Compositions and methods for treating hemoglobinopathies
a technology of hemoglobinopathies and compositions, applied in the field of compositions and methods for treating hemoglobinopathies, can solve the problems of newly formed inosine moiety, acute or chronic injury affecting any organ system, and misdiagnosis of sickle cell disease (scd)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Adenosine Base Editors with Increased Editing Efficiency
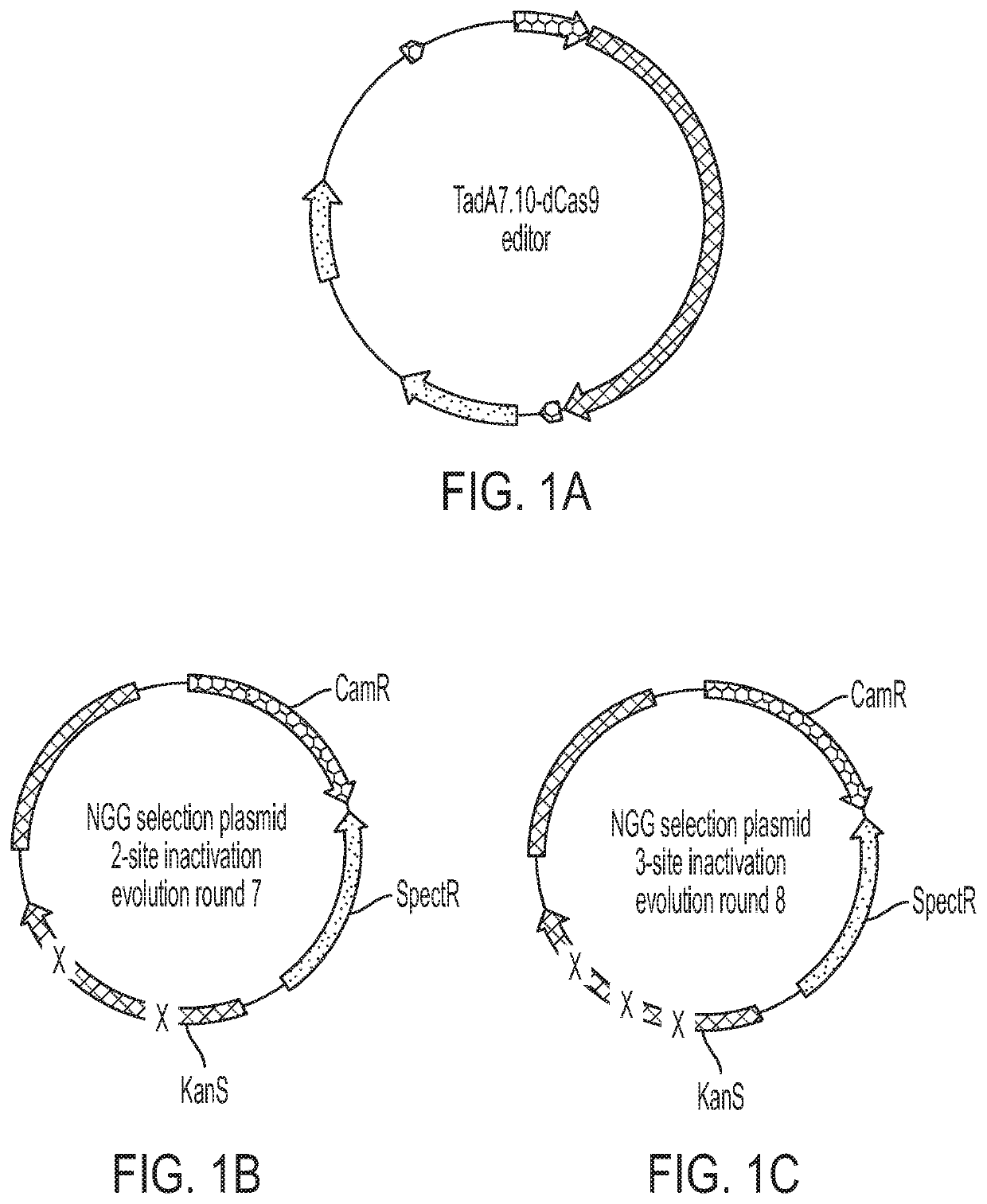
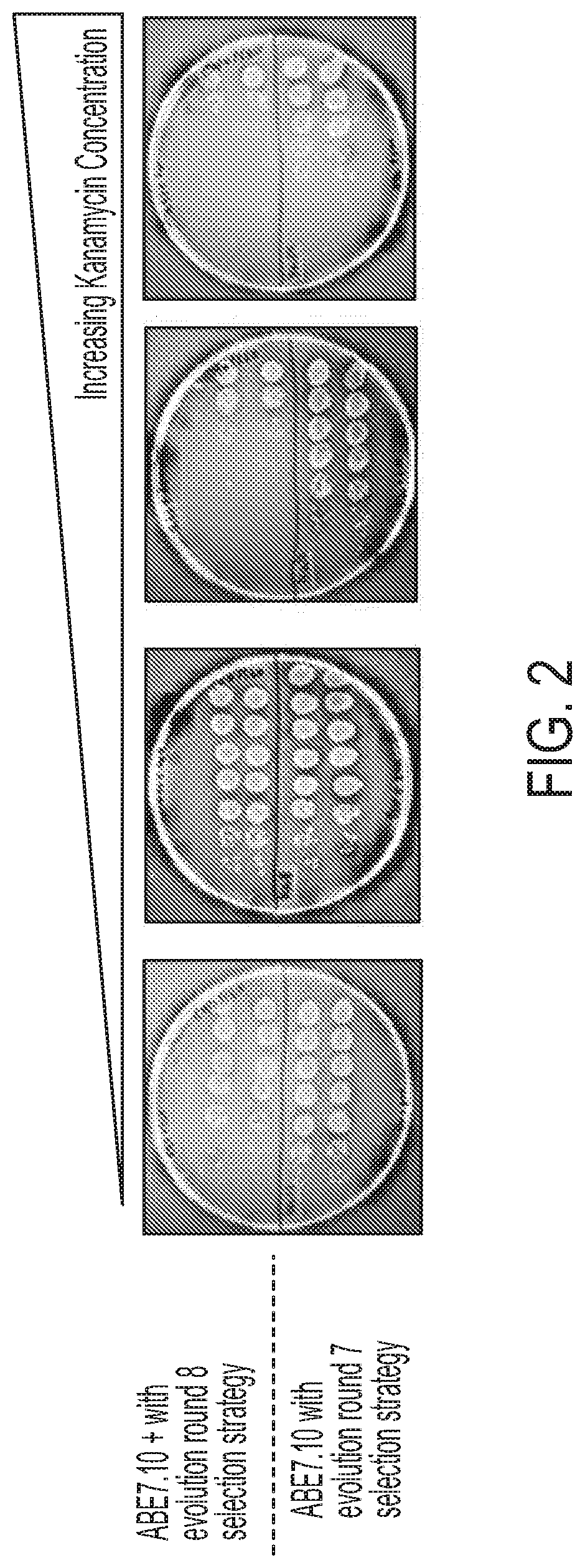
[0733]Base editing systems that include a Tad7.10-dCas9 fusion proteins are capable of editing a target polynucleotide with approximately 10-20% efficiency, but for uses requiring higher efficiency their use may be limited. In an effort to identify adenine base editors having increased efficiency and specificity, constructs comprising the adenosine deaminase TadA 7.10 were mutagenized by error prone PCR and subsequently cloned into an expression vector adjacent to a nucleic acid sequence encoding dCas9, a nucleic acid programmable DNA binding protein (FIG. 1A). The expression vectors comprising the adenosine deaminase variants were co-transformed into competent bacterial cells with a selection plasmid encoding chloramphenicol resistance (CamR) and spectinomycin resistance (SpectR) and having a kanamycin resistance gene that was rendered nonfunctional by two point mutations (evolution round 7 strategy) (FIG. 1B). The cells were ...
example 2
Adenine Base Editors for the Treatment of Hematological Disorders
[0740]Sickle cell disease (SCD) affects approximately 100,000 patients in the United States. Individuals carrying both the SCD mutation and mutations that cause persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH) do not typically present with sickle cell pathologies due to persistent fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels. Higher HbF levels correlate with greater benefit for individuals with blood disease, such as reduction in disease symptoms and improved overall health. A T to C mutation at the -198 position in the HGB promoter causes HPFH by interference of binding to 7-globulin repressor proteins, such as BCL11A.
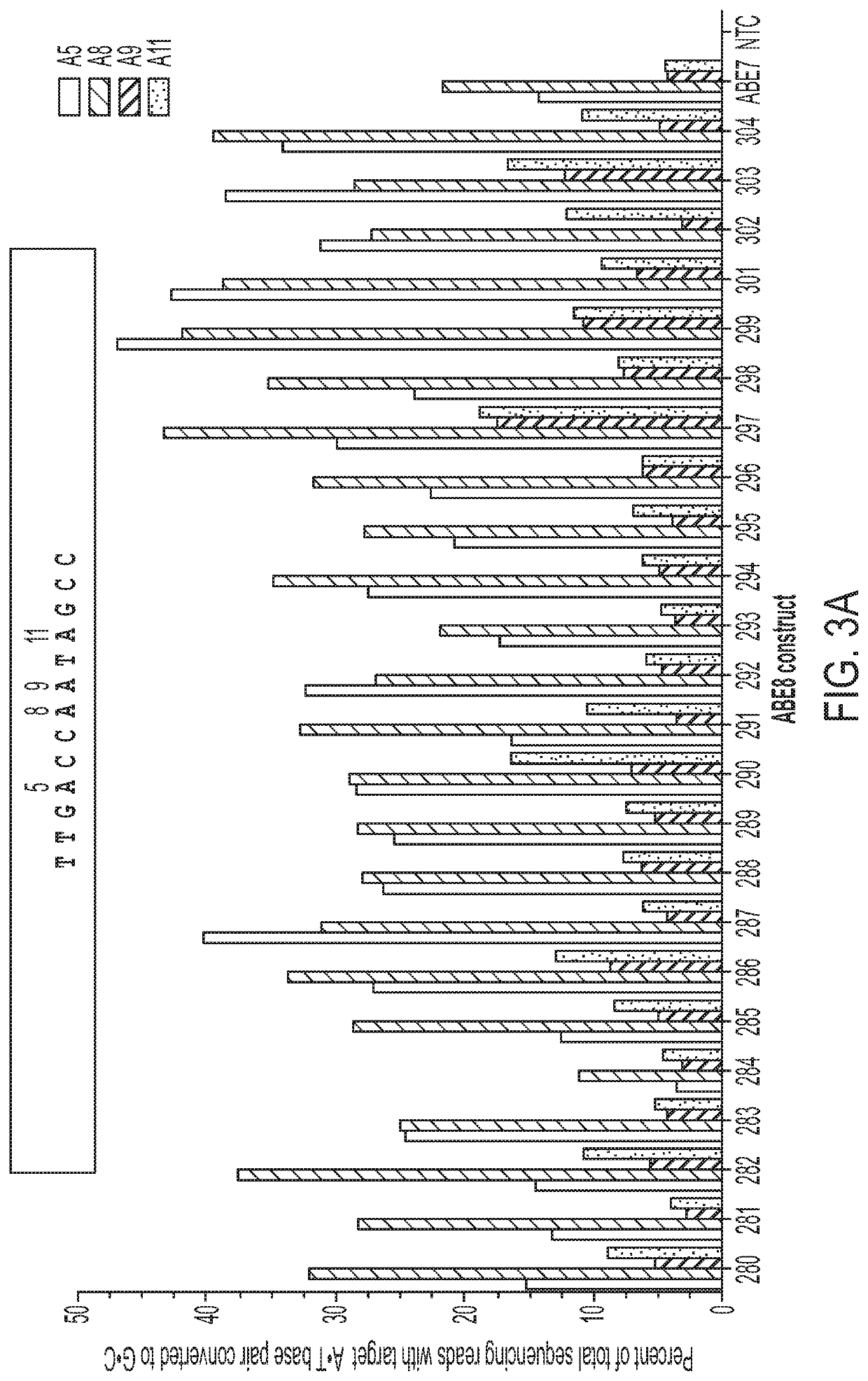
[0741]ABE8 constructs were evaluated in human hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). Ex vivo manipulation and / or editing of HSCs prior to administration to patients as a cell therapy is a promising approach for the treatment of hematological disorders. It has been previously demonstrated that ABEs can introduce a T to C substitution at...
example 3
Complementary Base Editing Approaches for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease and Beta Thalassemia (β-Thalassemia)
[0747]Sickle cell disease (SCD) and Beta thalassemia are disorders of beta globin production and function that lead to severe anemia and significant disease complications across a multitude of organ systems. Autologous transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells engineered through the upregulation of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) or correction of the beta globin gene have the potential to reduce disease burden in patients with beta hemoglobinopathies. Base editing is a recently developed technology that enables precise modification of the genome without the introduction of double strand DNA breaks.
[0748]Gamma globin gene promoters were comprehensively screened with cytosine and adenine base editors (ABE) for the identification of alterations that would derepress HbF. Three regions were identified that significantly upregulated HbF, and the most effective nucleotide residue con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap