Semiconductor luminescent device and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for light-emitting devices and manufacturing methods, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in growing GaN, poor crystal integrity, and increasing device operating voltage, so as to eliminate current blocking effect, improve current expansion effect, The effect of lowering the operating voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
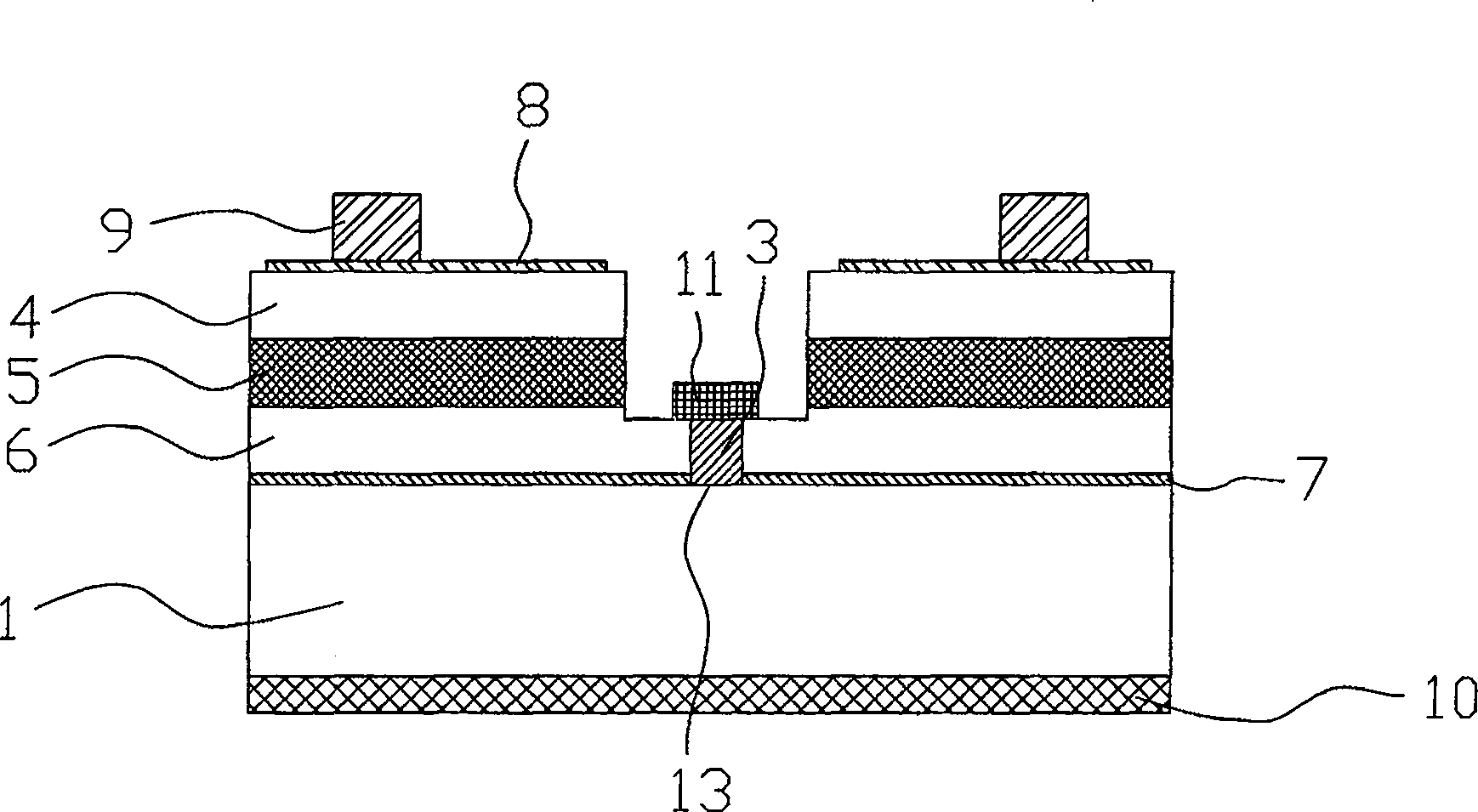
[0026] refer to figure 1 , a semiconductor light-emitting device, which comprises a substrate 1 and a semiconductor epitaxial stack stacked on the substrate 1, the semiconductor epitaxial stack comprises an N-type layer 6, a light-emitting layer 5 and a P-type layer 4 sequentially from bottom to top, A layer of transparent conductive film 8 is formed on the upper surface of the P-type layer 4, a P-type electrode 9 is arranged on the transparent conductive film 8, an electrode 10 is arranged on the lower surface of the substrate 1, and the N-type layer 6 is provided with a The conductor has one end exposed to the N-type layer 6 , and is provided with an N-type electrode 11 , and the other end of which is in electrical contact with the substrate 1 .
[0027] The conductor is composed of a columnar through hole 13 and a conductive substance 3 filled in the through hole 13 . The through hole 13 is a cylindrical through hole with a circular or square cross section.
[0028] In or...
Embodiment 2
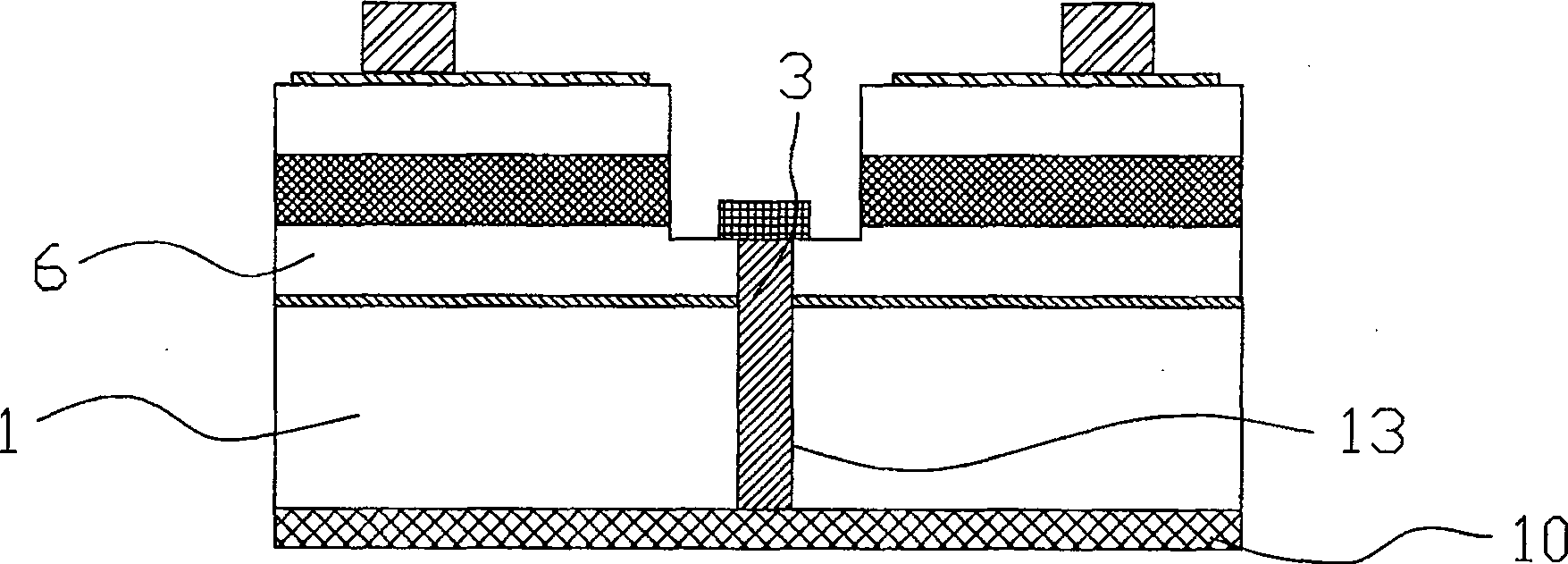
[0043] like figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is similar to Embodiment 1, with the difference that: in this embodiment, in order to reduce the internal resistance of the substrate 1, when the through hole 13 is etched, the entire substrate 1 can be etched to form a full through hole. The conductive material 3 is filled in the through hole 13 , and the N-type layer 6 is directly in electrical contact with the electrode 10 at the lower end of the substrate 1 through the conductive material 3 .
[0044] Of course, according to different requirements on the internal resistance of the semiconductor light emitting device in practical applications, the through hole 13 may also partially penetrate the substrate 1 .
Embodiment 3
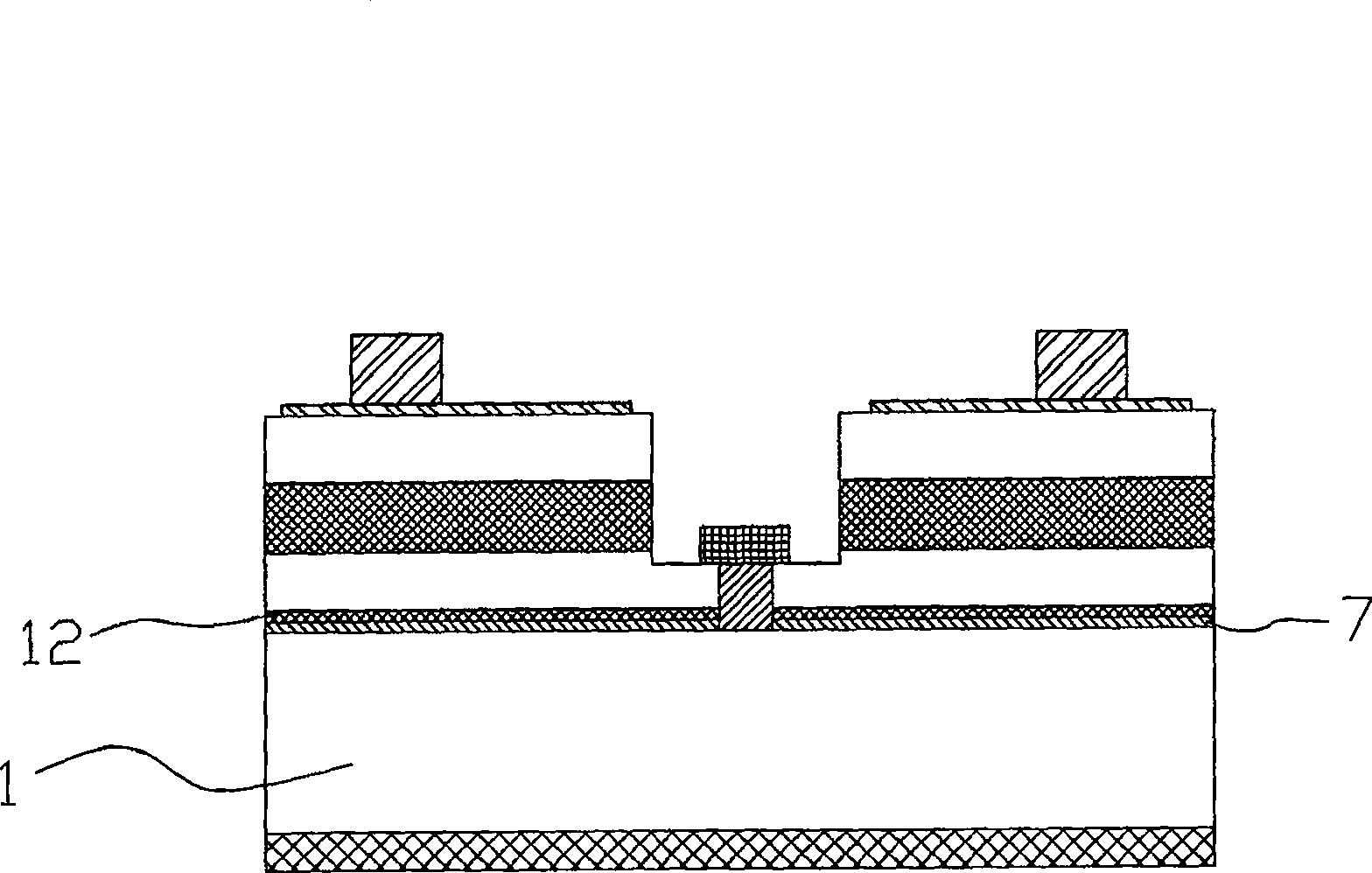
[0046] like image 3 As shown, this embodiment is similar to Embodiment 1, with the difference that: in this embodiment, in order to improve the light extraction efficiency of the semiconductor light-emitting device, aluminum gallium indium nitride (InxGayAl1-x-yN, InxGayAl1-x-yN, InxGayAl1-x-yN, 0<=x<=1, 0<=y<=1) DBR reflective layer 12 (typical structure is AlGaN / AlN, etc.), the through hole 13 structure at this time needs to be etched through the dry etching process. The substrate 1 is reached through the DBR reflective layer 12 and the buffer layer 7 .
[0047] Of course, according to the different requirements on the internal resistance of the semiconductor light emitting device in practical applications, the through hole 13 may also partially or completely penetrate the substrate 1 by using a method similar to that in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com