Technique to verify underground targets utilizing virtual reality imaging and controlled excavation
a virtual reality imaging and controlled excavation technology, applied in the direction of survey, directional drilling, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problem of relative poor resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
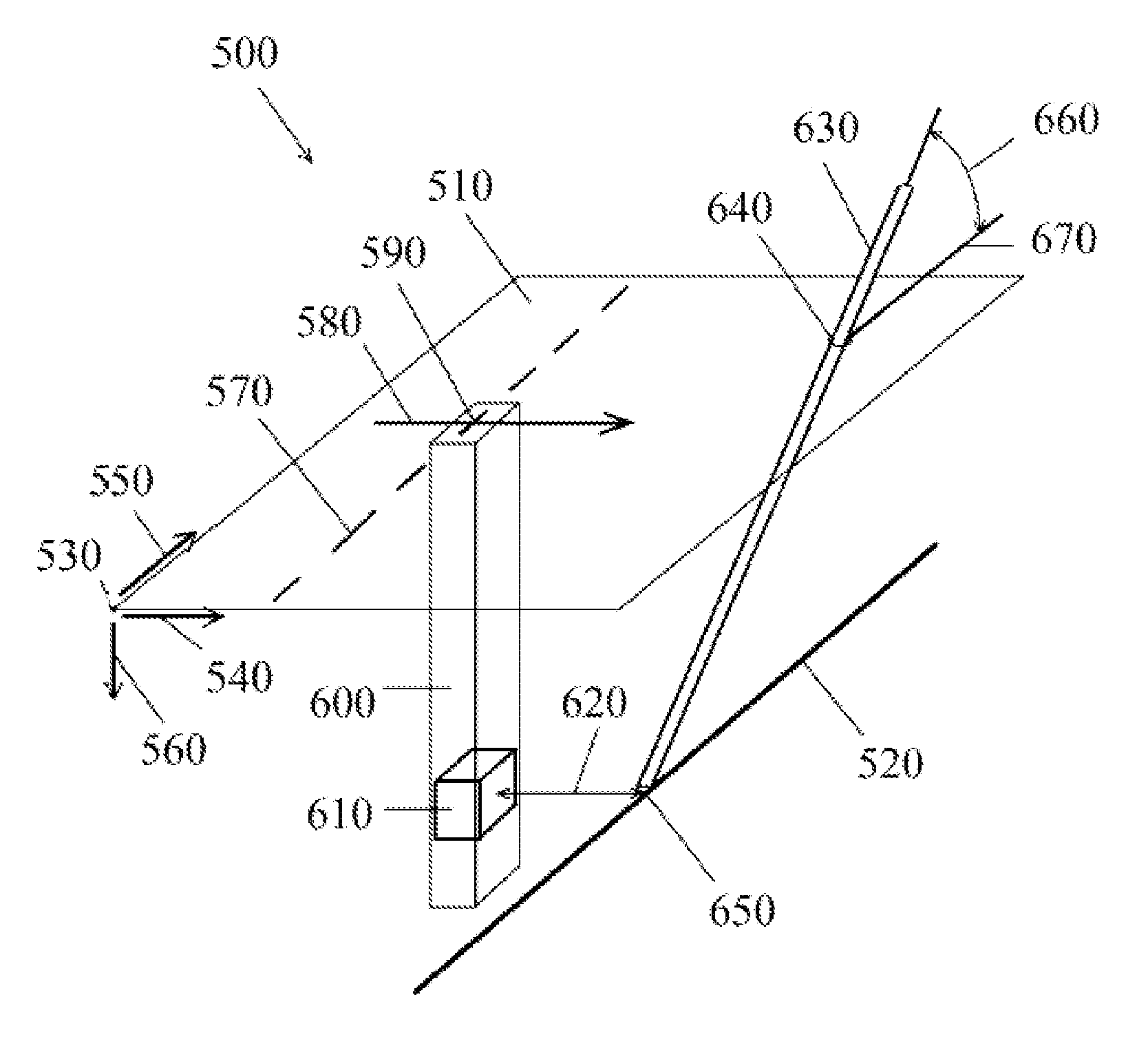
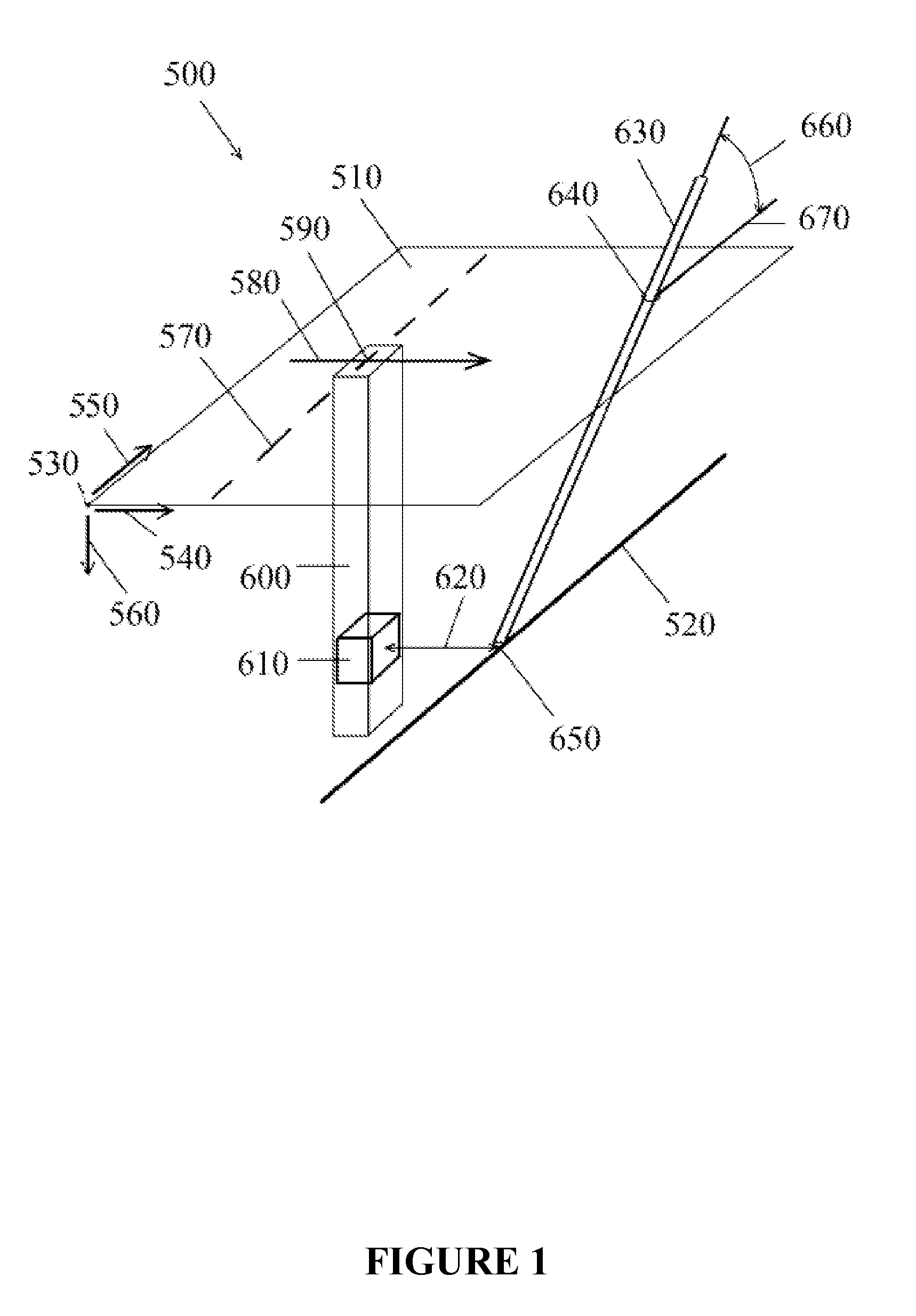
[0029]FIG. 1 illustrates a field excavation site (500) in an isometric view. A ground surface plane (510) is located above a buried utility target (520). This particular target (520) is linear, however any shape target may be located using this method. The target may also be a virtual-only target. A base point (530) is at a known location including coordinates used in the Global Positioning System (GPS). From the base point (530), the coordinates of any point on the surface plane (510) can be determined by horizontal distances in the x axis (540) and y axis (550) from any point to the base point (530). Vertical coordinates are defined by the z axis (560).
[0030]In this embodiment, a surface marking (570) is placed above the target (520) by locating equipment such as Ground Penetrating Radar (“GPR”) which can also display a depth of the target (520). The accuracy of such location varies and cannot typically be relied upon for a precise location of the target (520). Visual verification...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com