Antigen binding proteins
a technology of binding proteins and antigens, applied in the field of antigen binding proteins, can solve the problems of difficult separation from the desired heterodimer monobodies, formation of undesired homodimers,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of MoAb-Dimer Antigen Binding Proteins
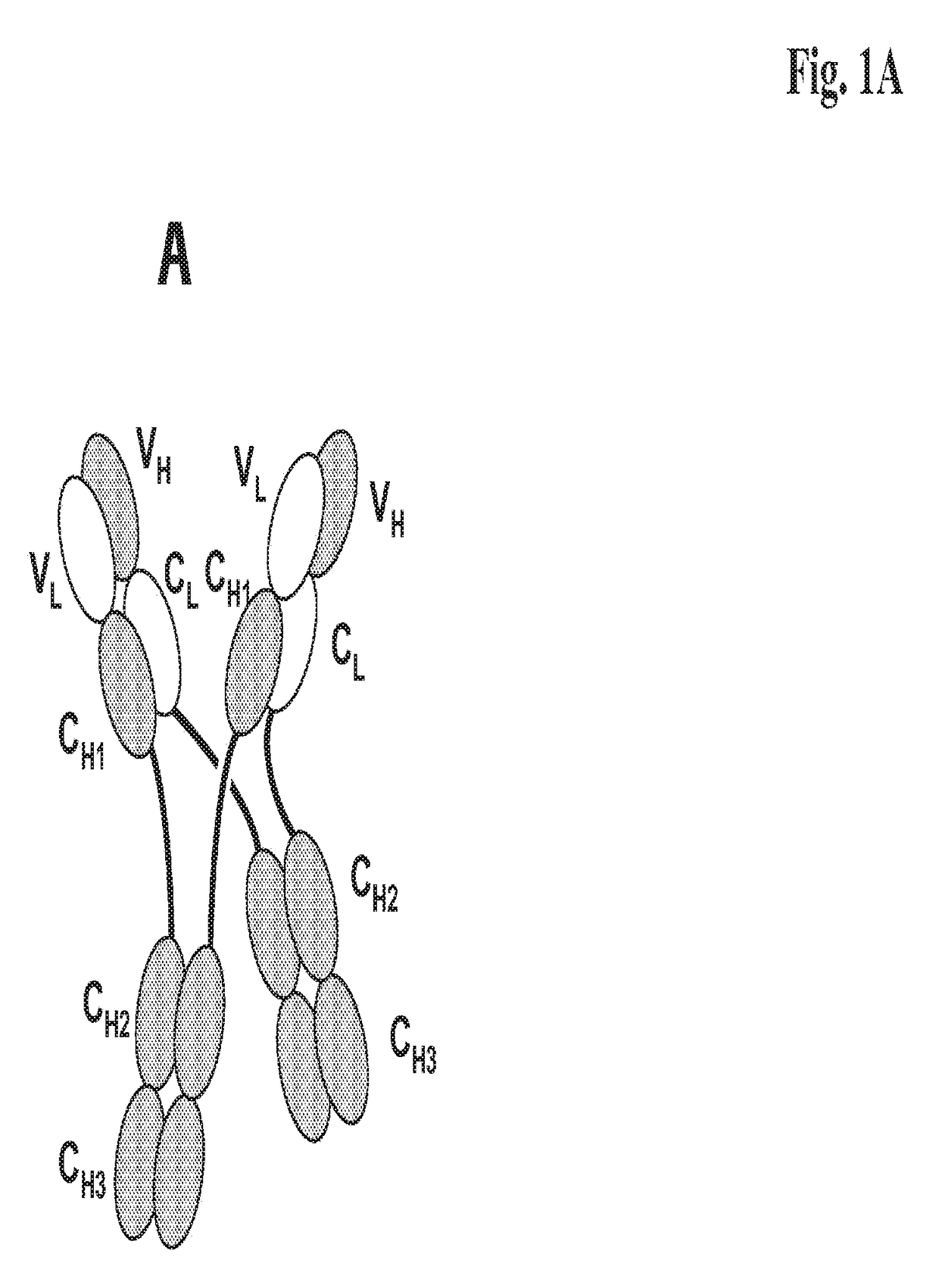
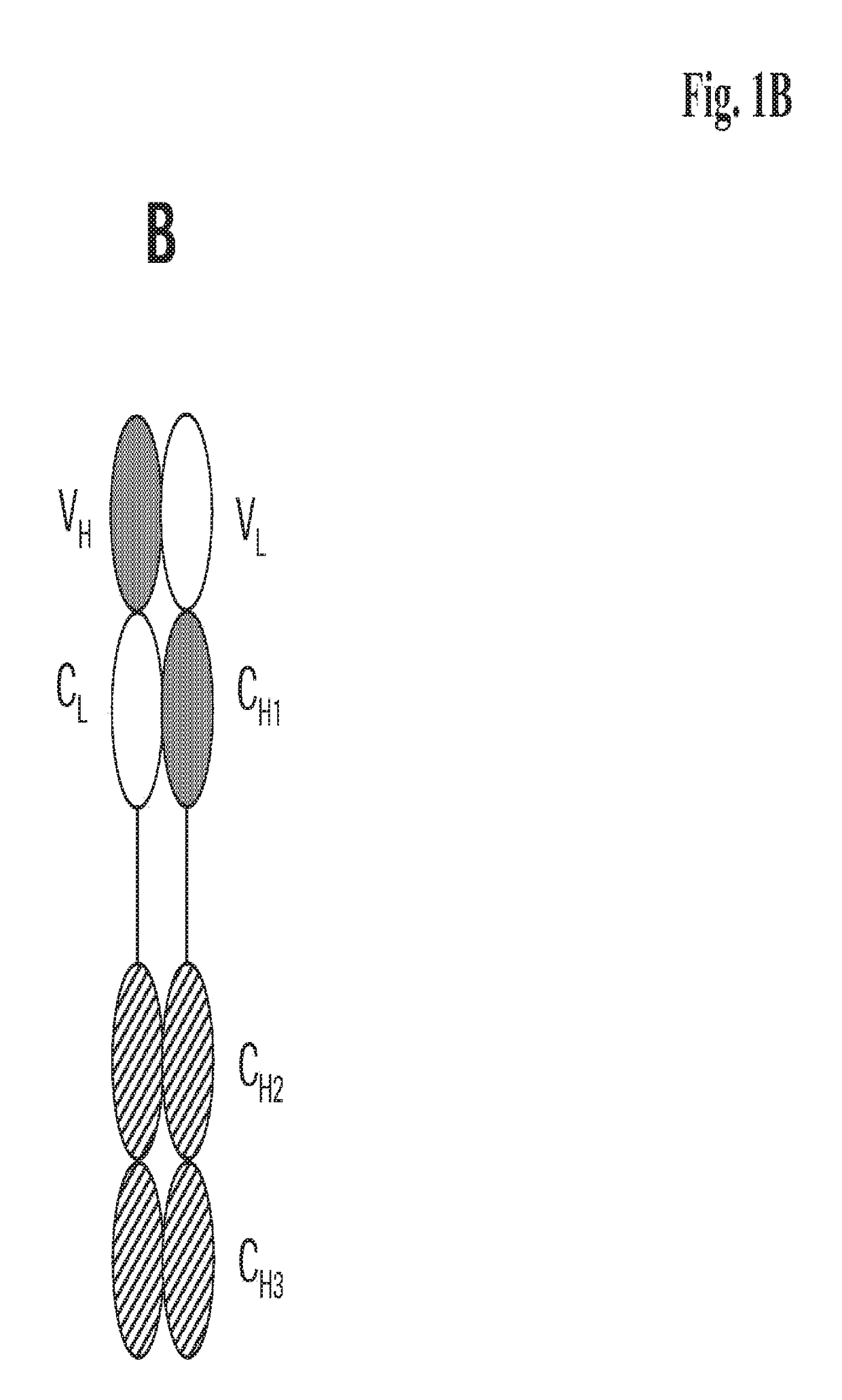
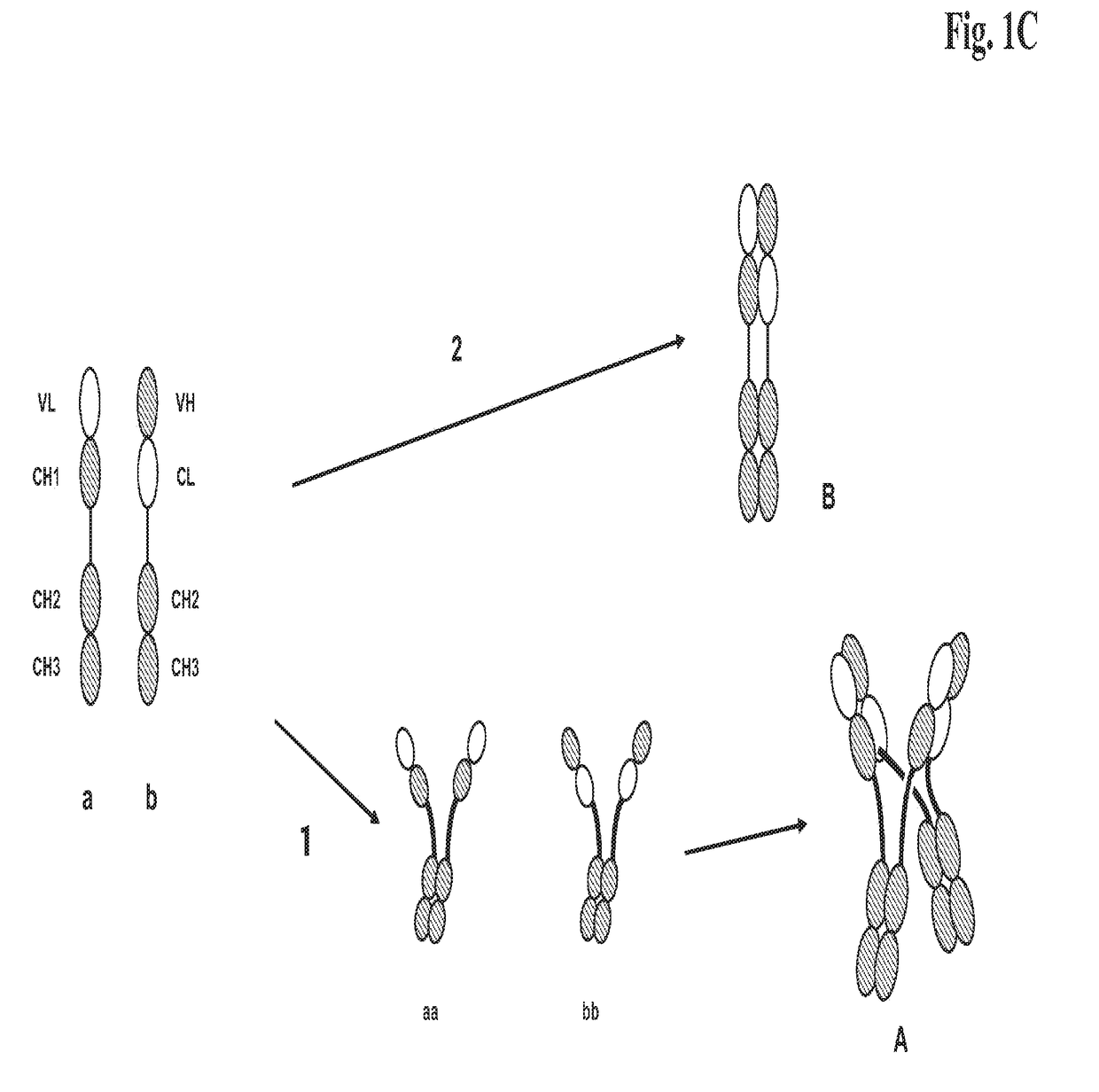
[0276]We designed antigen binding proteins according to the invention against c-Met (SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2), IGF-1R (SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4) and HER3 (SEQ ID NO:5 and SEQ ID NO:6) based on the design principle as shown in FIG. 1A. The respective constructs were transiently expressed in HEK293 cells as described above, and subsequently purified via Protein A affinity chromatography followed by size exclusion. FIGS. 2-4 depict the chromatograms of the size exclusion chromatography of the three different productions of antigen binding proteins as well as the corresponding SDS-PAGE under non-reducing and reducing conditions. In addition to peak 3 in FIG. 2, peak 2 in FIG. 3, peak 3 in FIG. 4 proteins eluting at earlier timepoints from the column peak 2 in FIG. 2, peak 1 in FIG. 3, peak 4 in FIG. 7 were observed. Based on their retention time it was calculated that they exhibited the double the molecular weight of the monovalent...
example 2
IGF-1R Binding Affinity
[0280]IGF-1R extracellular domain binding of the IGF1R AK18 MoAb-Dimer (“CH3-wt”) was compared to the binding of the parental IgG1 antibody by surface Plasmon resonance (SPR). FIG. 5 depicts the scheme of the SPR assay to determine the affinity. The analysis (double determination) showed that the IGF-1R binding affinity is retained in the IGF1R AK18 MoAb-Dimer (“CH3-wt”).
k(on)k(off)KDMab (IGF-1R)1.74E+06 6.63E−03 3.80E−09MoAb-Dimer (IGF-1R)1.5E+063.0E−032.01E−09(1. deter.)MoAb-Dimer (IGF-1R)1.5E+063.0E−032.05E−09(2. deter.)
example 3
Cellular Binding to IGF-1R Expressing Cell Lines
[0281]Cellular binding of IGF-1R MoAb-Dimer was demonstrated on A549 cells. A549 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were detached with accutase (Sigma) and 2×10e5 cells were used for each individual antibody incubation. IGF-1R antibody and MoAb-Dimer were added in a threefold dilution series (100-0.0003 μg / mL). Bound antibodies were visualized with a secondary Alexa488-coupled antibody (5 μg / mL) binding to the constant region of human immunoglobulin. Dead cells were stained with 7-AAD (BD) and excluded from the analysis. Fluorescence intensity of single cells was measured on a FACS Canto (BD Biosciences) flow cytometer. The data show that the MoAb-Dimer showed very similar halfmaximal binding to cells comparable to the parental IGF-1R IgG1 antibody. This implies that the MoAb-Dimer can bind with two arms to IGF-1R on cells and exhibits an avidity effect. However, the total mfi (mean fluorescence intensity) is higher for the MoAb-Dim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com