Sequence allocation method and device
A sequence and sequence group technology, applied in the field of communication sequence allocation, can solve problems such as strong interference and interference effects, and achieve the effects of small interference, reducing strong interference, and reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
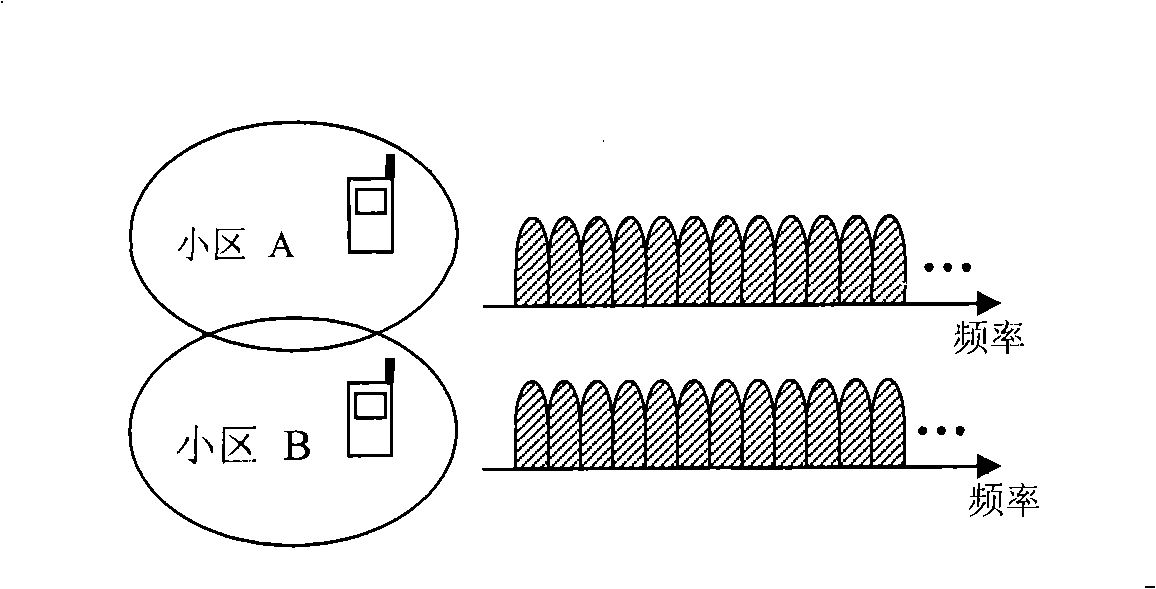
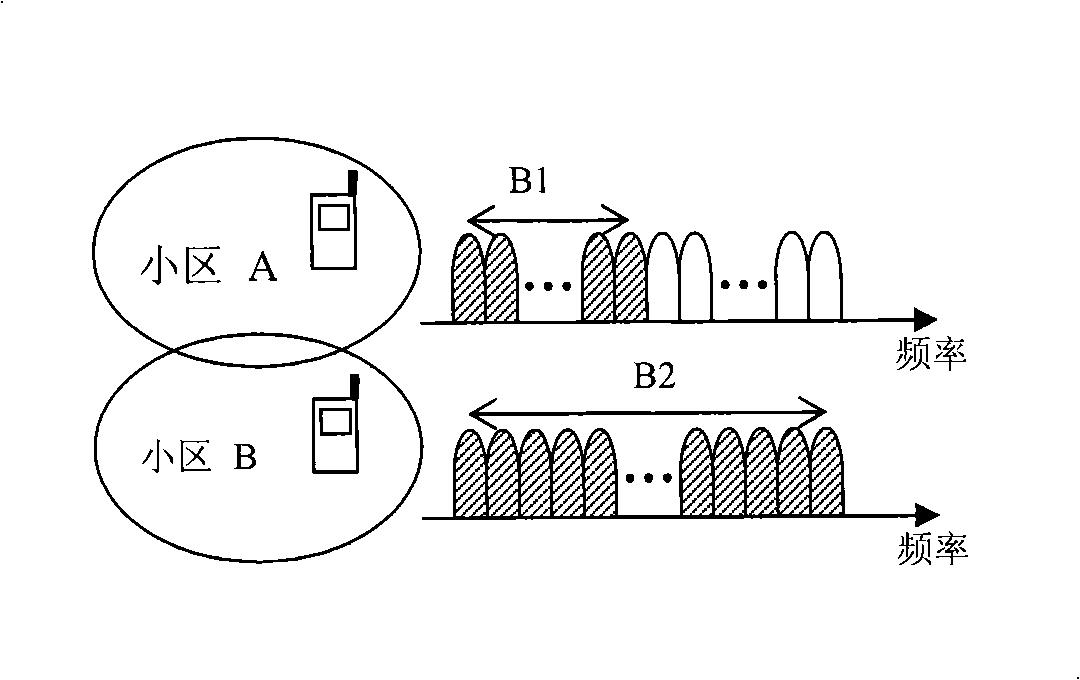
[0040] In a specific embodiment of the present invention, the system assigns sequence groups to cells, wherein the sequences in each sequence group are divided into several subgroups; each subgroup corresponds to a time-frequency resource occupation mode, and how many time-frequency resources are there in the communication system? There are as many subgroups as there are resources occupied; the sequences in each subgroup are selected from the set of candidate sequences corresponding to the subgroup according to certain rules. The user or the channel selects the sequence in the corresponding sequence subgroup to transmit or receive according to the allocated sequence group and the specific time-frequency resource occupancy mode of the transmitted signal adopted.
[0041] The specific rules above are: for any subgroup m, determine the function f corresponding to a subgroup m (·), the domain of this function is the candidate sequence set corresponding to the subgroup; where the f...
specific Embodiment approach 2
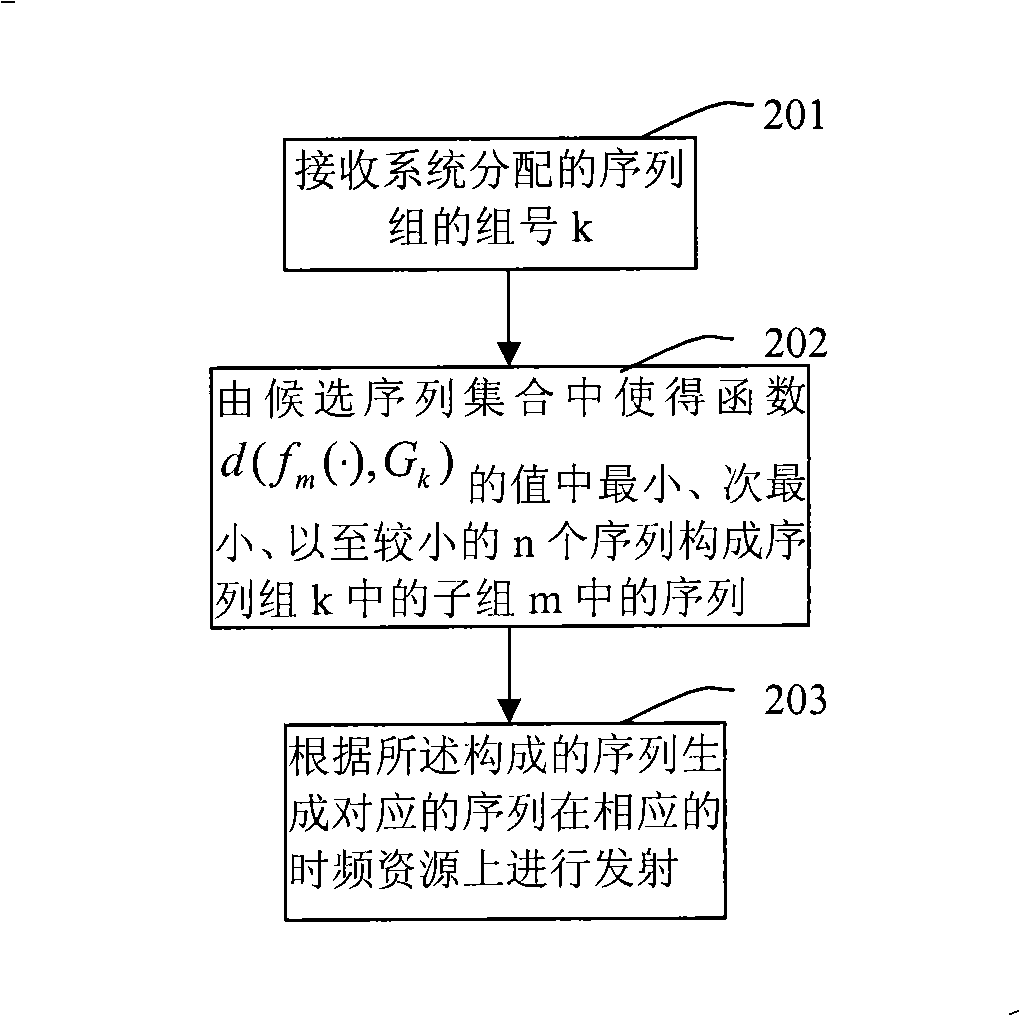
[0073] Consistent with the above-mentioned method in which the network assigns sequence groups to cells according to certain rules, a communication sequence transmission method is introduced below, refer to image 3 , the specific process is:
[0074] Step 201 receives the group number k of the sequence group assigned by the system.
[0075] Step 202 makes the function d(f m (·), G k ) in the value of the smallest, second smallest, and smaller n sequences constitute the sequence in the subgroup m in the sequence group k, where n is a natural number dependent on m, where m is the sequence number of the subgroup, d(a, b) is a binary function, G k is a quantity determined by the group number k, the function f m (·) is a function corresponding to the subgroup m determined by the system, and the domain of this function is the set of candidate sequences corresponding to the subgroup m.
[0076] Step 203 generates a corresponding sequence according to the composed sequence and t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0080] The following provides a transmitting device that applies the above sequence transmitting method, refer to Figure 5 , the device consists of:
[0081] Sequence selection unit: used to receive the group number k of the sequence group assigned by the system, and make the function d(f m (·), G k ) in the value of the smallest, second smallest, and smaller n sequences constitute the sequence in the subgroup m in the sequence group k, where m is the sequence number of the subgroup, and n is a natural number dependent on m, where d(a, b) is a binary function, k is the group number of the sequence group, G k is a quantity determined by the group number k, the function f m (·) is a function corresponding to the subgroup m determined by the system, and the domain of this function is the set of candidate sequences corresponding to the subgroup m.
[0082] A sequence transmitting unit: used to select or generate a corresponding sequence according to the constructed sequence, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com