Efficient computation of spatial filter matrices for steering transmit diversity in a MIMO communication system
A technology of spatial filter and steering matrix, applied in the field of communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The word "exemplary" is used herein to mean "serving as an example, illustration or illustration". Any embodiment described herein as "exemplary" should not be construed as preferred or advantageous over other embodiments.
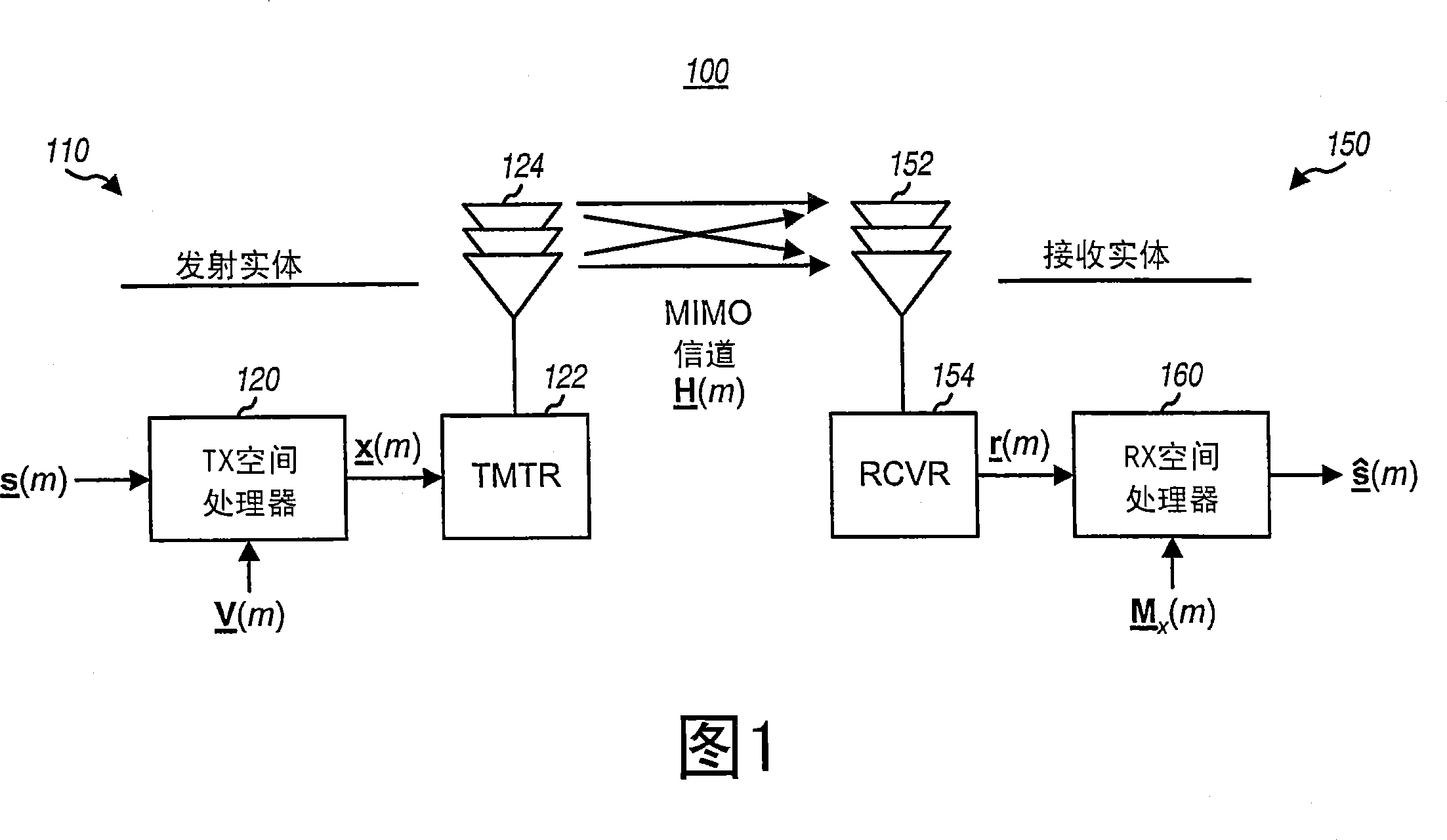
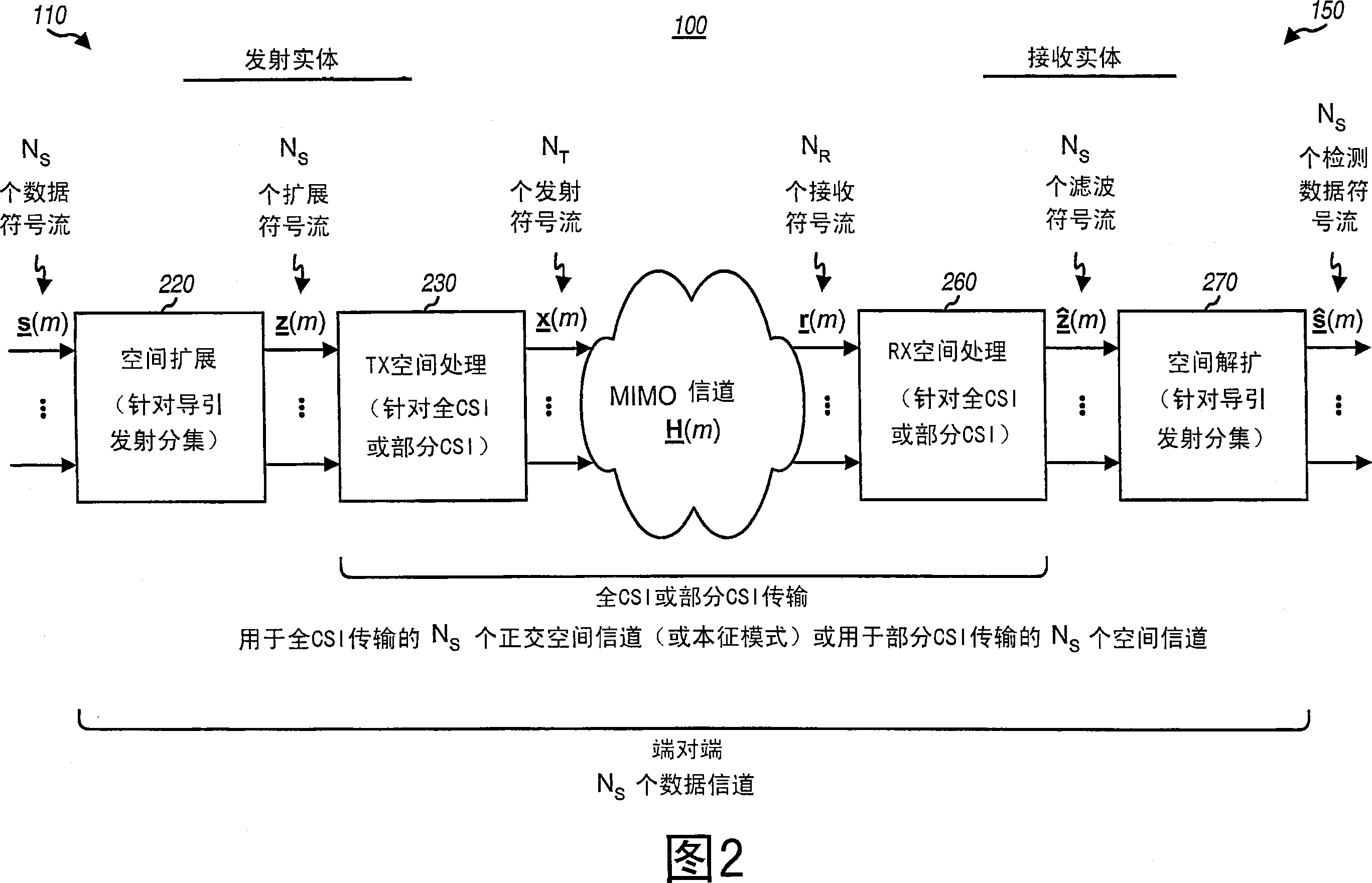
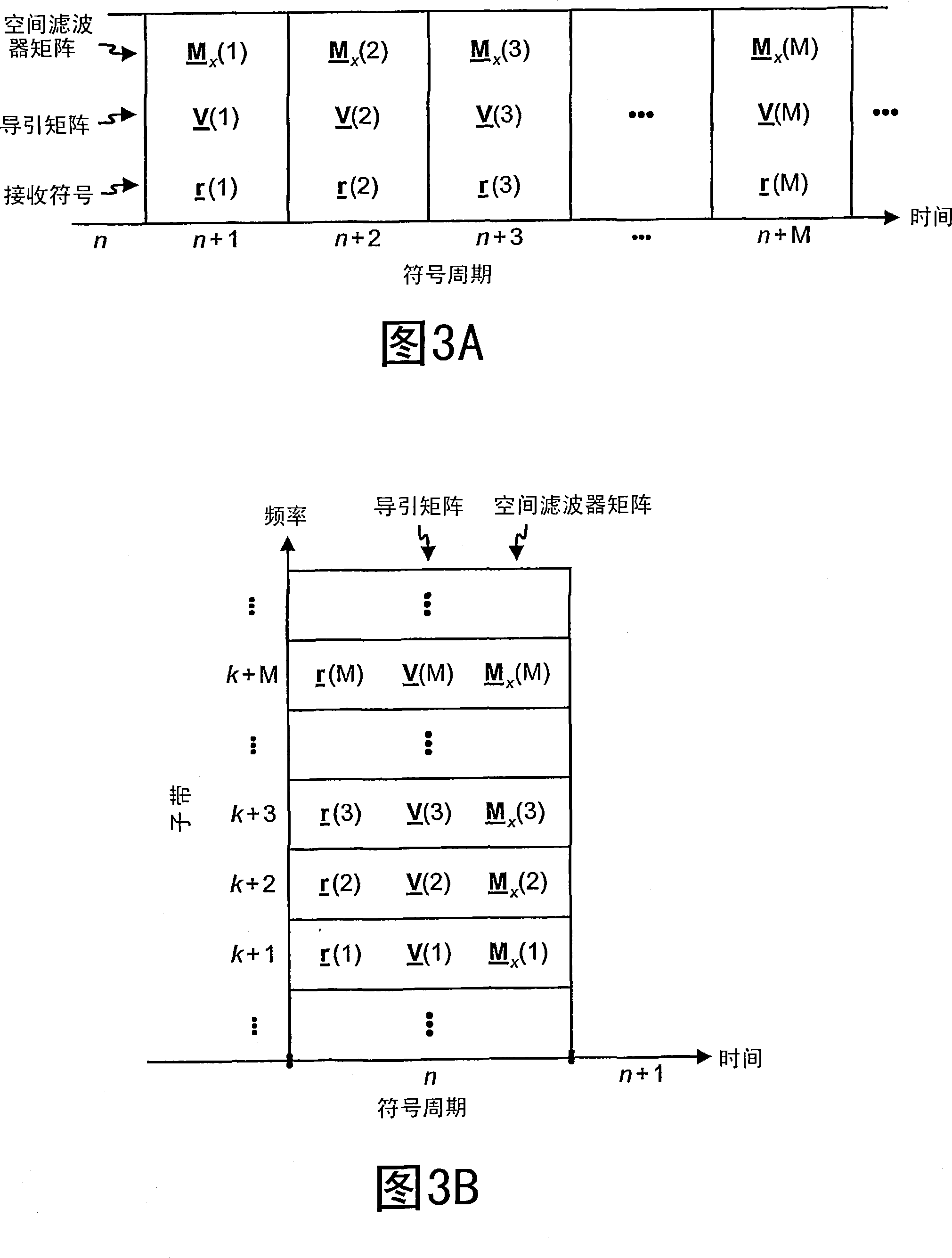
[0018] FIG. 1 shows a simple block diagram of a transmitting entity 110 and a receiving entity 150 in a MIMO system 100 . In the transmitting entity 110, a transmit (TX) spatial processor 120 processes the data symbols (using the vector s (denoted by (m)) is spatially processed to generate transmitted symbols (denoted by x (m) indicates). As used herein, "data symbols" are modulation symbols for data, "pilot symbols" are modulation symbols for pilot information (i.e., data known a priori to both the transmitting entity and the receiving entity), and "transmit symbols" are the symbols sent from the transmitting antenna. The "received symbol" is the symbol obtained from the receiving antenna, and the modulation symbol is the complex value of a poin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com