Network, method and access point for sharing bandwidth
A technology for sharing bandwidth and access points, applied in data exchange networks, data exchange through path configuration, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve high implementation costs, waste of link resources, and low throughput (only one or two and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing implementation costs, balancing fixed network bandwidth, and improving bandwidth utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
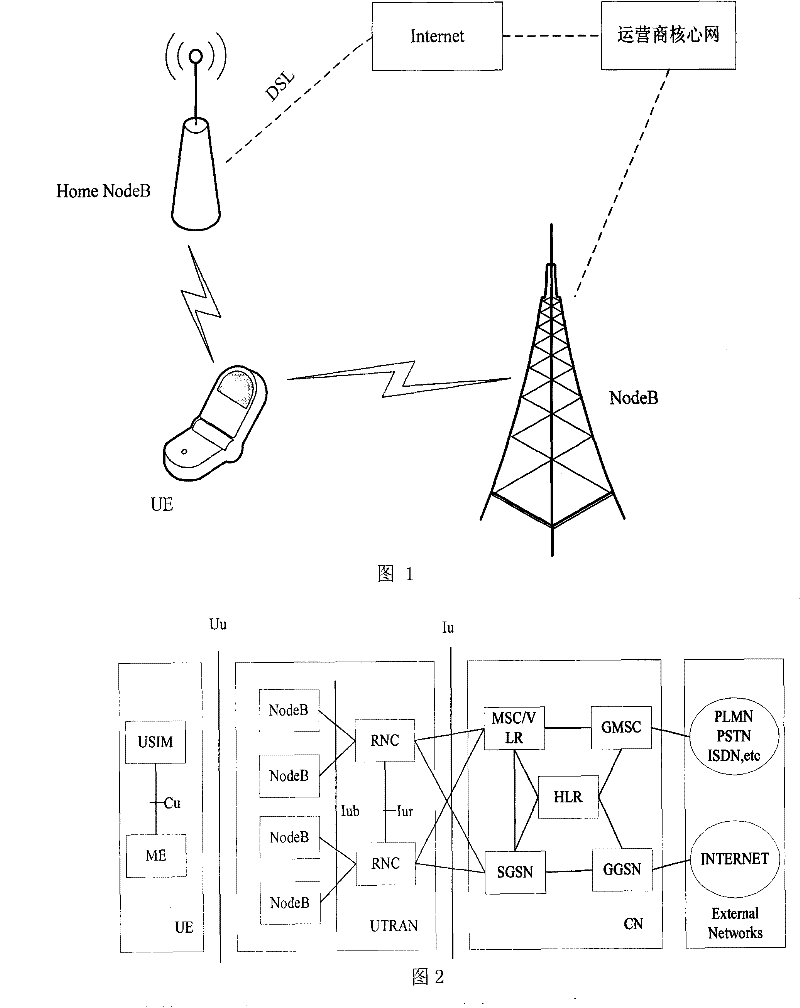
[0038] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for sharing bandwidth, which can be applied to aggregation between NodeBs in a UMTS network, between NB+s in an HSPA+ network, and between eNodeBs in an LTE network, as well as Wimax, WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network , wireless local area network) aggregation of AP (Access Point, access point). Other resources, such as data resources, memory resources, computing resources, and signaling resources, can also be shared by using the technical solutions described in the embodiments of the present invention.
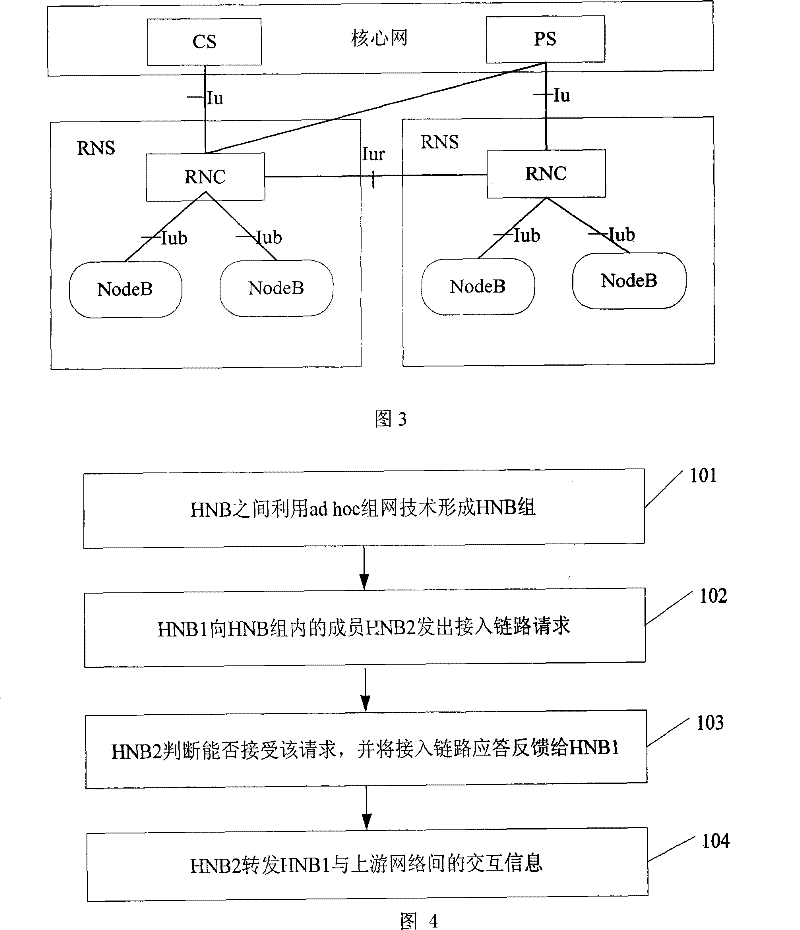
[0039] In the embodiment of the present invention, HNB is taken as an example. After the HNBs are aggregated into a group, each HNB can directly communicate with the upstream network, and each HNB is capable of accepting requests from other HNBs in the group to access the communication link. like Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0040] Step 101: HNBs form an HNB group using adhoc netwo...
Embodiment 2
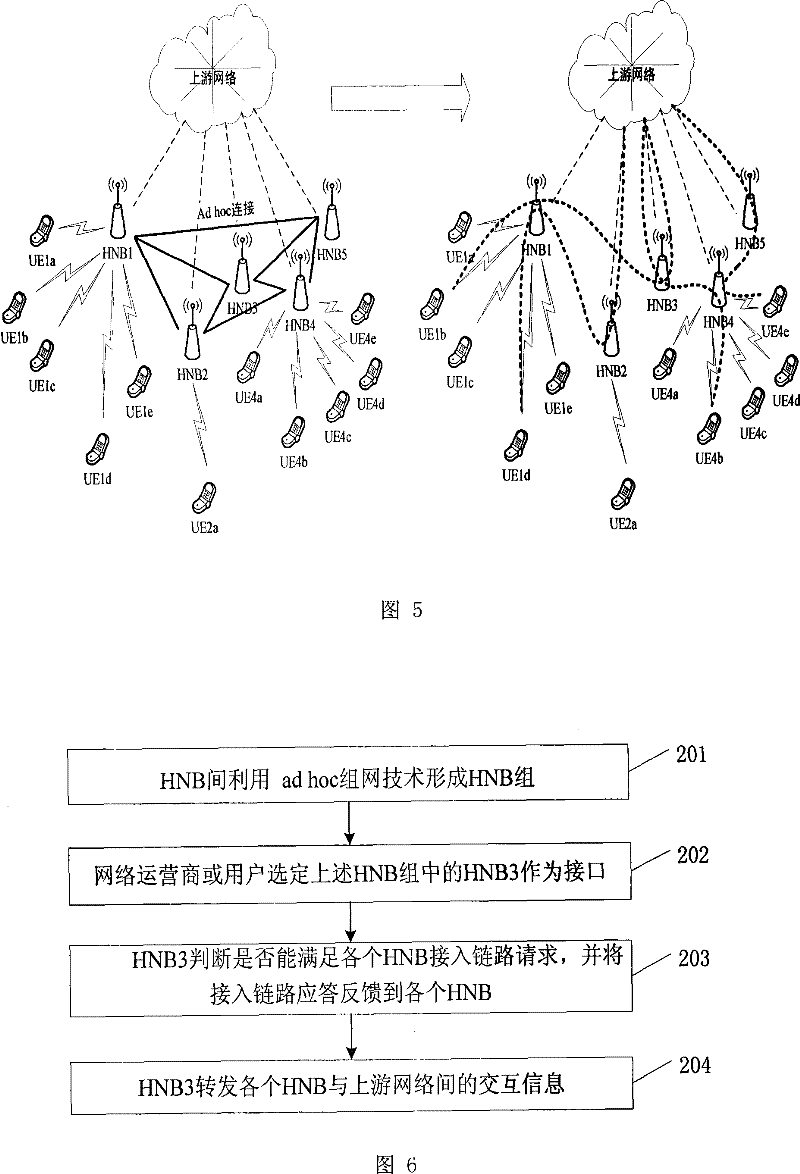
[0059] In Embodiment 1 of the present invention, after HNBs are aggregated into a group, each HNB can receive an access link request. In this embodiment of the present invention, a specific HNB can also be selected by a network operator or user as a group. All other HNBs use the fixed network link of the selected HNB to access the upstream network. like Image 6 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0060] Step 201: HNBs form an HNB group using adhoc networking technology.
[0061] The specific steps are the same as step 101 and will not be repeated here.
[0062] Step 202: The network operator or the user selects one HNB (such as HNB3) in the above HNB group as the interface. When any HNB in the group needs to access the upstream network, it will send a link access request to HNB3 fixedly.
[0063] Step 203: HNB3 judges whether the access link request of each HNB can be satisfied, and feeds back the access link response to each HNB. The specific steps are simi...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The embodiment of the present invention describes the situation that the technical solution of the present invention is applied to the HSPA+ network architecture, such as Figure 8 As shown, the 3G HNB is connected to the SGSN node in the upstream network through the Iu interface. Both the Iu interface and the SGSN node are logical entities, the Iu interface represents the fixed network link between the 3G HNB and the SGSN, and the SGSN may contain one or more physical devices. The solutions in Embodiments 1 and 2 of the present invention are applicable under the network architecture.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com