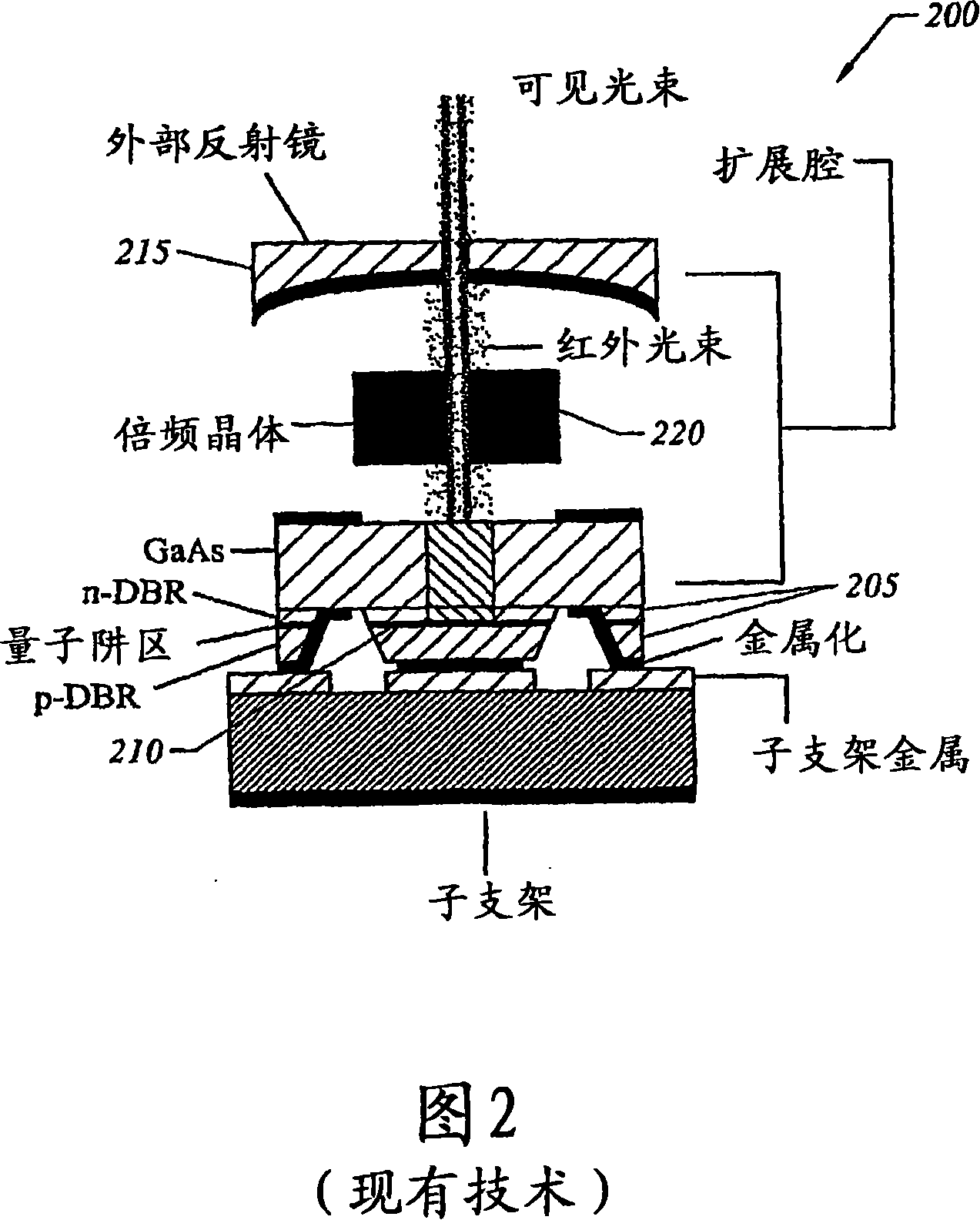
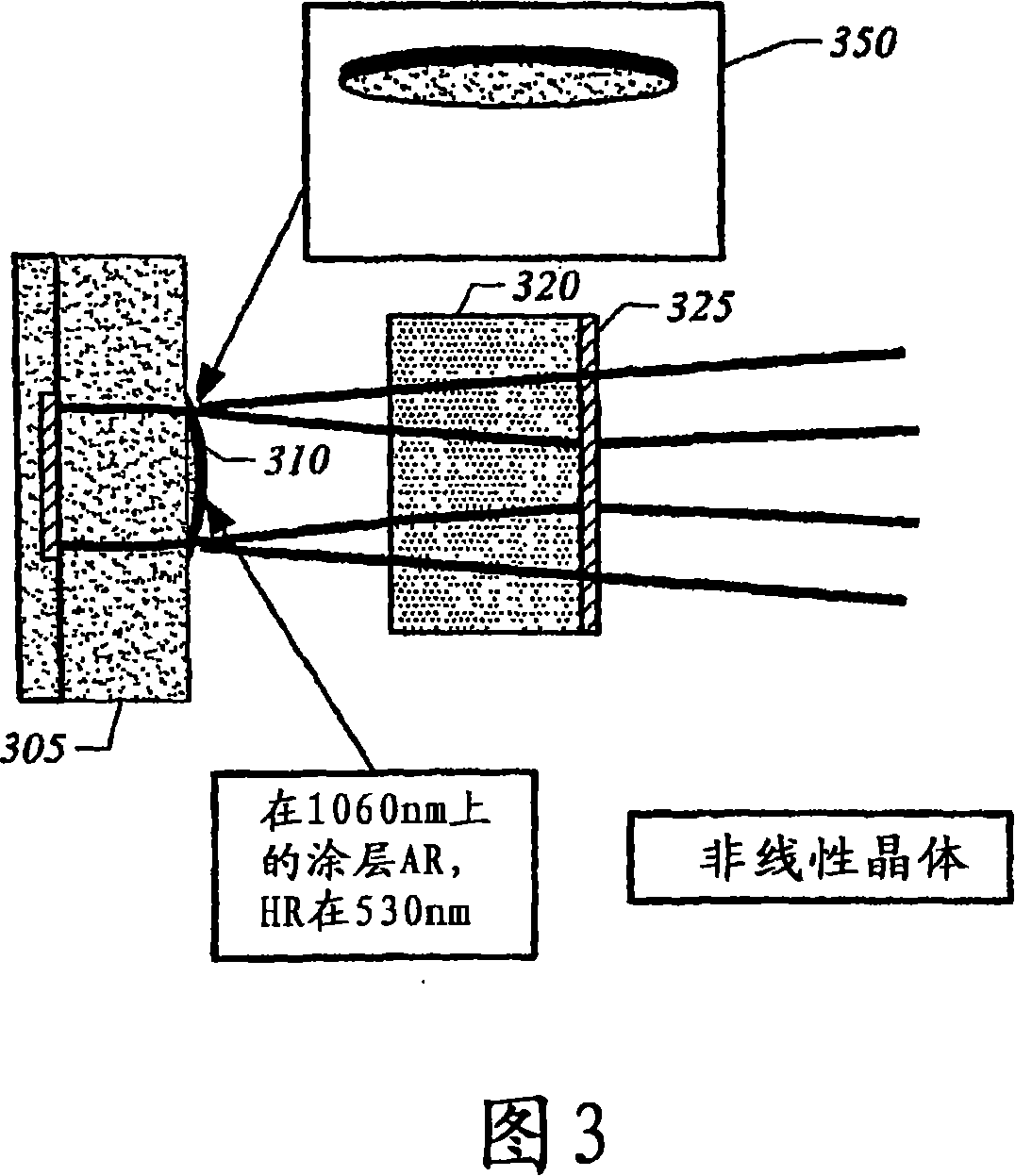
Frequency stabilized vertical extended cavity surface emitting lasers
A technology of surface emission and extended cavity, applied in the field of light source, can solve the problem of not fully exploiting the benefits of semiconductor lasers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
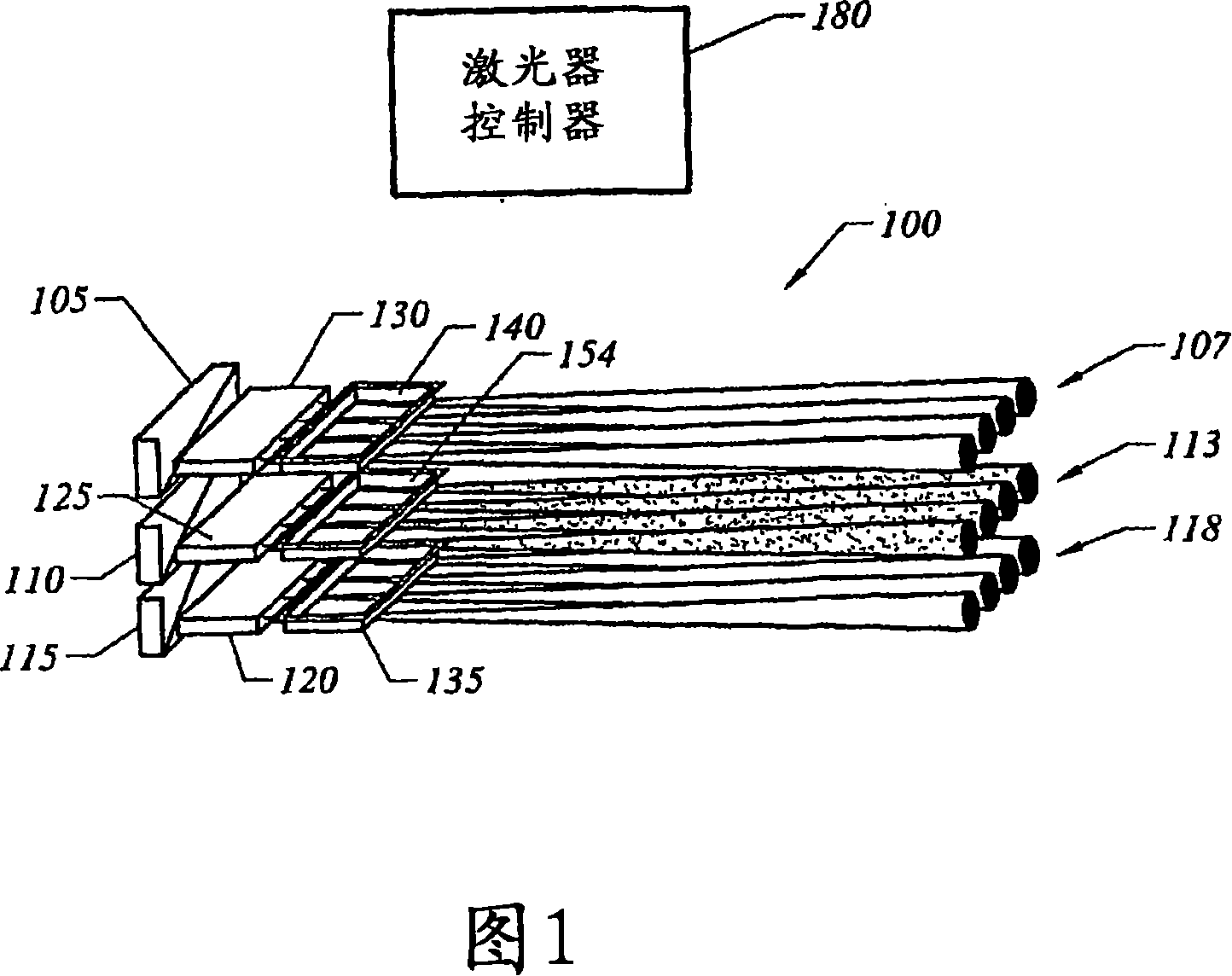
[0060] FIG. 1 is an outline diagram illustrating a light source 100 that produces light of several different colors required by a light processing (LP) system. In a red-green-blue (RGB) LP system, a light source produces red, green, and blue light. A first array 105 of semiconductor lasers is used to generate a plurality of blue light beams 107 from two or more individual lasers. A second array 110 of semiconductor lasers is used to generate a plurality of red light beams 113 from two or more individual lasers. A third array 115 of semiconductor lasers is used to generate a plurality of green light beams 118 from two or more individual lasers. Therefore, the light source 100 comprises different groups of lasers. Individual groups of two or more lasers that produce light of a specific color for an LP system. However, as detailed above, in preferred embodiments, to reduce speckle, individual lasers in a group are designed to be substantially incoherent (eg, out of phase) with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com