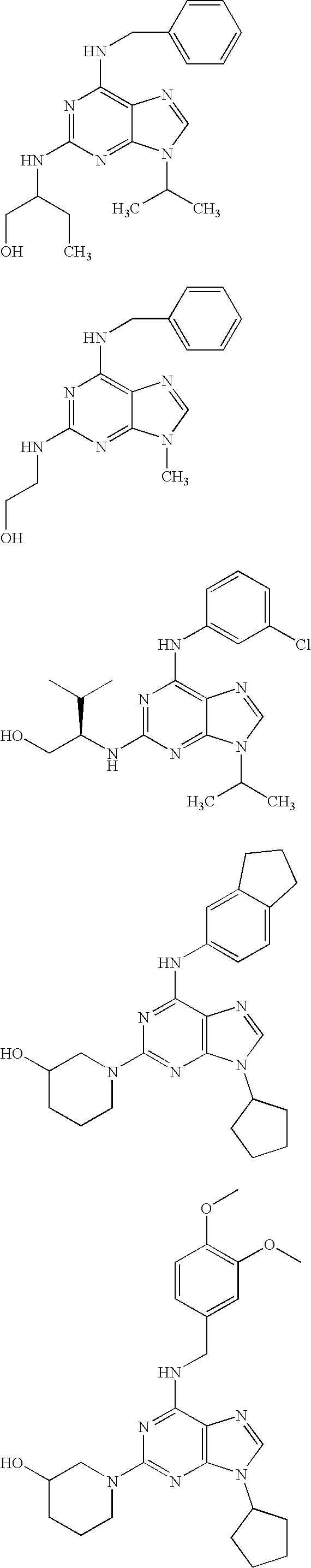
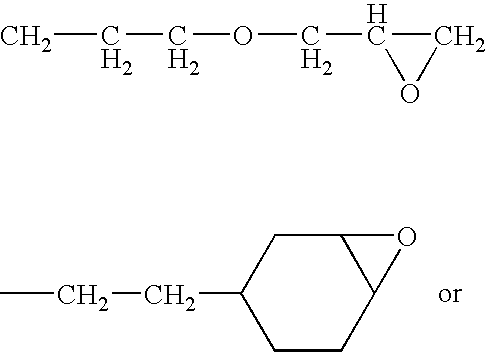
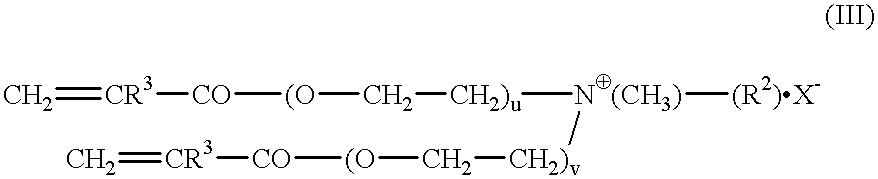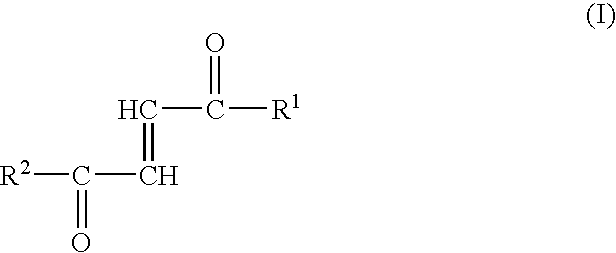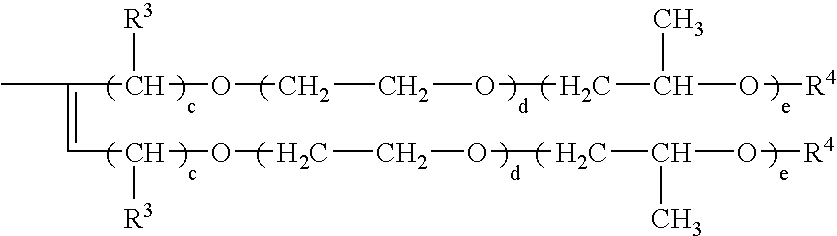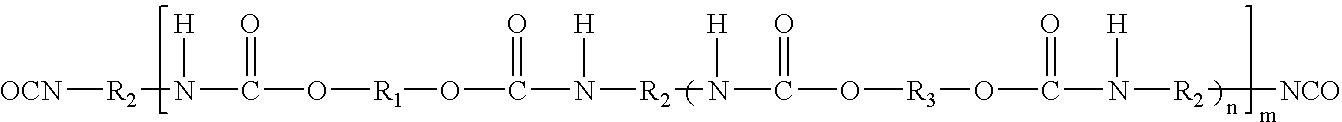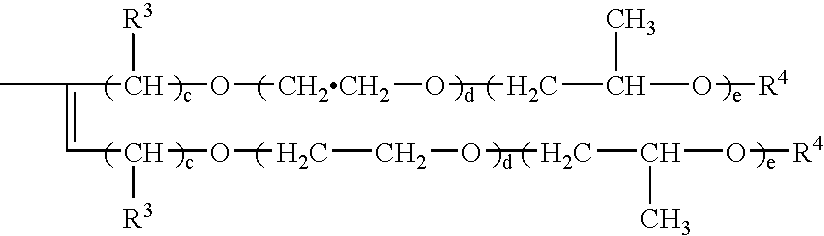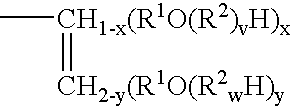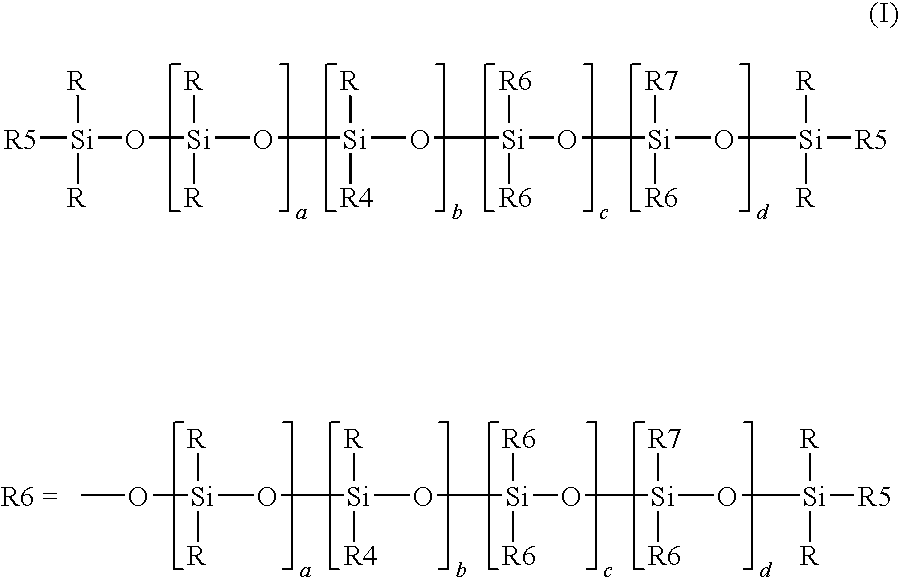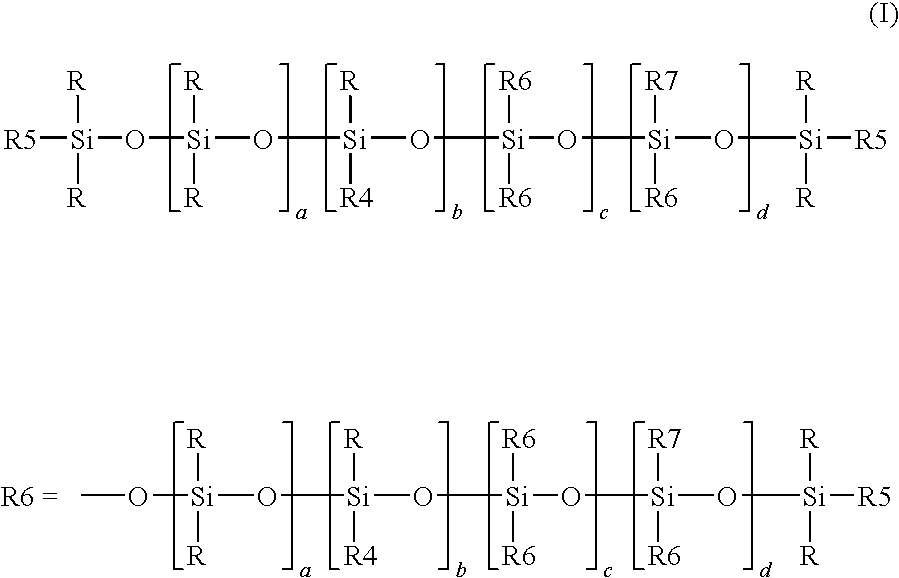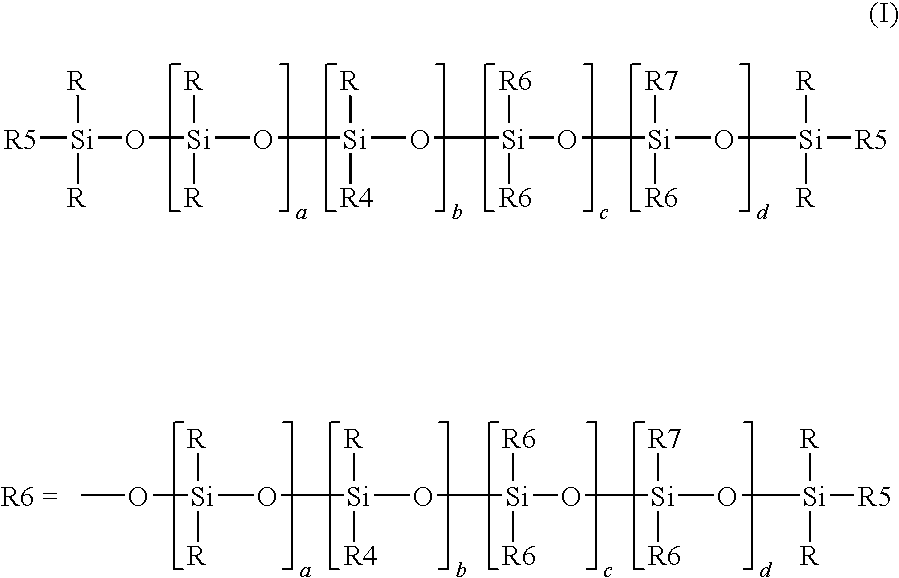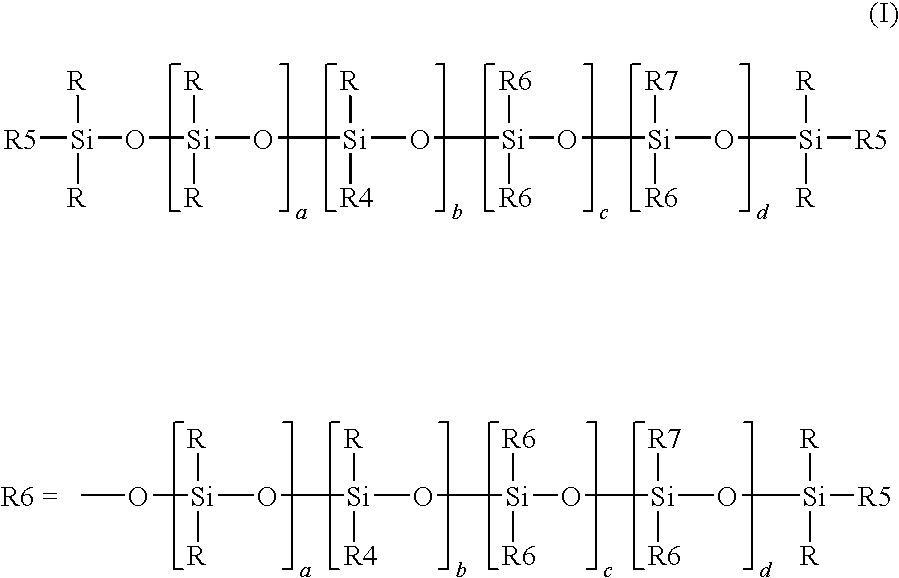Patents
Literature
539 results about "Alkyl radicals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alkyl Radicals. Alkanes from which one atom of hydrogen has been removed become monovalent radicals. These radicals, which are molecular fragments having an unpaired electron, are known as alkyl groups.
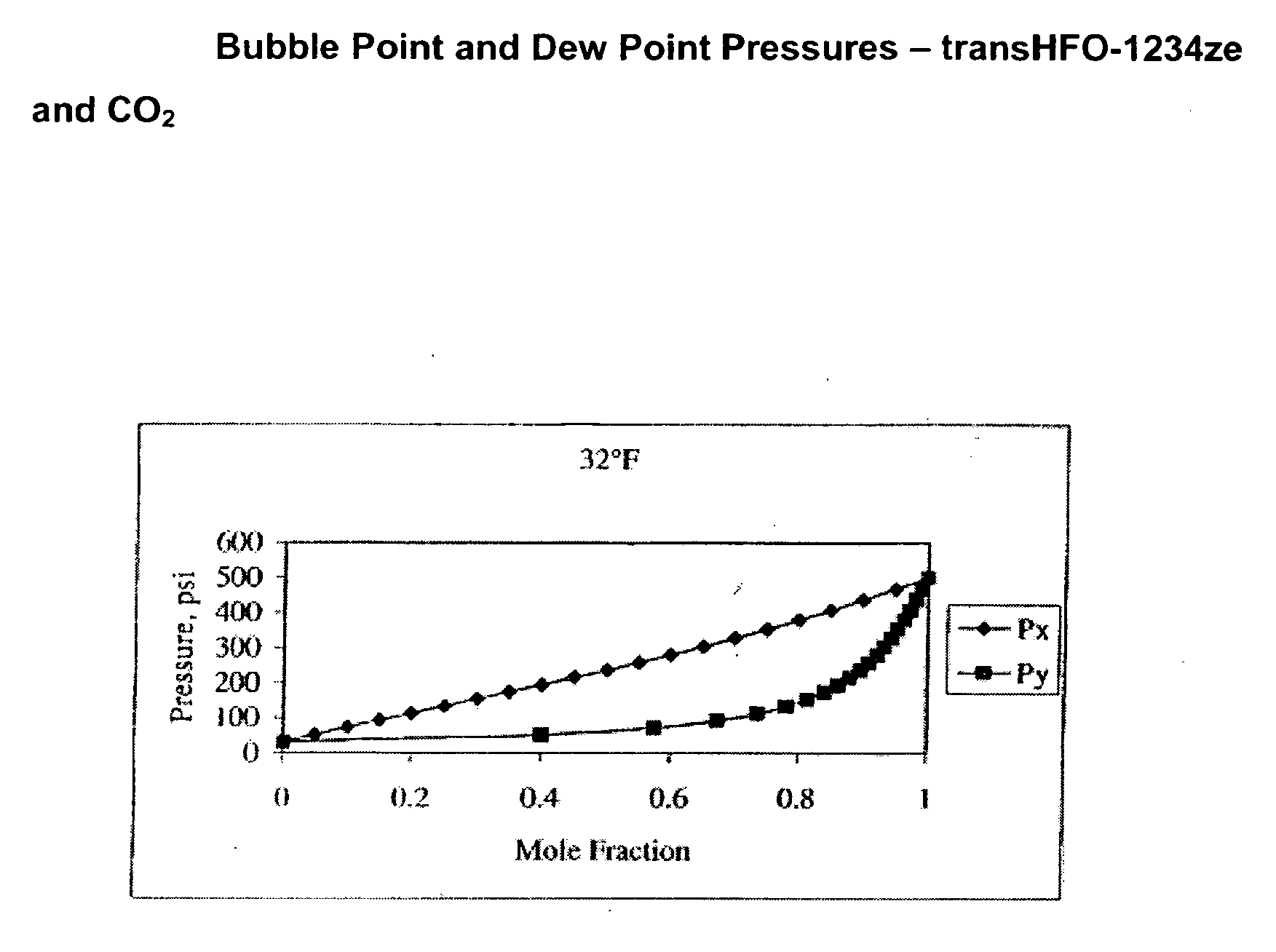
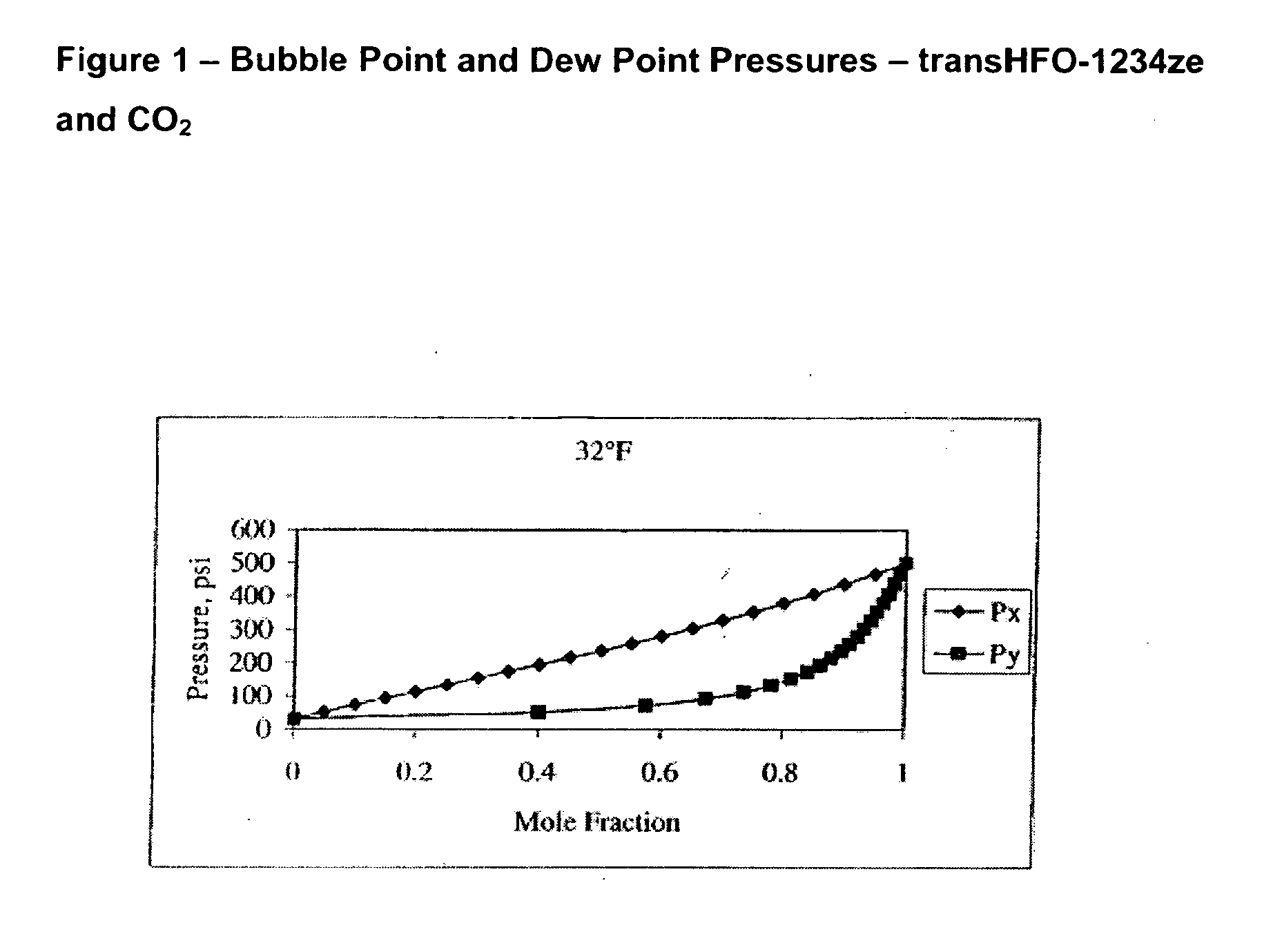
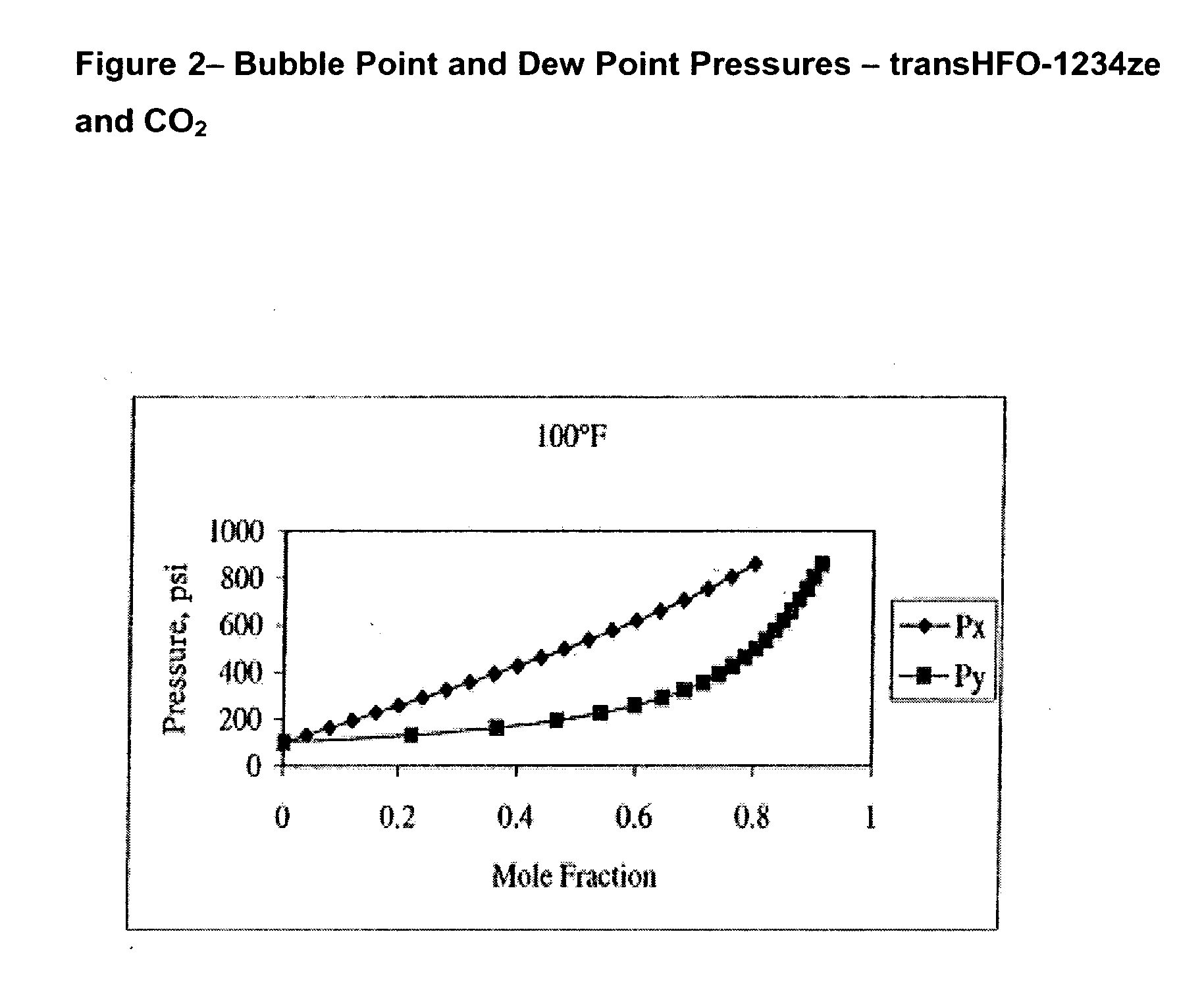
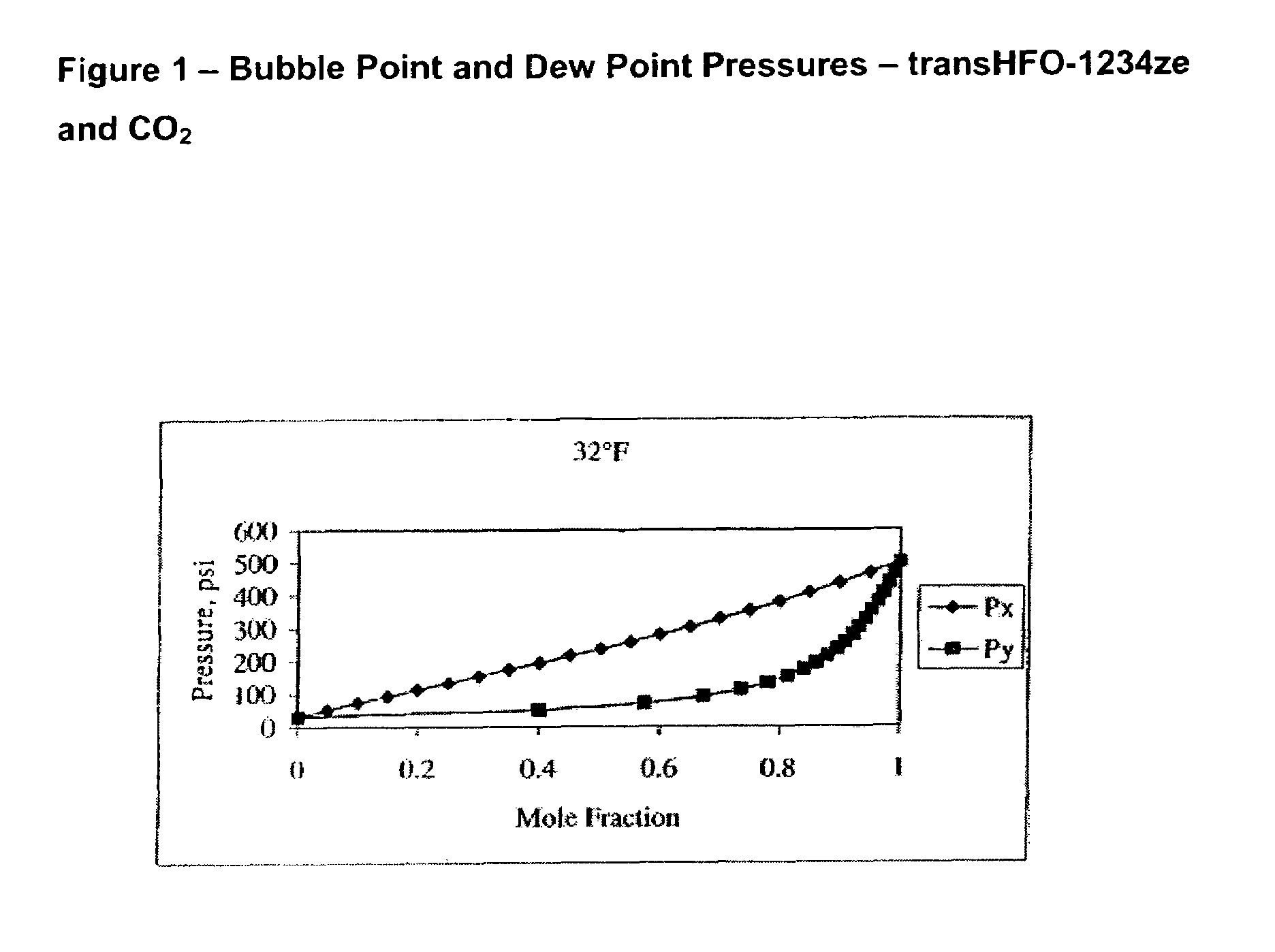
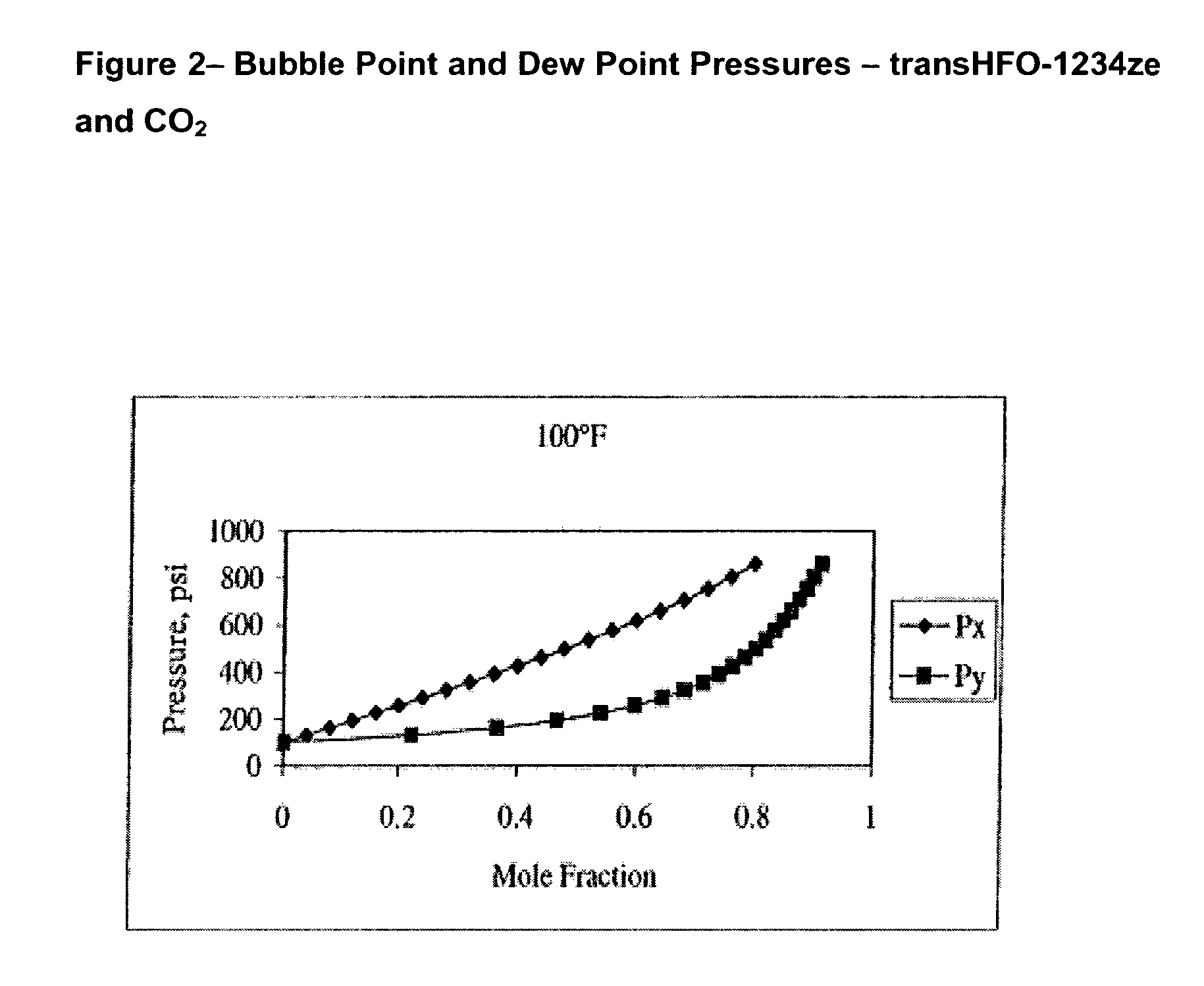
Compositions comprising tetrafluoeopropene & carbon dioxide
ActiveUS20060043331A1Maintain good propertiesReducing and eliminating deleterious ozone depletion potentialHeat-exchange elementsLiquid soapsHeat transfer fluidPhotochemistry
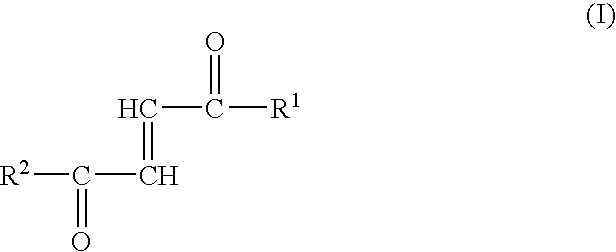
Disclosed are compositions useful in a wide variety of applications, including heat transfer fluids which possess a highly desirable and unexpectedly superior combination of properties, and heat transfer systems and methods based on these fluids. The preferred heat transfer fluid comprises from about 1 to about 40 percent, on a weight basis, of carbon dioxide (CO2) and from about 99 to about 60 percent, on a weight basis, of a compound having the Formula I XCFzR3-z (I), where X is a C2 or a C3 unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, alkyl radical, each R is independently Cl, F, Br, I or H, and z is 1 to 3. A preferred compound of Formula I is tetrafluoropropene, particularly 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene and / or 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Polymers with anti-microbial properties
The invention relates to polymers with antimicrobial properties, consisting of: a) 99-40 wt % non functional vinylically polymerizable monomers and b) 1-60 wt % functional vinylically polymerizable monomers of general formula (I) wherein V=vinyl, (meth)acroyl, allyl or styryl, A=a possibly available linking unit, which can be alkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or hydroxy alkyl, which can also be interrupted by hetero atoms, e.g. by hetero atoms in urethane, carbonate, ester, amide or ether groups, wherein y=0 or is 1, Hsp=a hydrophilic spacer of general formula (i) -(O-CH2-CH2)r- and / or (ii) -(O-CH2-CH(CH3))s with r=0-40, s=0-40 and r+s=2-40, also m=1.2 or 3 and R1=CH3, ethyl or benzyl, R2=an alkyl radical with 8-20 C-atoms, wherein t=1, 2 or 3 and X-=Cl-, Br-, I- or alkyl sulphate.
Owner:EVONIK ROEHM GMBH
Intercalates formed by co-intercalation of monomer, oligomer or polymer intercalants and surface modifier intercalants and layered materials and nonocomposites prepared with the intercalates
The present invention discloses intercalates formed by contacting a layered material, e.g., a phyllosilicate, with an intercalant monomer surface modifier including an alkyl radical having at least 6 carbon atoms and a polymerizable monomer, oligomer or polymer. The intercalant monomer surface modifier converts the interlayer region of the layered materials from hydrophilic to hydrophobic, therefore, polymerizable monomers, oligomers or polymers can be easily intercalated into the interlayer spacing. The co-presence of the intercalant monomer surface modifier and polymerizable monomer, oligomer or polymer provide an environment for more polymerizable monomers, oligomers or polymers to be intercalated into the interlayer spacing and the intercalates are readily exfoliated into polymer matrices to form nanocomposites. The nanocomposites (e.g., epoxy-clay) prepared from the intercalates demonstrated enhanced mechanical, thermal and chemical resistance compared with pristine polymer matrices.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Fumaric acid amides
InactiveUS7157423B2More resistant to hydrolysisEasy to handleAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseSide chain
Fumaric acid amides of the general formula (I)wherein R1 represents OR3 or a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR4—COOH bonded via an amide bond, wherein R3 is hydrogen, a straight-chained or branched, optionally substituted C1-24 alkyl radical, a phenyl radical or C6-10 aralkyl radical and R4 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid and R2 represents a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR5—COOH bonded via an amide bond or a peptide radical comprising 2 to 100 amino acids bonded via an amide bond, wherein R5 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid, are used for preparing a drug (1) for the therapy of an autoimmune disease; (2) for use in transplantation medicine; (3) for the therapy of mitochondrial diseases; or (4) for the therapy of NF-kappaB mediated diseases.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
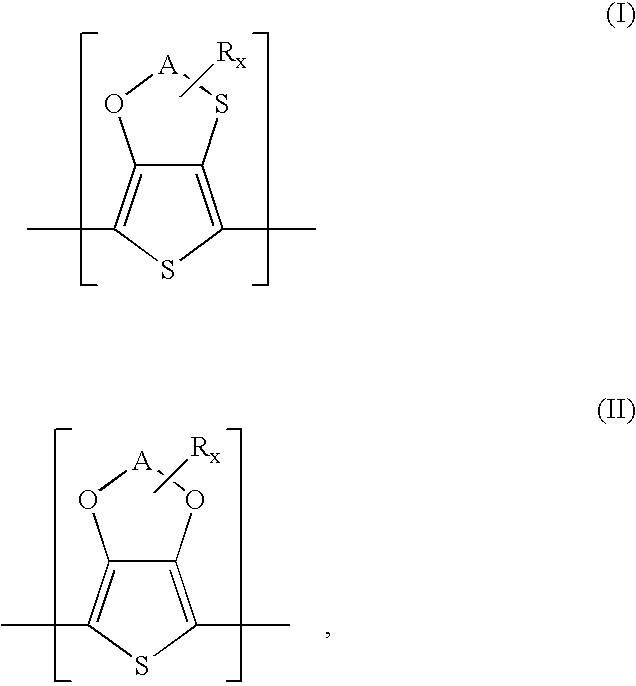
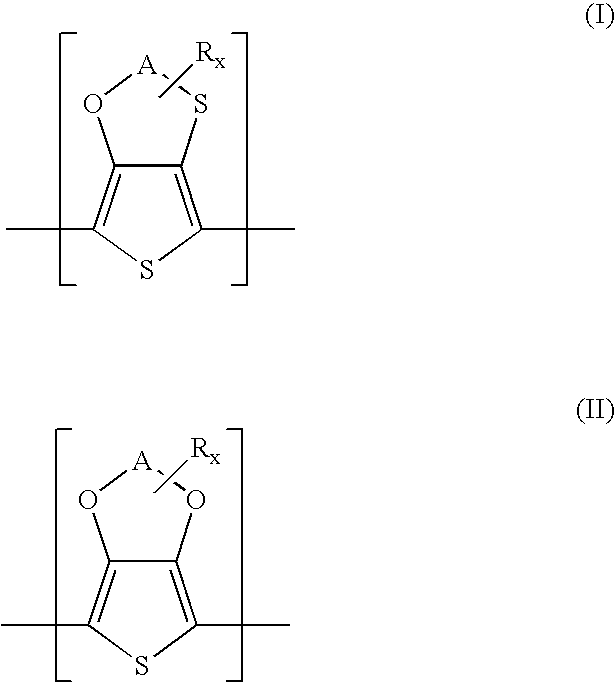
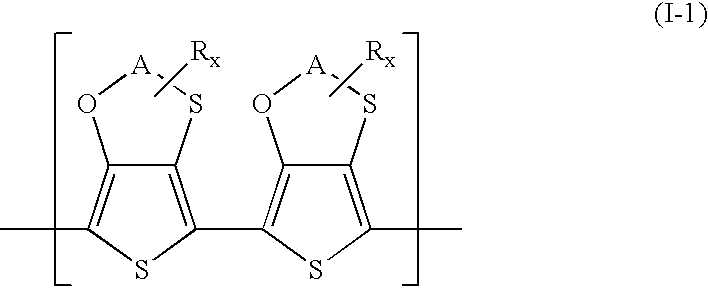
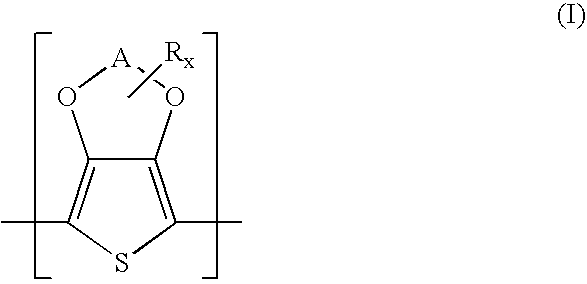
Polythiophenes having alkyleneoxythia thiophene units in electrolyte capacitors
InactiveUS7341801B2Reduce conductivityConductivity adjustableHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesPolymer scienceElectrolysis
Electrolyte capacitors containing certain polythiophenes are described. More particularly, the polythiophenes have backbones containing repeating units of the following general formula (I) and / or repeating units of the following general formula (II),wherein A is, for example, a C1-C5-alkylene radical, R is, for example, a C1-C18-alkyl radical, and x is an integer from 0 to 8. Also described are dispersions comprising such polythiophenes, and the use of such polythiophenes or dispersions thereof for producing conductive layers.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
Catalyst for olefine polymerizing reaction and its components
The present invention provides one kind catalyst component for CH2=CHR olifine polymerization, where R is H or alkyl radical or aryl radical of C1-C6. The catalyst component contains Mg, Ti, halogen and electron donor.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Organopolysiloxanes for defoaming aqueous systems
InactiveUS6858663B2Improve balanceRapid foam collapseGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesWater insolublePrinting ink
The invention relates to the use of water-insoluble organopolysiloxane derivatives of the general formula (I) in which the radicalsR1 are alkyl radicals, preferably having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or aryl radicals, but at least 80% of the radicals R1 are methyl radicals, andR2 at least once in the molecule has the definition (a) for defoaming aqueous media, especially printing inks and paints.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Fumaric Acid Amides
InactiveUS20060205659A1Easy to handleMore resistant to hydrolysisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune conditionHydrogen
Fumaric acid amides of the general formula (I) wherein R1 represents OR3 or a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR4—COOH bonded via an amide bond, wherein R3 is hydrogen, a straight-chained or branched, optionally substituted C1-24 alkyl radical, a phenyl radical or C6-10 aralkyl radical and R4 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid and R2 represents a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR5—COOH bonded via an amide bond or a peptide radical comprising 2 to 100 amino acids bonded via an amide bond, wherein R5 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid, are used for preparing a drug (1) for the therapy of an autoimmune disease; (2) for use in transplantation medicine; (3) for the therapy of mitochondrial diseases; or (4) for the therapy of NF-kappaB mediated diseases.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
Injection molding method for neutral and acidic-group containing (meth)acrylate copolymers
InactiveUS20020160042A1Reduce contentOrganic dyesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMeth-Additive ingredient
The invention relates to a process for producing mouldings by injection moulding, the steps in the process being A) Melting a mixture made from a) a (meth)acrylate copolymer composed of from 40 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized C1-C4-alkyl esters of acrylic or methacrylic acid and from 0 to 60% by weight of (meth)acrylate monomers having an anionic group in the alkyl radical, where the copolymer comprises b) from 0.1 to 3% by weight of a release agent, and, where appropriate, the mixture may comprise c) from 0 to 50% by weight of a drier, d) from 0 to 30% by weight of a plasticizer, e) from 0 to 100% by weight of additives or auxiliaries, f) from 0 to 100% by weight of an active pharmaceutical ingredient, g) from 0 to 20% by weight of another polymer or copolymer, where the amounts given for components b) to g) are based on the (meth)acrylate copolymer a) and the mixture prior to melting has a content of more than 0.5% by weight of low-boiling constituents with vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C., B) Devolatilizing the mixture in the thermoplastic state at temperatures of at least 120° C., thereby lowering to not more than 0.5% by weight the content of the low-boiling constituents with vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C., C) Injecting the molten and devolatilized mixture into the mould cavity of an injection mould, the temperature of the mould cavity being below the glass transition temperature of the (meth)acrylate copolymer by at least 10° C., cooling the molten mixture, and removing the resultant moulding from the mould.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Method for injection moulding moulded bodies consisting of (meth) acrylate copolymers
InactiveUS20040104501A1Reduce contentLittle reabsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEndocrine system disorderPolymer scienceMeth-
The invention relates to a process for producing mouldings by injection moulding the steps in the process being a) melting and mixing of a (meth)acrylate copolymer composed of from 85 to 98% by weight of C1-C4-alkyl (meth)acrylates capable of free-radical polymerization and from 15 to 2% by weight of (meth)acrylate monomers having a quaternary ammonium group in the alkyl radical, with from 10 to 25% by weight of a plasticizer, and also from 10 to 50% by weight of a dryers [sic] and / or from 0.1 to 3% by weight of a release agent, and, where appropriate, with other conventional pharmaceutical additives or auxiliaries and / or with an active pharmaceutical ingredient, b) devolatilizing the mixture at temperatures of at least 120° C., thus reducing the content of the low-boiling constituents with a vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C. to not more than 0.5% by weight, and c) injecting the devolatilized mixture at a temperature of from 80 to 160° C. into the mould of an injection moulding system and removing the resultant moulding from the mould.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG +1
Heat transfer fluid comprising 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoeopropene and carbon dioxide
ActiveUS20050241805A1Reducing and eliminating deleterious ozone depletion potentialReduce and eliminate negative global warming effectOther chemical processesNon-surface-active detergent compositionsHeat transfer fluidPhotochemistry
Disclosed are compositions useful in a wide variety of applications, including heat transfer fluids which possess a highly desirable and unexpectedly superior combination of properties, and heat transfer systems and methods based on these fluids. The preferred heat transfer fluid comprises from about 1 to about 40 percent, on a weight basis, of carbon dioxide (CO2) and from about 99 to about 60 percent, on a weight basis, of a compound having the Formula I XCFzR3-z (I), where X is a C2 or a C3 unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, alkyl radical, each R is independently Cl, F, Br, I or H, and z is 1 to 3. A preferred compound of Formula I is tetrafluoropropene, particularly 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Cross-linkable polymers, method for the production thereof, and shaped bodies made of cross-linked polymers
InactiveUS6528585B1Low levelExtended maintenance periodPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a process for preparing crosslinkable polymers containing silane groups having at least one hydrolyzable radical by free-radical-initiated grafting of the base polymers with an olefinically unsaturated silane having at least one hydrolyzable radical, wherein the grafting is carried out in the presence of(a) an alkylsilane of the formula I, whereR1 is a monovalent hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 33 carbon atoms or a divalent hydrocarbon radical having from 4 to 24 carbon atoms,R2 is a hydrocarbon radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms,X are identical or different hydrolyzable radicals,n is 0, 1 or 2 andm is 1 or 2 and / or(b) a fluoroalkylsilane of the formula whereR3 is a fluoroalkyl radical,R4 is an alkyl radical andX is a hydrolyzable radical,x is an integer from 1 to 3,y is 0, 1 or 2 andz is an integer from 1 to 3, with the proviso that the sum x+y+z=4.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Intercalates and exfoliates formed with long chain (C6+) or aromatic matrix polymer-compatible monomeric, oligomeric or polymeric intercalant compounds, and composite materials containing same
InactiveUS6242500B1Efficient electrostatic complexingEasy to separateOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesOrganic liquidsPlatelet
Intercalates formed by contacting a layered material, e.g., a phyllosilicate, with an intercalant surface modifier selected from the group consisting of a compound having an alkyl radical containing at least 6 carbon atoms, a compound containing an aromatic ring, and mixtures thereof, said surface modifier including a matrix material-reactive functional group, to sorb or intercalate the intercalant surface modifier between adjacent platelets of the layered material. Sufficient intercalant surface modifier is sorbed between adjacent platelets to expand the adjacent platelets to at least about 10 Å, up to about 100 Å. The intercalated complex can be combined with an organic liquid into a viscous carrier material, for delivery of the carrier material, or for delivery of an active compound; or the intercalated complex can be combined with a matrix polymer to form a strong, filled polymer matrix.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Use of non-spreading silicone surfactants in agrochemical compositions
InactiveUS6734141B2Improve performanceReduce decreaseBiocideAnimal repellantsHydrogenChemical composition
This invention provides for, inter alia, a method for increasing the rainfastness of an agrochemical composition without increasing its spreading properties, which comprises adding to said agrochemical composition an effective amount of one or more silicone surfactants of the formulawhereinn is 1 to 3,R is an alkyl radical with 1 to 6 carbon atoms,R' is a radical of the structurewhereinm is 2 to 6,R'' is independantly methyl, ethyl or phenyl,Z is hydrogen, an alkyl radical with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an acyl radical with 2 to 6 carbon atoms,y is 6 to 30,z is 0 to 10,with the proviso that the ratio y / z is 1 or greater, and that the total number of alkylene oxide groups n*(y+z) in the siloxane polymer (I) is at least 12.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
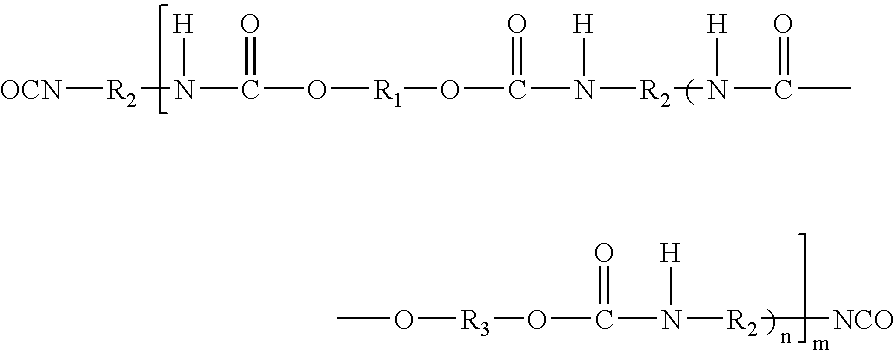
Polyurethane dispersions for use in personal care products
The invention relates to an aqueous polyurethane dispersion suitable for use in personal care products, the dispersed polyurethane comprising the reaction products of:A) a prepolymer according to the formula:whereinR1 represents a bivalent radical of a dihydroxyl functional compound,R2 represents a hydrocarbon radical of an aliphatic or cycloaliphatic polyisocyanate,R3 represents a radical of a low molecular weight diol, optionally substituted with ionic groups,n is from 0 to 5, andm is >1;B) at least one chain extender according to the formula:H2N—R4—NH2 wherein R4 represents an alkylene or alkylene oxide radical not substituted with ionic or potentially ionic groups; andC) at least one chain extender according to the formula:H2N—R5—NH2 wherein R5 represents an alkylene radical substituted with ionic or potentially ionic groups.
Owner:COVESTRO LLC
Transparent electrode for electro-optical structures
InactiveUS20050053801A1Conductive layers on insulating-supportsElectroluminescent light sourcesPolyanilinePhotochemistry
A transparent electrode that includes a first layer that is interposed between a substrate (e.g., of inorganic glass) and a second layer, is described. The first layer includes a conductive polymer (e.g., a polythiophene), and the second layer includes at least one polymeric anion and at least one of a polyanaline, a substituted polyaniline and a polythiophene represented by the following general formula (I), in which A may be a C1-C5 alkylene radical, R may be a linear or branched C1-C18 alkyl radical, and x is 0 to 8, provided that when x is greater than 1, each R may be the same or different. Also described is a method of preparing the transparent electrode, and articles of manufacture (e.g., an electroluminescent array) that include the transparent electrode of the present invention.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
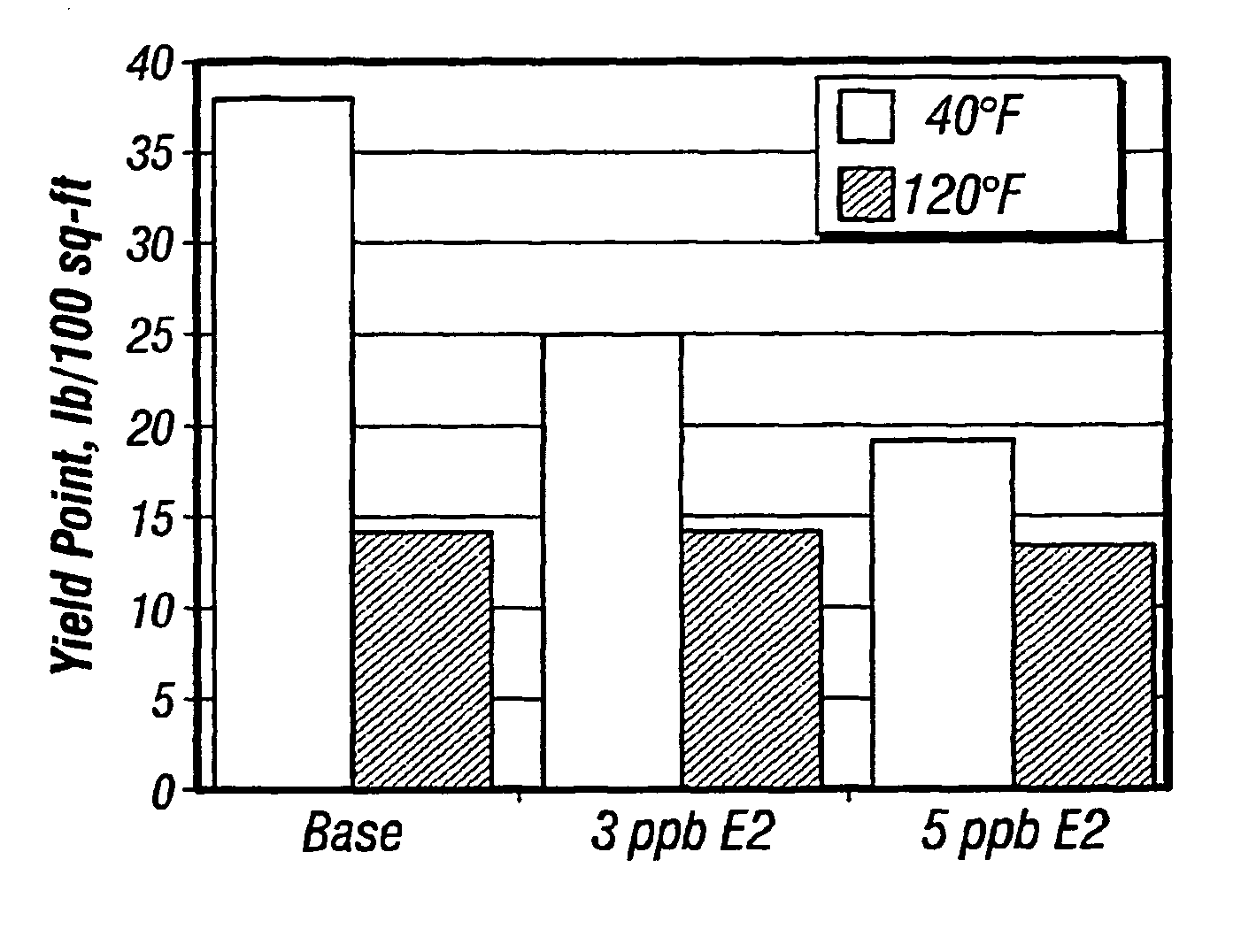
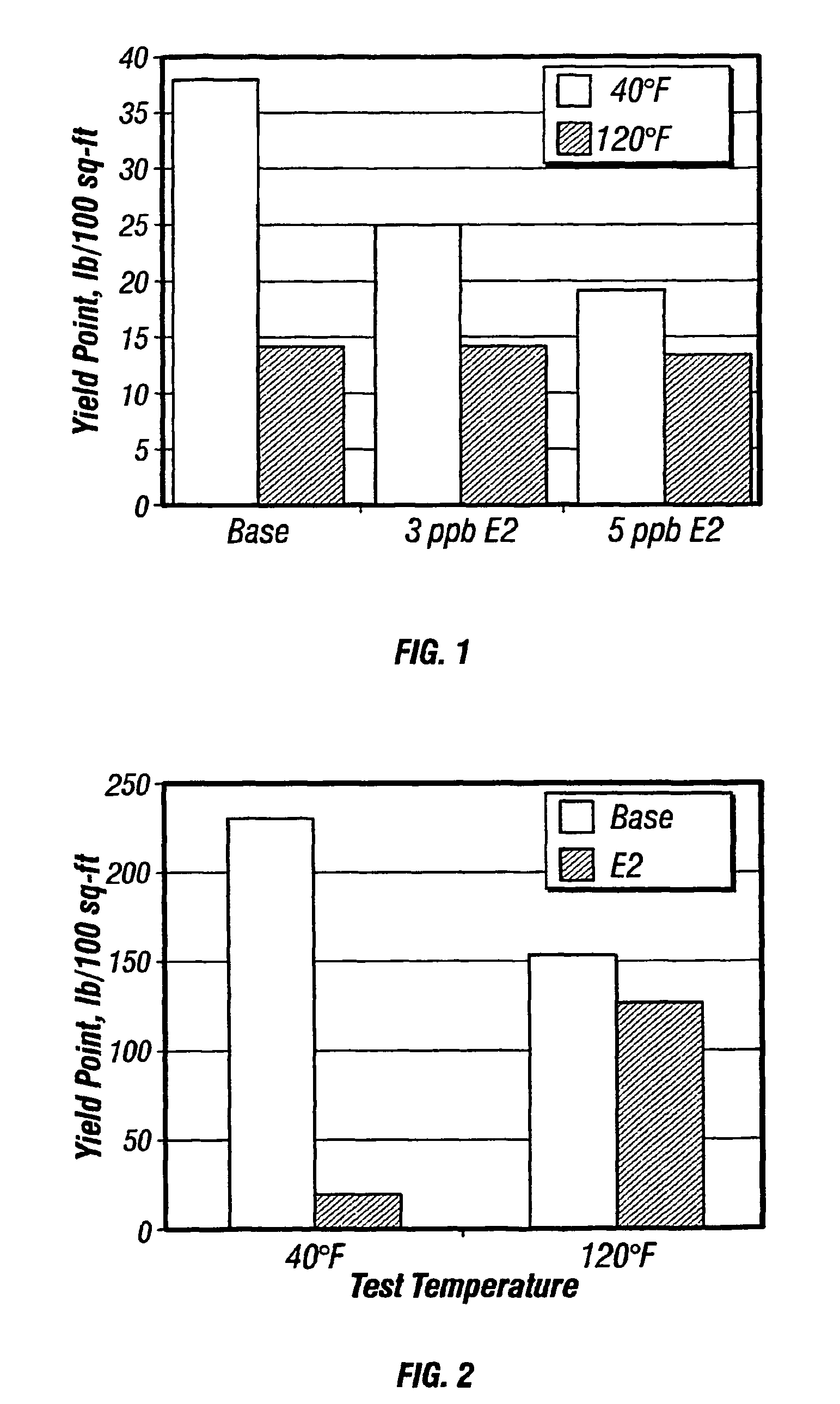
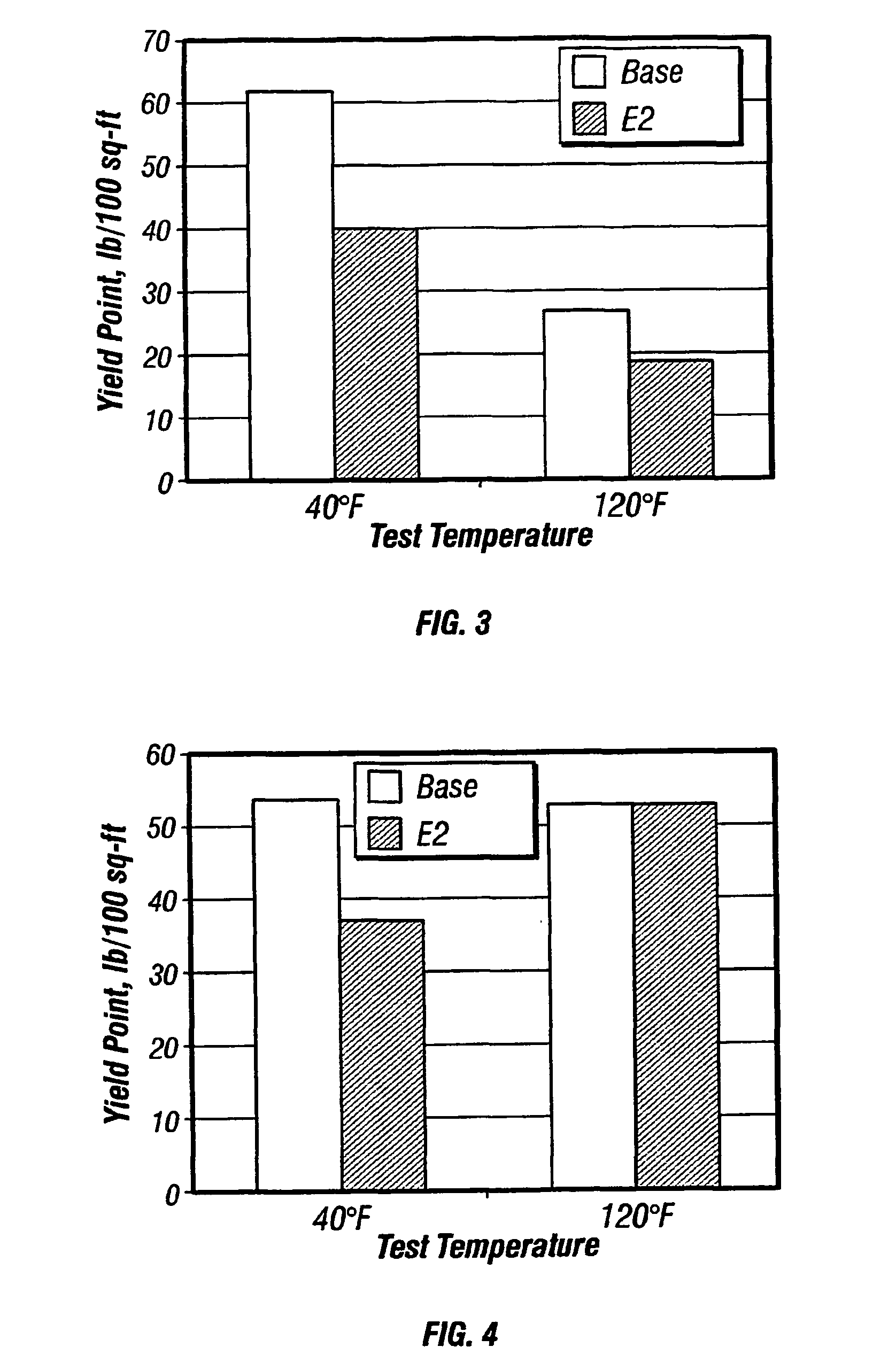
Thinners for invert emulsions
A method of reducing the viscosity of oil-based drilling fluids and well service fluids at low temperatures and a thinner compound for use in such drilling fluids and well service fluids is disclosed. The method comprises adding to said drilling fluids or well service fluids a thinner having the formula:R—(C2H4O)n(C3H6O)m(C4H8O)k-Hwhere R is a saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched alkyl radical having about 8 to about 24 carbon atoms, n is a number ranging from about 1 to about 10, m is a number ranging form about 0 to about 10, and k is a number ranging from about 0 to about 10.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Intercalates and exfoliates formed with long chain (C6+) or aromatic matrix polymer-compatible monomeric, oligomeric or polymeric intercalant compounds and composite materials containing same
InactiveUS6124365AEfficient electrostatic completingEasy to separateOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesOrganic liquidsPlatelet
Intercalates formed by contacting a layered material, e.g., a phyllosilicate, with an intercalant surface modifier selected from the group consisting of a compound having an alkyl radical containing at least 6 carbon atoms, a compound containing an aromatic ring, and mixtures thereof, said surface modifier including a matrix material-reactive functional group, to sorb or intercalate the intercalant surface modifier between adjacent platelets of the layered material. Sufficient intercalant surface modifier is sorbed between adjacent platelets to expand the adjacent platelets to at least about 10 ANGSTROM , up to about 100 ANGSTROM . The intercalated complex can be combined with an organic liquid into a viscous carrier material, for delivery of the carrier material, or for delivery of an active compound; or the intercalated complex can be combined with a matrix polymer to form a strong, filled polymer matrix.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Multilayer dosage forms, which contain active substances and which comprise a neutral core, and an inner and outer coating consisting of methacrylate copolymers and methacrylate monomers
The invention relates to a multilayer dosage form comprised of: a) a neutral core; b) an inner coating consisting of a methacrylate copolymer; c) an outer coating consisting of a copolymer of which 40 to 95% by weight is composed of radically polymerized C1 to C4 alkyl esters of acrylic acid or of methacrylic acid and of which 5 to 60% by weight is composed of (meth)acrylate monomers having an anionic group in the alkyl radical. The invention is characterized in that the inner coating is essentially comprised of a methacrylate copolymer, of which at least up to 90% by weight consists of (meth)acrylate monomers with neutral radicals, which, in accordance with DIN 53 787, has a minimum film formation temperature of no higher than 30° C., and which contains the pharmaceutical active substance in bound form.
Owner:EVONIK ROEHM GMBH
Biocidally active combination for agricultural applications
InactiveUS20050130842A1High activityUse concentration can be reducedBiocideDead animal preservationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCompound (substance)
The present invention provides a biologically active combination for agricultural applications, comprising A) at least one biocidal, agriculturally acceptable active compound and B) a bioactivator for the active substance according to A) and C) if appropriate, customary auxiliaries and additives, which comprises the use, as bioactivator B), at least one compound of the formula (I) R—C(O)NH—(CH2)a—N+(R1,R2)—(CH2)b—COO— (I) in which R is a hydrocarbon radical having 6 to 22 carbon atoms, preferably 8 to 18 and in particular 10 to 14 carbon atoms, which is optionally branched and / or contains multiple bonds and / or functional groups, [0001]R1, R2 independently of one another are C1-4-alkyl radicals, in particular —CH3, a is 1 to 5, preferably 2 or 3, b is 1 or 2, in an effective concentration.
Owner:EVONIK GOLDSCHMIDT GMBH
Compositions comprising tetrafluoropropene and carbon dioxide
ActiveUS7629306B2Reducing and eliminating deleterious ozone depletion potentialLow toxicityHeat-exchange elementsNon-surface-active detergent solventsHeat transfer fluidPhotochemistry
Disclosed are compositions useful in a wide variety of applications, including heat transfer fluids which possess a highly desirable and unexpectedly superior combination of properties, and heat transfer systems and methods based on these fluids. The preferred heat transfer fluid comprises from about 1 to about 40 percent, on a weight basis, of carbon dioxide (CO2) and from about 99 to about 60 percent, on a weight basis, of a compound having the Formula I XCFzR3-z (I), where X is a C2 or a C3 unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, alkyl radical, each R is independently Cl, F, Br, I or H, and z is 1 to 3. A preferred compound of Formula I is tetrafluoropropene, particularly 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene and / or 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Agrochemical compositions comprising alkylenediol-modified polysiloxanes
InactiveUS20070213226A1Good curative effectImprove performanceBiocideAnimal repellantsCarboxyl radicalHydrogen
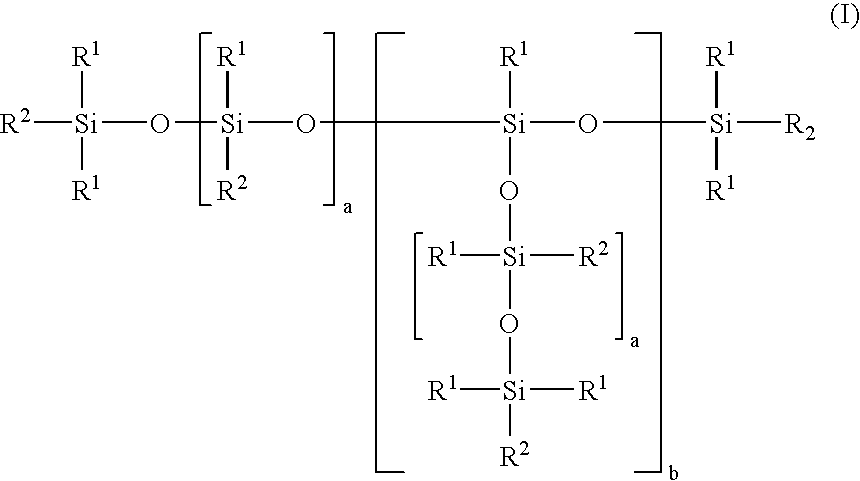
Described are agrochemical compositions which comprise of one or more one agrochemical active ingredient(s) and alkylenediol-modified polysiloxanes of the general formula (I): wherein R1 are alkyl radicals having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or aryl radicals, wherein at least 80% of the radicals R1 are methyl radicals , R2 in the molecule are identical or different and can have the following definitions: a) in which R3 is a hydrogen or alkyl radical, R4 is a hydrogen, alkyl or carboxyl radical, c is a number from 1 to 20, d is a number from 0 to 50, e is a number from 0 to 50 or b) correspond to R1, with the provisio that in the average molecule at least one radical R2 has the definition (a), a is a number from 1 to 200; b is a number from 0 to 10; and optionally one or more other agrochemically acceptable ingredients. The agrochemical compositions of the invention have enhanced efficacy, enhanced hydrolytic stability and / or decreased foaming properties.
Owner:EVONIK GOLDSCHMIDT GMBH
Compositions containing polyether-polysiloxane copolymers
InactiveUS8623984B2Storage stability is not ensuredQuality improvementSilicon organic compoundsHydrogenCopolymer
The present invention relates to compositions containing polyether-siloxane copolymers which are based on branched SiH-functional siloxanes, where at least one of the polyether-siloxane copolymers has a radical —OR8 where R8=hydrogen or an alkyl radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms which is bound to a silicon atom, a process for producing polyurethane foam in which these compositions are used as foam stabilizers, polyurethane foams containing these compositions and the use of these polyurethane foams.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polymeric Binder for Fused Salts Electrolytes Based Batteries
The present invention relates to polymeric binders of formula: [(—CH2CF2—)x′(—CF2CF2—)y′[—CH2CH(R)—]z′]m wherein: x′+y′+z′=1, only one x′, y′ or z′ could be simultaneously equal to zero; R is an alkyl radical CnH2n+1— with 0≦n≦8, 10≦m≦106.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +3
After-treatment method for oil-and water-repellency of fibrous substrates
A method is provided for after-treating fabric with a fluoroacrylate emulsion by spraying or immersion. The immersion can be carried out in a laundering process (preferably in a late cycle of the process) or even under poorly-controlled conditions (e.g. field conditions). The spraying embodiment of this method is useful for treating large, previously manufactured items comprising fabric (e.g. upholstered furniture, tents, awnings, and the like) with an aerosol spray containing micrometer or submicrometer-sized droplets of a diluted version of the fluoroacrylate emulsion. In all embodiments, the fluoroacrylate emulsion contains, dispersed therein with the aid of a surfactant system, essentially a single hydrophobic component comprising a particulate fluoroacrylate copolymer having repeating units of the formulas I and II wherein Rf is a C8-rich fluorinated alkyl radical; R and R1 are hydrogen or alkyl; and R2 is hydrogen or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl. The aqueous dispersion further contains, in addition to the surfactant system, a minor amount of polar organic liquid. Depending upon the melting or softening point of the fluoroacrylate copolymer, drying under heat can be optional and in any event can be carried out at temperatures below 100 DEG C.
Owner:MOODY RICHARD J
Treatment of autoimmune disorders
InactiveUS20030229105A1Ease of preparation and detectabilityGood metabolic stabilityBiocideAnimal repellantsImmunologic disordersDisease
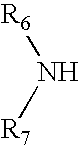
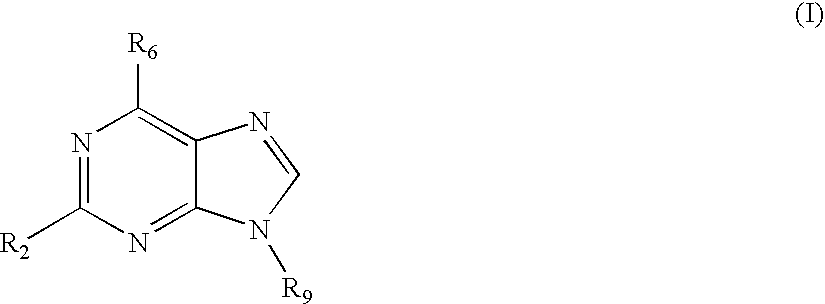
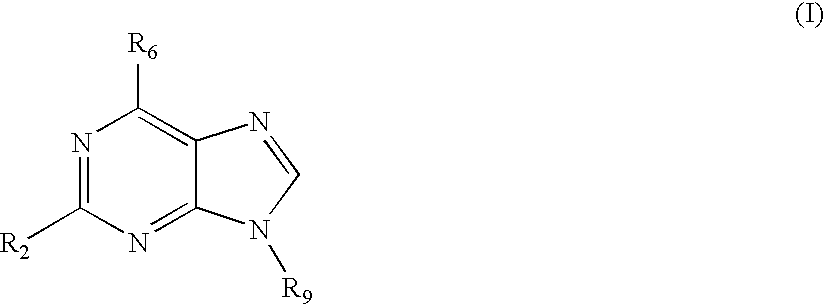
The present invention relates to the use of a compound of formula I wherein R2 is R-NH wherein R is a branched or unbranched alkyl radical, a piperidinyl group or pyrrolidinyl group, each of which may be optionally substituted by one or more -OH, halogen, amino or hydroxyalkyl groups; R6 is phenylamino, benzylamino or pyridyl-methylamino, indan-5-amino, where in each case the aryl group may be unsubstituted or substituted by one or more -OR'', halogen, NO2, amino or COOR' groups, wherein R' and R'' are each independently H or a branched or unbranched alkyl group; and R9 is a branched or unbranched alkyl group or a cycloalkyl group; in the treatment of an autoimmune disorder. The invention further relates to a method of treating an autoimmune disorder comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I.
Owner:CYCLACEL
Rubber composition for a colored tire
InactiveUS6344506B2Assess the hardness of the compositionsReduce clearanceOrganic chemistrySpecial tyresElastomerPolymer science
The invention concerns a white, light-colored tire rubber composition, devoid of carbon black, comprising at least a diene elastomer, a reinforcing white or colored filler, and an anti-photo-oxidizing system, wherein said protective system comprises (A) a 2,2'-methylene-bis-[4-alkyl (C1-C10)-6-alkyl(C1-C12)phenol]; (B) a dialkylthiodipropionate, the alkyl radicals thereof, which may be identical or different, are (C1-C20), radicals; (C) a 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl) benzotriazole; and (D) a "HALS" amine derived from 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Use of organomodified siloxanes branched in the silicone part for producing cosmetic or pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS8841400B2Pleasant, velvety-silky skin feelBiocideCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientPharmaceutical formulation
The invention relates to organomodified additives, emulsifiers, dispersants and / or active nourishing ingredients present in the silicon part of branched siloxane block copolymers, to the use thereof, in particular for producing cosmetic, dermatological or pharmaceutical formulations as well as care and cleansing products, and to the preparations as such. Specifically the invention relates to branched polysiloxanes having trifunctional T units as well as polyether groups, alkyl radicals of more than 7 carbon atoms or multi-hydroxy functional radicals.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Touch-sensitive display panel, composition for forming sealant and sealant
InactiveCN101630210AElasticIncrease elasticityOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveInput/output processes for data processingHydrogenEngineering
The invention discloses a touch-sensitive display panel, a composition for forming a sealant and the sealant. The touch-sensitive display panel comprises a first base panel, a second base plate, a touch-sensitive structure, a display medium and the sealant, wherein the touch-sensitive structure and the display medium are sealed between the first base panel and the second base panel by the sealant; and the sealant is formed by the polyreaction of the composition. The composition comprises the components by weight percent: 20 to 50% of bisphenol A epoxy acrylate monomer, 2 to 8% of acrylic acid monomer, 0.5 to 5% of light initiating agent and 1 to 5% of hardening agent. The chemical formula of the acrylic acid monomer is showed in the formula 1, wherein R1 is hydrogen or an alkyl radical with 1 to 3 carbon atoms and R2 is hydrogen or an alkyl radical with 1 to 20 carbon atoms.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Compositions containing polyether-polysiloxane copolymers
The present invention relates to compositions containing polyether-siloxane copolymers which are based on branched SiH-functional siloxanes, where at least one of the polyether-siloxane copolymers has a radical —OR8 where R8=hydrogen or an alkyl radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms which is bound to a silicon atom, a process for producing polyurethane foam in which these compositions are used as foam stabilizers, polyurethane foams containing these compositions and the use of these polyurethane foams.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com