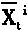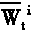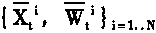Method for tracking dimension self-adaptation video target with low complex degree
A scale-adaptive, low-complexity technology, applied in image data processing, instrumentation, computing, etc., can solve problems such as lack of particle samples, failure to consider impact, and sequential Monte Carlo filter diversity destruction
Inactive Publication Date: 2010-02-03
SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
View PDF2 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
However, these improvements still have some disadvantages: the particles are too concentrated and the samples are scarce, so that the diversity of sequential Monte Carlo filtering is destroyed
The root cause is that the method of combining sequential Monte Carlo filtering and mean shift in these works is too simple, and does not consider the influence of the embedded mean shift optimization method on the original sequential Monte Carlo filtering framework, which mainly shows that the particle state space presents new probability distributed
Therefore, from the perspective of the probability of Monte Carlo sampling, a complete mean shift combination method is proposed, and it can effectively reduce the estimation error of the target scale with the change of the target size during the tracking process, which is still blank.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
A scale self-adapting video target tracking method with low complexity in the video intelligent monitoring technical field, including: initializing the state of the particle sample; randomly generating two scale factors on each sampling point for the particle sample, computing the sample second autoegression center, storing as the mean drifting center; obtaining a mean drift field with neighborhood uniformity according to the second autoegression center of the sampling point in the sample set; building the important sampling density function for each sampling point, and obtaining the updatingstate X1' of the sample combining with the mean drifting method from the sampled probability angle of the Monte Carto, and updating the weight value w' under the state X1', then sampling again on thesample set {x1', w1'}, wherein 1=1...N, to obtain the posterior probability distribution dispersion estimation set {x1', w1'} of the object final state at the moment, wherein 1=1...N. The invention advances the tracking accuracy of the object scale space, reduces the computing complexity in the realtime video tracking.
Description
technical field The invention relates to a method in the technical field of video intelligent monitoring, in particular to a low-complexity scale-adaptive video target tracking method. Background technique In many applications in the field of computer vision, such as intelligent monitoring, robot vision, and human-computer interaction interface, it is necessary to track moving objects between frames of video sequences. Due to the diversity of tracking target shapes and the uncertainty of target motion, how to achieve robust real-time tracking in various environments and achieve reliable estimation of variable scales as the target distance changes has always been a research hotspot. Sequential Monte Carlo filtering method is a tracking method widely used in recent years, which uses the posterior probability distribution of the target in the state space to represent the most likely state of the target, such as position and size. Different from the traditional Kalman filter, t...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G06T7/20
Inventor 徐奕宋利解蓉张文军王兆闻
Owner SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com