A route selection method, system and router
A router and routing technology, applied in the direction of transmission systems, digital transmission systems, branch offices to provide special services, etc., can solve the problems that the next-hop router cannot be selected, and the load sharing of multicast data streams cannot be achieved. To achieve the effect of load sharing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
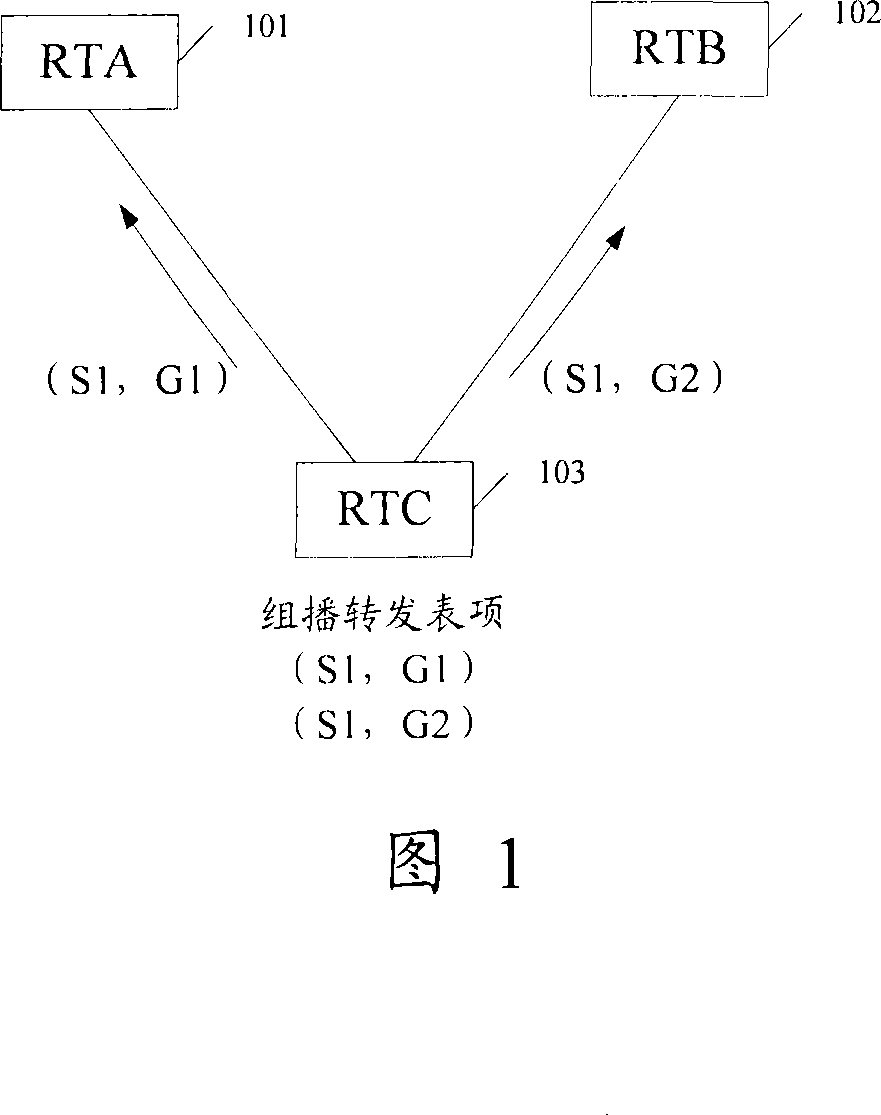
[0030] Embodiment 1: Routing with the same multicast source but different multicast groups. As shown in FIG. 1 , FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a routing selection method with the same multicast source but different multicast groups according to an embodiment of the present invention. There are two equal-cost routes from router RTC103 to multicast source S1, and the next-hop routers corresponding to these two routes are RTA101 and RTB102 respectively. There are (S1, G1) and (S1, G2) multicast forwarding table entries on router RTC103, S1 is the multicast source address, and G1 and G2 are multicast group addresses. The multicast sources of the two multicast forwarding entries are the same, but the multicast groups are different.
[0031] When selecting the next-hop router corresponding to (S1, G1), router RTC103 uses the hash algorithm:
[0032] Value(G1, M1, N) =
[0033] (1103515245*((1103515245*(G1&M1)+12345)XOR N)+12345)mod2^31
[0034] The values corresponding to t...
Embodiment 2
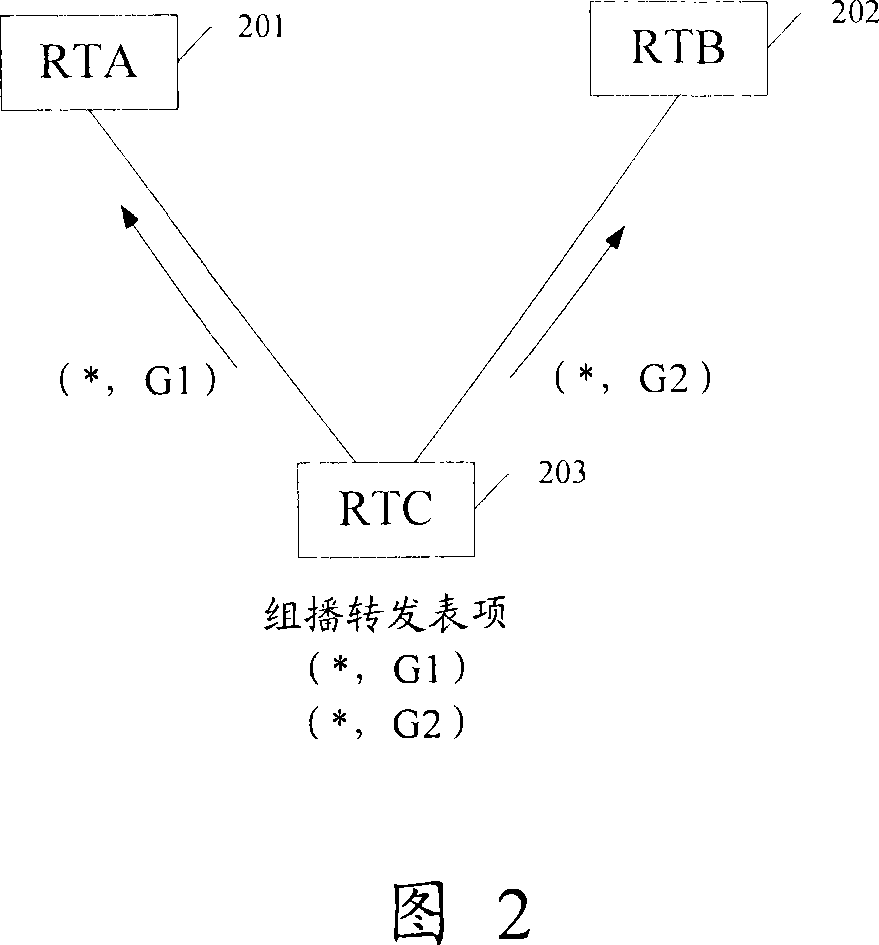
[0042] Embodiment 2: Routing with the same multicast RP and different multicast groups. As shown in FIG. 2 , FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a routing selection method with the same multicast RP but different multicast groups according to an embodiment of the present invention. There are two equal-cost routes from router RTC203 to multicast RP1, and the next-hop routers corresponding to these two routes are RTA201 and RTB202 respectively. There are (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding table entries on router RTC203, wherein "*" represents all source addresses, and G1 and G2 are multicast group addresses. The multicast RPs of the two multicast forwarding entries are the same, but the multicast groups are different.
[0043] When selecting the next-hop router corresponding to (*, G1), the router RTC203 uses the hash algorithm:
[0044] Value(G1, M1, N) =
[0045] (1103515245*((1103515245*(G1&M1)+12345)XOR N)+12345)mod2^31
[0046] The values corresponding to the addre...
Embodiment 3
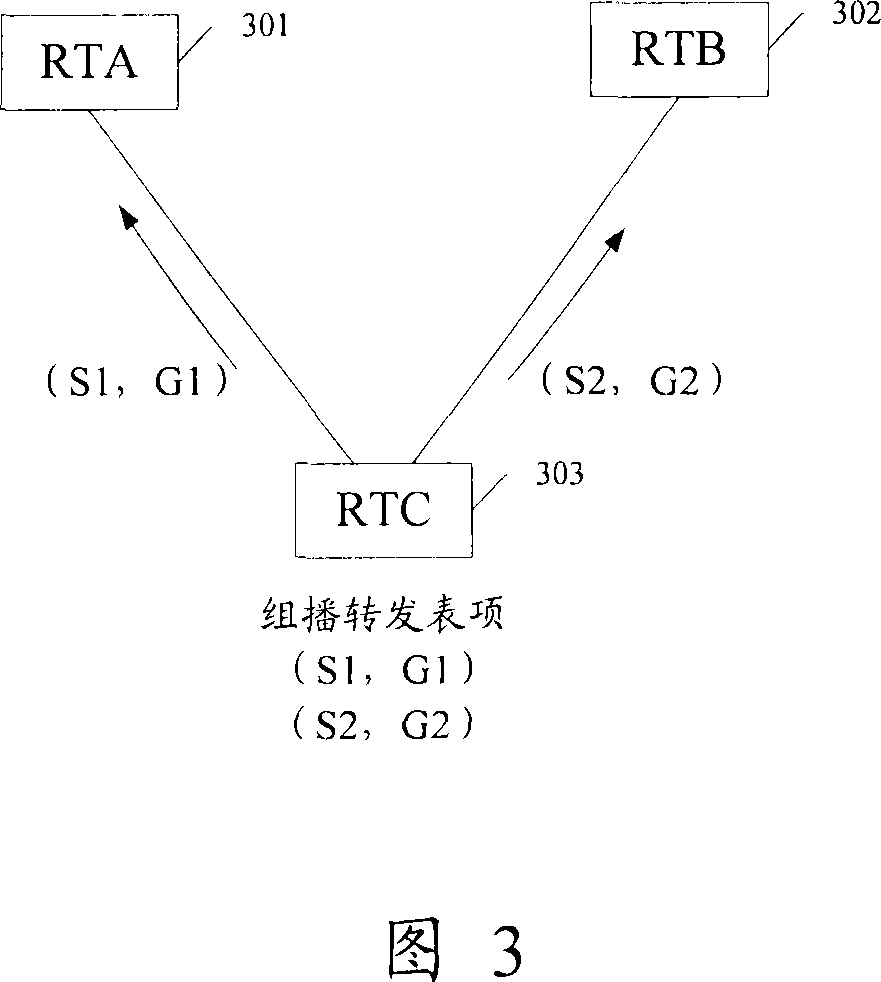
[0054] Embodiment 3: Routing selection with different multicast sources and different multicast groups. As shown in FIG. 3 , FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of a routing selection method with different multicast sources and different multicast groups according to an embodiment of the present invention. There are two equal-cost routes from router RTC303 to multicast sources S1 and S2, and the corresponding next-hop routers are RTA301 and RTB302 respectively. There are (S1, G1) and (S2, G2) multicast forwarding entries on router RTC303, S1 and S2 are multicast source addresses, and G1 and G2 are multicast group addresses. The multicast sources and multicast groups of the two multicast forwarding entries are different.
[0055] When selecting the next-hop router corresponding to (S1, G1), the router RTC303 uses the hash algorithm:
[0056] Value(S1, G1, M1, N) =
[0057] (1103515245*((1103515245*((S1^G1)&M1)+12345)XOR N)+12345)mod 2^31
[0058] The values corresponding to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com