Dummy gate technology to avoid shorting circuit
a dummy gate and shorting circuit technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical apparatus, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of vsub>cc /sub>contacts, shorting through the dummy gate line of the edge cell, and contact ss /sub>contacts,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
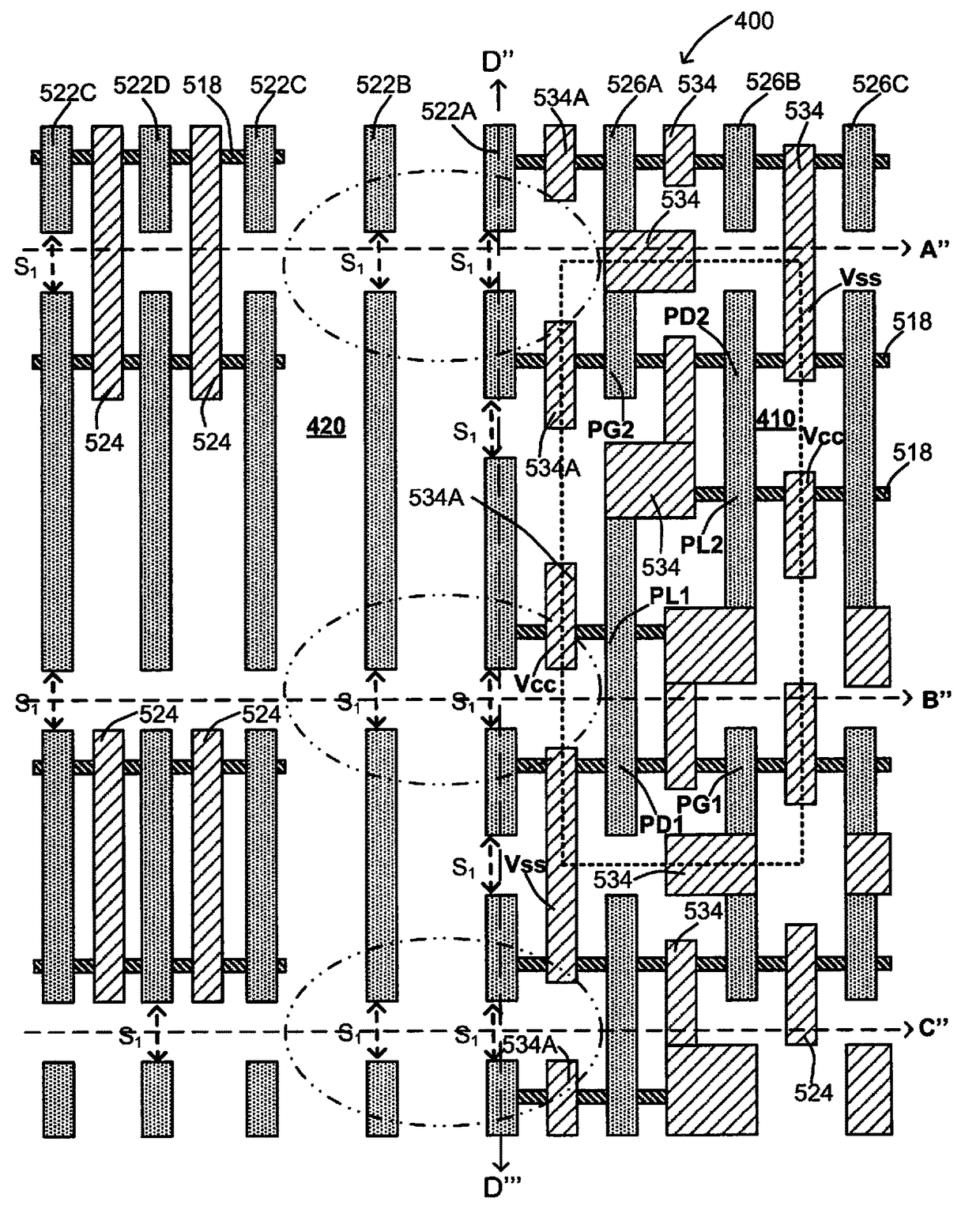
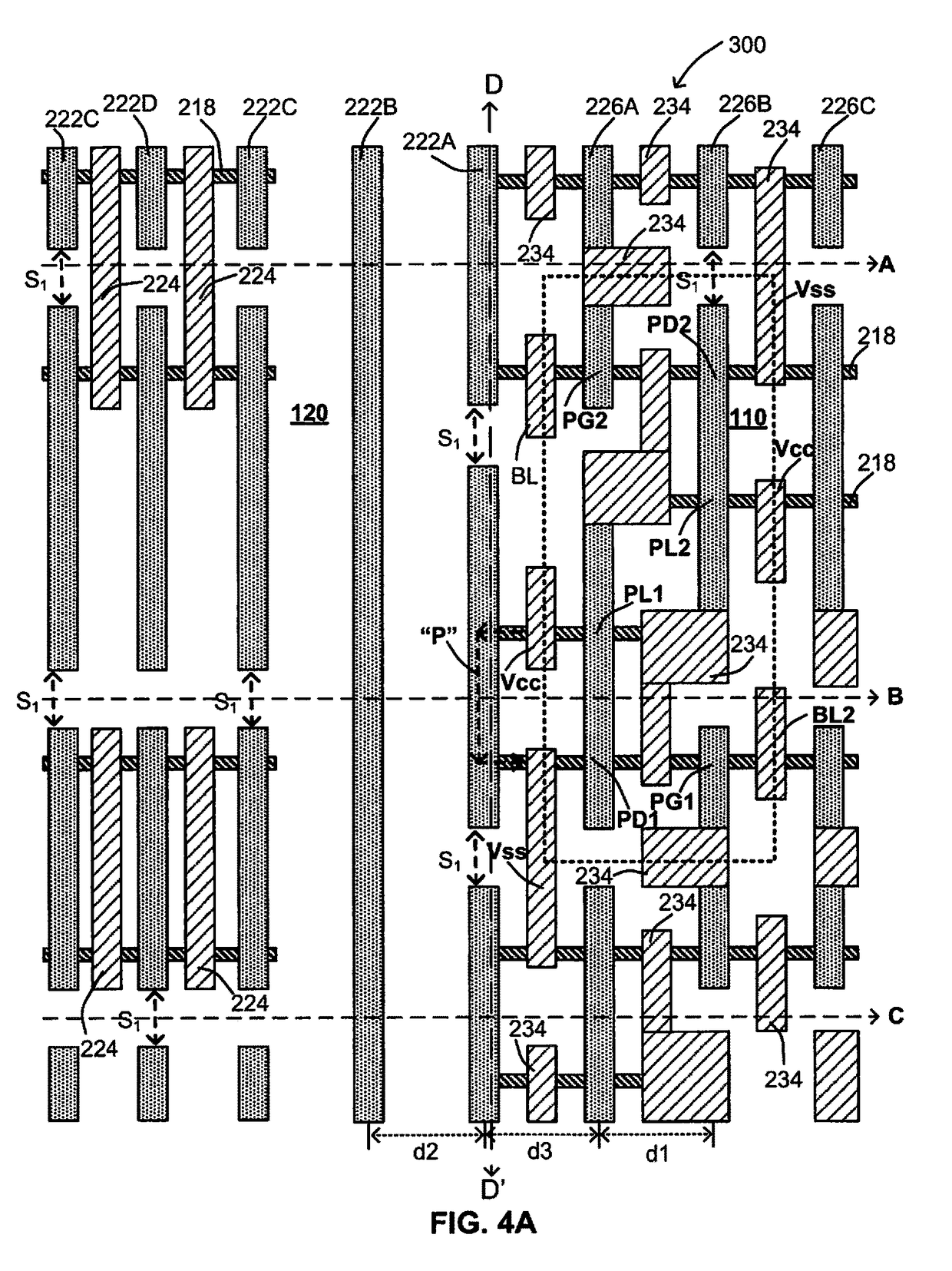
[0045]Embodiments of this invention provide a novel static random access memory (SRAM) comprising fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) structures to prevent electrical short to the dummy gate of an edge cell between a high VCC supply voltage of a metal contact disposed in an bit cell to a low VSS voltage of a nearby metal contact disposed in the same bit cell. In addition, the corresponding design layouts and a process of fabricating such improved SRAM (FinFETs) devices according to the improved device design layout for the corresponding edge cells and bit cells are presented.
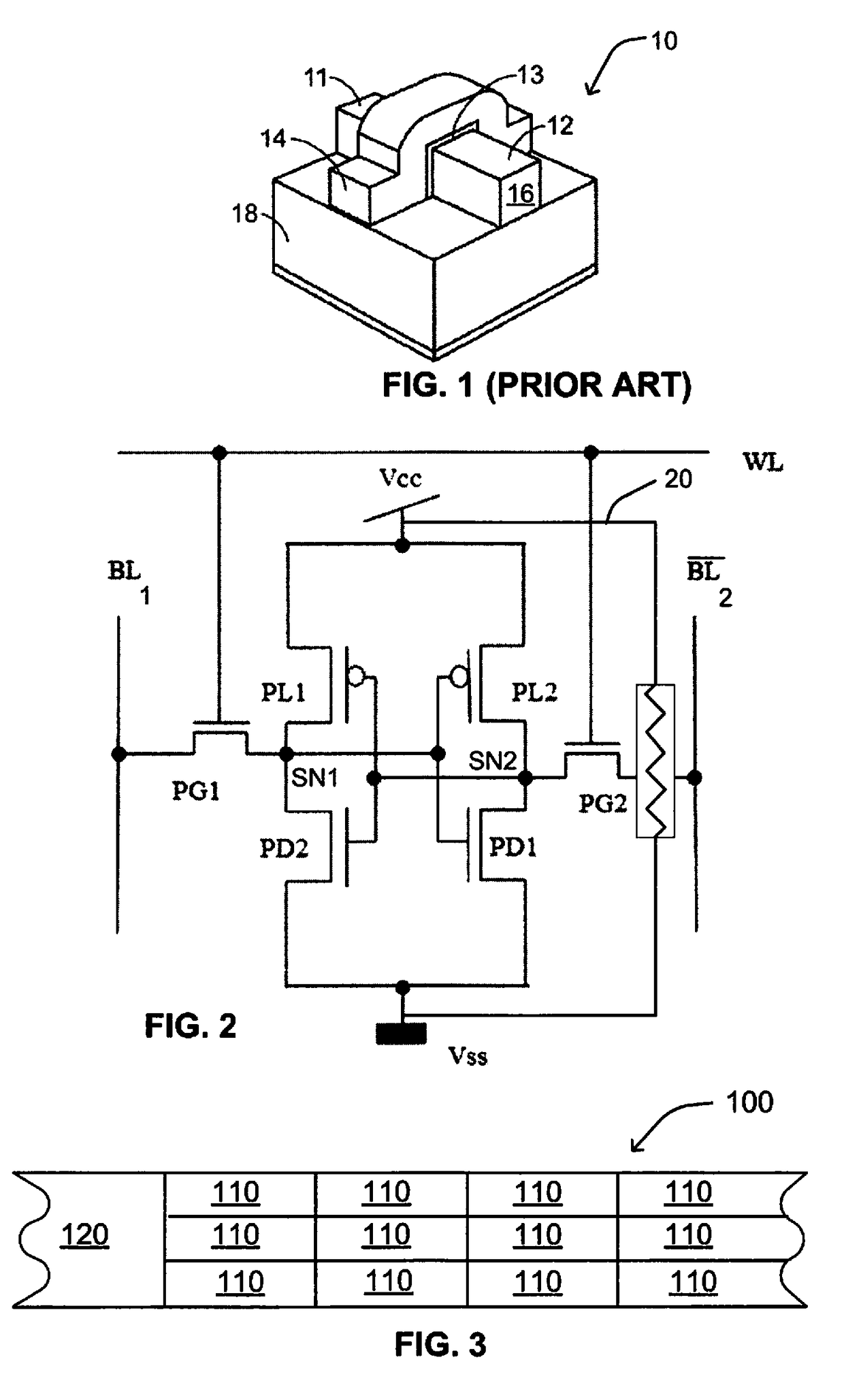
[0046]FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of a static random access memory (SRAM) cell with 6 FinFET transistors (6T). The SRAM cell includes pass-gate transistors PG1 and PG2, pull-up transistors PL1 and PL2, and pull-down transistors PD1 and PD2. The gates of pass-gate transistors PG1 and PG2 are controlled by word-line (WL) that determines whether the current SRAM cell is selected or not. The storage portion of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com