Methods for therapeutic administration of messenger ribonucleic acid drugs
a messenger ribonucleic acid and drug technology, applied in the direction of drug composition, viruses/bacteriophages, immunological disorders, etc., can solve problems such as undesirable immune responses reduce or and inhibit accelerated blood clearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
mRNA Encoding hEPO Elicits an Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) Response in Non-Human Primates
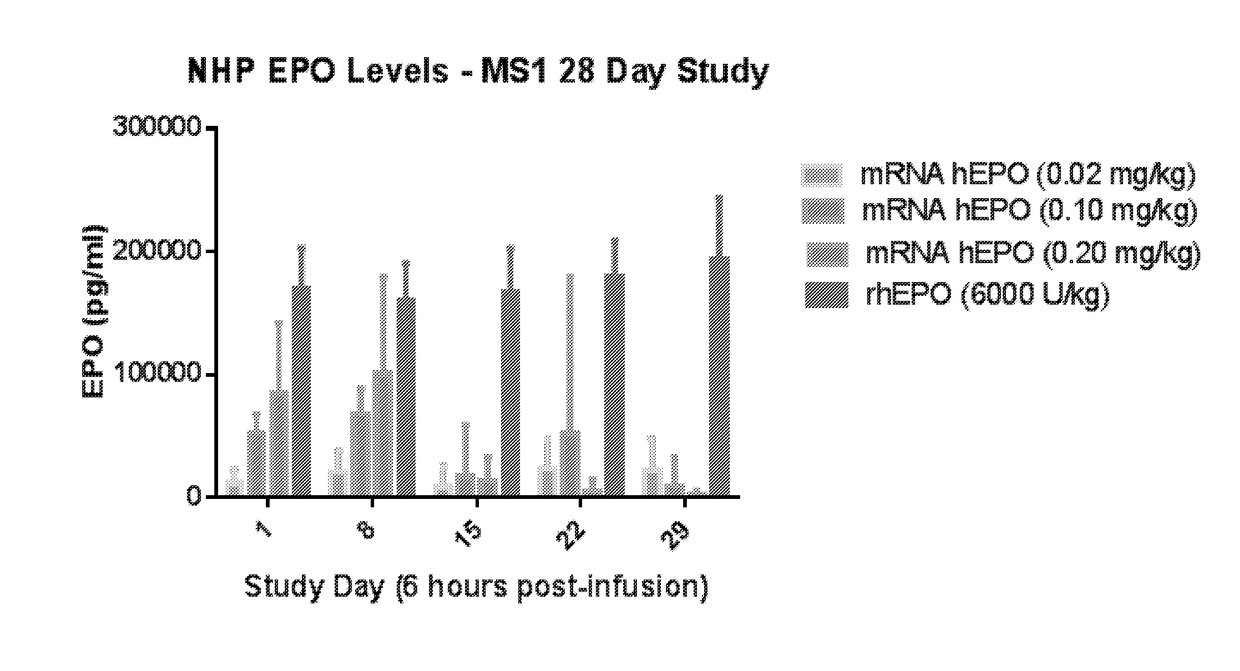
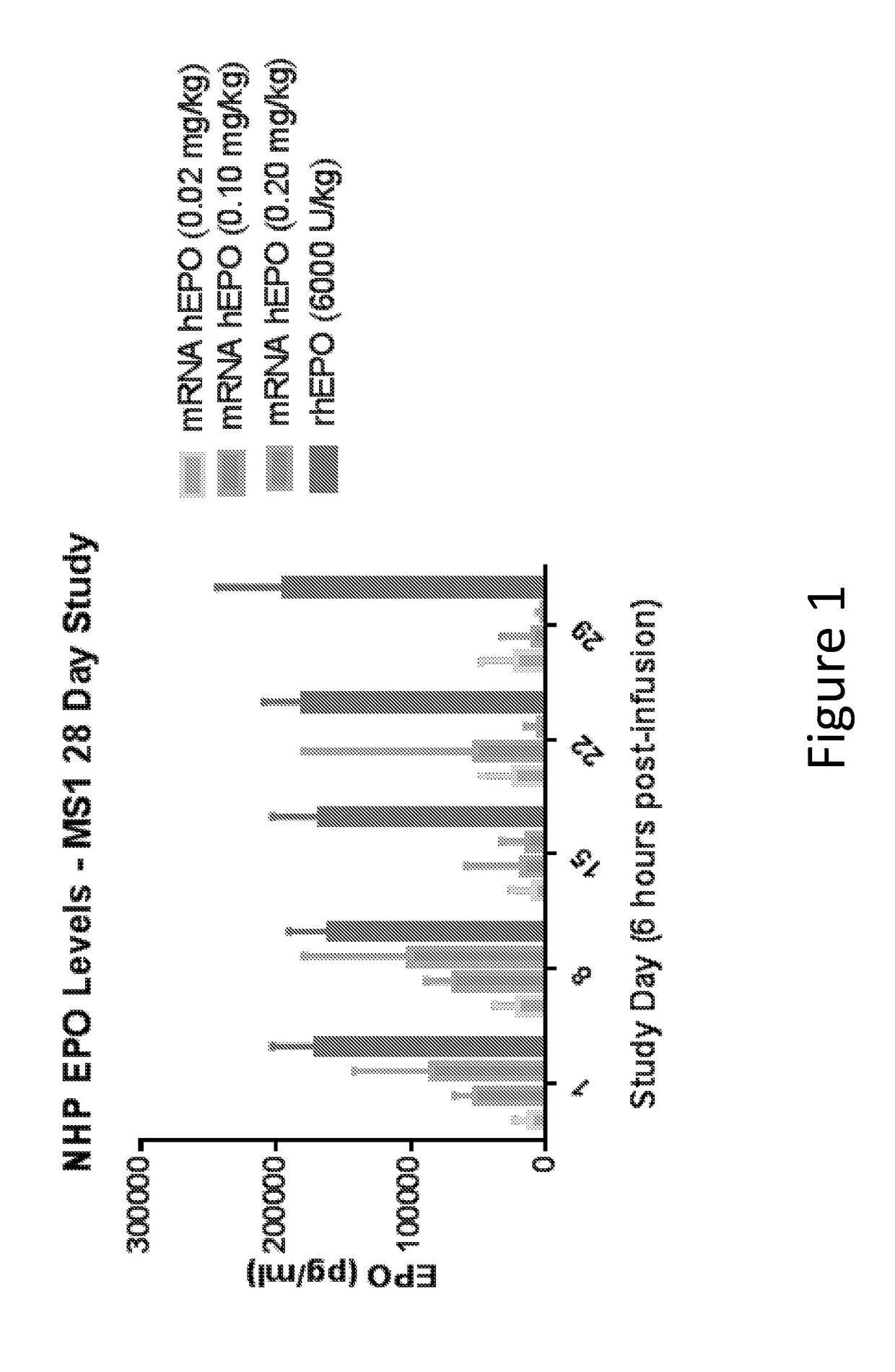
[0428]In this example, modified mRNA (mmRNA) encoding human erythropoietin (hEPO), but lacking any miR binding sites, was administered to cynomolgus macaques in a four week study to examine expression of hEPO in the animals.
[0429]mmRNA encoding hEPO was formulated into MC3 lipid nanoparticles (LNP), which include MC3 50%, DSPC 10%, Cholesterol 38.5%, PEG-DMG 1.5%, N:P ˜5.5. (Values are based on mol. %). The mmRNA construct contained a Cap 1 5′ Cap structure (7mG(5′)ppp(5′)NlmpNp), was fully modified with 5-methylcytosine and 1-methylpseudouridine and comprised a 140 nucleotide poly A tail. The mmRNA construct lacked the presence of any inserted miR binding sites. The nucleotide sequence of this hEPO-encoding construct without any inserted miR binding sites is shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 (without the polyA tail shown).
[0430]The study comprised seven groups of animals. The negative control group was treated...
example 2
tion of an miR-142-3p Binding Site into mmRNA Inhibits an ADA Response to the Encoded Protein
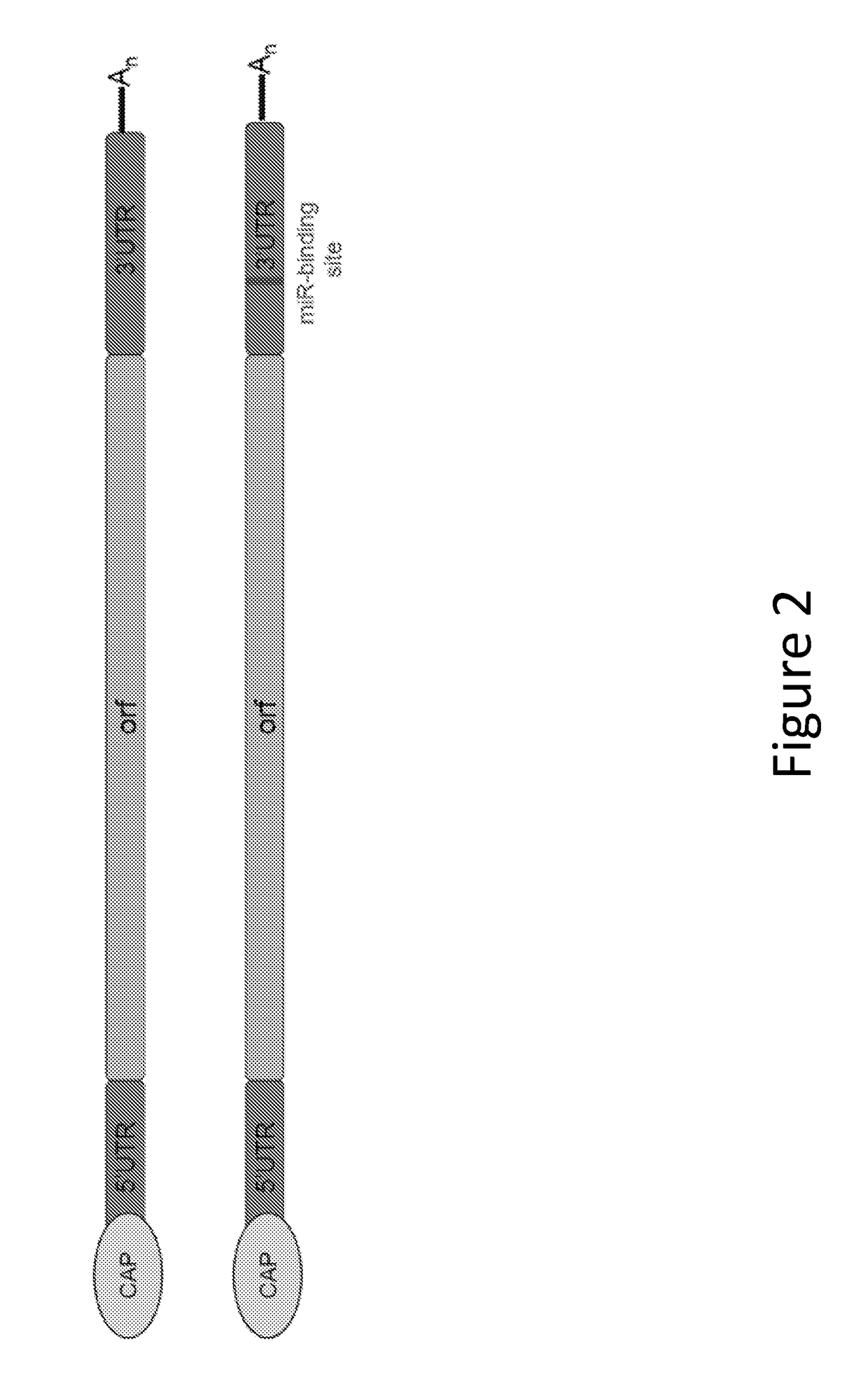
[0436]In this example, a human EPO-encoding mmRNA construct was prepared that incorporated an miR-142-3p binding site into the 3′ UTR of the construct. The mmRNA construct comprised a Cap 1 5′ cap (7mG(5′)ppp(5′)NlmpNp), was fully modified with 5-methylcytosine and 1-methylpseudouridine and comprised a polyA tail of approximately 140 nucleotides. A schematic diagram of the construct is shown in FIG. 2. The nucleotide sequence of this human EPO-encoding mmRNA is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (without the poly A tail). The nucleotide sequence of the 3′ UTR comprising the miR-142-3p binding site is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The nucleotide sequence of the miR-142-3p binding site is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. Other than the addition of the miR-142-3p binding site, the mmRNA construct and the LNP preparation were the same as in Example 1.
[0437]Cynomolgus macaque monkeys were treated with the construct comprising...
example 3
tion of an miR-126 or miR-142 Binding Site into mmRNA Inhibits B Cell Activation and Cytokine Expression
[0444]In this example, human EPO-encoding mmRNA constructs were prepared that incorporated either a miR-142-3p binding site or a miR-126-3p binding site, or both the miR-142-3p and miR-126-3p binding sites, into the 3′ UTR of the construct. The mmRNA constructs were administered to mice to examine the effects of incorporating the miR binding sites on various immune parameters in the mice.
[0445]The mmRNA constructs contained a Cap 1 5′ Cap structure (7mG(5′)ppp(5′)NlmpNp), were fully modified with 5-methylcytosine and 1-methylpseudouridine and comprised a 140 nucleotide poly A tail. The control mmRNA construct lacked the presence of any inserted miR binding sites. The nucleotide sequence of this control hEPO-encoding construct without any inserted miR binding sites is shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 (without the polyA tail shown). The nucleotide sequence of the hEPO-encoding construct with t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com