Taxi driving range metering method based on GPS and electronic geographic information
A technology of geographical information and geographical location information, which is applied in the field of taxi meters, can solve the problems of uncertainty and achieve the effect of accurate measurement and high repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
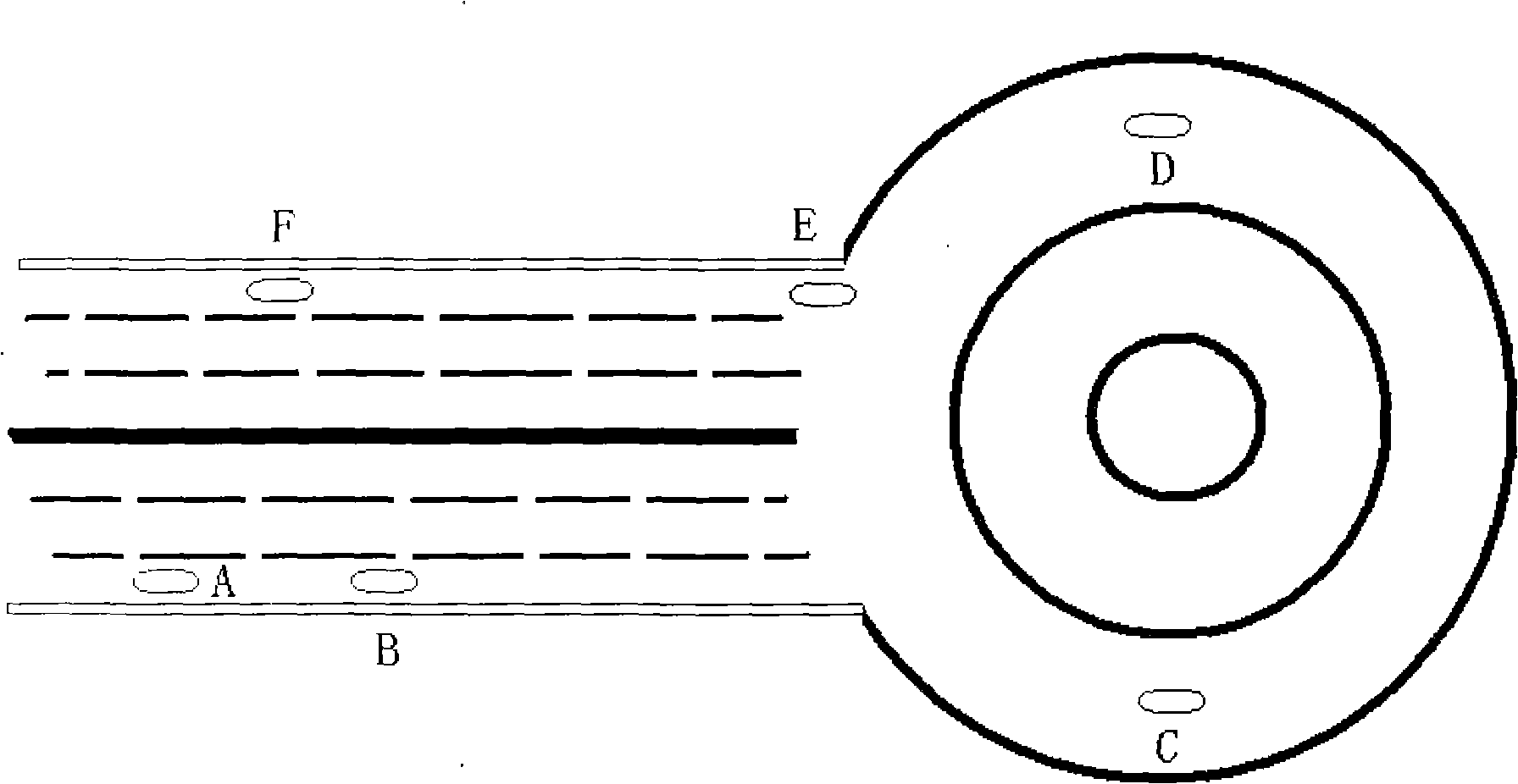
[0022] When a taxi equipped with such a taxi meter is driving in figure 1 On the graph line, after starting to drive from point A, the processor continuously detects the GPS geographic information of the taxi departure point A and the GPS geographic information of each point of the taxi driving process path, such as B, C, D, E, All geographic location information on the taxi travel route is stored in storage unit 12 in advance, and these geographic location information include surveying and mapping by GPS and surveying and mapping device in advance, find out actual driving by the geographic information given by current GPS by geographic location information The route name and the title of important point can calculate the actual mileage of each point of the driving process path such as B, C, D, E by the geographic location information in the memory 12. Due to the influence of the GPS measurement accuracy we use (the poor accuracy is about 10 meters), relying entirely on GPS to...
Embodiment 2
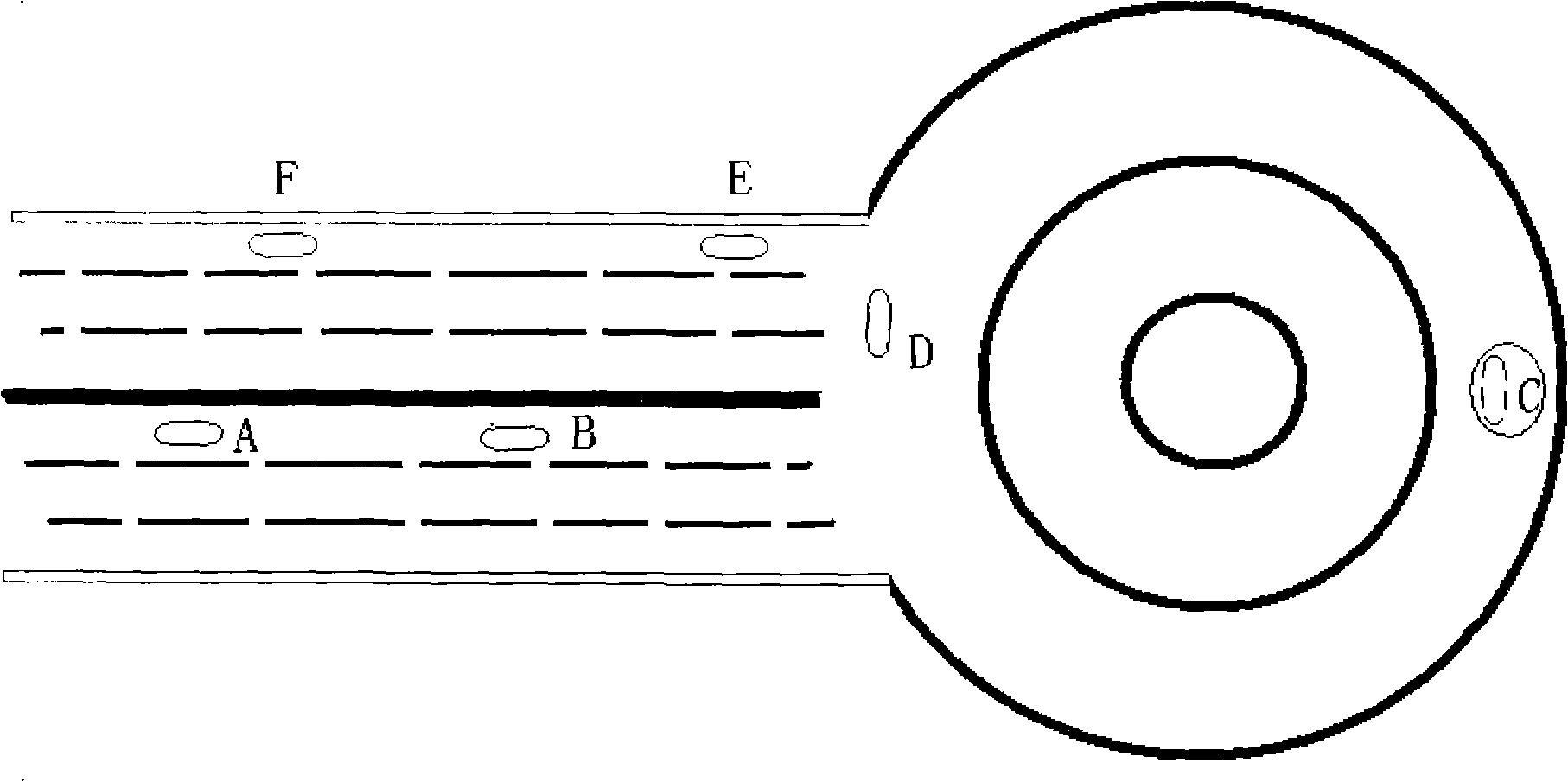
[0024] Of course, due to the influence of GPS measurement accuracy, in figure 2 Under the situation of the situation, the U-turn of the taxi at the crossing will also affect the measurement of the actual mileage result. In this case, the processor 7 can also be used by the route as long as the geographic location information storehouse of the taxi route track and memory 12 is stored. The trajectory is converted to the actual mileage information.
Embodiment 3
[0026] figure 1 and figure 2 Most of the cases in the city appear. However, when the condition of the line is good and the accuracy of GPS measurement is improved (such as after the application of the Beidou system developed by our country), the cumulative calculation is carried out completely relying on GPS geographic information, and all driving routes can be counted with the geographic location information. Such as image 3 As shown, if the road is straight on the high-speed driving route, it is completely possible to use GPS geographic information to continuously accumulate and calculate.
[0027] Figure 4 It is a current state display 4 of the display 1 that the present invention can provide different driving routes 2 for passengers to reach the destination before the taxi 3 travels. After the passenger arrives at the destination given by the input unit 11 such as the touch screen circuit or the voice recognition circuit, the display 1 shows that there can be two li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com