High-frequency heating power supply device
A high-frequency heating and equipment technology, applied in microwave heating, electric/magnetic/electromagnetic heating, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of current drop and achieve the effect of increasing the margin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
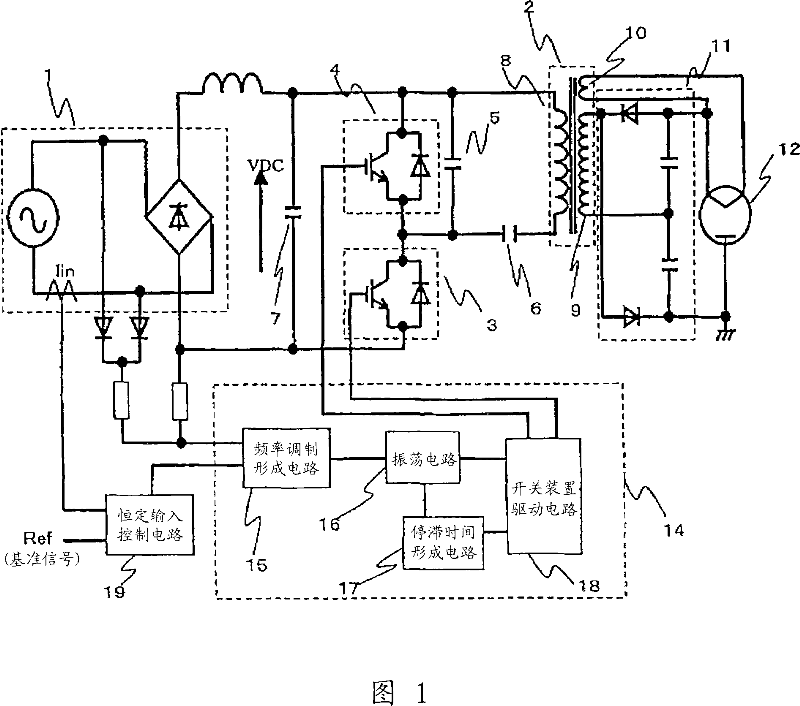
[0074] FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a circuit configuration for driving a magnetron according to the present invention. DC power supply 1, flux leakage transformer 2, first semiconductor switching element 3, second semiconductor switching element 4, first capacitor 5, second capacitor 6, third capacitor 7, drive control IC unit 14, full-wave voltage multiplier rectification The circuit 11 and the magnetron 12 constitute the overall circuit. Since the overall circuit is the same as that shown in FIG. 12, a description thereof will be omitted.
[0075] In the drive control IC unit 14 for driving the semiconductor switching elements 3 and 4, the frequency modulation forming circuit 15 forms a frequency modulation waveform using a resistance-divided waveform according to the voltage of a commercial power supply. The frequency modulation forming circuit 15 performs feedback control receiving a signal from the constant control circuit 19 to obtain the above-mentioned required input ...
no. 2 approach
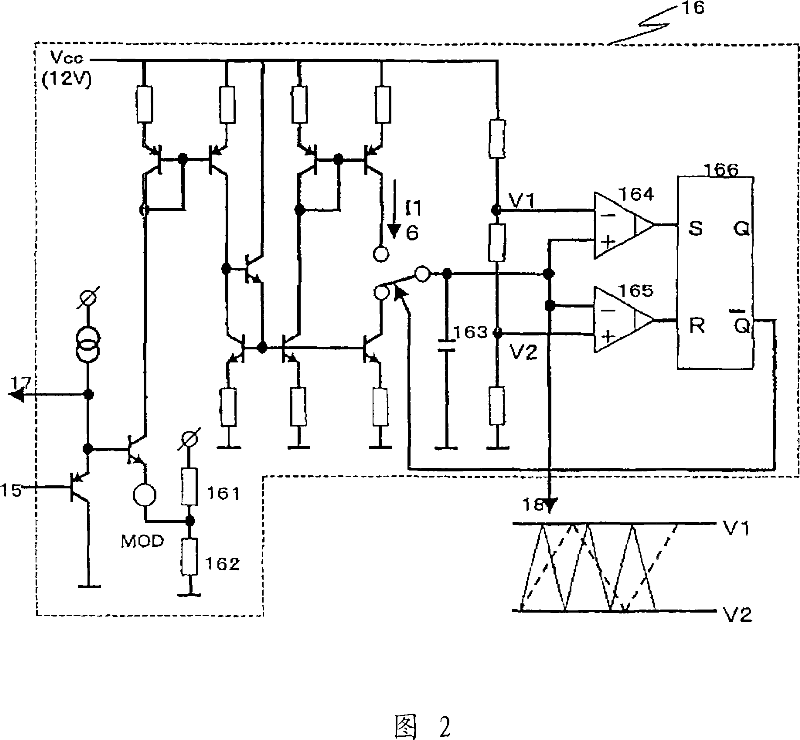
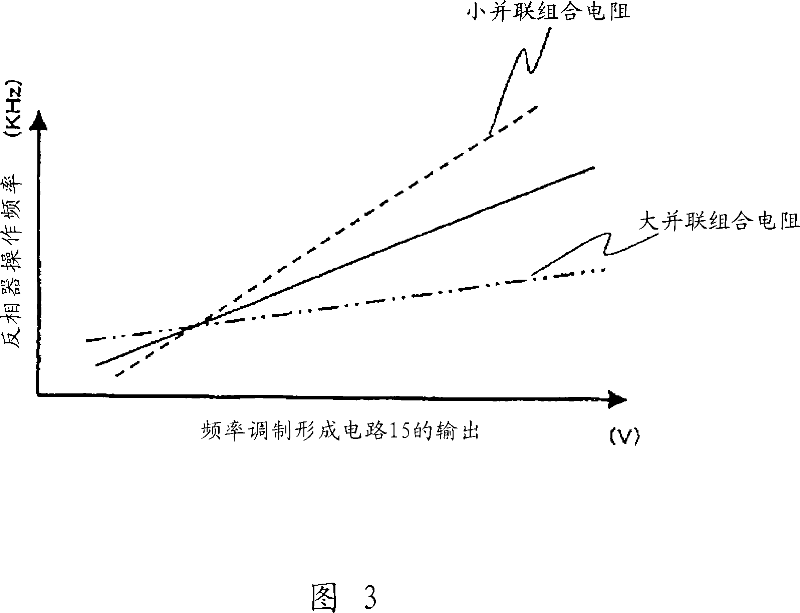
[0080] FIG. 4 is an exemplary diagram illustrating in detail the frequency modulation forming circuit shown in FIG. 1 . The fixed voltage obtained in the resistors 151 and 152 becomes the upper limit according to the voltage division waveform after rectifying the commercial power supply (aspects 3 and 8). Fig. 6(a) shows the frequency modulation waveform at this time. The waveform is divided according to the rectified voltage of the commercial mains indicated by the dotted line, and the upper value is given as realized. Subsequently, when diodes 158 and 159, and resistors 155, 156, and 157 are provided to the upper clamp shown in FIG. The voltage varies with certain curves instead of fixed values (aspect 9). Fig. 6(b) shows the curve indicated by the solid line. Furthermore, in order to determine the upper limit as a variable value instead of a fixed value, either increase or decrease according to the voltage information of the commercial power source is possible (aspects...
no. 3 approach
[0082] FIG. 7 is a diagram showing an example of the frequency modulation forming circuit 15 shown in FIG. 1 . The lower limit value is limited to a fixed value given from the resistors 153 and 154 according to the voltage division waveform after rectifying the commercial power supply. In this case, lower limit clamping means that the lower limit value corresponds to the lowest frequency limit (facets 4, 5, 12 and 16). FIG. 9( a ) shows the frequency modulation waveform in this case, and represents the lower limit indicated by the solid line (lower limit corresponding to the lowest frequency) from the commercial power rectified voltage division waveform indicated by the broken line. Subsequently, when the resistors are provided to the lower limit clamp shown in FIG. 8, the frequency modulation waveform can be formed as a curve with some variation from the reference values obtained in resistors 153 and 154, instead of a fixed value (facet 13). Fig. 9(b) shows the curve indi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com