Computer-implemented risk evaluation systems and methods
a risk evaluation and computer-implemented technology, applied in the field of computer-implemented risk evaluation systems and methods, can solve problems such as complicated decision making processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
application example
Direct Response Application Example
Situations involving a direct response application can include:
[0288]1) New Account Acquisition
[0289]2) Inactive Account Stimulation
[0290]3) Retail Outlet CO-OP Promotion
[0291]4) Solo Direct Mail Merchandising[0292]A) Loans[0293]B) Insurance[0294]C) Goods[0295]D) Services
Objective Functions that can be Used within the Risk Evaluation System can Include:
[0296]1) Response
[0297]2) Approved Response
[0298]3) Higher Purchase Activity
[0299]4) Profitability
[0300]5) Heighten Consumer Awareness
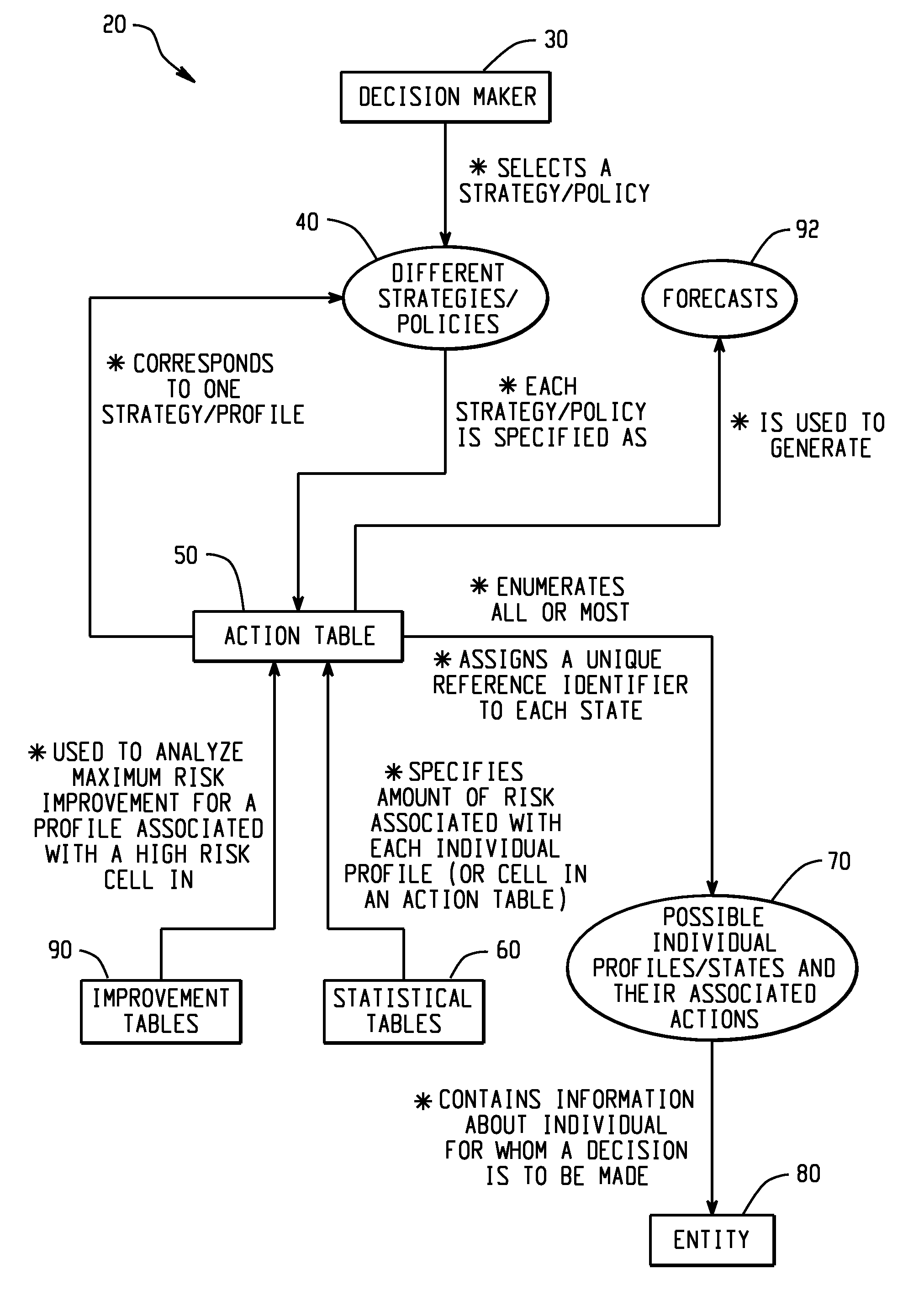
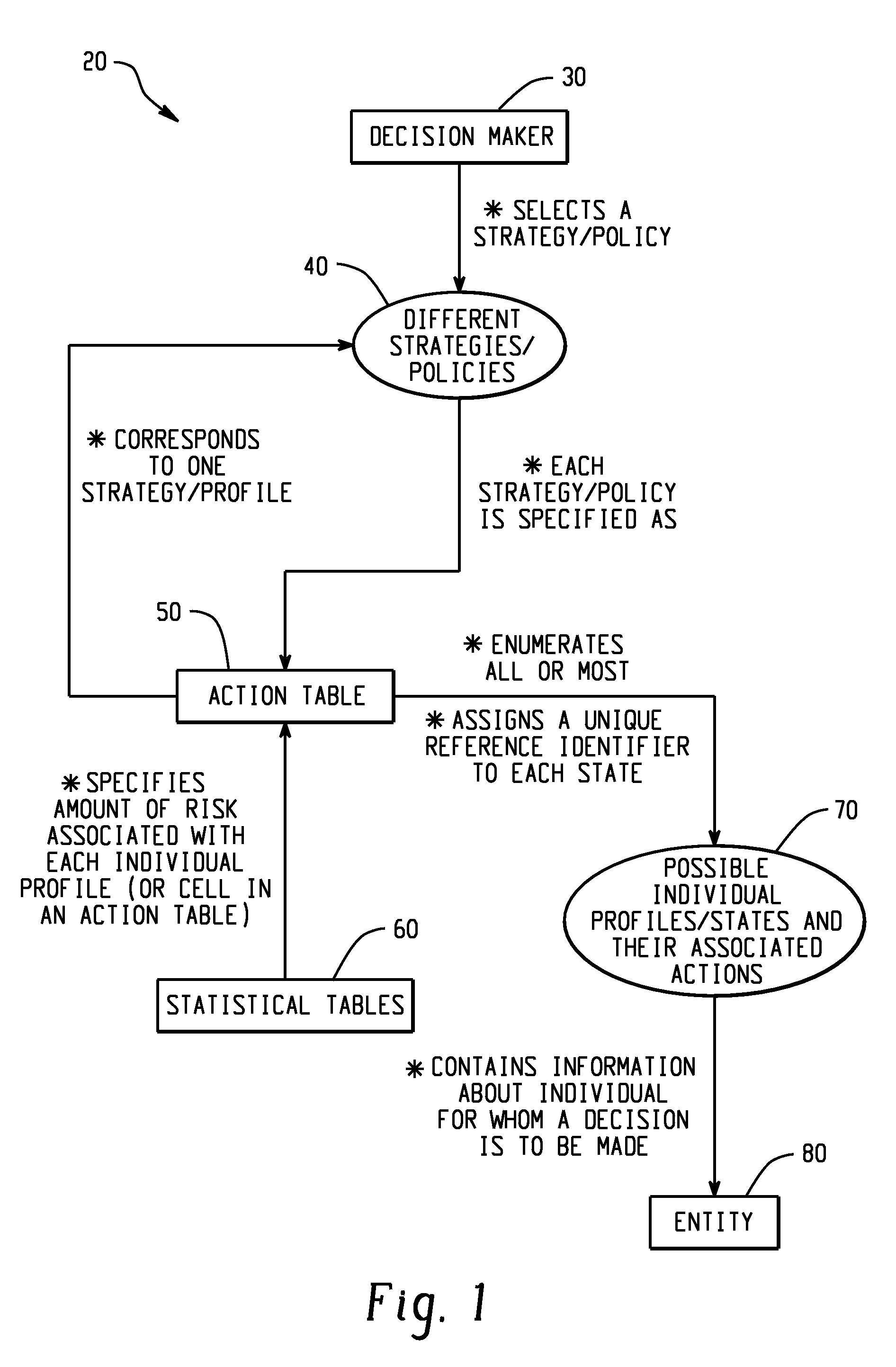
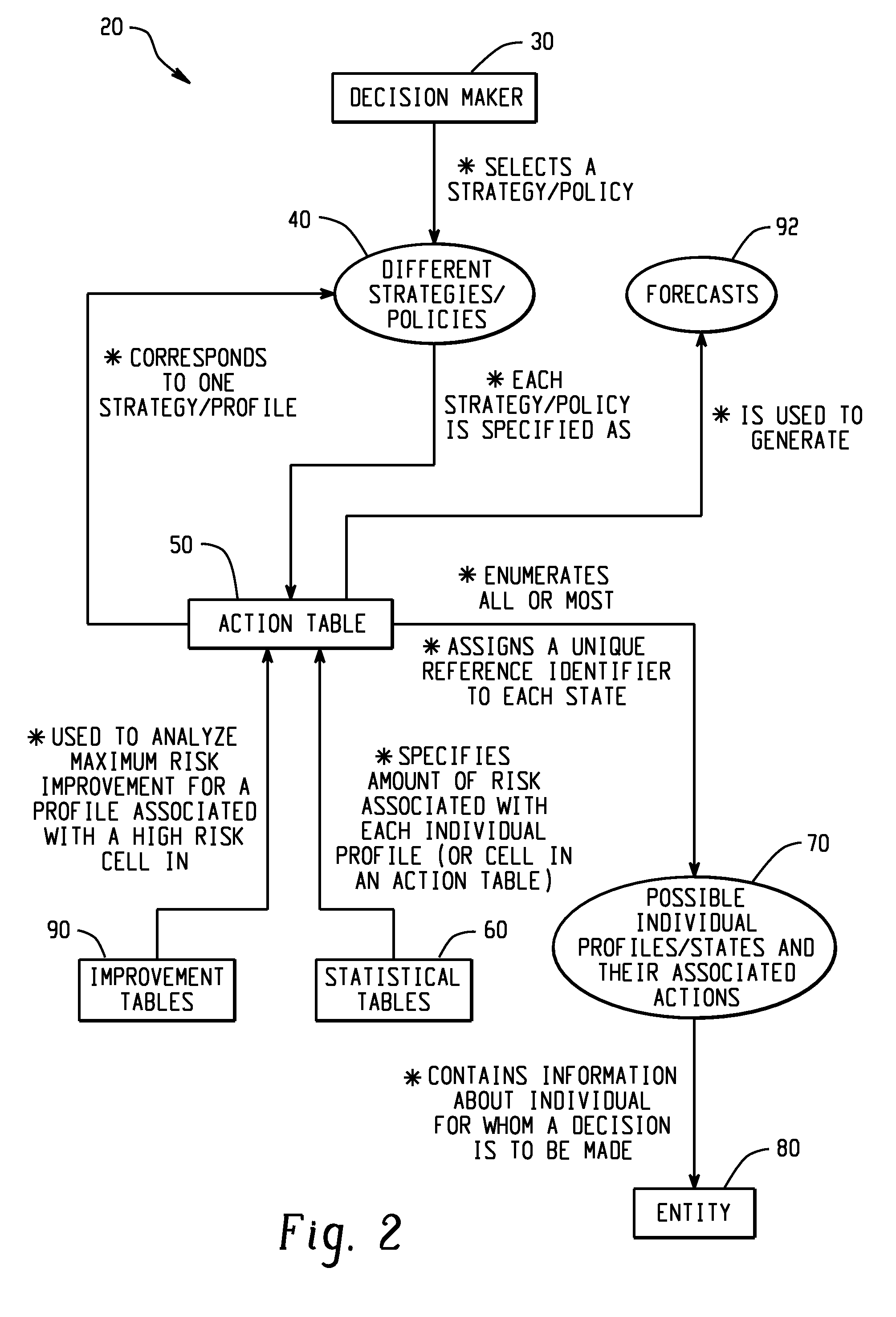
[0301]A single or multistage risk evaluation and policy formulation system is constructed for each type of promotion having a specified goal. Given a properly designed test structure, this system will enable the user to isolate specific profiles which characterize the type of individual who is the most desirable to promote. Here the term profile refers to a set of variables associated with an individual which specify all of the information pertinent to the selection pr...
example 1
New Account Acquisition
[0313]Two objective functions are specified, namely response and high purchase activity. The first system will isolate profiles corresponding to those individuals who are most likely to respond to the promotion. After a required period of time a second system is developed which will identify those respondents who are most likely to have high purchase activity. Each system associates a response index and activity index, respectively, with every profile. Selection for future mailouts is then based on a function of these two sets of indices.
example 2
Inactive Account Stimulation
[0314]A subset of inactive accounts is promoted. The balance of inactive accounts serve as a control group. Promoted activation is observed along with spontaneous reactivation in the control. First a respond / no respond system is built which isolates respondent profiles and provides their corresponding response indices. Next, using suitable data transformations and multivariate estimation techniques, the extent of spontaneous reactivation in the promoted group is inferred from the control group. A second system is then constructed which forecasts the net response due to the promotion.
Detailed Credit Approval Example
[0315]In this detailed credit approval example, a component of a risk evaluation system is an action table which assigns a specific action for each individual applicant profile. Let us consider a one stage, six characteristic system for granting credit at XYZ Department Store. An action table corresponding to one of eighty-four possible policies...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com