Method of making a lead-on-chip device
a technology of lead-on-chip and plastic molding, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of total exfoliation, cracks in semiconductor chips, and increasing in size of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
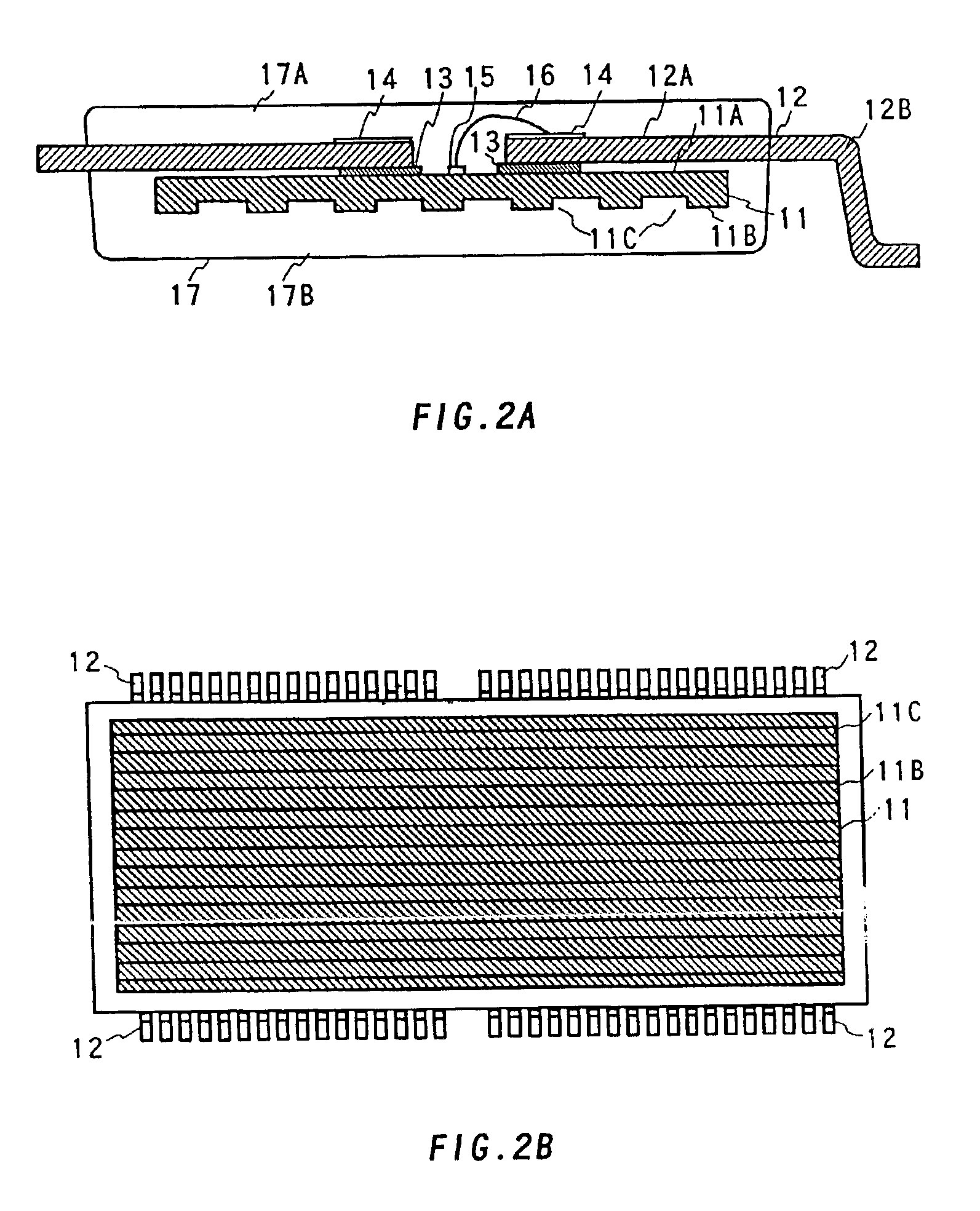
[0041]FIG. 2A is a cross sectional view of the semiconductor device of the first embodiment and FIG. 2B shows the bottom of the semiconductor chip mounted in the semiconductor device.
[0042]The semiconductor device is an LOC (Lead On Chip) semiconductor device, and in particular, a TSOP (Thin Small Outline Package) semiconductor device. Therefore, the thickness of the semiconductor device is required to be below 1.27 mm as explained above.
[0043]The semiconductor device incorporates a semiconductor chip 11, a plurality of leads 12, a plurality of insulation tapes 13, a plurality of electrode pads 15, a plurality of bonding wires 16, and a plastic sealing layer 17. Examples of the materials used for these components are as follows. The insulation tapes 13 are made of a thermoplastic resin, wherein both the top side and the bottom side of the insulation tapes 13 are adhesive. The electrode pads 15 are made of Ni—Fe and Cu. The bonding wires 16 are made of alloy.
[0044]On the top side 11A...
second embodiment
[0049]the semiconductor device according to the present invention will now be described.
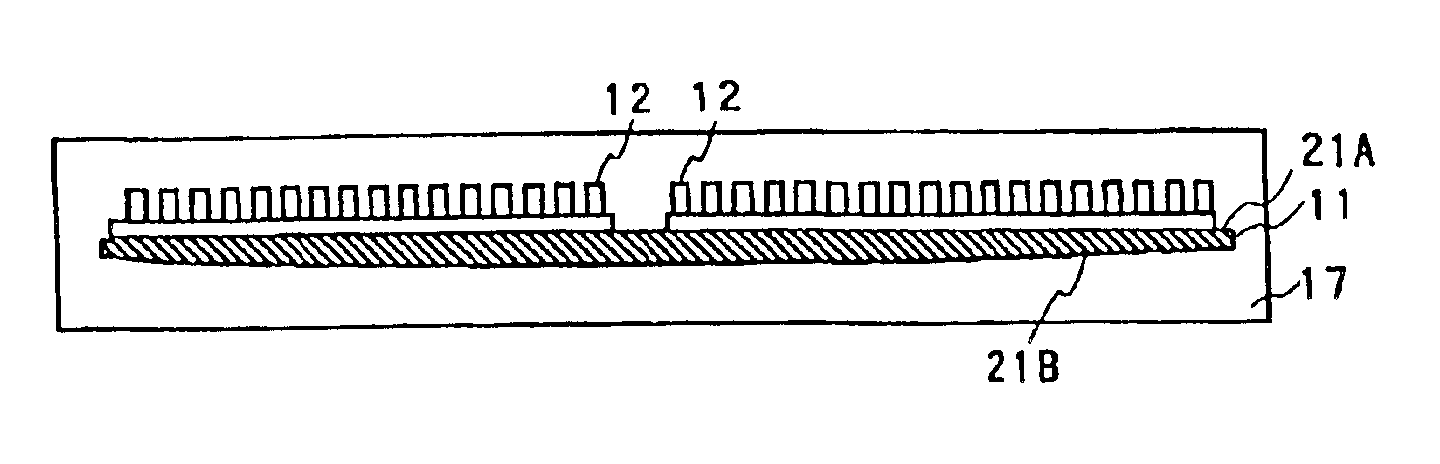
[0050]FIG. 3A is a cross sectional view of the semiconductor device of the second embodiment, and FIG. 3B shows the bottom of the semiconductor chip mounted in the semiconductor device of the second embodiment. The principal feature of the second embodiment is that the thickness of the center portion of the semiconductor chip is greater than that of the other portions. In other words, the main feature is that the semiconductor chip has a curved bottom.
[0051]The components of the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment are almost the same as those of the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment; therefore, for ease of explanation, a discussion of the feature of the second embodiment will be made below. In FIG. 3A, the semiconductor chip 11 has a curved or convex shape. The convex portion of the semiconductor chip 11 acts as a resisting member for preventing the semico...
third embodiment
[0053]the semiconductor device according to the present invention will now be described in detail.
[0054]FIG. 4A is a cross sectional view of the semiconductor device of the third embodiment, and FIG. 4B shows the bottom of the semiconductor chip mounted in the semiconductor device. The components of the semiconductor device of the third embodiment are almost the same as those of the semiconductor device of the first embodiment. Therefore, the distinguishing feature of the third embodiment will principally be discussed below.
[0055]The third embodiment is distinguished in that an adhesive 22 is applied between the semiconductor chip 11 and the plastic sealing layer 17, such that the adhesive 22 serves to prevent the semiconductor chip 11 from being warped or bent. Specifically, the adhesive 22 is made of polyimide resin. In FIGS. 4A and 4B, the entire bottom side of the semiconductor chip 11 is coated with the polyimide resin 22 to avoid exfoliation of the semiconductor chip 11 from t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com