Inverse tone mapping for bit-depth scalable image coding adapted to variable block sizes
A tone mapping and codec technology, applied in the field of image encoding and decoding, can solve the problem of reducing the quality of inverse tone mapping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
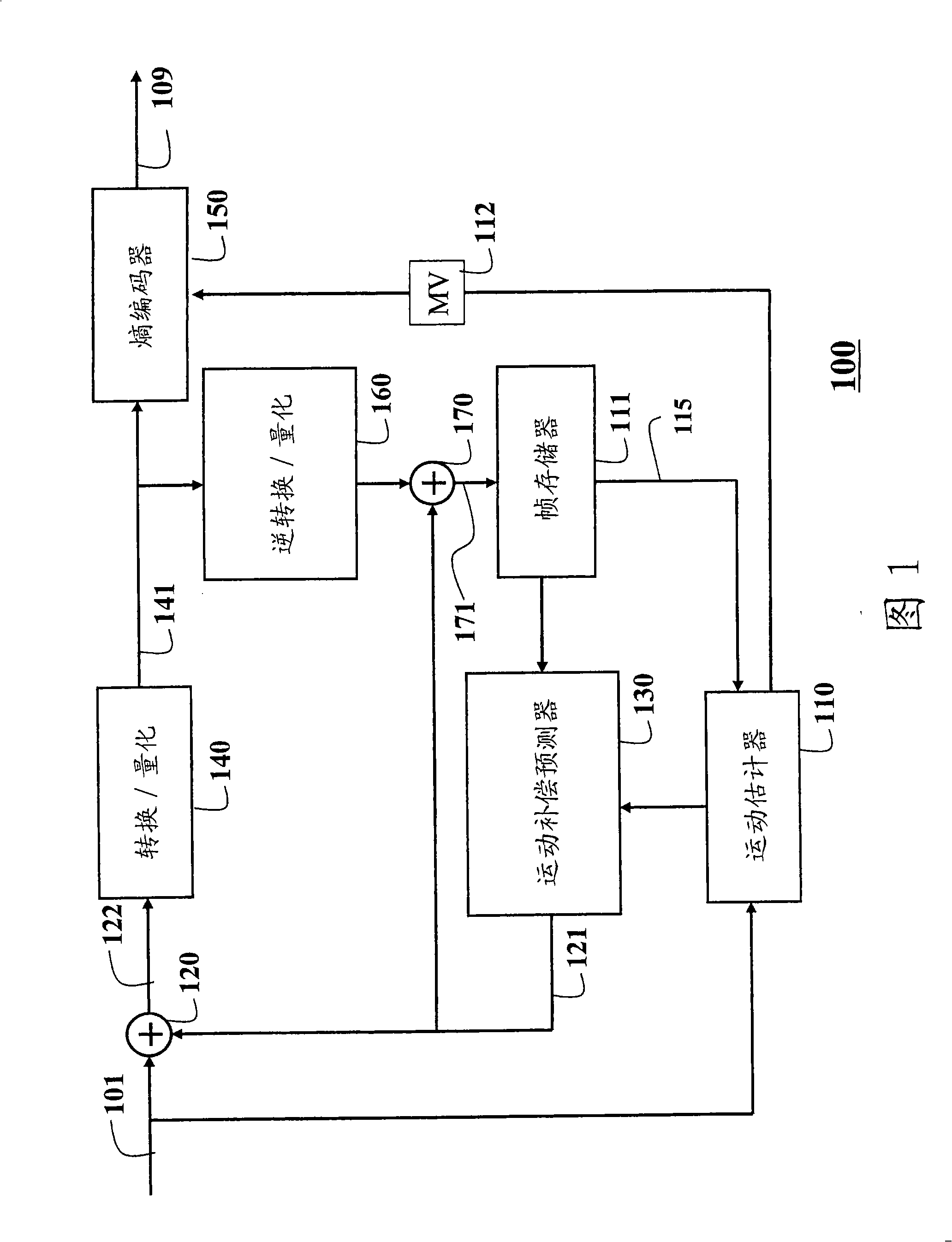
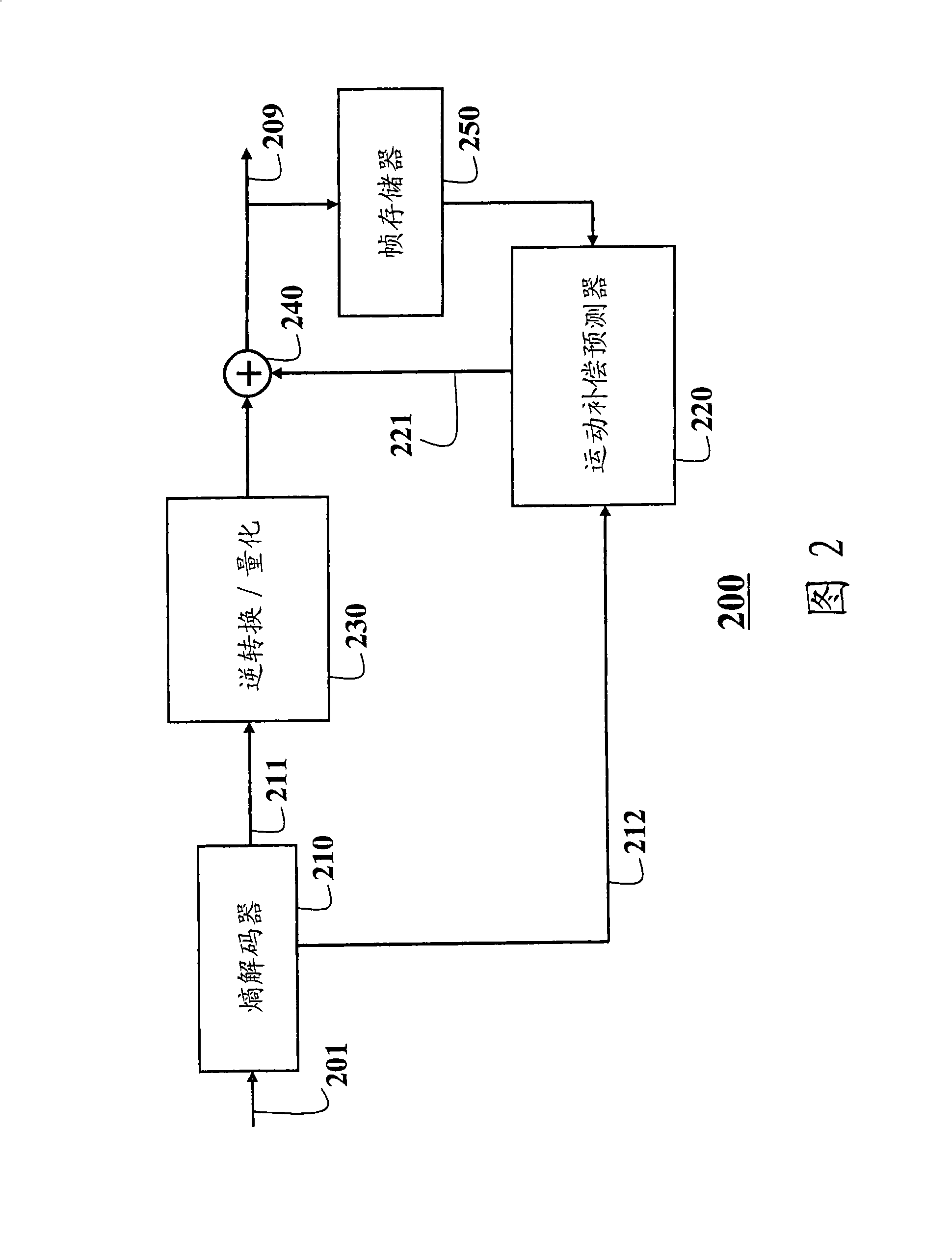
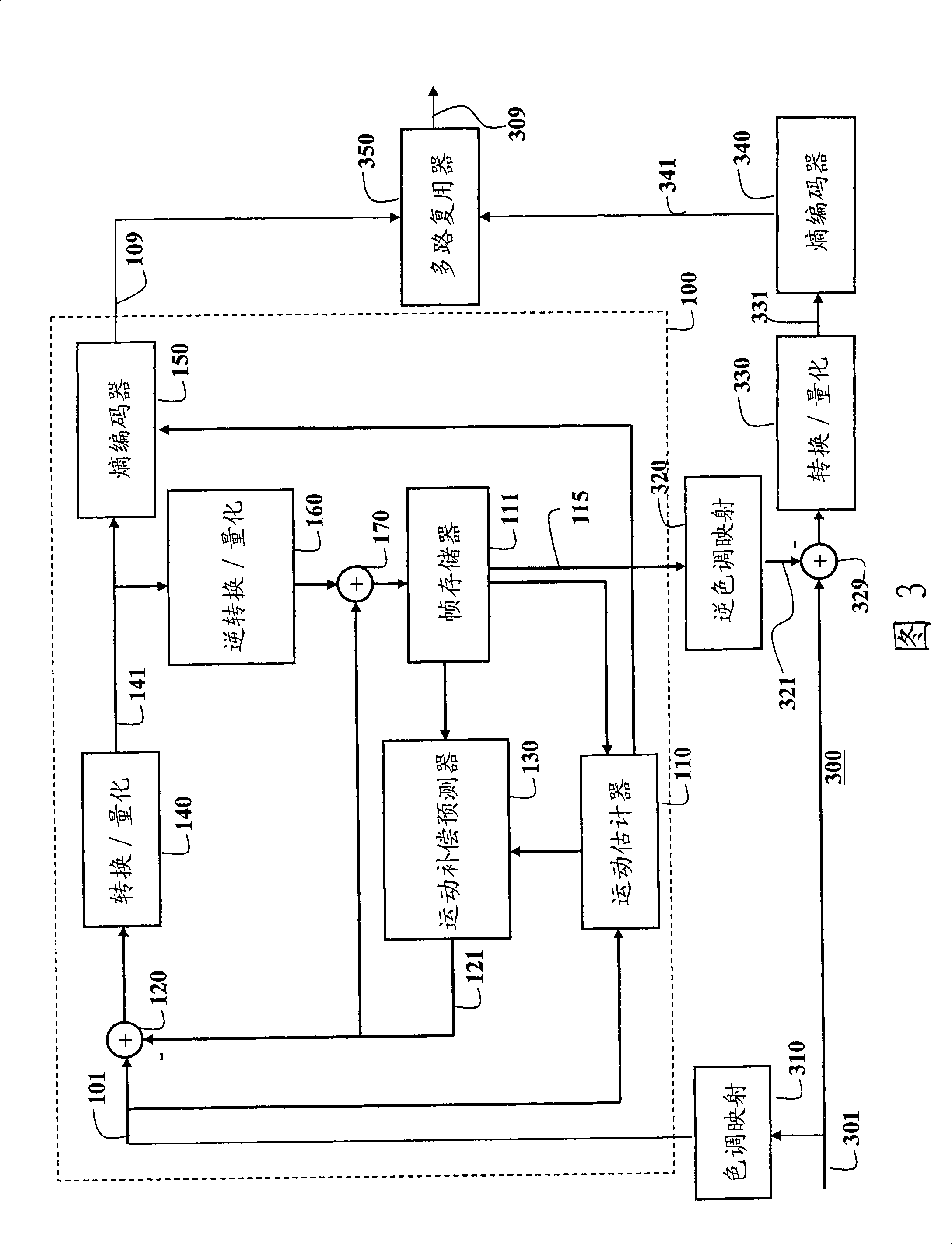
[0026] The present invention provides a system and method for converting between bit depth representations of images and video using tone mapping. The bit depth conversion can be from low to high (LDR→HDR) or from high to low (HDR→LDR). Images and video can be either single-channel monochrome or multi-channel color. The block size is variable. This method takes the following parameters: scale factor, offset value, and forecast direction. These parameters are determined for each block of each color channel. We also describe the procedure used to determine the optimal scale factor. Compared to conventional methods of fixing or limiting the set of scale factors, the scale factors of the present invention can be customized and the range of scale factors can be adaptively and dynamically increased to accommodate a larger dynamic range of images. The corresponding offset value and prediction direction are determined according to the scale factor.
[0027] In order to efficientl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com