Method and base station for identifying downlink component carrier in random access process
A random access process and component carrier technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as waste of system resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
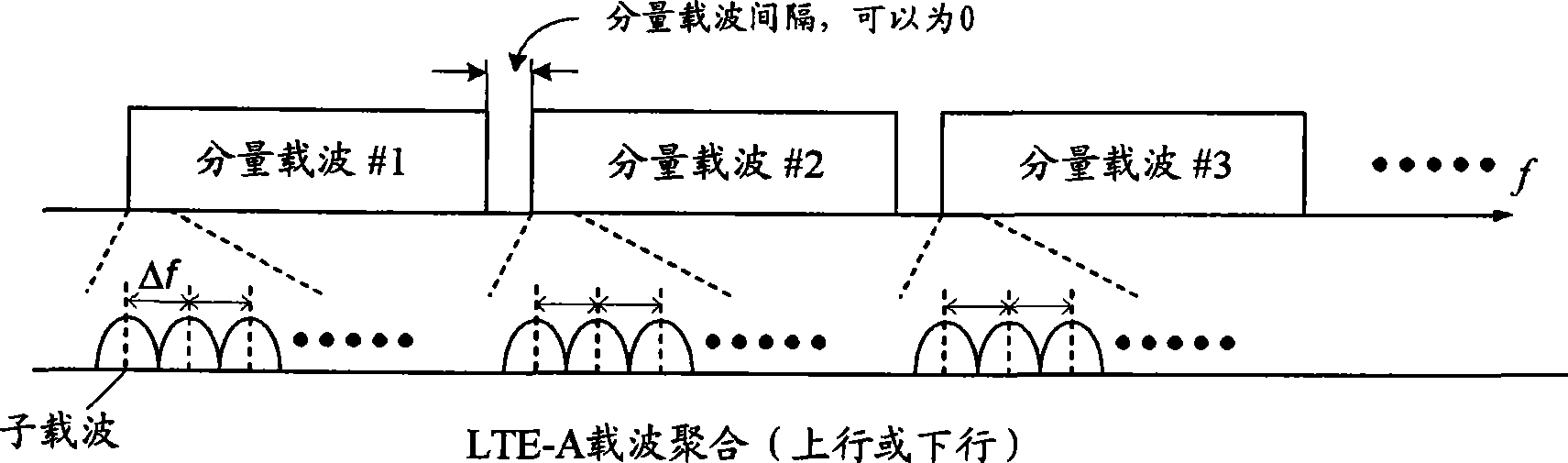
[0074] Suppose an LTE-A system works in FDD mode, there are 2 downlink component carriers, the bandwidth of each downlink component carrier is 20MHz, and there is 1 uplink component carrier, the bandwidth is 20MHz, such as Figure 6 shown.
[0075] The broadcast channels of downlink component carriers 1 and 2 broadcast the following information (not limited to the following information)
[0076] 1) Frequency location information and bandwidth of the uplink component carrier 1.
[0077] 2) Physical random access channel configuration parameters on the uplink component carrier 1.
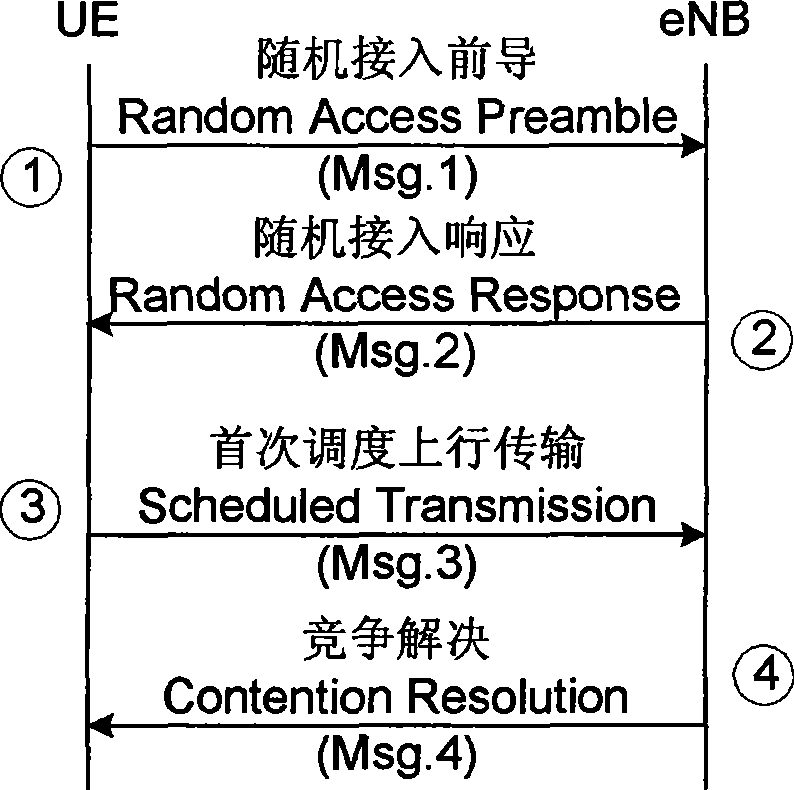
[0078] If a terminal is downlink synchronized to downlink component carrier 1, the terminal sends a random access preamble on uplink component carrier 1. After receiving the random access preamble sent by the terminal, the base station detects the uplink timing advance of the terminal, and sends the timing advance to the terminal through a random access response. Since it cannot be determined that ...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Suppose an LTE-A system works in FDD mode, there are 2 downlink component carriers, the bandwidth of each downlink component carrier is 20MHz, and there is 1 uplink component carrier, the bandwidth is 20MHz, such as Figure 8 shown.
[0083] The broadcast channels of downlink component carriers 1 and 2 broadcast the following information (not limited to the following information)
[0084] 1) Frequency location information and bandwidth of the uplink component carrier 1.
[0085] 2) Physical random access channel configuration parameters on the uplink component carrier 1.
[0086] If a terminal is downlink synchronized to downlink component carrier 1, the terminal sends a random access preamble on uplink component carrier 1. After receiving the random access preamble sent by the terminal, the base station detects the uplink timing advance of the terminal, and sends the timing advance to the terminal through a random access response. Since it cannot be determined that ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Suppose an LTE-A system works in FDD mode, there are 5 downlink component carriers, and the bandwidth of each downlink component carrier is 20MHz, and there are 2 uplink component carriers, and the bandwidth of each uplink component carrier is 20MHz, such as Figure 10 shown.
[0091] The broadcast channels of downlink component carriers 1, 2, and 3 broadcast the following information (not limited to the following information)
[0092] 1) Frequency location information and bandwidth of the uplink component carrier 1.
[0093] 2) Physical random access channel configuration parameters on the uplink component carrier 1.
[0094] The configuration parameters of the physical random access channel on the uplink component carrier 1 broadcast on the downlink component carriers 1 and 2 are the same, that is, the configuration index of the physical random access channel is 9 (the format of the corresponding physical random access channel is 0, in the uplink sub-carrier Frame 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com