System encrypting method using multifunctional assistant SCM
An encryption method and single-chip microcomputer technology, applied in computer security devices, internal/peripheral computer component protection, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of low confidentiality, achieve the effect of improving security, reducing the probability of being copied, and simple functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
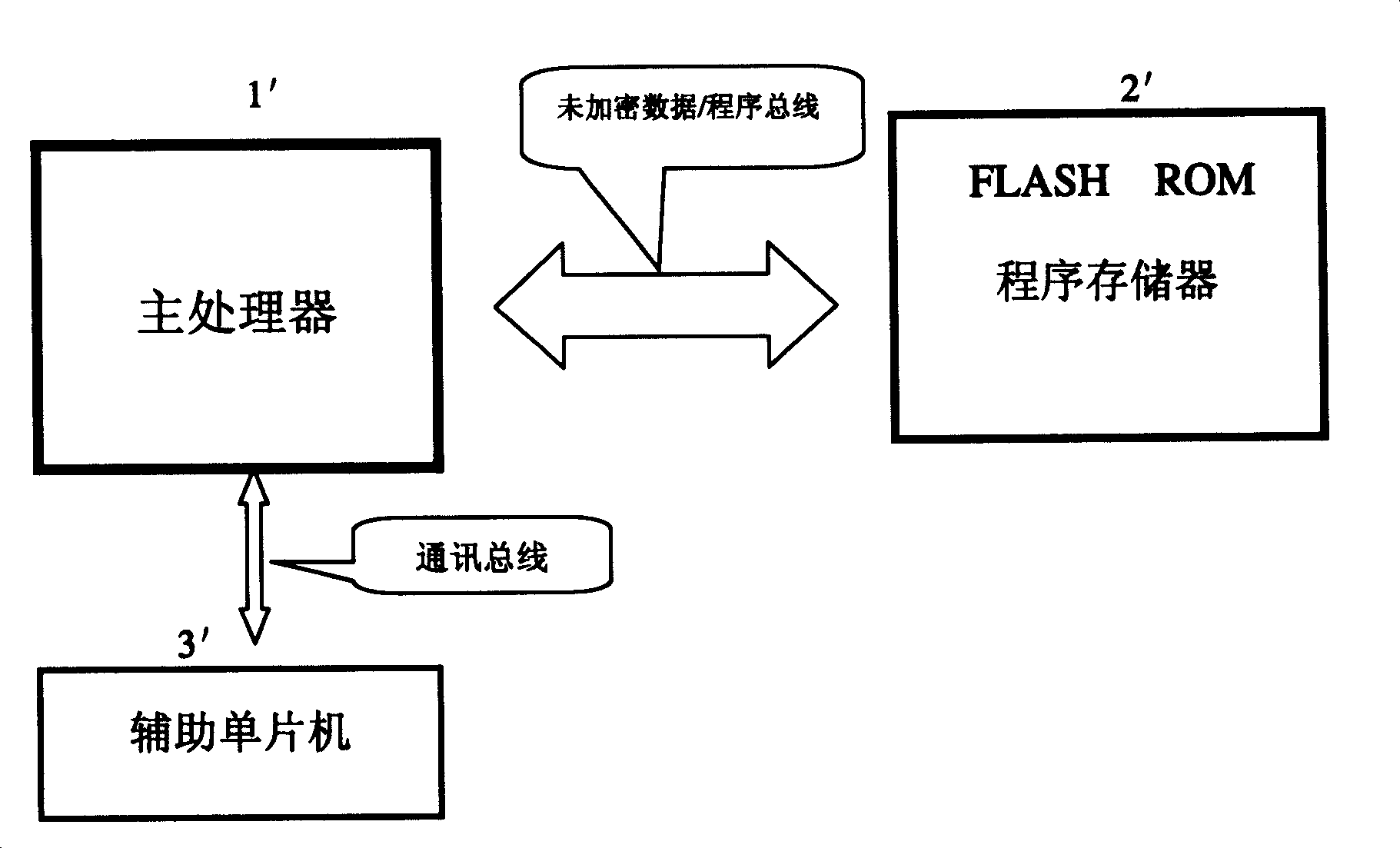
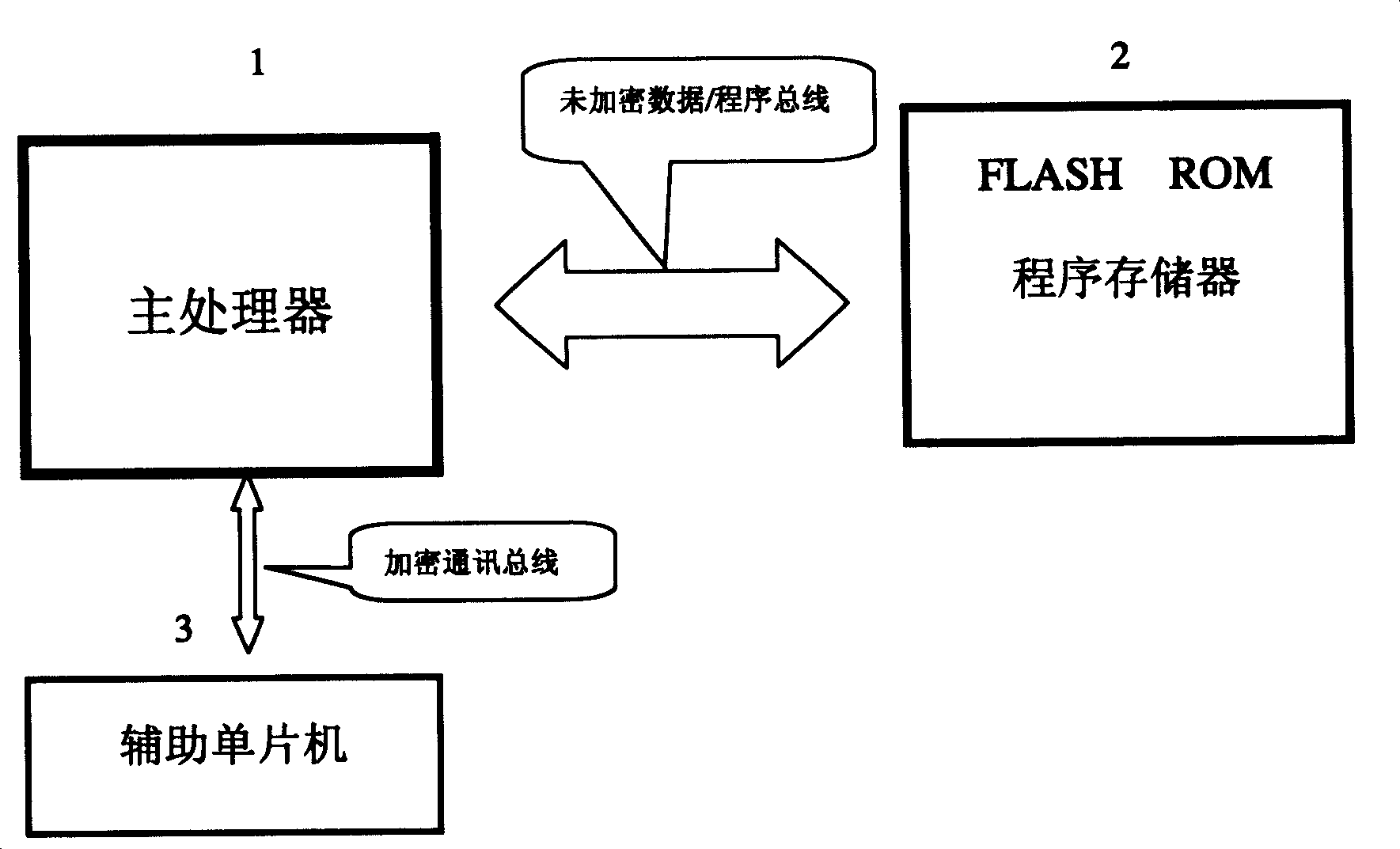
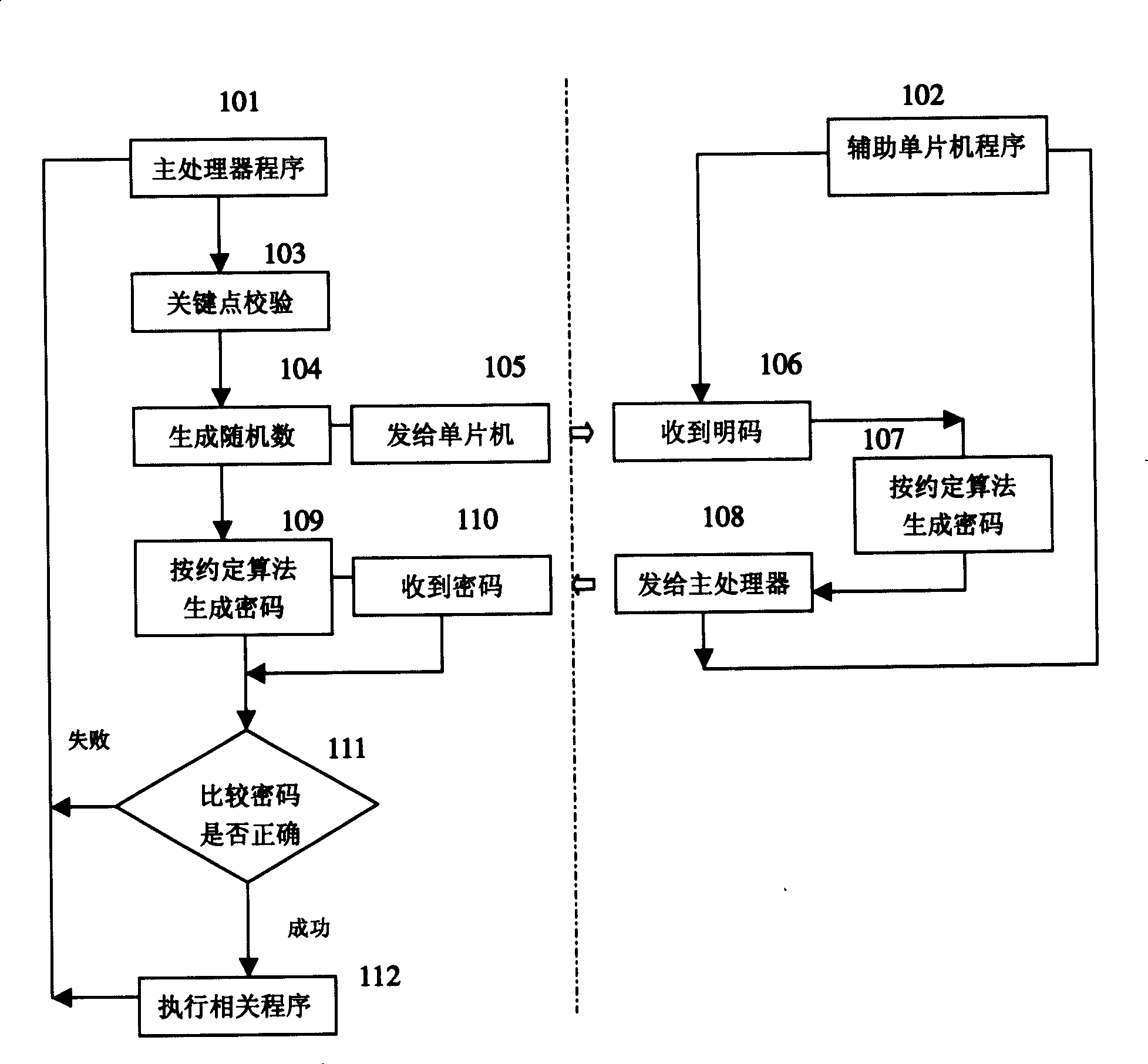
[0033] Example one, see Figure 2 to Figure 4 As shown, a system encryption method using a multi-purpose auxiliary single-chip microcomputer of the present invention is based on the use of a single-chip computer with a built-in burn-out (anti-reading) program memory, by adding the main processor program and the auxiliary single-chip microcomputer program The method of cryptographic verification of the encryption protocol algorithm is agreed so that the system program cannot be read and cannot be copied to achieve the purpose of system encryption. The system hardware usually includes the main processor 1, the FLASH ROM program memory 2, the auxiliary single-chip 3, and The main processor 1 and the external FLASH ROM program memory 2 communicate and store in an unencrypted manner, so that maintenance work such as software modification and upgrade can be facilitated. The key points in the software operation of the main processor 1 are all password-checked, that is, the check points ar...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example two, see Figure 6 As shown, the system encryption method of the present invention using a multi-purpose auxiliary single-chip microcomputer is different from the first embodiment in that the encryption protocol algorithm used is a reversible algorithm; therefore,
[0055] In step e: the main processor 1 decrypts and restores the password sent by the auxiliary single-chip microcomputer 3 into a clear code according to the encryption protocol algorithm of the reversible algorithm, and compares the decrypted and restored clear code with the originally generated clear code;
[0056] In step f: when the corresponding two plain codes are consistent, the main processor 1 continues to run subsequent programs or includes repeating step c;
[0057] When the corresponding two plain codes are inconsistent, the main processor 1 refuses to run the subsequent program, and the system ends the operation.
[0058] Figure 6 Schematic flow chart of encryption of reversible algorithm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com