HIV-1 GP41 neutralization domain and use thereof
a technology of neutralization domain and hiv-1, which is applied in the field of hiv-1 gp41 neutralization domain, can solve the problems of poor immunogenicity, region would not be a useful vaccine target, and the inability of most individuals to produce similar antibodies with hiv-neutralizing properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Neutralizing Activity of 53M Serum Samples
[0053]Studies were conducted on two sets of Envs and sera isolated from a cohort in Zambia (Li, et al. (2006) J. Virol. 80:5211-18). Sera samples 53M and 133M both possessed high autologous neutralizing titers, but while 133M serum did not neutralize any of the heterologous Envs, 53M serum also had a lower neutralizing activity for a number of additional primary Envs. To map the general location of the autologous neutralization targets in 53M Env, a series of recombinants was generated in which various domains were exchanged between 53M Env and 133M Env, a second primary clade C Env that was resistant to neutralization by 53M serum (FIG. 1). This approach utilized conveniently placed restriction sites present in the conserved regions following the V2 (BglII) and V5 (MfeI) domains, resulting in the generation of infectious recombinant Envs in which N-terminal gp120 domain (through C2, including V1 / V2), C-terminal gp120 domains (V3-V5) and gp4...
example 2
Localization of gp41 Sequence that Mediates Autologous Neutralization
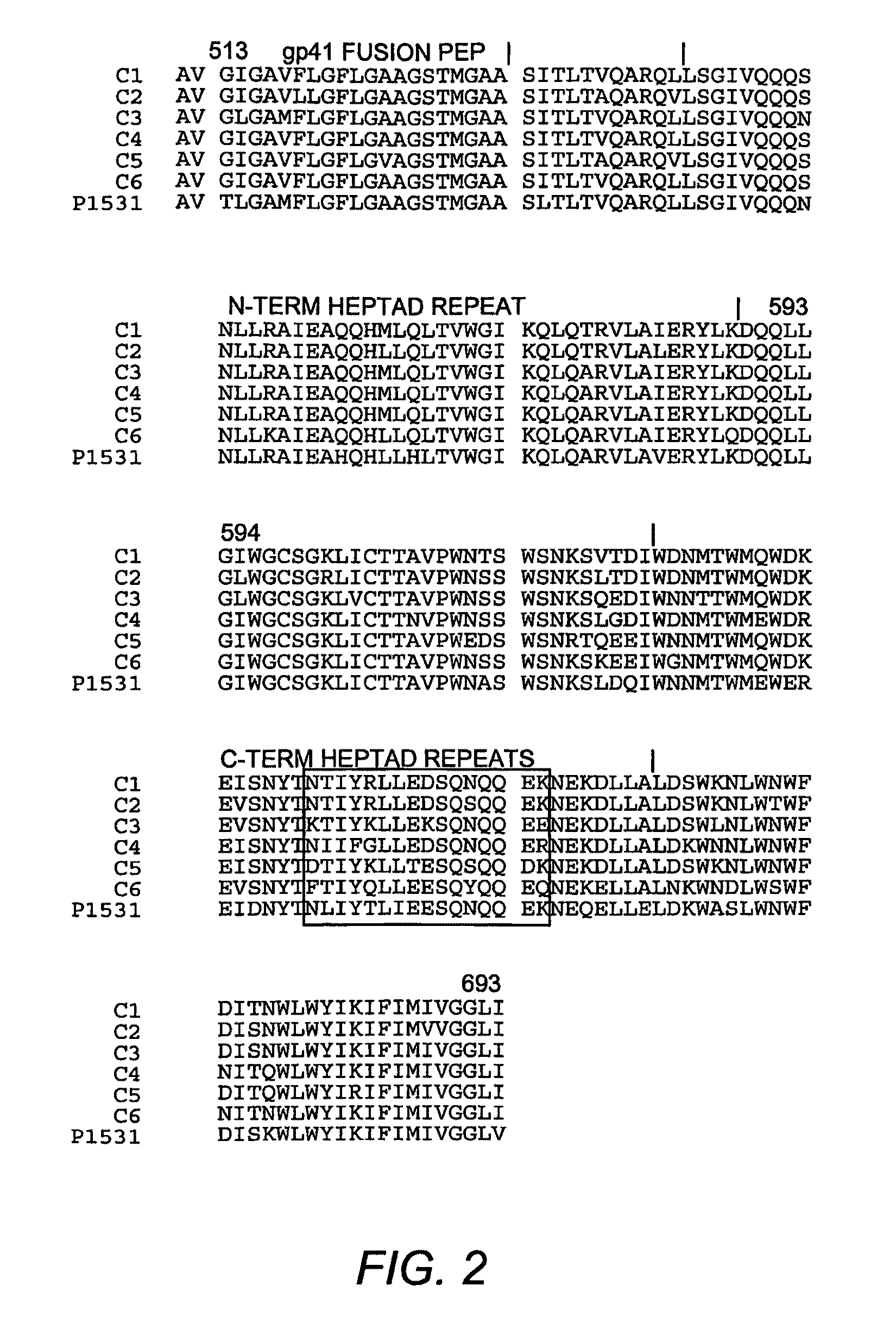
[0057]To identify the location of the epitope(s) responsible for the autologous neutralizing activity of 53M serum, the gp41 ectodomain sequences of six subtype isolates were analyzed to identify a sequence distinct from the other sequences. One particular region in the HR2 region was notably polymorphic, and the 53M sequence contained several charged resides that were unique for this sequence (indicated by the box in FIG. 2). This sequence was located approximately in the middle of the HR2 domain, and N-terminal to the MPER epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies 2F5 and 4E10.
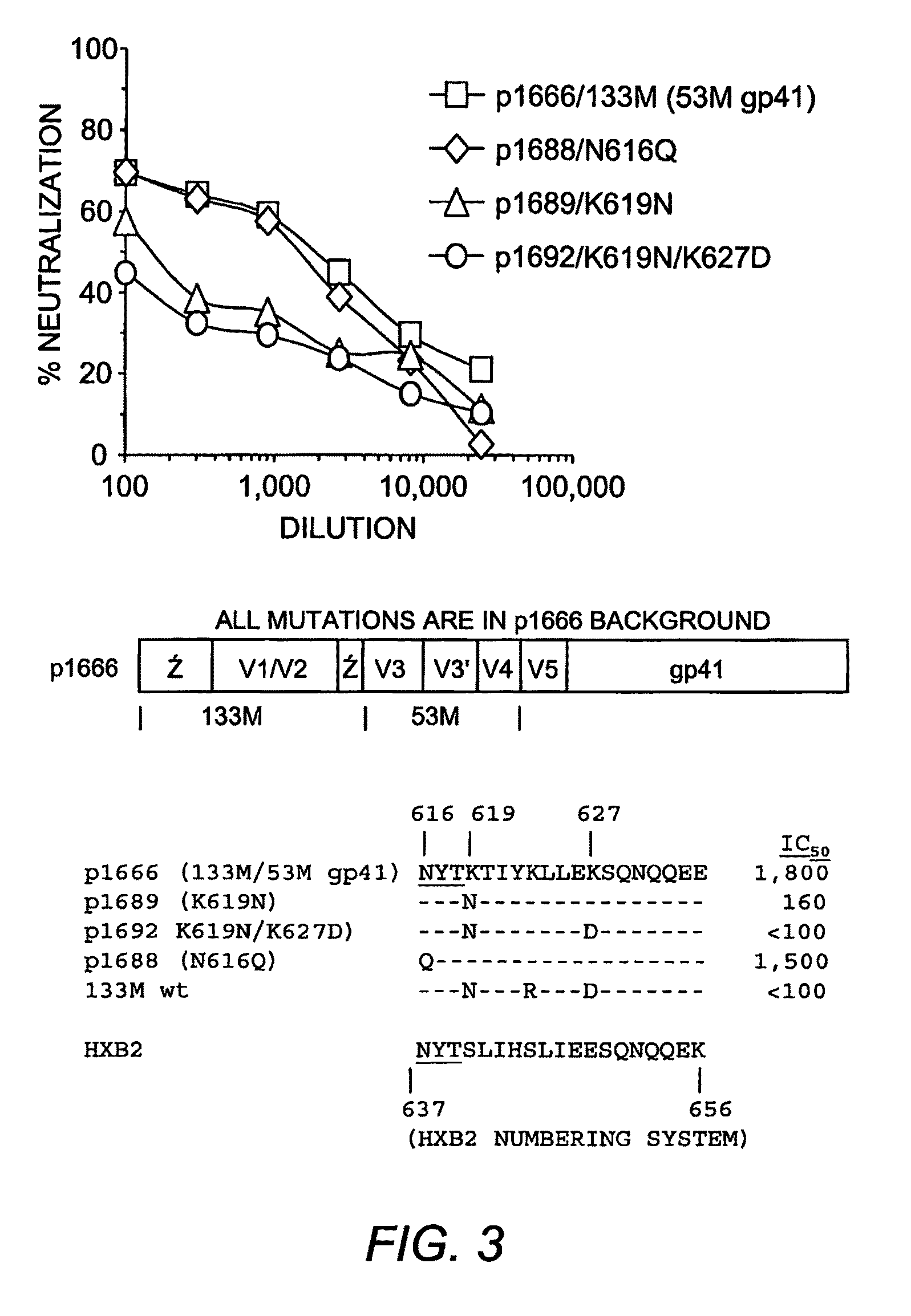
[0058]To determine whether this region participated in the 53M gp41 neutralization epitope, several mutations were introduced at the polymorphic positions of this region in the chimeric Env that contained the gp41 region of 53M Env in the 133M Env background (p1666 in FIG. 1). The use of this chimeric Env allowed the isolation of the 53M...
example 3
Neutralization Sensitivity of Mutant 135M Env to 53M Serum
[0060]To further confirm the role of the region in HR2 identified as a neutralization determinant, it was determined whether substituting sequences from this region into a resistant Env could introduce neutralization sensitivity to 53M serum. The HR2 sequence of the 135M Env was the most closely related to that of 53M, so 135M Env was selected as the recipient. Six positions in the 640-655 region of HR2 differed in sequence for 53M and 135M Envs; Lys vs. Asp at 640, Glu-Lys vs. Thr-Glu at 647 / 648, Asn vs. Ser at 651 and Glu-Glu vs. Asp-Lys at 654 / 655 (FIG. 4). The first four of these changes were introduced into 135M Env resulting in a 135M (K / EK / N) mutant, and the effect on neutralization by 53M was examined. As shown in FIG. 5, mutating these four residues in the autologous 135M Env resulted in sensitization to 53M serum. Whereas the parental virus was not neutralized at serum dilutions of 1:100 or 1:20, the mutant was neut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reactivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com