
[0159]A high purity sintered alumina, T60 obtainable from the firm ALMATIS GmbH in Ludwigshafen, with the following grain size composition:
Coarse-grained1-2mm50 wt. %Medium-grained0.2-0.5mm10 wt. %Flourmm40 wt. %
was homogenously mixed with 4 wt. parts of compound A. For comparison, a molding mix was produced with 4 wt. parts of sulfite liquor (without compound A). Test pieces were made from the mixtures under a compression pressure of 100 MPa and then fired at 600° C. and 1500° C. for 2 hrs. After firing, the test pieces had the following characteristics:
WithWithoutcompound Acompound A600° C.1500° C.600° C.1500° C.Cold crushing strength (MPa)>50>100(as per DIN EN 993-1)
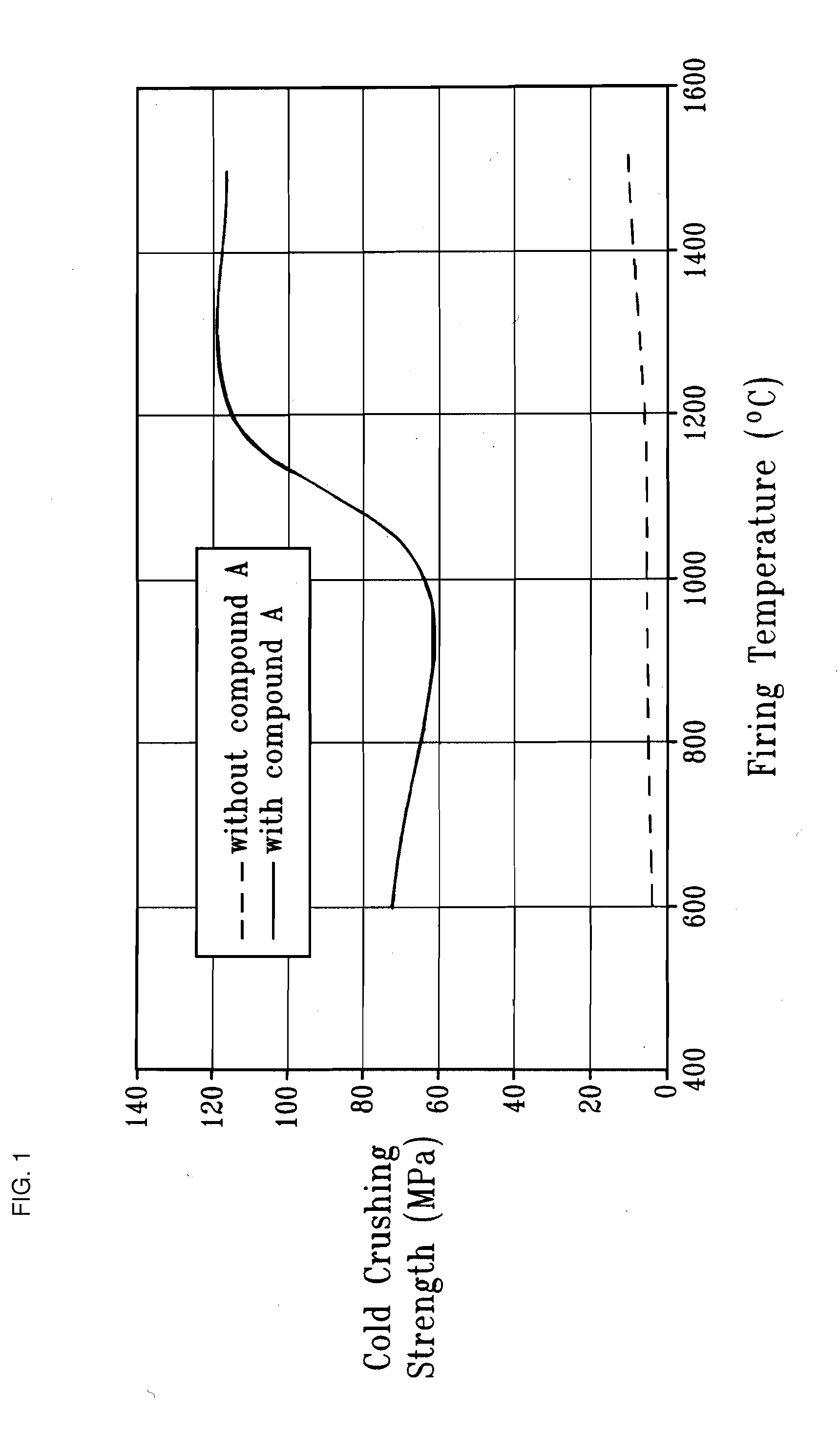
[0160]The differences in the development of the cold crushing strength depending on the firing temperature in samples with and without compound A are shown in FIG. 1.
[0161]The addition of compound A causes an enormous rise in the strength of the ceramics.
example 2
Binding Strength of Different Compounds
[0162]A high purity sintered alumina, T60 obtainable from the firm ALMATIS GmbH in Ludwigshafen, with the following grain size composition:
Coarse-grained1-2mm50 wt. %Medium-grained0.2-0.5mm10 wt. %Flourmm40 wt. %
was homogenously mixed with 4 wt. parts of compound A, B, C and D respectively. Test pieces were made from the mixtures under a compression pressure of 100 MPa and then fired at 600° C. for 2 hrs. After firing, the test pieces had the following characteristics:
CompoundABCDCold crushing strength (MPa)>50>80>60>10(as per DIN EN 993-1)
[0163]The addition of compounds A, B and C causes a large increase in the strength of the corundum bricks. The compound D develops an increased binding strength or strength of the corundum bricks after firing at 600° C.
example 3
Binding Strength of an Aqueous Emulsion
[0164]A high purity sintered alumina, T60 obtainable from the firm ALMATIS GmbH in Ludwigshafen, with the following grain size composition:
Coarse-grained1-2mm50 wt. %Medium-grained0.2-0.5mm10 wt. %Flourmm40 wt. %
was homogenously mixed with 5 wt. parts of a 50% aqueous emulsion of compound B. For comparison, a molding mix was produced with 4 wt. parts of sulfite liquor (without compound B). Test pieces were made from the mixtures under a compression pressure of 100 MPa and then fired at 600° C. and 1400° C. for 2 hrs. After firing, the test pieces had the following characteristics:
With emulsion ofWithoutcompound Bcompound B600° C.1400° C.600° C.1400° C.Cold crushing strength (MPa)>10>25(as per DIN EN 993-1)
[0165]The aqueous emulsion of compound B is suitable as a binder for corundum bricks.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| firing temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| powder density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap