Device and Method for Needle/Catheter Location Utilizing Correlation Analysis
a technology of correlation analysis and device, which is applied in the field of devices and methods for determining the location of the needle or the catheter in the patient utilizing correlation analysis, can solve problems such as the dislocation of the needle or the catheter from a site, and achieve the effects of preventing the movement of the catheter, facilitating assessment, and precise control of the physical for
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
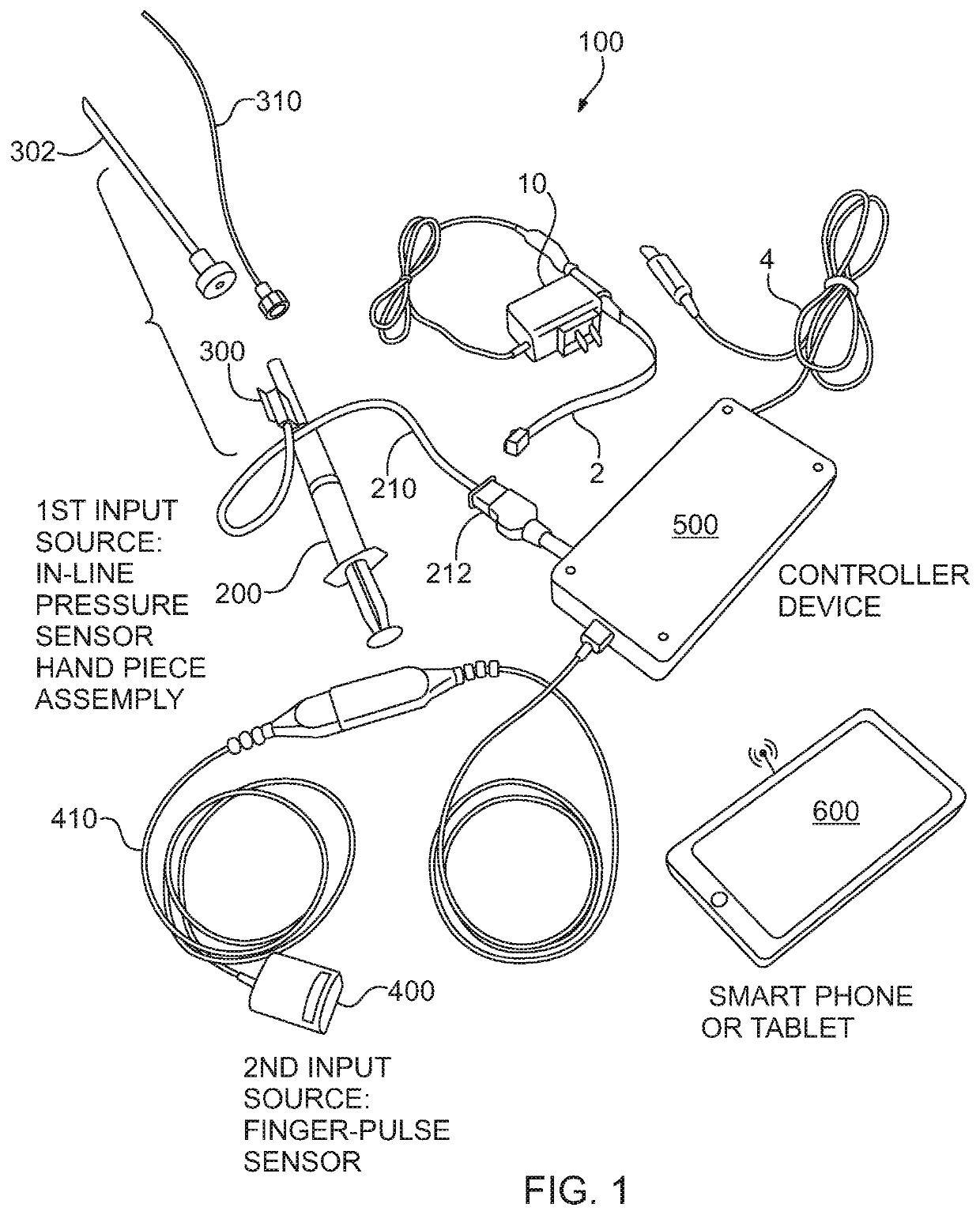
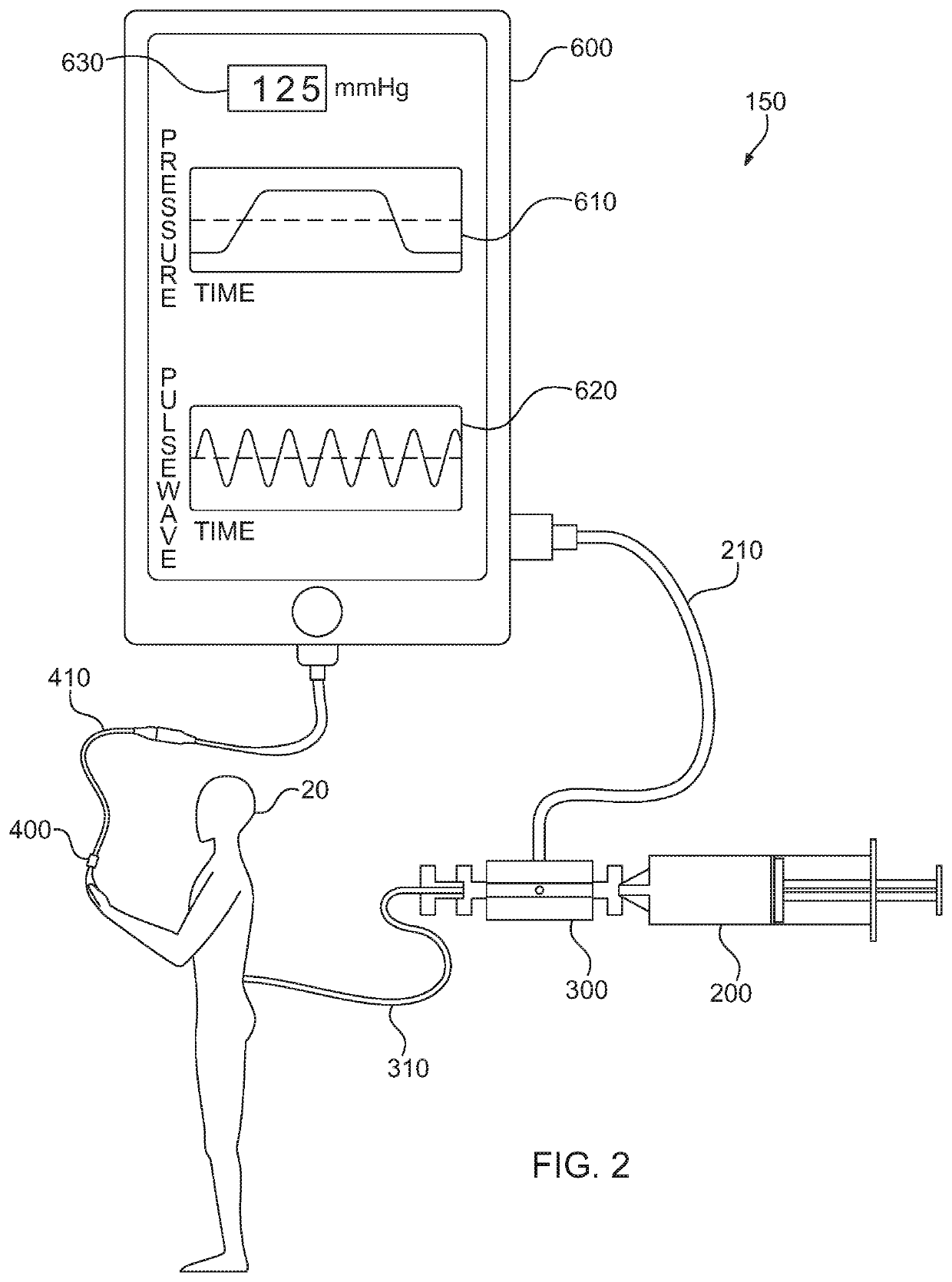
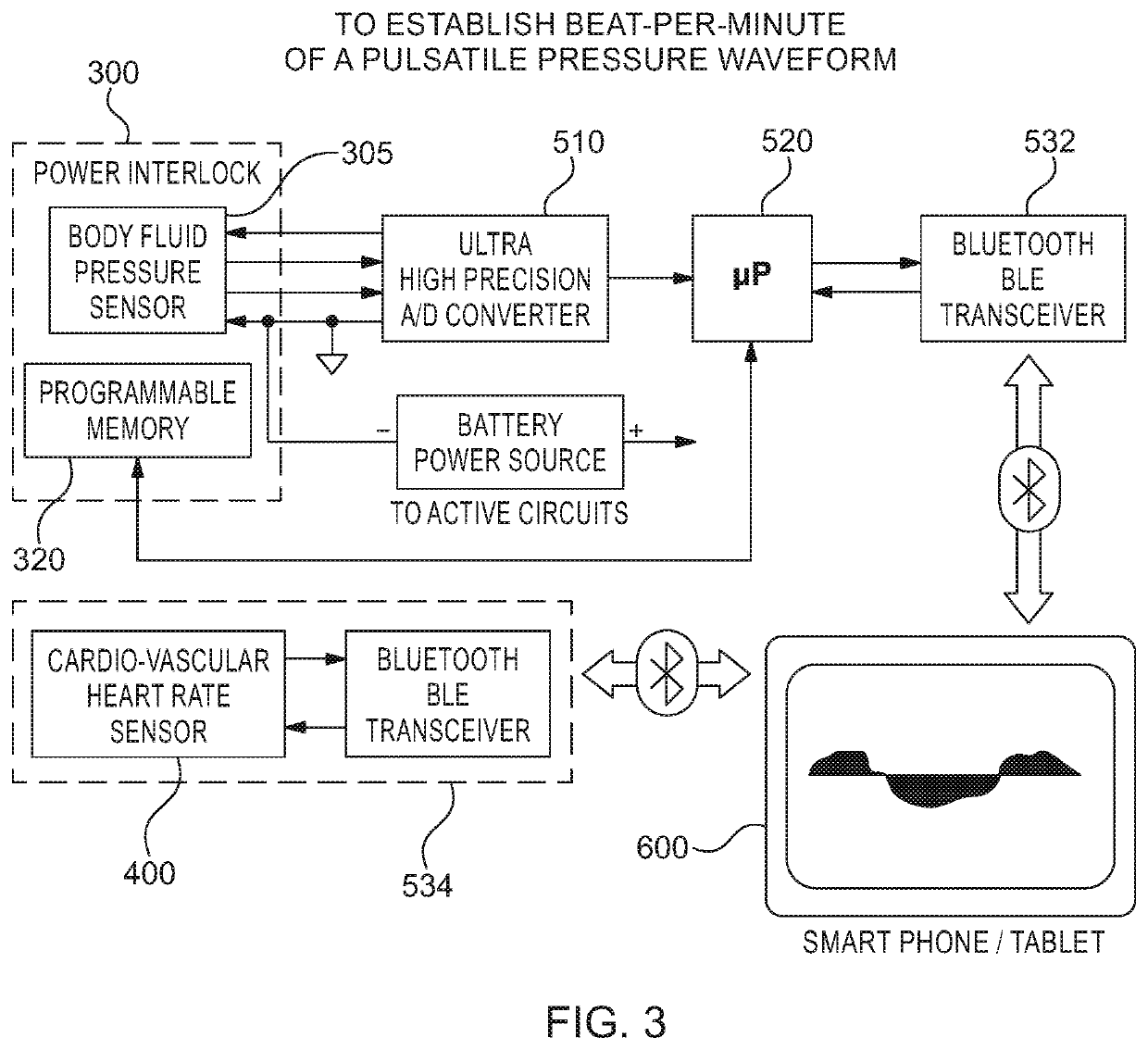
[0025]Referring now to the figures, wherein like elements are numbered alike throughout, FIGS. 1, 2 schematically illustrate exemplary configurations of devices 100, 150 of the present invention for determining proper placement of a hollow-bore structure, such as a needle 302 and / or catheter 310, at a selected treatment location in a patient 20 using at least two independent measurements of the cardiac pulse, one of which measurements is detected via the hollow-bore structure. For example, the detection of the cardiac pulse via the needle 302 and / or catheter 310 may be accomplished by sensing a physical property in the lumen of the needle 302 and / or catheter 310, such as a physical property representing the pressure or fluid volume change in the lumen, where the variation in the pressure or fluid volume change contains a signal created by, and indicative of, the cardiac rhythmic contraction, e.g. the cardiac pulsewave. In particular, an in-line pressure sensor 300 may be provided in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com