Apparatus for detecting impurities in material and detecting method therefor
a technology for impurities and detecting devices, applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, instruments, tobacco, etc., can solve the problems of hard to detect impurities and cannot be detected practically, and achieve the effect of accurately detecting impurities in other bulk materials and accurately detecting impurities in materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example # 1
EXAMPLE #1
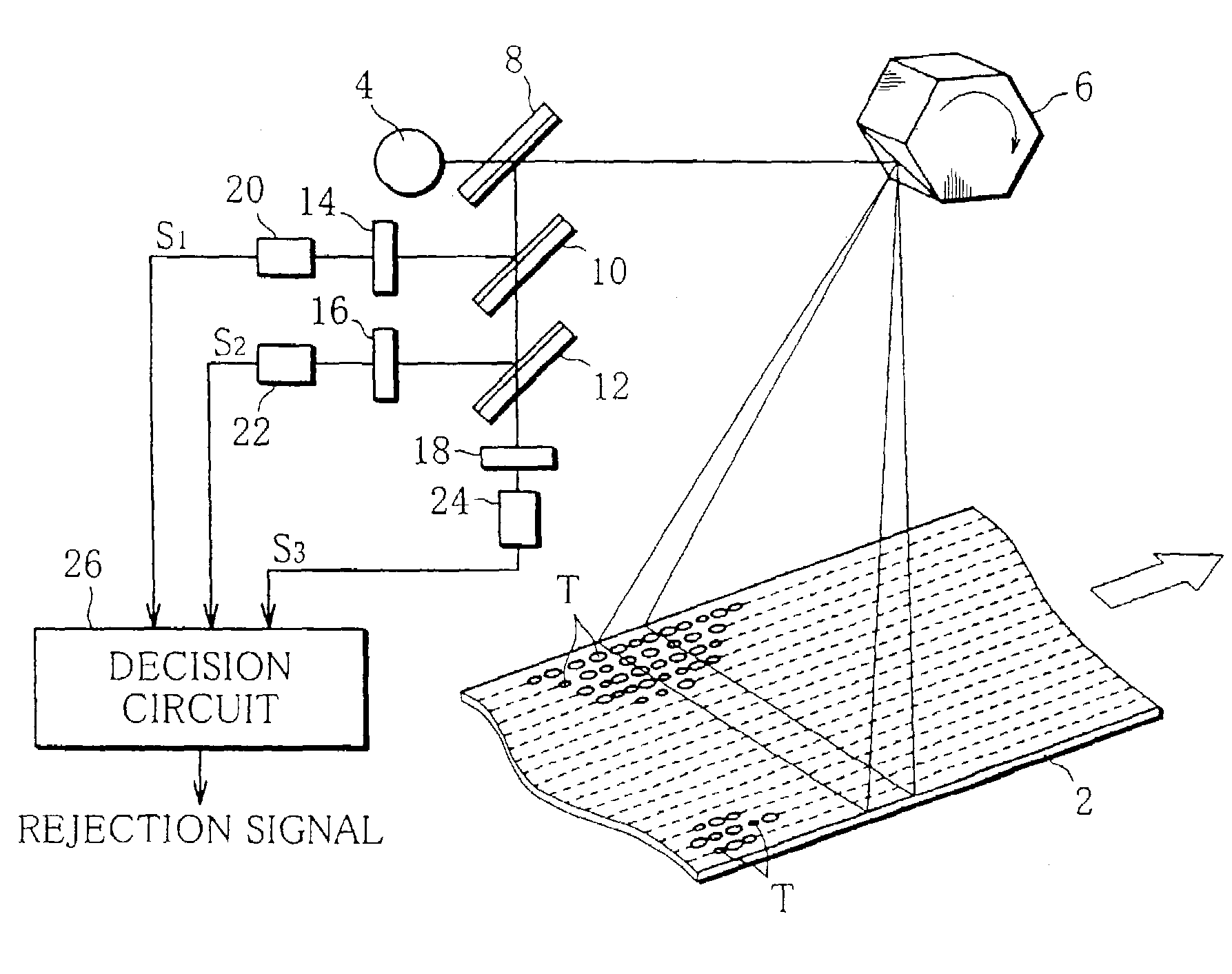
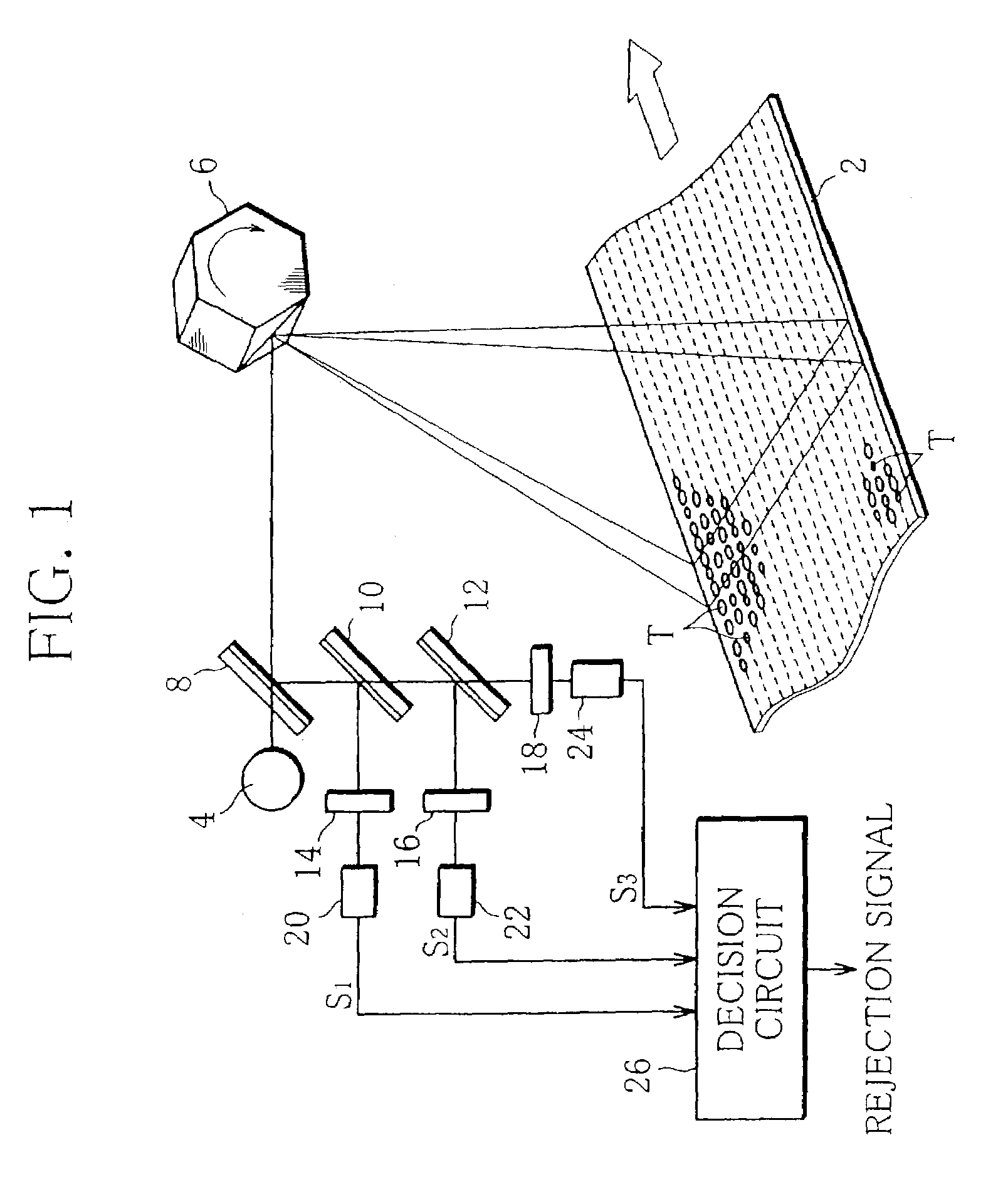
[0041]The following is a description of the reason why the aforesaid first to third reflection components are selected.
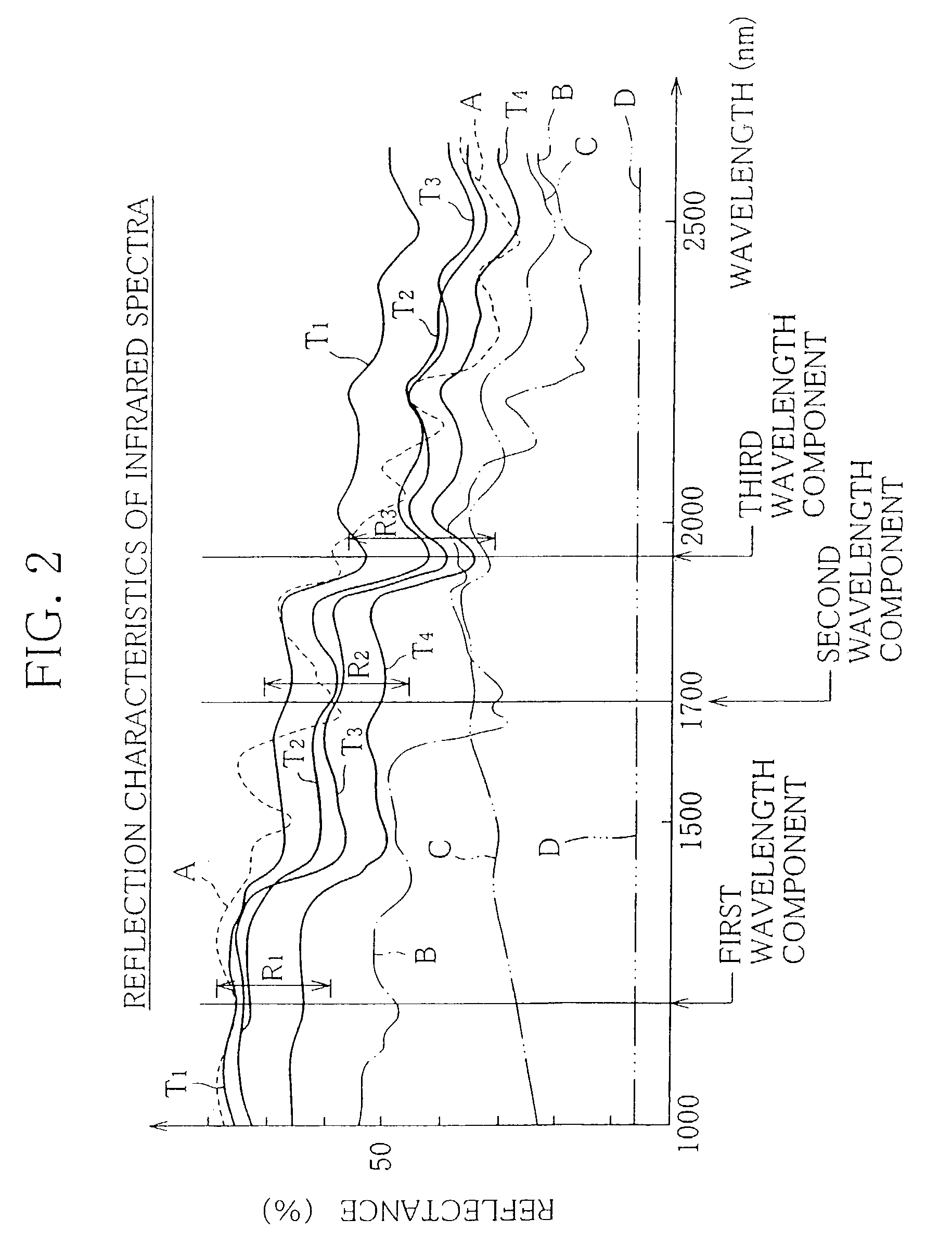
[0042]In FIG. 2, full lines T1, T2, T3, and T4 represent the reflection characteristics of infrared spectra reflected by the domestic, barley, oriental, and yellow varieties, respectively.
[0043]In FIG. 2, on the other hand, broken line A, dashed line B, and two-dot chain line C represent the reflection characteristics of infrared spectra reflected by various impurities, individually. More specifically, the reflection characteristics A, B and C are obtained from a plastic material, such as a wrapper of string, used to pack tobacco leaves, urethane foam that forms a package, and moisture-proof paper used to line the package, respectively. Further, a reflection characteristic D indicated by three-dot chain line in FIG. 2 is obtained from black synthetic rubber that forms a belt of the conveyor 2.
[0044]As seen from FIG. 2, the reflection characteristics T1, T2...
example # 2
EXAMPLE #2
[0081]The detecting apparatus and method for detecting impurities is not limited to use with tobacco leaves as described above. Next another example of the detecting apparatus and a method capable of accurately detecting impurities in other materials will be described. In this second example the materials are made from harvest plants in bulk.
[0082]FIG. 10 describes Example #2 and illustrates the first wavelength region from which the first wavelength component is selected and the second wavelength region from which the second wavelength component is selected. The third wavelength component can be selected from the first or the second wavelength region.
[0083]Various materials made from harvest plants all include water which absorbs predetermined wavelength components of infrared rays. Especially in case that one of the wavelength components has a wavelength of 1,940 nm, the specific wavelength component is significantly absorbed by the moisture content of the material.
[0084...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength region | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength region | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com